Overview of Transcription
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Transcription
What is the process by which a segment of DNA directs the synthesis of an RNA?
Complementary RNA Sequence
In transcription, DNA does not produce proteins directly.
One strand of DNA must first be copied into a _________.
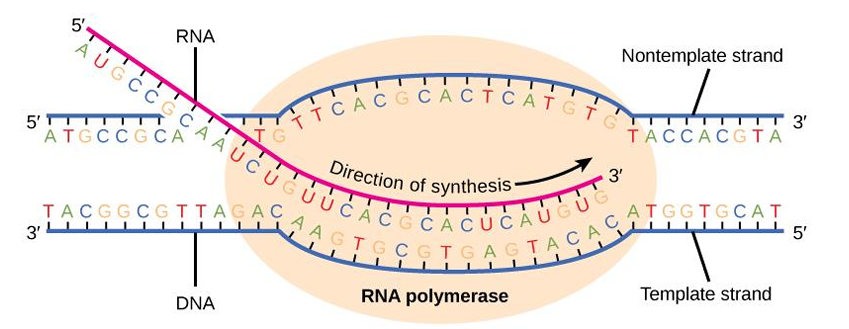
RNA polymerase
Process of Transcription
In the 5’ to 3’ direction, an enzyme called _________ unwinds the DNA (responsible for polymerization of RNA).
Opening and Unwinding
Complementary Base Pairing
Process of Transcription
Like DNA replication, transcription starts with the (1)_________ of a small portion of the DNA double helix, followed by (2)_________ between incoming nucleotides and the DNA template.
Remain Hydrogen Bonded
Process of Transcription
Unlike DNA replication, the RNA strand does not _________ to the DNA template strand in transcription.
Shorter
Process of Transcription
RNA molecules synthesized during transcription are much _________ than DNA molecules.
RNA Polymerase
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
What enzyme catalyzes the linkage of ribonucleotides?
RNA Polymerase
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
What enzyme can start an RNA chain without a primer?
RNA Polymerase
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
What enzyme replicates less accurate genetic information from the DNA template?
DNA Polymerase
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
What enzyme catalyzes the linkage of deoxyribonucleotides?
DNA Polymerase
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
What enzyme requires a primer to start the elongation process?
DNA Polymerase
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
What enzyme replicates genetic information from the DNA template with high accuracy?
Promoters (Upstream)
Process of Transcription
In eukaryotes, the binding of several transcription factors that make the binding of RNA polymerase possible is activated by unique regions in the DNA called _________.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
The Different Types of RNAs
What type of RNA codes for proteins?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
The Different Types of RNAs
What type of RNA forms the basic structure of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis?
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
The Different Types of RNAs
What type of RNA acts as adaptors between the mRNA and the amino acids?
Small Nuclear RNA (snRNA)
The Different Types of RNAs
What type of RNA functions in different nuclear processes like mRNA splicing?
Small Nucleolar RNA (snoRNA)
The Different Types of RNAs
What type of RNA is used to process and modify rRNAs?
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
What are the three stages of transcription?
RNA Polymerase (RNAP)
Promoter (ρ factor)
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
In prokaryotes, (1) this enzyme can recognize and bind itself to the (2)_________.
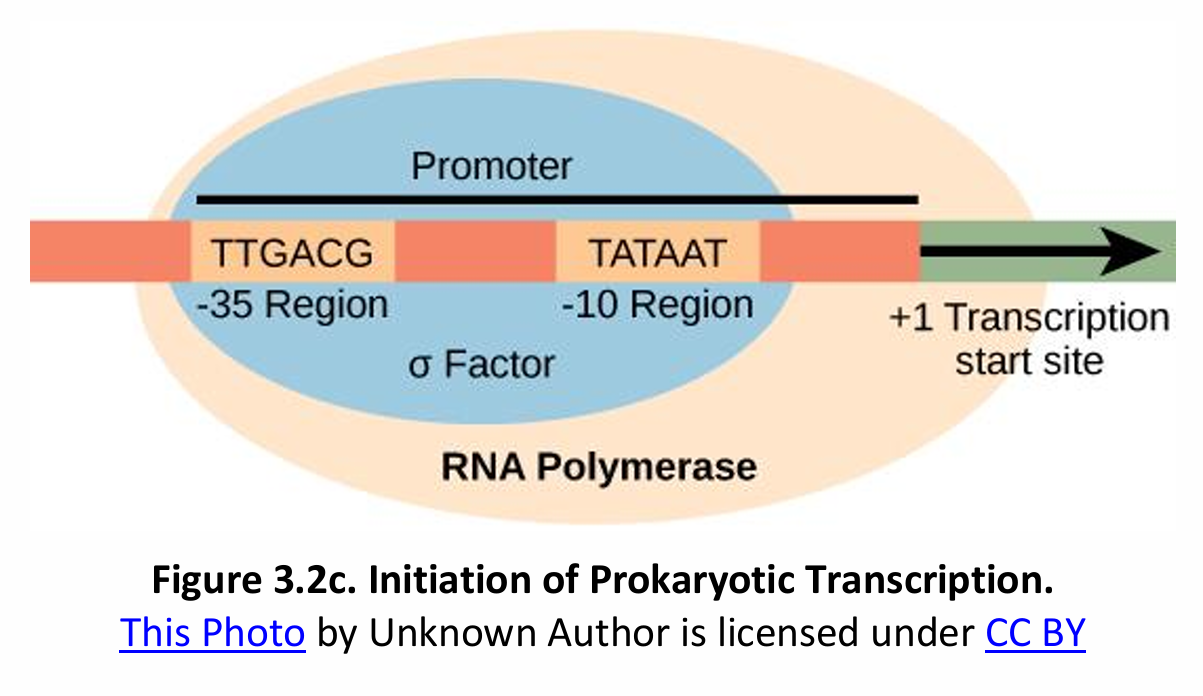
Initiation Complex
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
In prokaryotes, no _________ occurs.
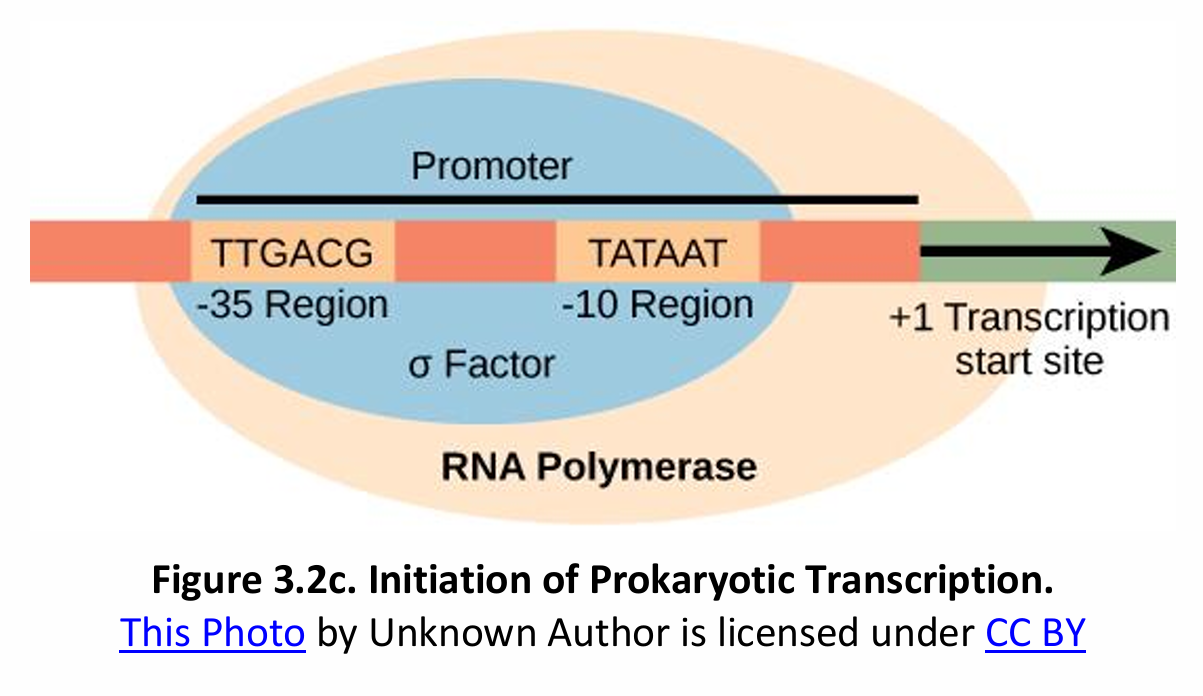
Pribnow Box – TATAAT
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
In prokaryotes, the consensus sequence of the promoter (AT-rich regions) is called the _________.
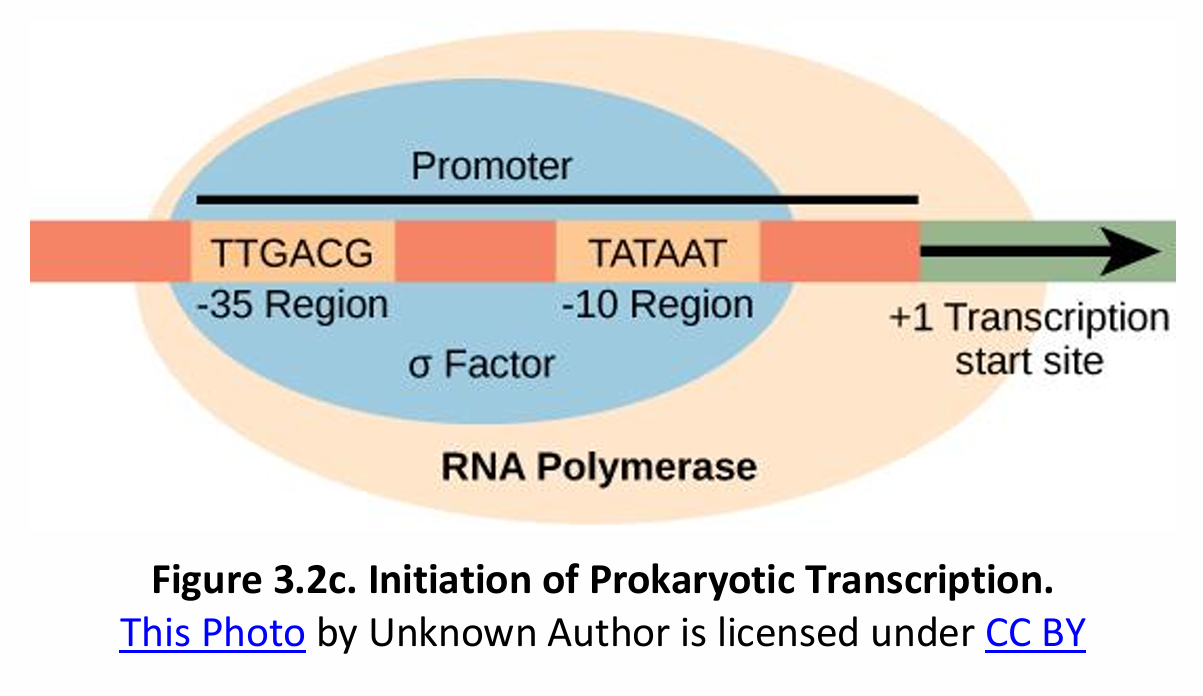
Transcription Factors (TFs)
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
In eukaryotes, _________ mediate RNA polymerase binding and transcription initiation.
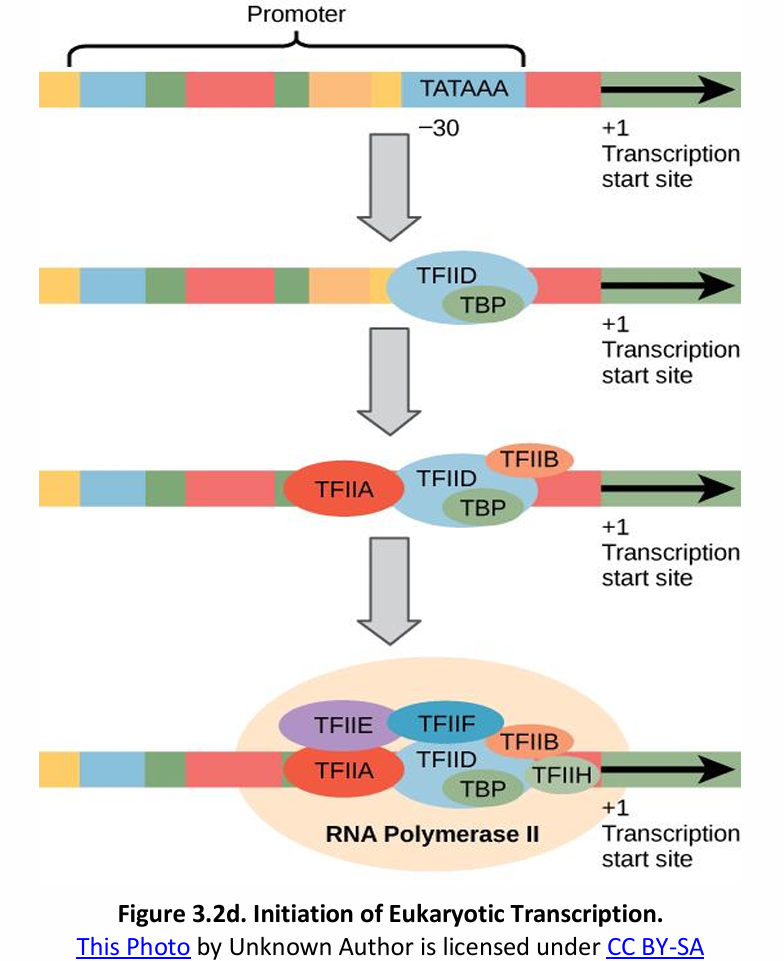
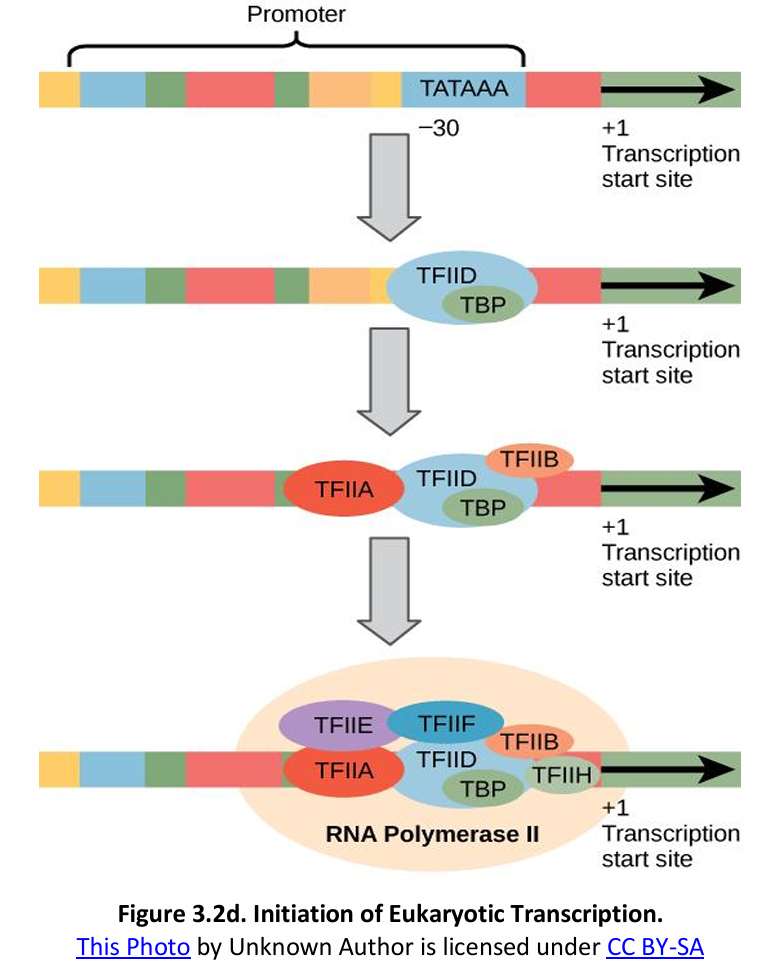
Transcription Initiation Complex (TIC)
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
In eukaryotes, TFs + RNAP II = _________.
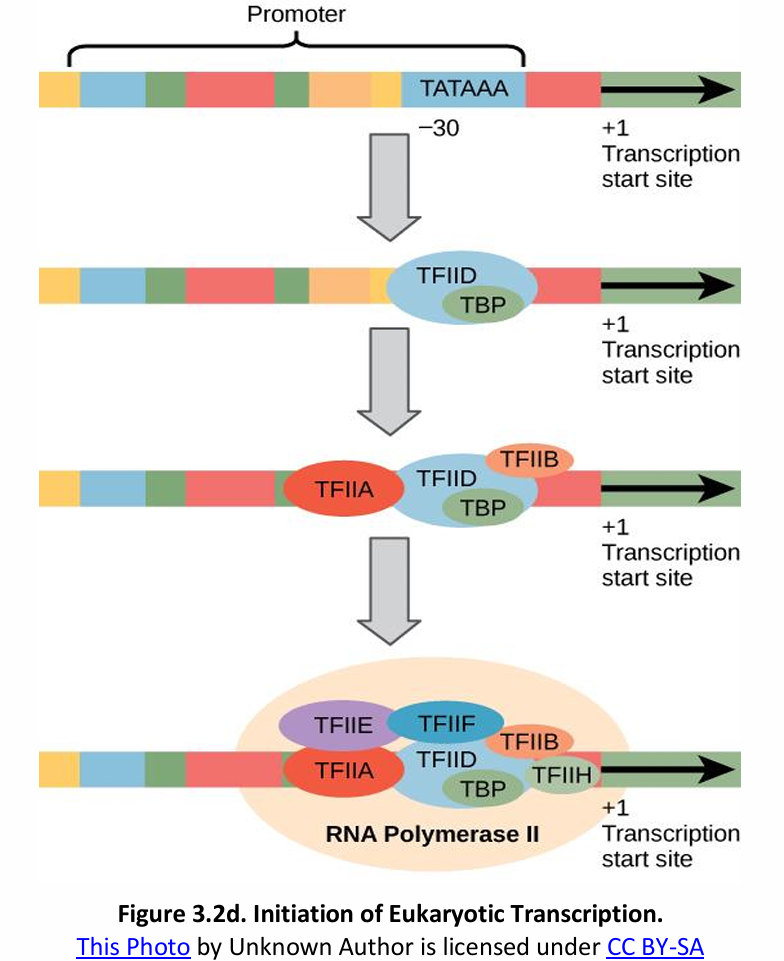
TATA box – TATAAA
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
In eukaryotes, the consensus sequence of the promoter (AT-rich regions) is called the _________.
Simultaneously
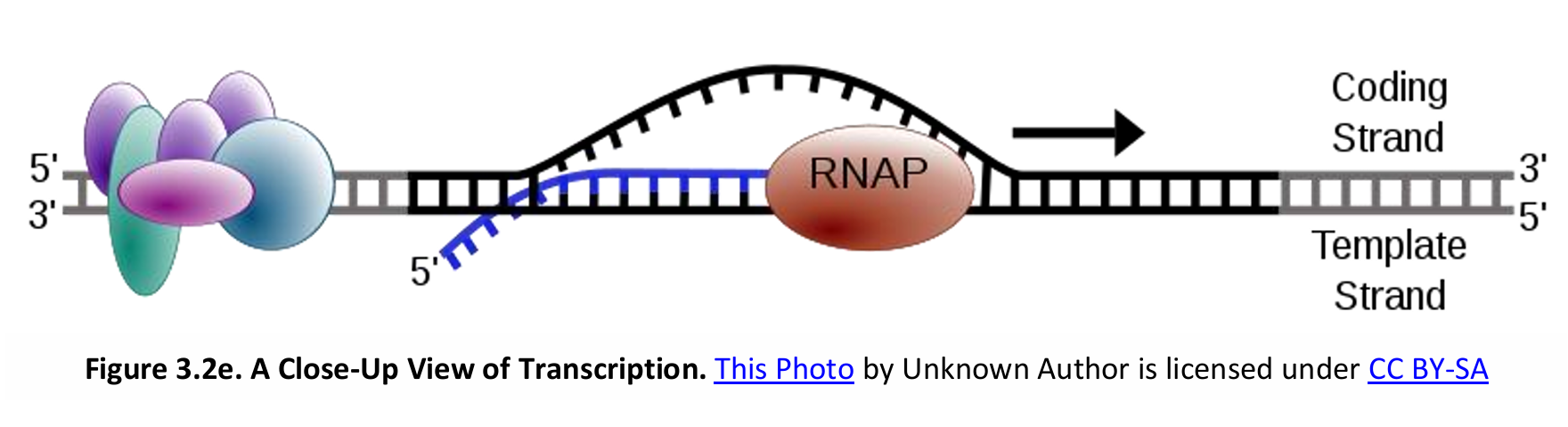
Elongation of Transcription
In the elongation process of transcription, a single gene can be transcribed _________ (i.e. more than one mRNA molecule are being transcribed at the same time).
Sense Strand (Coding Strand or Non-template Strand
Antisense Strand (Non-coding strand or Template Strand)
Elongation of Transcription
DNA is double stranded. In transcription, what are these two strands called?
Growing
10-20 Bases
Elongation of Transcription
RNA nucleotides complementary to the template strand of the DNA are added to the 3’ end of the (1)_________ strand. DNA unwinds (2)_________ at a time for pairing with RNA nucleotides, then the double helix reforms.
Rho (ρ) Factor
Elongation of Transcription
Before the transcription of a gene is completed, a protein called _________ binds to the termination site and brings about the termination of transcription.
Termination of Prokaryotic Transcription
(Rho-Dependent Termination)
Termination of Transcription
What does this image illustrate?
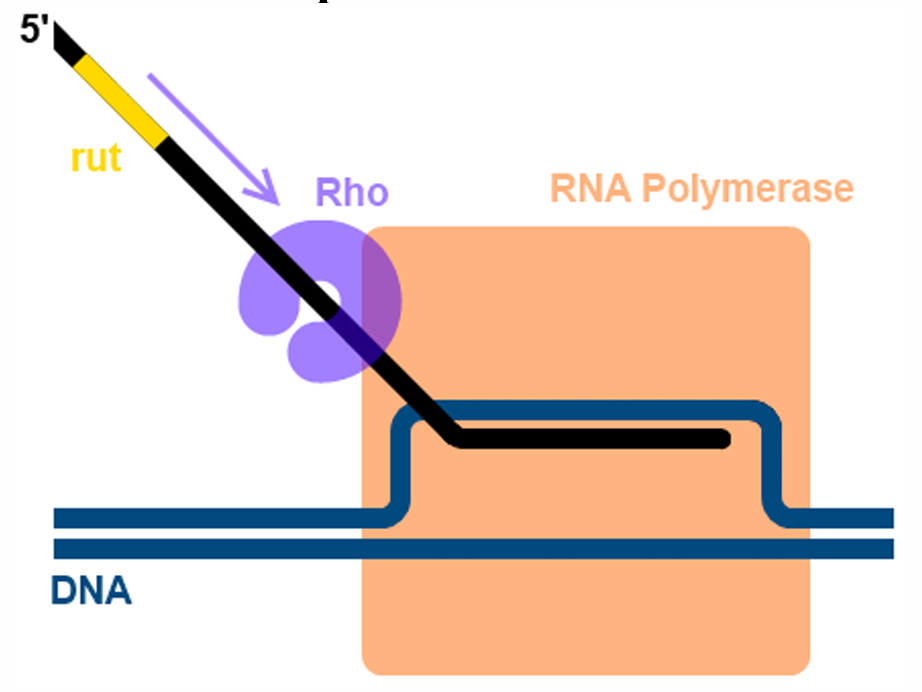
Termination of Eukaryotic Transcription
Termination of Transcription
What does this image illustrate?
Rho (ρ) Factor
Transcribed RNA Rut (C-rich)
Termination of Transcription
In prokaryotes, the termination process of transcription starts with the (1)_________ recognizing the (2)_________ , upstream of the real terminator sequence.
Terminator (RNA sequence)
Termination of Transcription
In prokaryotes, the _________ serves as the termination signal.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Termination of Transcription
In prokaryotes, the _________ can be translated without further modification.
Rho (ρ) Factor
RNA Polymerase II (RNAP II)
Termination of Transcription
In prokaryotes, the (1)_________ catches up with the (2)_________ (paused at termination sequence) and allows release.
RNA Polymerase II (RNAP II)
Termination of Transcription
In eukaryotes, the _________ continues along the DNA strand until it reaches the terminator sequence.
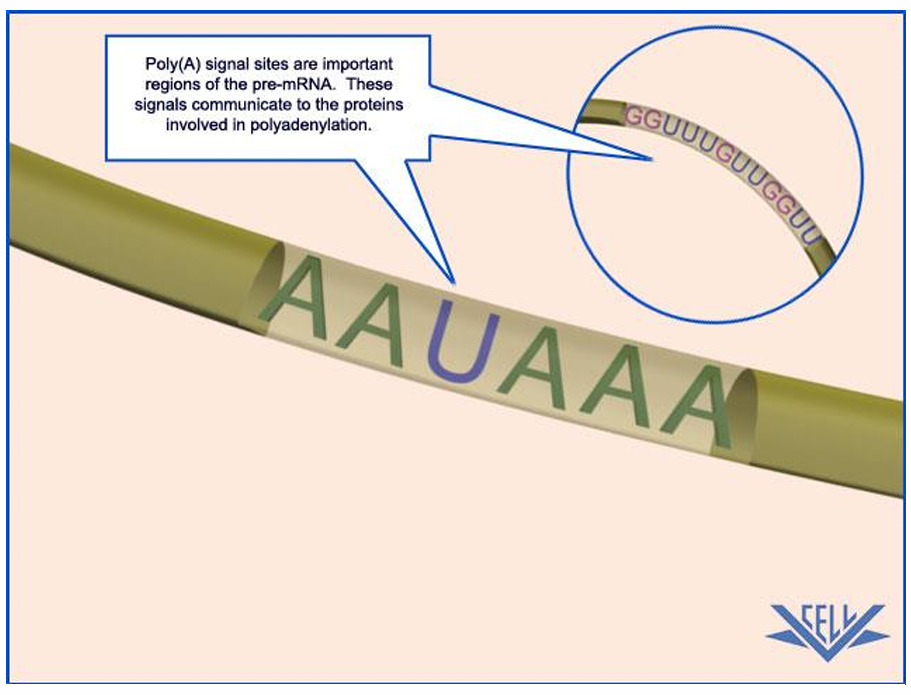
Polyadenylation Signal Sequence
Termination of Transcription
In eukaryotes, the _________ transcribes the polyadenylation signal (AAUAAA).
Pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA)
Termination of Transcription
In eukaryotes, after 10-35 nucleotides downstream from AAUAAA, a _________ is released.
Transcribe
Dissociated
Termination of Transcription
In eukaryotes, the RNAP II continues to (1)_________ and is eventually (2)_________.
pre-mRNA-processing Proteins
Nascent RNA
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
The RNAP II does not only transcribe DNA into RNA, but also bears _________ on its tails, which are then transferred to the _________ at the appropriate time.
The Production of Eukaryotic mRNA from pre-mRNA into mature mRNA
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What does this image illustrate?
Untranslated Regions (UTRs)
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What are the regions of mRNA that will not be translated called?
Introns
Exons
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
Some non-coding sequences called (1)_______ are interspersed between coding (expressed) sequences called (2)_______.
snRNPs (Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Particles)
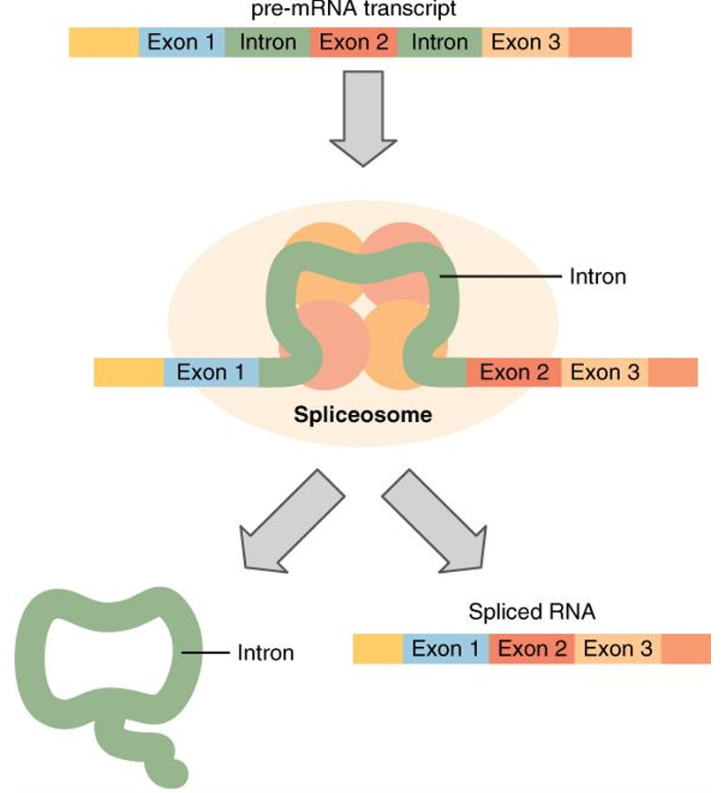
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
The intron loops out as _________; complexes of snRNAs and proteins) which bind to signals at the end of each intron.
Spliceosome
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
snRNPs join with other proteins to form a _______. The intron is excised and the exons are then spliced together.
RNA Processing
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What does this image illustrate?
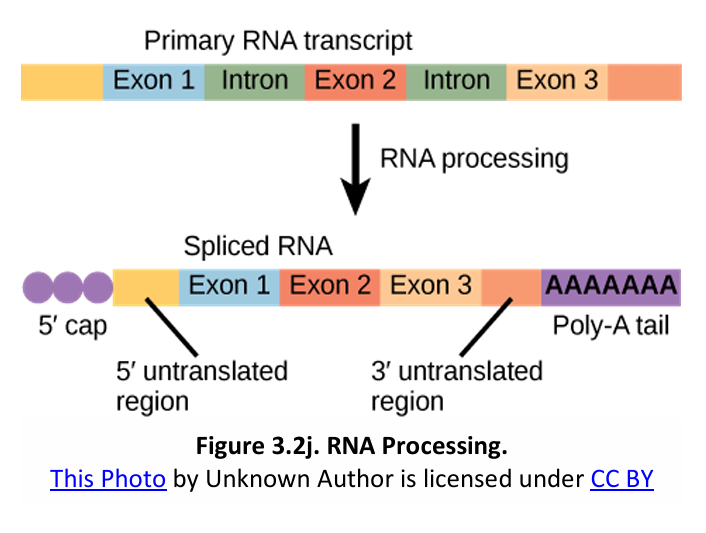
5’ capping or the addition of a modified G cap;
3’ polyadenylation or the addition of a poly-A tail;
UTRs (untranslated regions) for
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What are the three processes in the alteration of mRNA ends?
The addition of a modified G cap takes place.
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What happens in the 5’ capping process of the alteration of mRNA ends?
The addition of a poly-A tail takes place.
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What happens in the polyadenylation process of the alteration of mRNA ends?
It acts as ribosome binding signals.
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What happens with the UTRs (untranslated regions) process of the alteration of mRNA ends?
to facilitate the export of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What is the function of the 5’ capping process in the the alteration of mRNA ends?
To prevent the degradation of mRNA by hydrolytic enzymes.
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What is the function of the 3’ polyadenylation process in the the alteration of mRNA ends?
To serve as signals to the rRNA for attachment to the 5’ end.
Post-Transcriptional Processing in Eukaryotes
What is the function of the UTRs (untranslated regions) process in the the alteration of mRNA ends?