Promoting Health Literacy as a Health Professional
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Health Literacy for health professionals.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Medication Errors —>
In a study of 395 primary care patients in 3 states asked “How would you take this medicine?” (more than one label)
➢ __% did not understand the instructions on more than one label
➢ __% with adequate literacy missed at least one label Davis, et. al. 2006
➢ 46% did not understand the instructions on more than one label
➢ 38% with adequate literacy missed at least one label Davis, et. al. 2006
Reading vs. Comprehension —>
In a study of adults with literacy below the 6th grade level:
(reading the instructions “take two tablets by mouth daily”)
– 71% correctly read the instructions “take two
tablets by mouth daily”
– Only 35% could demonstrate the number of pills to actually take
Dosing Instructions —> lots of ways to get it wrong
Abbreviations
Uncommon measurements (ml, grams, CC)
Unfamiliar terms
Inconsistent markings
Most physicians ( __%) believed patients knew their diagnosis; however, __% of patients did
Most physicians (77%) believed patients knew their diagnosis; however, 57% of patients did
Health Literacy Definition
The ability to obtain, read, understand, and use health information and services (CDC, 2023).
A wide range of skills is needed to help people understand and use information to lead a health life
Understand appointment notices
Following instructions on medication labels
Get information about illness
Participate in discussion of informed consent
Making appropriate medical decisions
Health Literacy in the Public
Voting on smoking ordinances
Vaccinations
Emergency preparedness
Wearing a helmet
Causes of diabetes
OSHA workplace regulations
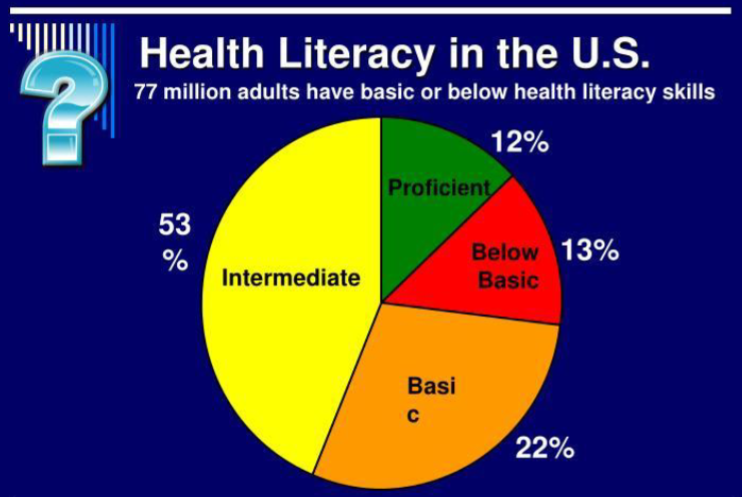
Proficient: Define medical terms, Calculate share of employee’s health insurance costs
Intermediate: Determine healthy weight from BMI chart, interpret prescription and OTC drug labels
Basic: Understand simple patient education handout
Below Basic: Circle date on appointment slip, understand simple pamphlet about pre- test instructions
Health Literacy in the US
_____ Americans have difficulty understanding and using health information
Over _____ additional Americans cannot read complex text
90 million Americans have difficulty understanding and using health information
Over 40 million additional Americans cannot read complex text
Health Literacy in MO
Approximately _____ Missourians have basic or below basic health literacy
Approximately 1.6 million Missourians have basic or below basic health literacy
Impact of Poor Health Literacy
Less compliance with treatment
Less use of preventative services
Risks of hospitalizations
Poor chronic condition management
Increased costs
Poor health outcomes
Increased mortality
Patient Recall of Health Information
What percentage of information do they remember? Correctly?
Patients/Parents forget 40%-50% of what their practitioner tells them as soon as they leave the office, and nearly 50% of what they do remember is recalled incorrectly.
The more information a patient is given, the less they can recall
Costs of Low Health Literacy
$____ average annual costs for low health literacy
VS.
$____ for those with higher health literacy
People with low health literacy have over four
times higher annual health care costs
$13,000 average annual costs for low health literacy
VS.
$3000 for those with higher health literacy
Economic Costs of Poor Health Literacy
_____ dollars a year in Missouri
_____ dollars a year in the US
3.3 to 7 million dollars a year in Missouri
238 billion dollars a year in the US
Human Costs of Poor Health Literacy
Increased pain and suffering
Mental health
Lost work and leisure time
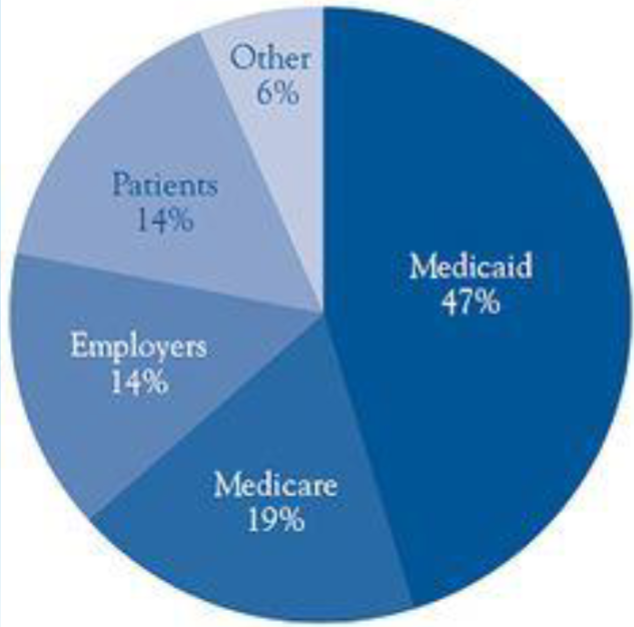
Who Pays the Costs?
Health Literacy Affects Health Outcomes
Quality is affected by
Later diagnosis of diseases and ailments
Poor medication and treatment adherence
Less preventative care utilization
Increased need for chronic care measures
Greater costs for person and system
Universal Precautions Definition
A communication strategy that assumes all healthcare encounters are at risk for communication errors and aims to minimize risk for all.
Why Learn Health Literacy Now?
Most patient instructions are;
Complex
Delivered rapidly
Easy to forget under stress
Healthcare is increasingly complex
More medications, tests, procedure
More self-care requirements
More individual input into decisions
Understanding the Patient
Understand how patients’ background affects their decision making
Aspects affecting Health Literacy
– Culture
– Religion
– Health disparities
– Compliance rates
– Education level
Universal Precautions
Strive to make visits consumer-centered
Explain thing clearly in plain language
Focus on key message and repeat
Universal Precautions Methods
Use the “teach back” or “show me” method for understanding
Use consumer-friendly educational material to enhance interactions
Use medical interpretation services
Explain in Common Language
Most patients don’t understand anatomy!
We use words differently in healthcare
If possible, use patient’s own words
Use common language
Use analogies that are relatable to the patient
Talking with Families
Use plain language
Slow down
Break it down to shorter statements
Focus on 2-3 most important concepts
Check for understanding