AP MACROECONOMICS: UNIT 2 ECONOMIC INDICATORS AND BUSINESS CYCLE
1/70
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
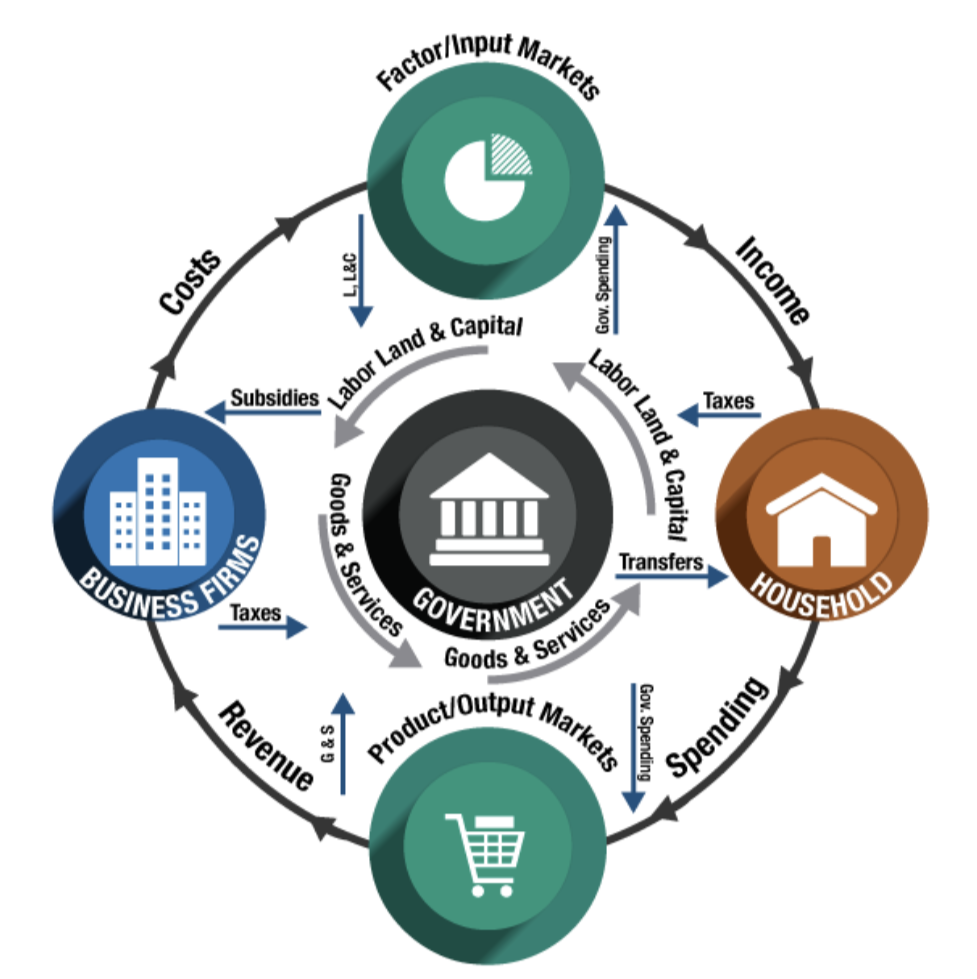
Product Markets
Where consumers purchase goods and services from businesses.
Revenue
The payment a business receives from customers for its products.
Factor Market
Where businesses purchase what they need to produce their goods and services.
Rents
Compensation paid to a property owner for land or capital in the factor market.
Wages
Compensation paid to workers/laborers in the factor market.
Interest Payments
A percentage of the amount of money borrowed that is paid for a loan.
Transfer Payment
Money granted by the government to households to influence their behavior in some way; income redistributed by the government.
Consumer Goods
Resource acquired for direct use.
Capital Goods
Resource obtained by a business from another in order to produce a consumer good or service (i.e., tools, machinery, intermediate goods).
Input and Output Markets
Gross Domestic Product
The market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a year.
Aggregates
The total amount or value; also, to combine several distinct items into one, such as adding the market value of all goods and services together into one number.
Market Value
The amount of money for which a good or service is freely purchased.
Double Counting
Adding the same value twice, a mistake economists try hard to avoid when calculating GDP.
Intermediate Good
A product used in making a final good or service—part of a final good.
Durable Goods
A long-lasting product that will be used for three years or more, such as a car.
Nondurable Goods
A good purchased for immediate consumption, such as food.
Expenditures Approach
Counting GDP using the sum of all purchases of final goods and services by consumers, businesses, the government, and foreign customers. Summarized with the formula Y = C + I + G + Nx.
Income Approach
Counting GDP by adding all payments for the factors of production as well as business profit: wages for labor, rent for land, interest for capital loans, and taxes involved in production.
Value-Added Approach
Counting GDP by summing all incremental increases in value from raw factors of production through to final product.
National Income =
National Expenditures
Y
GDP
C
The total amount that consumers spend
I
The total amount that businesses invest in capital goods
G
Government Spending on Goods and Services
Xn
The dollar value of exports – the dollar value of imports
Net Exports
The difference in value between a country's total exports and total imports; if negative, then the country is importing more goods than it exports.
Export
A product produced for and sold to a foreign country.
Import
A product produced in and purchased from a foreign country.
Inventory
The quantity of a good that a business stores with the intent to sell.
Indicator
A measurement used to assess how well or poorly an economy is functioning; the big three are GDP, the unemployment rate, and the inflation rate.
Depreciation
A decline in the value of a good over time, often due to deterioration from use, such as the wearing out of clothing.
Per Capita
A measure divided in value for each person in a given population.
Unemployment Rate
The percentage of the total labor force without a job and looking for work.
Unemployment Rate Equation
Number of Employed Workers/Labour Force * 100%
GDP Equation
Y = C + I + G + Xn
Labour Force Participation Rate
Labor Force/Population Age 16 or older * 100%
Frictional Unemployment
Joblessness between jobs or when first entering or re-entering the job market.
Structural Unemployment
Joblessness due to fundamental changes in supply and demand within the economy, often due to technological change or international trade.
Cyclical Unemployment
Joblessness that is neither frictional nor structural and is generally considered rising and fall periodically.
Transferable Skills
Specialized abilities that can be used in diverse kinds of labor; for example, typing quickly transfers between many different office jobs.
Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
The sum of frictional and structural unemployment, considered to be unemployment rate at full employment of resources for real output.
NRU
frictional employment + structural unemployment
Cyclical Unemployment Equation
the actual unemployment rate – the natural rate of unemployment
Full Unemployment
Efficient use of all land, labor, and capital, which in the real world includes the natural rate of unemployment. (Full Employment does not equal 0% Unemployment).
Discouraged Workers
A person who has not taken an action to gain employment for four weeks or more because they believe there are no available jobs for which they are qualified.
Inflation
The general rise of prices over time (negative inflation is deflation).
Inflation Rate
The percentage change in prices from year to year.
Inflation Rate Equation
Price level in Year 2 — Price level in Year 1/Price level in Year 1 × 100
Standard of Living
Consumers' ability to satisfy their wants and needs in an economy.
Disinflation
A slowing of the inflation rate; price level is still rising, just at a less rapid rate.
Nominal
Actual dollar value (not adjusted for inflation).
Consumer Price Index
Measurement of price changes in a fixed basket of goods determined to be representative of the purchases of a typical family in a United States city.
Market Basket
In a particular price index, the set of products for which the prices are tracked.
CPI
Total cost of basket in current year/Total cost of basket in base year * 100
Base Year
A given year used as the standard or marker with which to compare data for all other years in the period being analyzed.
Borrower
Person or institution that has taken out a loan; also known as a debtor.
Creditor
Person or institution that has loaned money (lender).
Interest
The price of a loan, most often expressed as a percentage of the principal, which is the amount borrowed.
Unexpected Inflation
An increase in the average price level that was not anticipated by any economic forecast.
Risk
The possibility of gain or loss accepted in investing.
Fixed Income
The same nominal income, regardless of inflation (such as when a person lives on disability payments).
Nominal GDP
The dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country, with no adjustment for inflation.
Real GDP
The dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country, with an adjustment for inflation using a base year's price level.
GDP Deflator
A price index that aggregates the price of everything produced in the economy, not just consumer goods and services, like the CPI; used to adjust nominal GDP figures to real GDP.
GDP Deflator Equation
Nominal GDP/Real GDP * 100
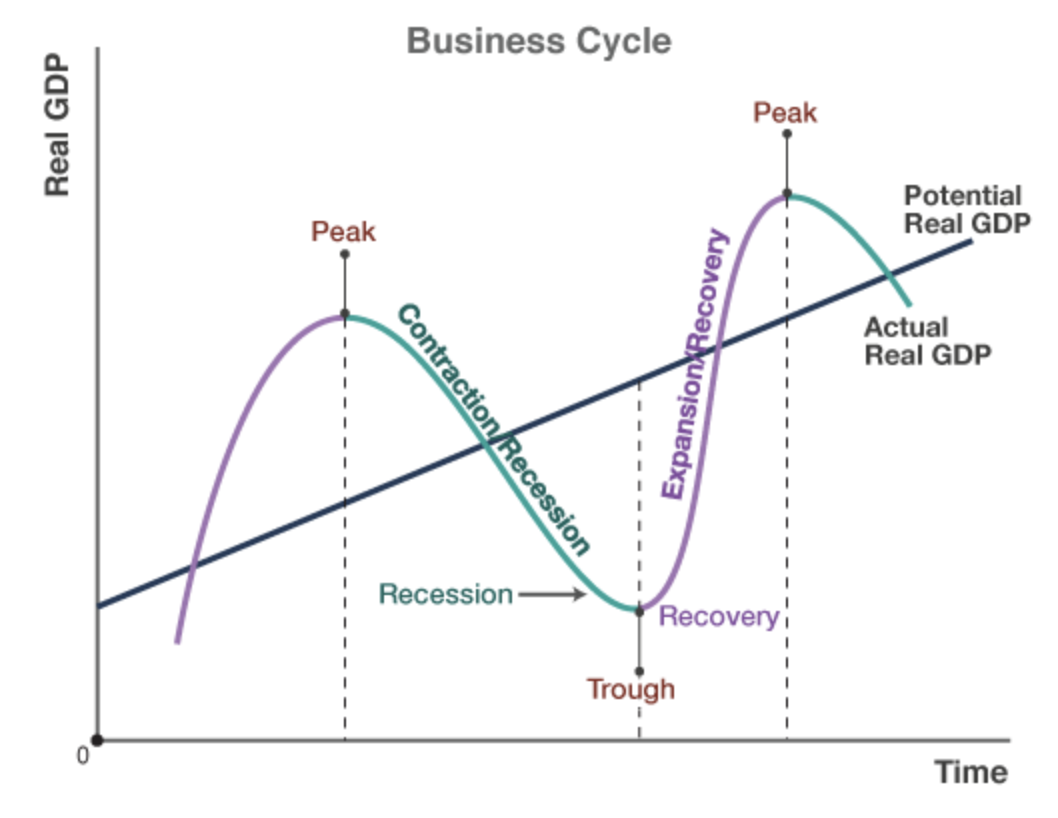
Business Cycle
An economic model showing fluctuations (changes) in aggregate output and employment because of changes in aggregate supply and/or aggregate demand.
Business Cycle Image
Recessionary Gap
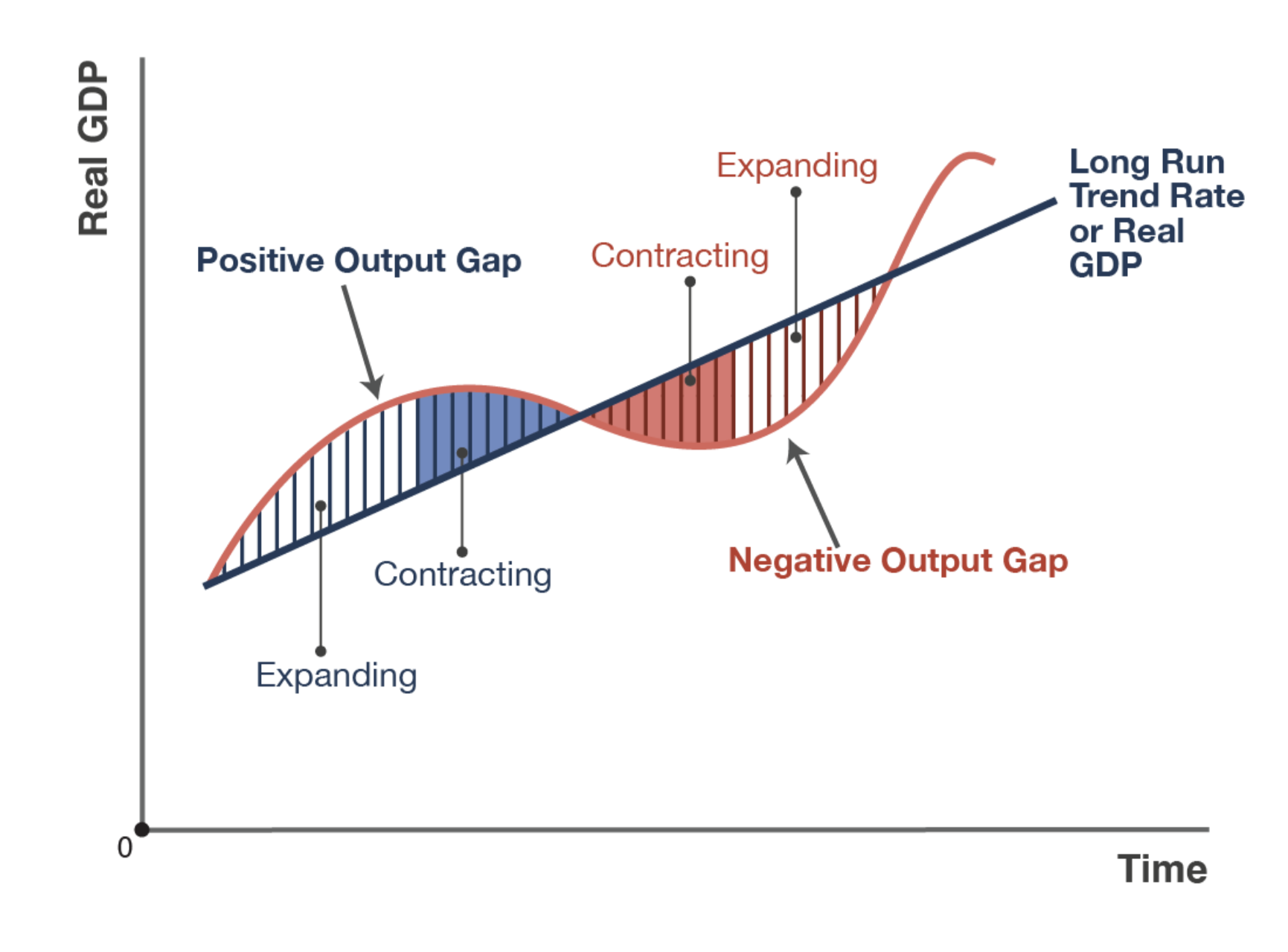
Also known as a negative output gap, when an economy's actual output is less than its potential output, characterized most often by an increasing unemployment rate.
Inflationary Gap
Also known as a positive output gap, when an economy's real output exceeds its potential output; unsustainable activity that will push prices up.
Gaps