Valence Bond Theory
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Why is the Valence Bond theory useful?
Provides qualitative picture of bonding
Useful for considering a series of molecules w/ one part in common (eg, functional group)
Used in infrared of large molecules
What is resonance in VB theory?
Used in VB theory when no single Lewis-like structure represents the bonding in a molecule
How do resonance forms contribute to the covalent bonding? (in H2)
H-H covalent form most important
Ionic forms EQUALLY important
How does VB theory work for H2?
1s orbitals between H atoms interact, forms WAVEFUNCTION for the molecule
Interactions causes a σ-bond orbital in region between the 2 atoms
How is the wave function expressed for 2 H atoms that are NOT interacting?
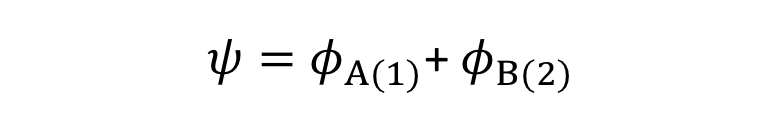
How is the wavefunction expressed for 2 H atoms that are close together?
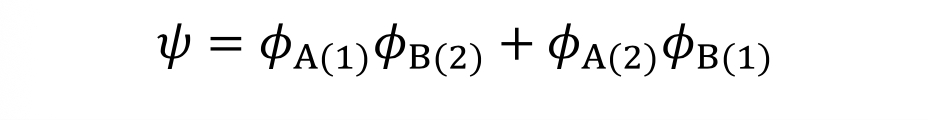
How is the wavefunction of a molecule expressed when ionic forms are included?

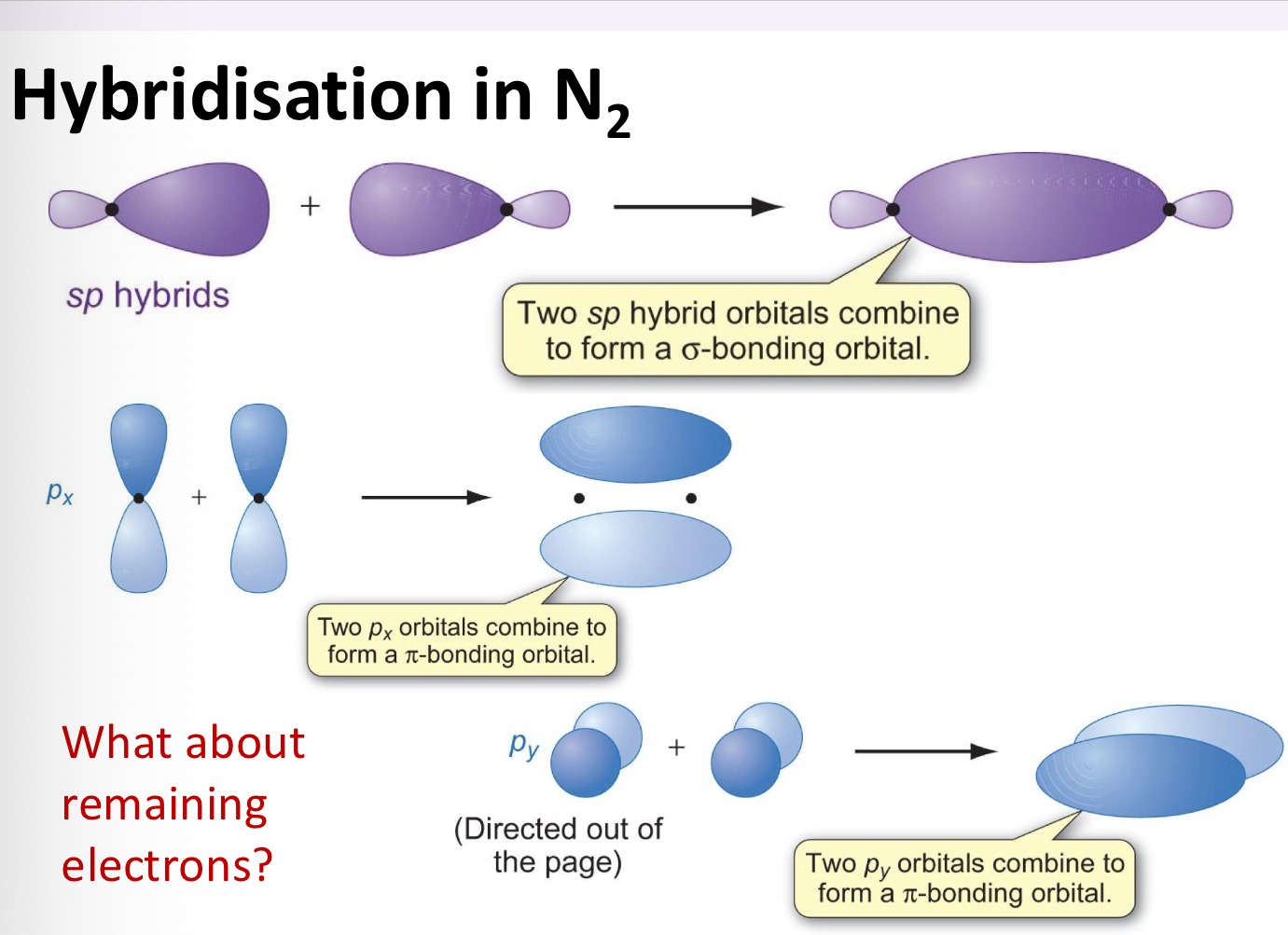
How would VB theory work for a molecule like N2?
Interaction between 2p orbital
Three p orbitals on each atom
Each contain 1 electron
3 covalent bonds formed
What is hybridisation?
Mixing of atomic orbitals w/ diff ANGULAR MOMENTUM (2ndary) quantum numbers
Occurs in N2
How does hybridisation occur between s and p orbitals?
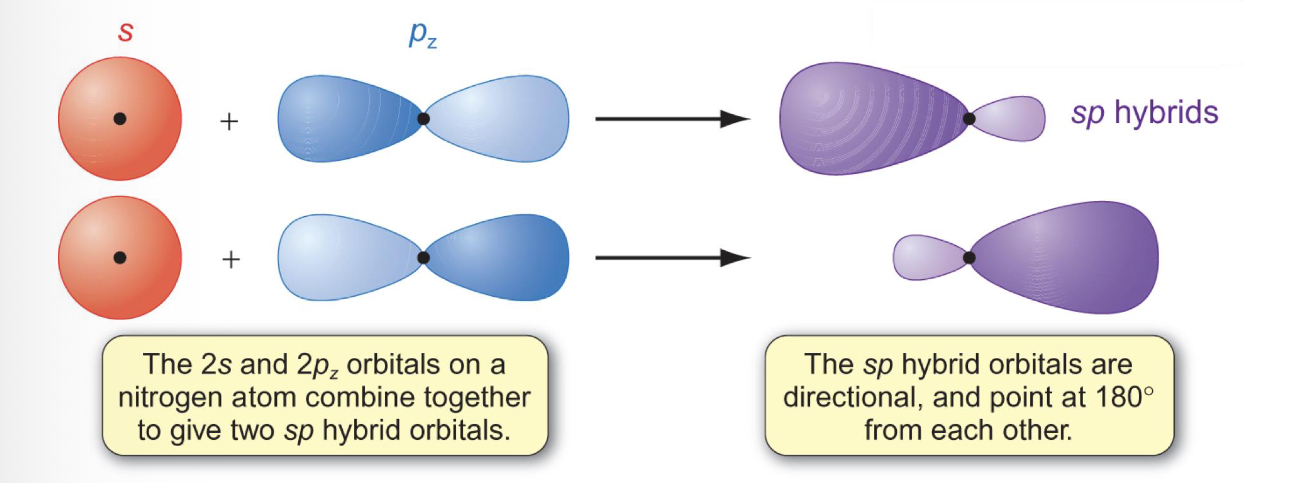
How does hybridisation occur in N2?
Greater overlap between atomic orbitals lead to more STABLE bonding orbitals
How is the VB wavefunction expressed for a HF molecule?

What are the disadvantages to the VB theory?
Works best for organic molecules
Doesn’t account for changes in energy for electrons in different orbitals
Assumes all electrons are localised in specific regions