Chemistry II Module of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse: Lesson 12: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives (Pro)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Lesson 12: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Lesson 12: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Draw the Decarboxylation Reaction Mechanism, starting with a β-ketoacid
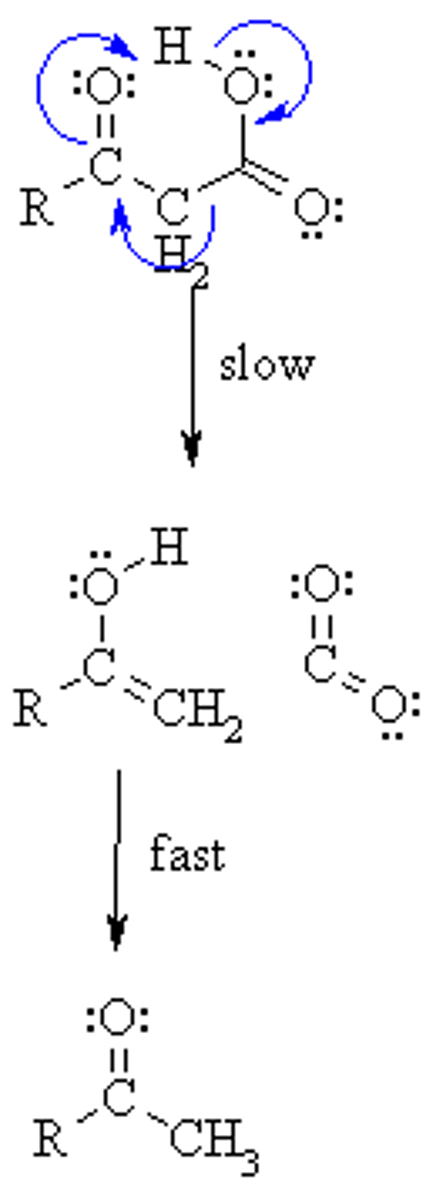
A decarboxylation reaction can occur when there is a(n) ___________________ functional group that is ____ to a Carboxylic Acid functional group.
(A) Carbonyl, α
(B) Carbonyl, β
(C) Alcohol, α
(D) Alcohol, β
(B) Carbonyl, β
A decarboxylation reaction can occur when their is a Carbonyl functional group that is β to a Carboxylic Acid functional group.
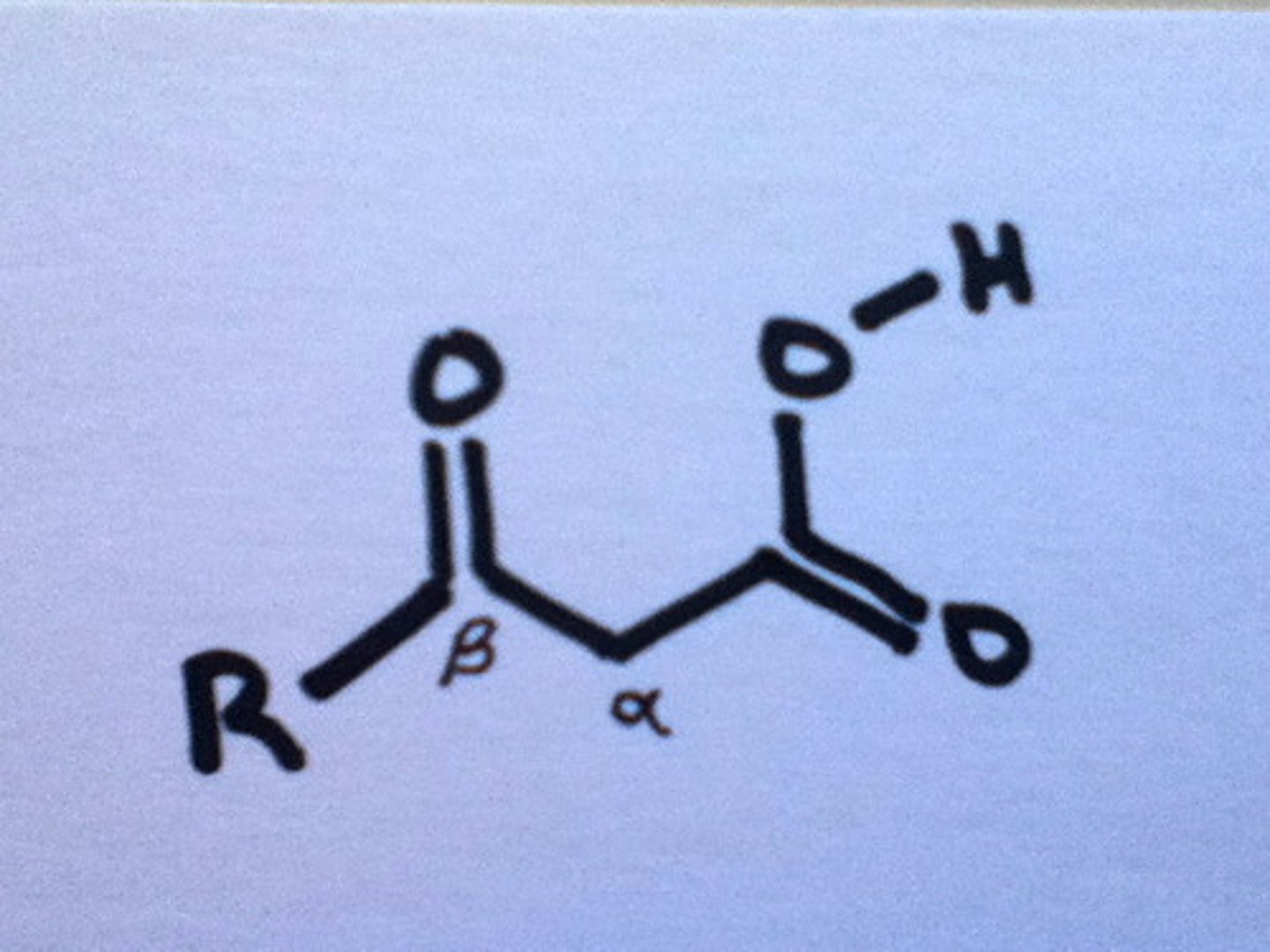
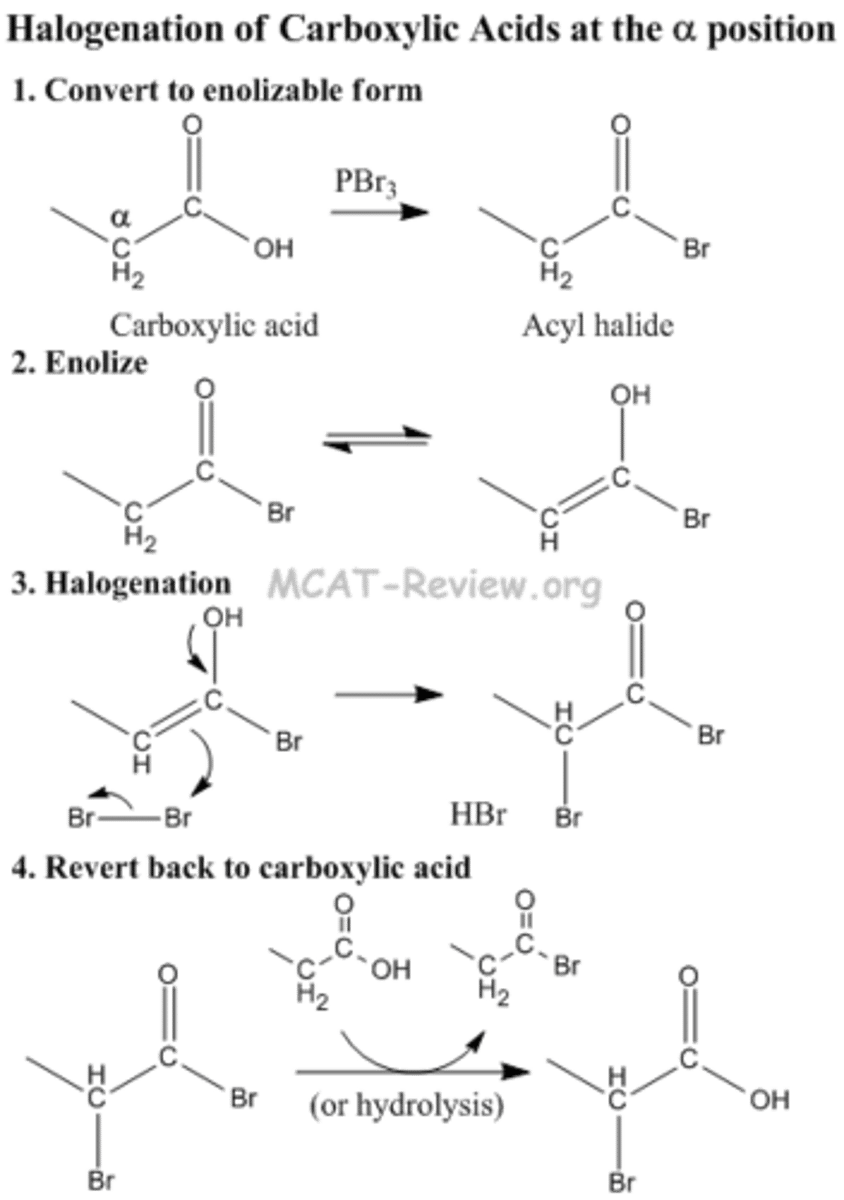
Draw the mechanism for the Alpha-substitution of a Carboxylic Acid resulting in a 2-bromo-carboxylic acid. Keep in mind the two steps:
(1) Br2, PBr3
(2) H2O
This is also called the HVZ reaction.
Adding Ammonia to your 2-bromo-carboxylic acid will result in what important biomolecule?
(A) NAD
(B) Purine
(C) Pyrimidine
(D) Amino Acid
(D) Amino Acid!!!
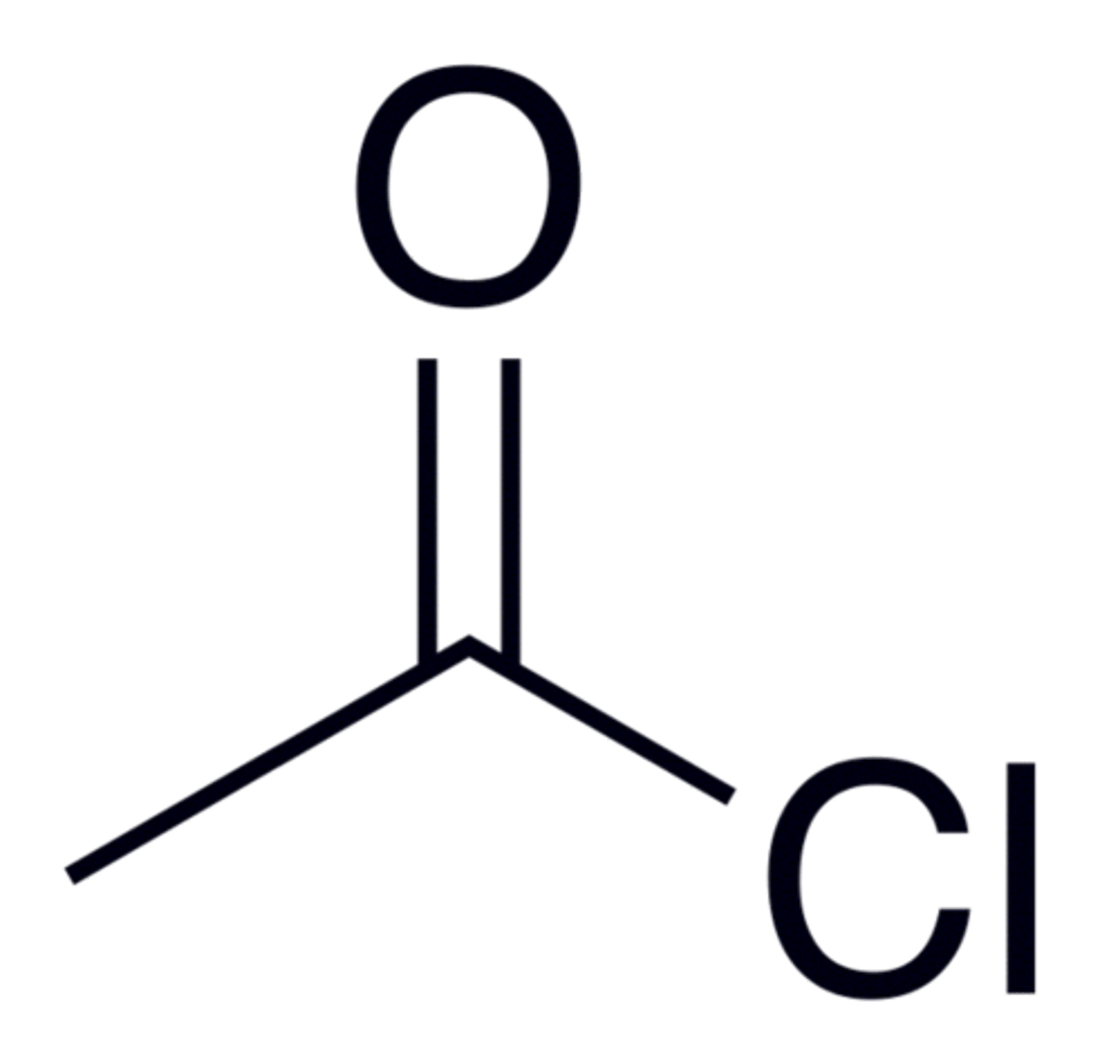
You chlorinate Acetic Acid. What is the name of the resulting acyl (acid) halide?
Acetyl Chloride.
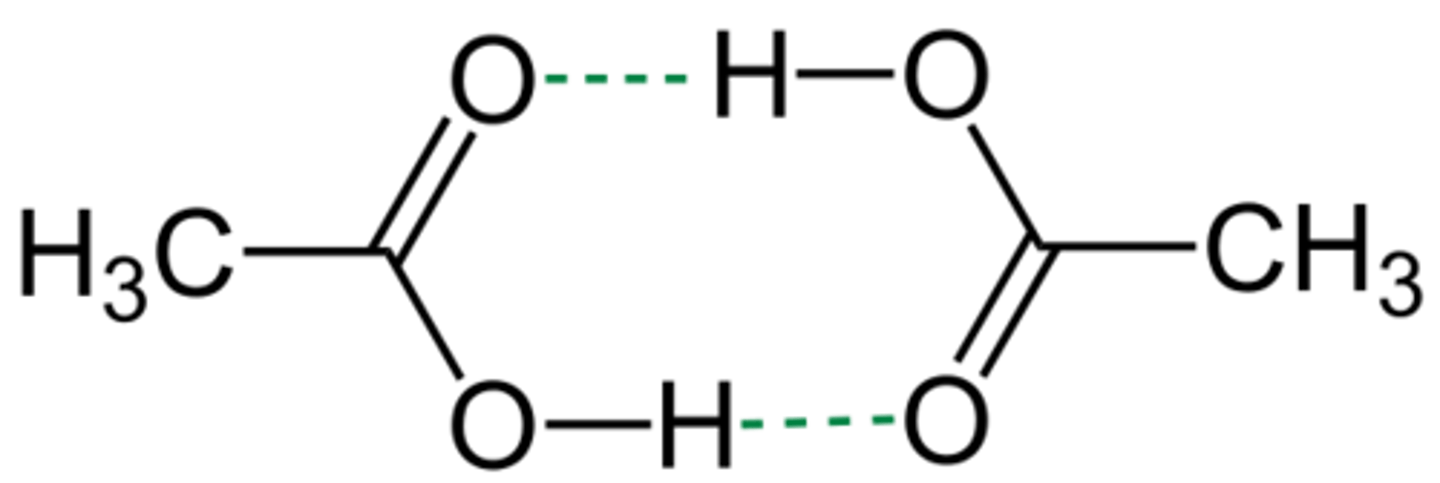
Which has a higher boiling point? Acetic Acid or Acetyl Chloride?
Acetic Acid. This is due to the fact that Acetic Acid can participate in hydrogen bonding while acetyl chloride only has dipole-dipole interactions.
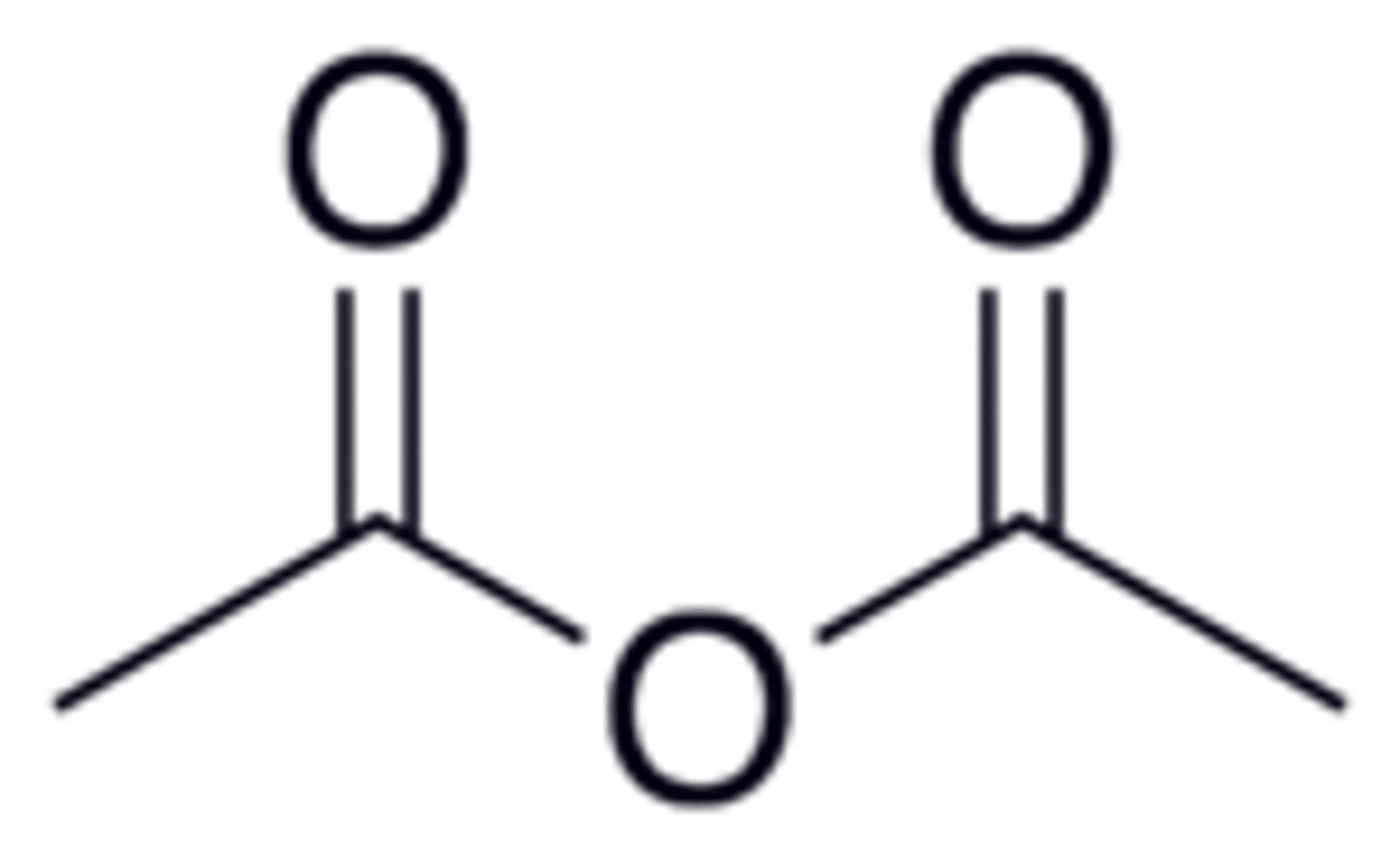
You react two acetic acid molecules together to form an Anhydride. What is the name of your product?
Acetic Anhydride
You react an acetic acid molecule with a benzoic acid molecule together to form an Anhydride. What is the name of your product?
Acetic Benzoic Anhydride
Note: Keep in mind alphabetical order
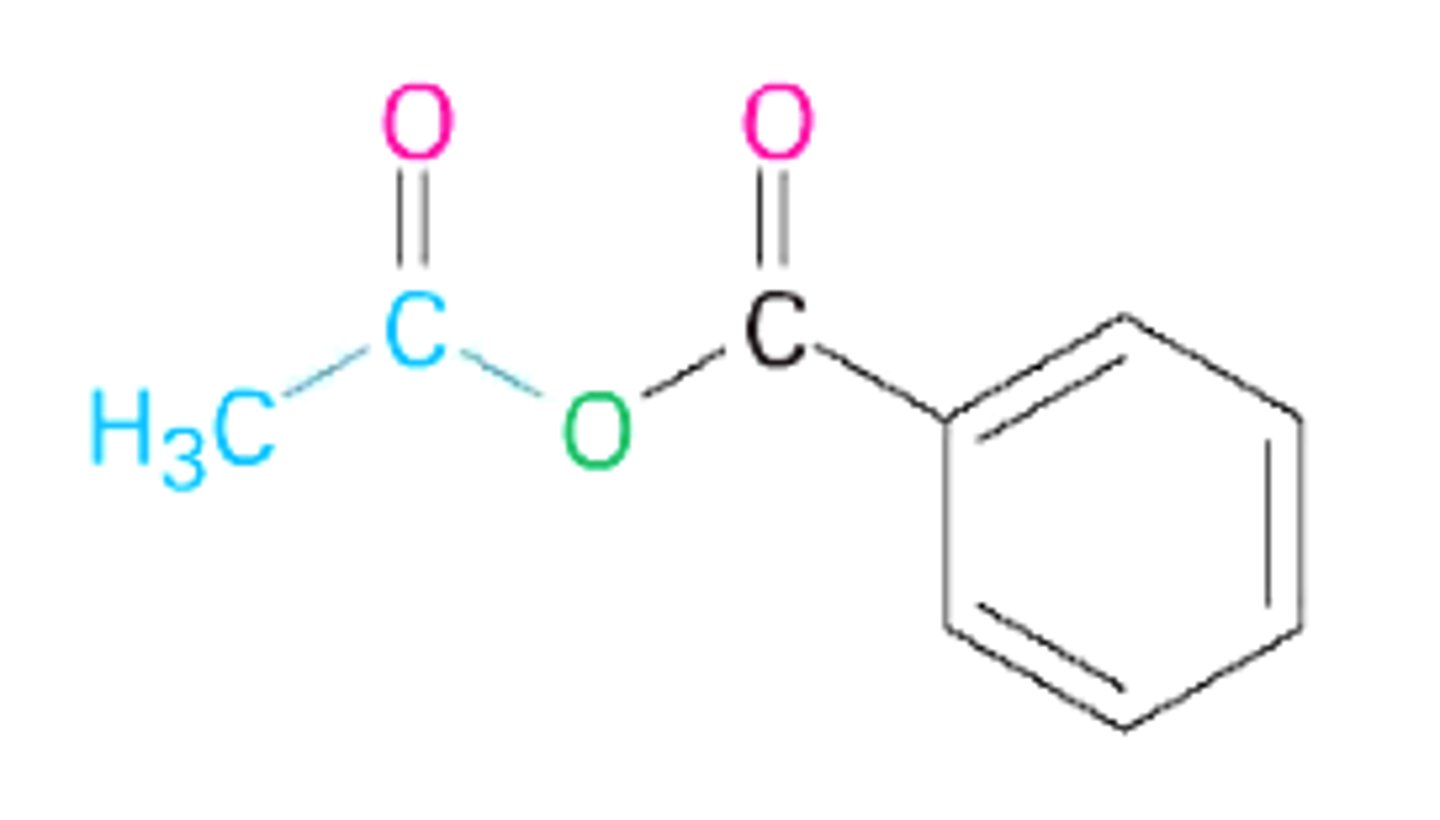
Order the following compounds in terms of increasing boiling points:
I. Acetic Anhydride
II. Acetyl Chloride
III. Acetic Acid
(A) I < II < III
(B) II < I < III
(C) III < I < II
(D) II < III < I
(D) II < III < I
In terms of increasing boiling points: Acetyl Chloride (dipole-dipole) < Acetic Acid (hydrogen bonding) < Acetic Anhydride (dipole-dipole but much larger molecular weight)
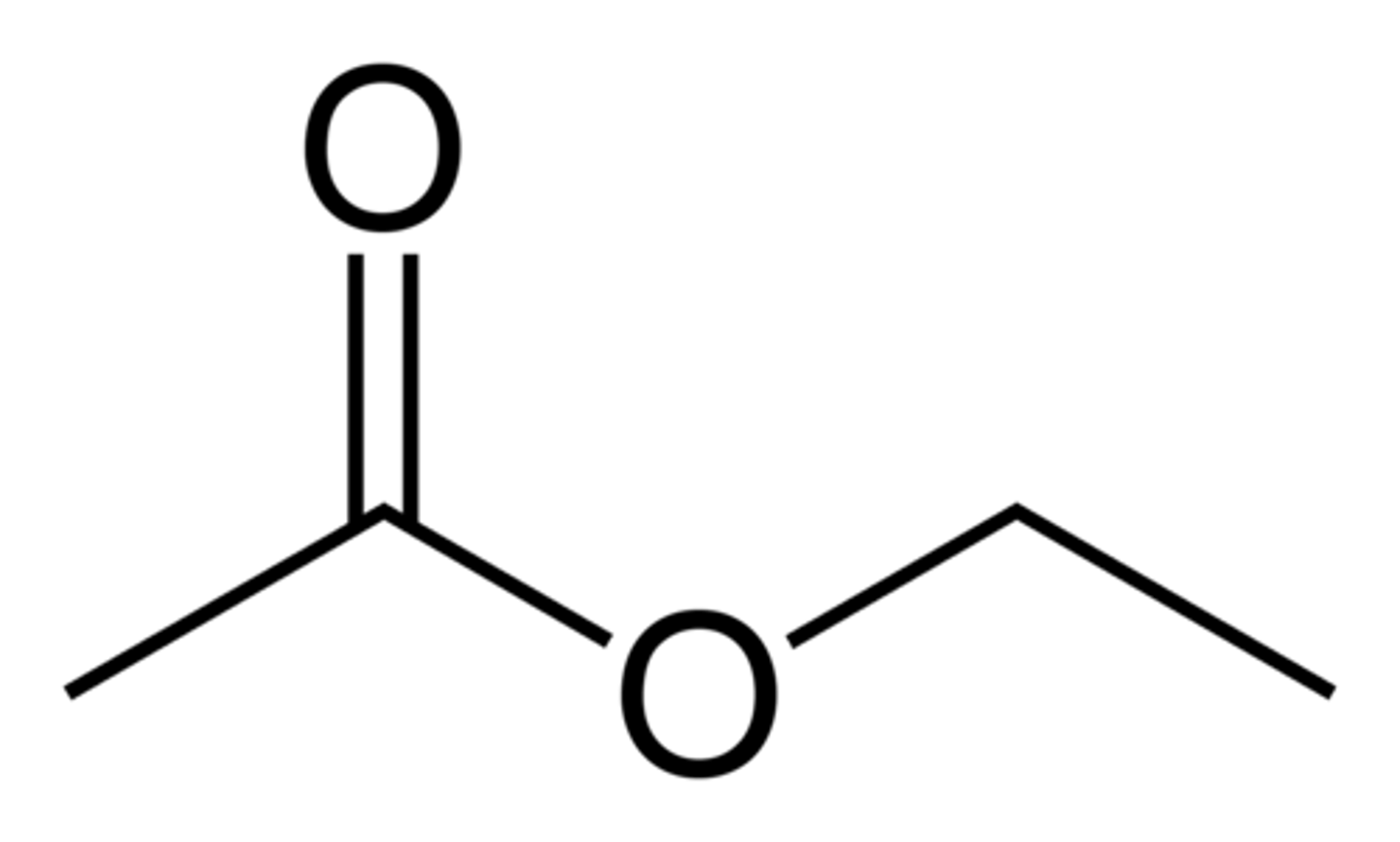
Draw Ethyl Acetate (Ethyl Ethanoate).
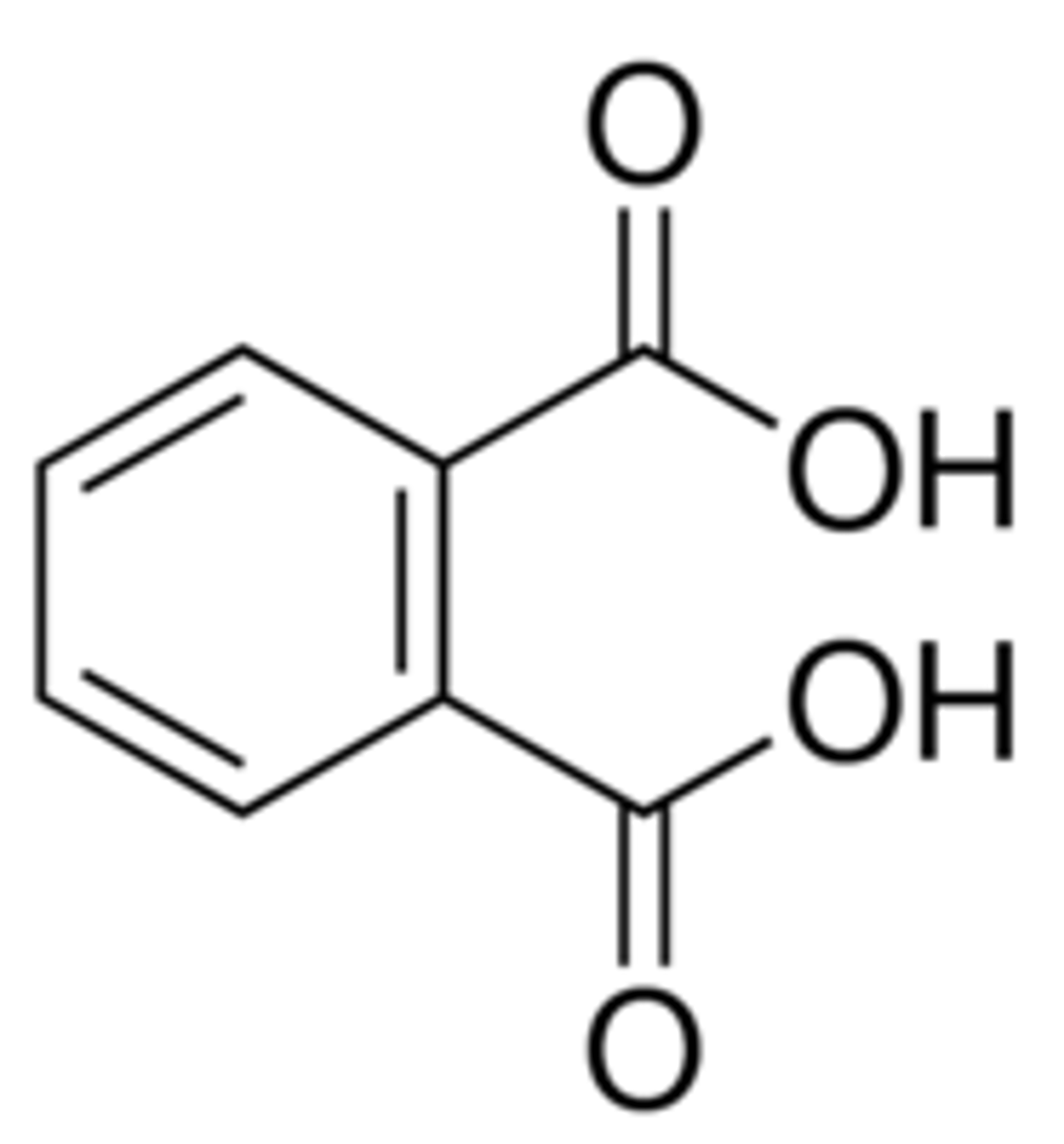
CRB A currently-researched health concern are phthalates in everyday products. Draw ortho-phthalic acid.
CRB True or false? A phthalate can undergo an intramolecular Esterification between its two carboxylic acids.
False. A phthalate can undergo an intramolecular Anhydride Formation between its two carboxylic acids.
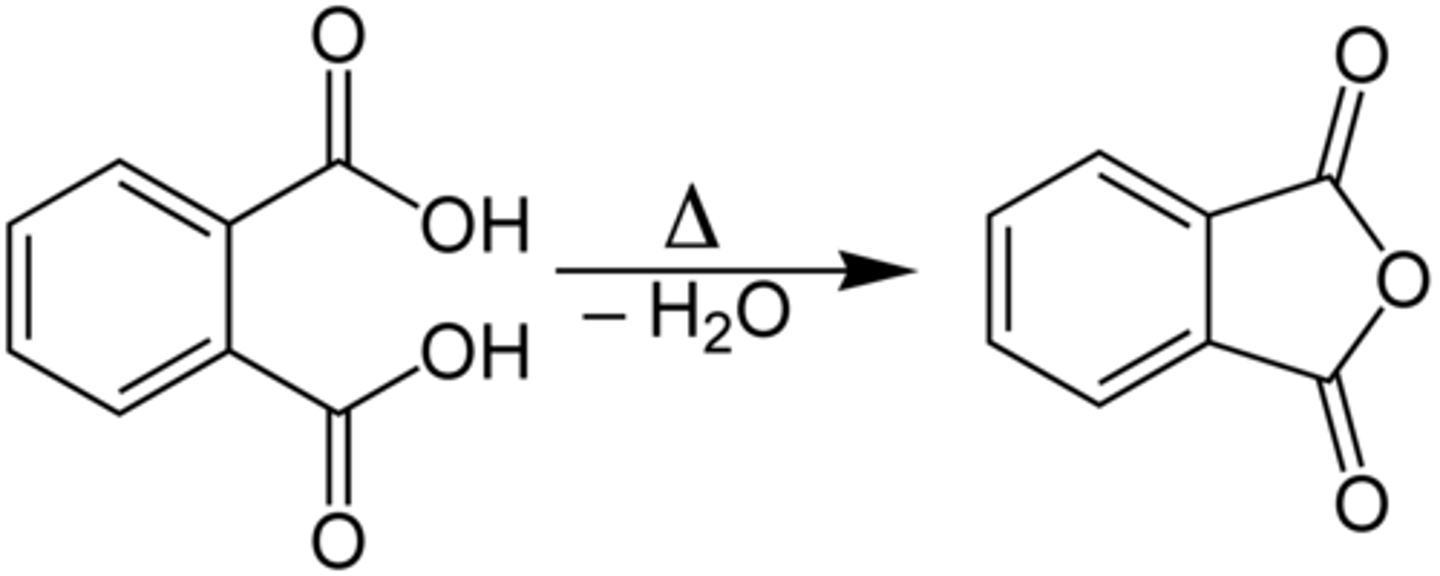
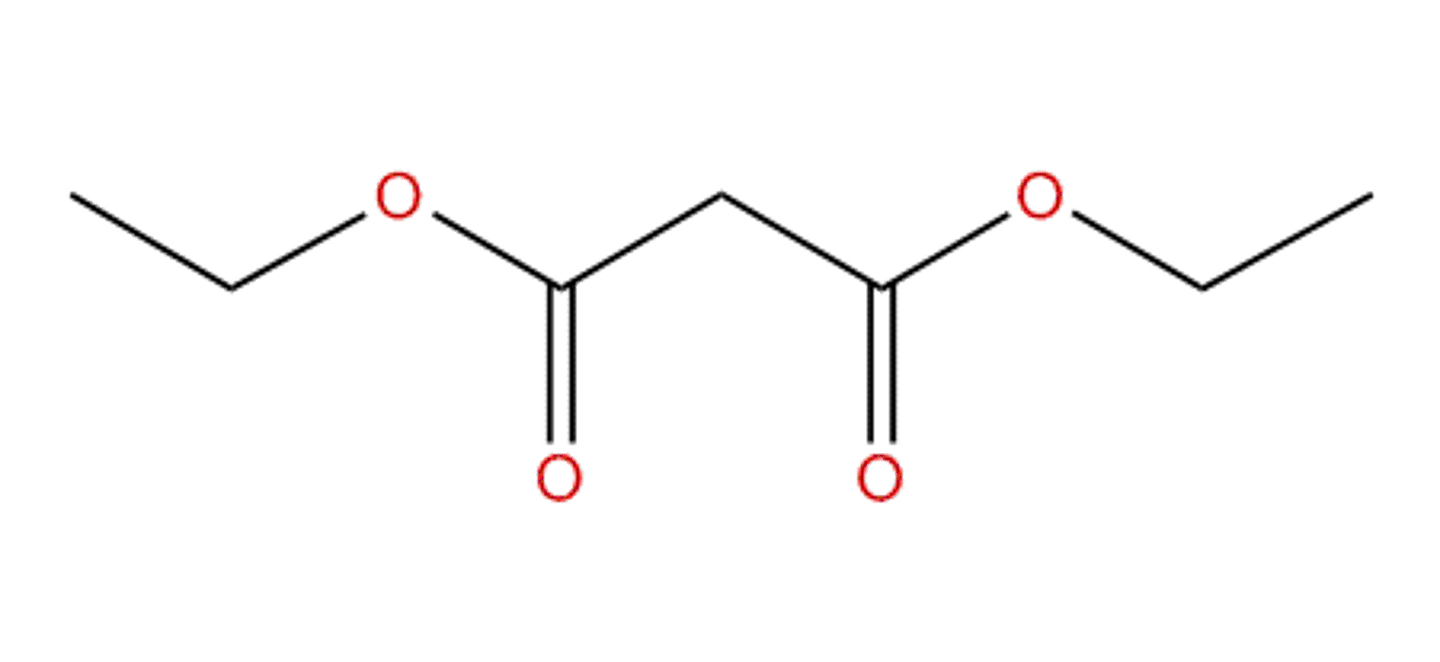
Draw Diethyl Malonate.
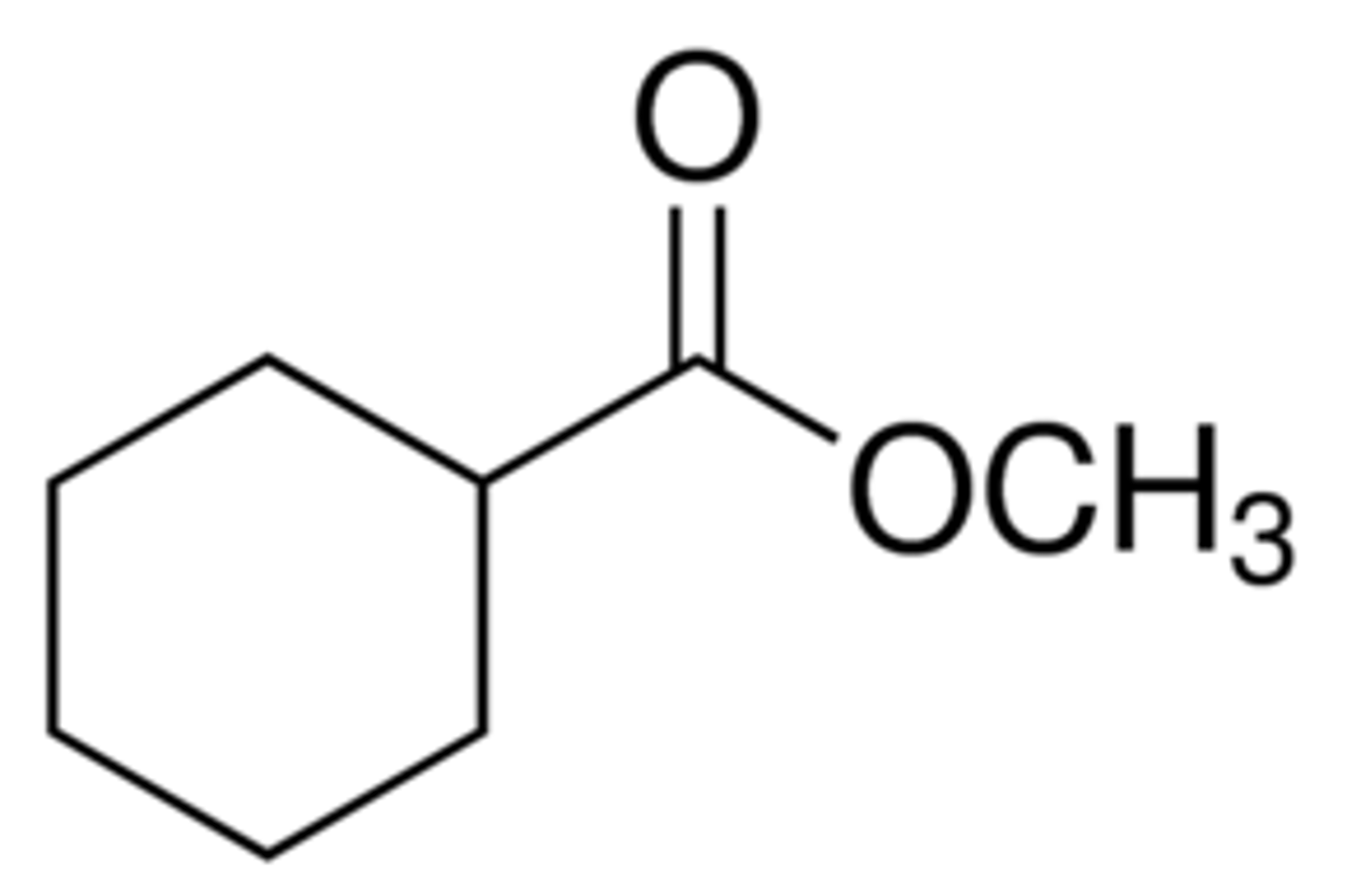
Draw Methyl Cyclohexanecarboxylate
Order the following compounds in terms of increasing boiling points:
I. Methyl Acetate
II. 2-butanol
III. 2-methylbutane
(A) I < II < III
(B) II < I < III
(C) III < I < II
(D) I < III < II
(C) III < I < II
In terms of increasing boiling points: 2-methylbutane (London Dispersion Forces) < Methyl Acetate (Dipole-dipole) < 2-butanol (Hydrogen Bonding)
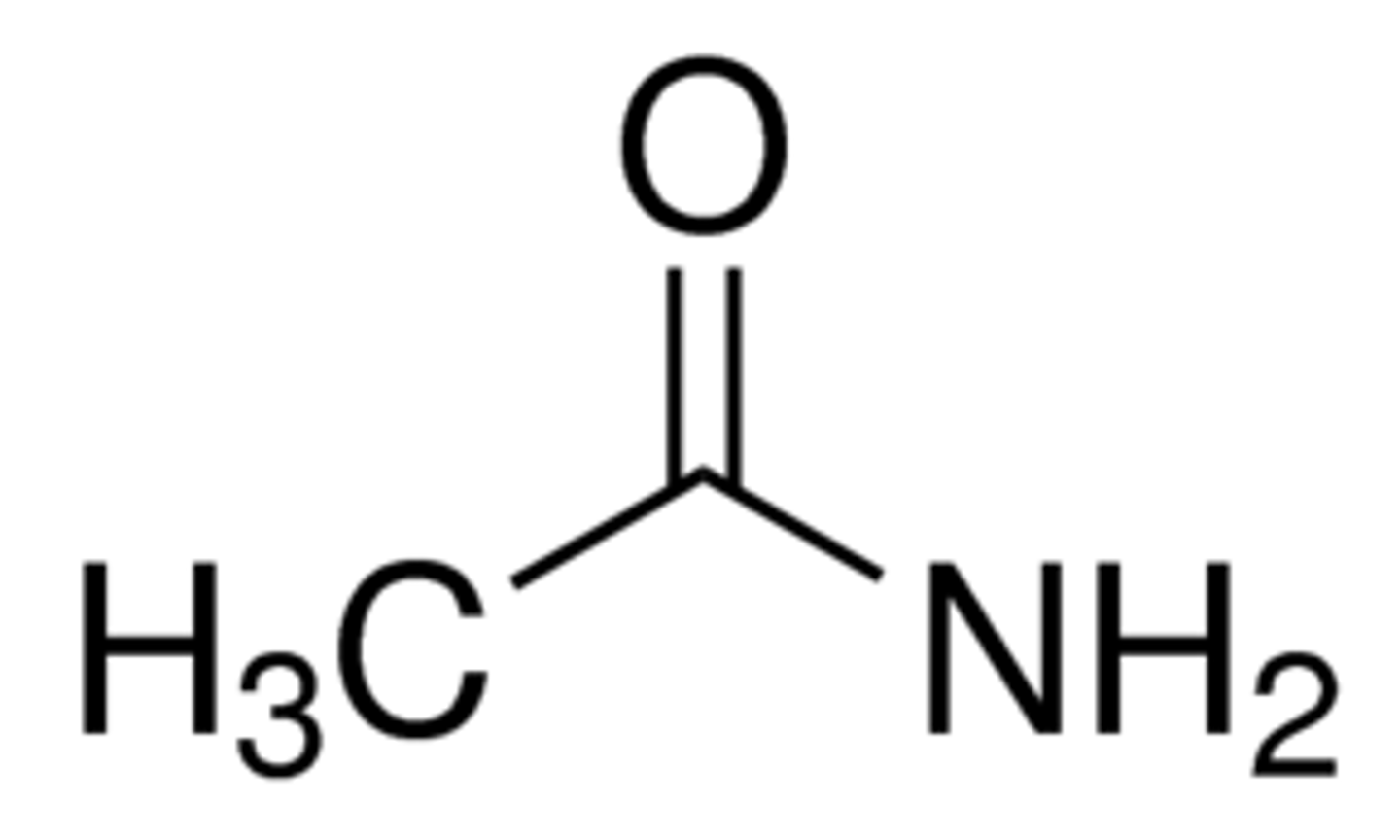
Draw Ethanamide (Acetamide)
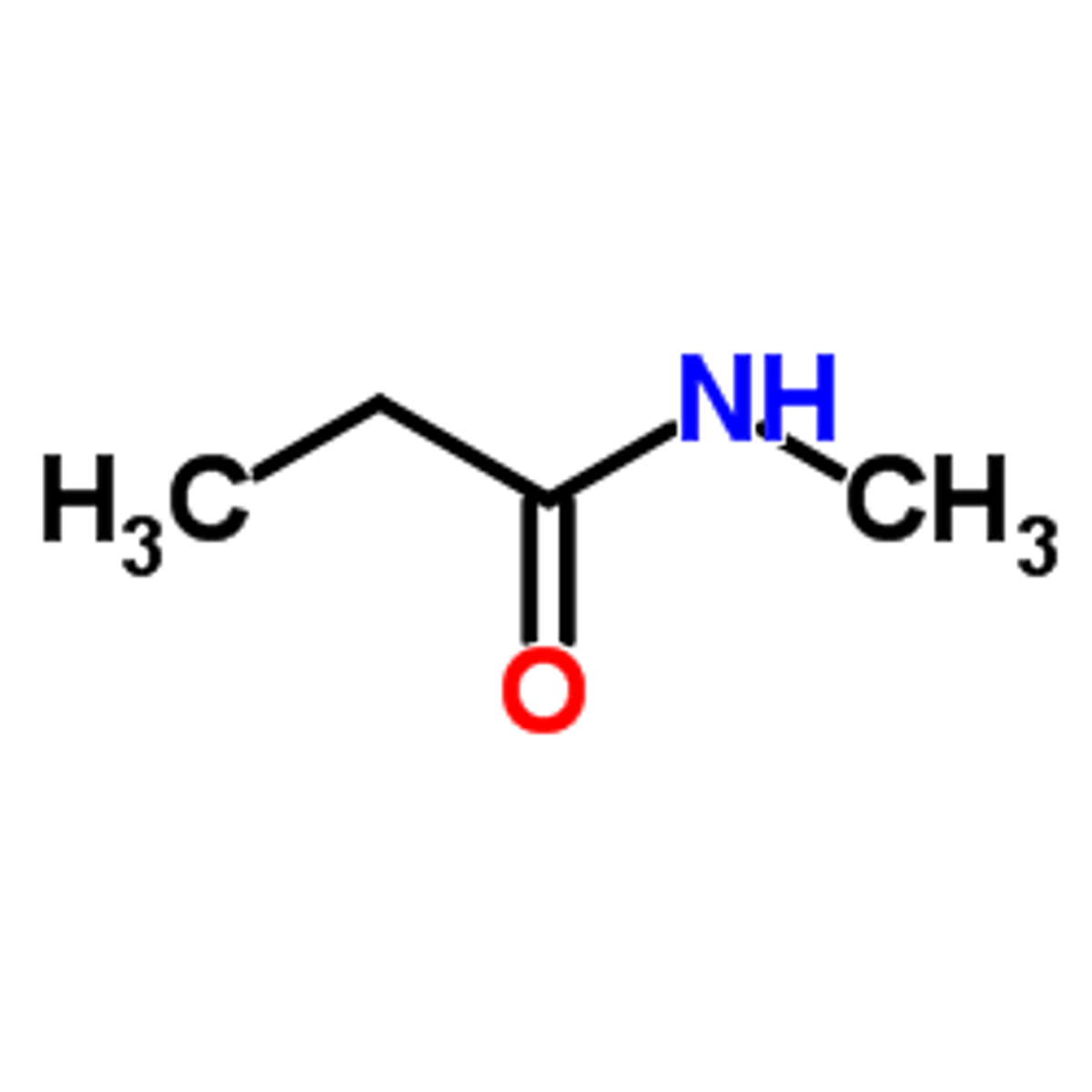
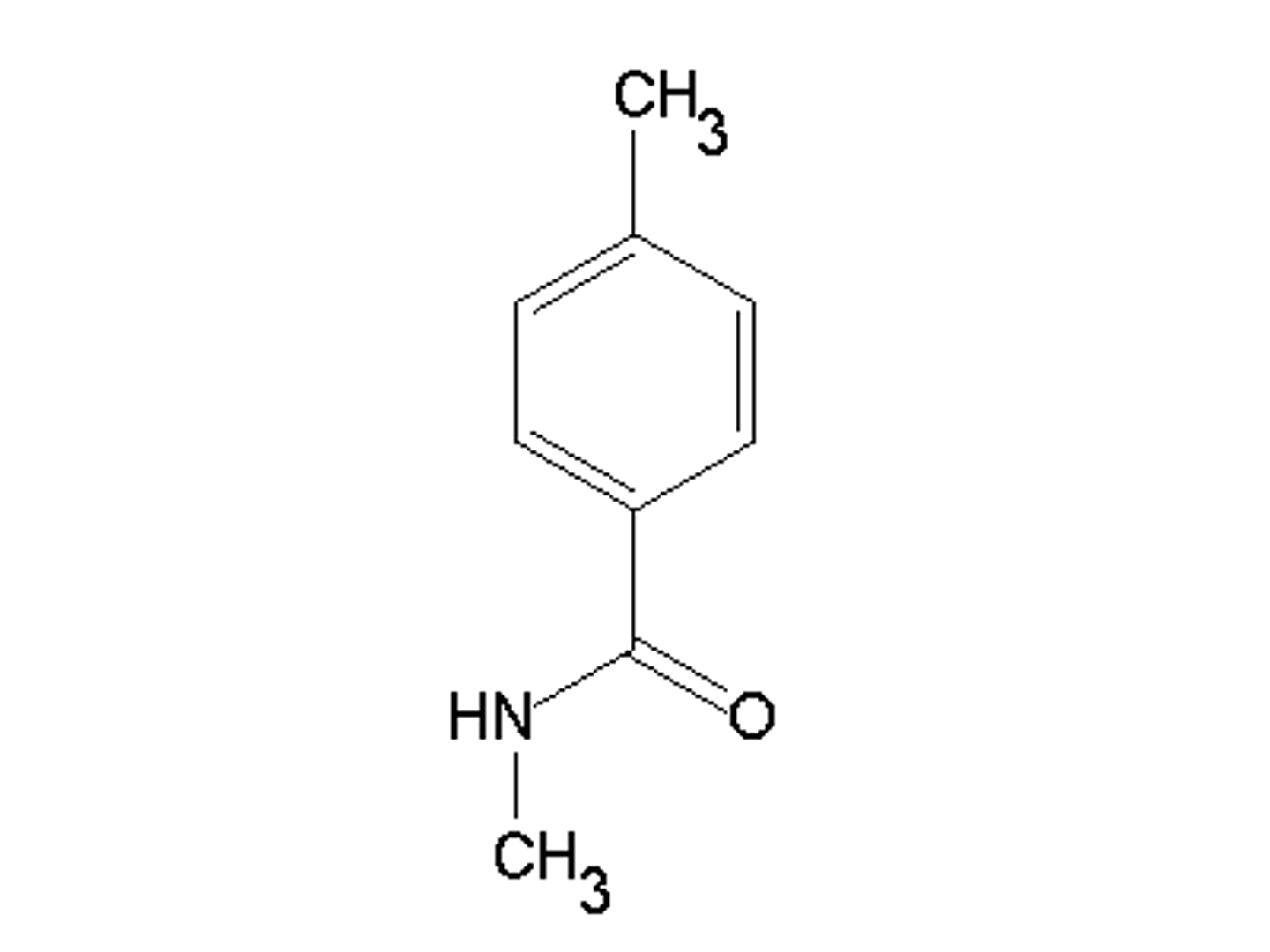
Draw N-methyl Propanamide.
Draw N,N-dimethyl Butanamide.
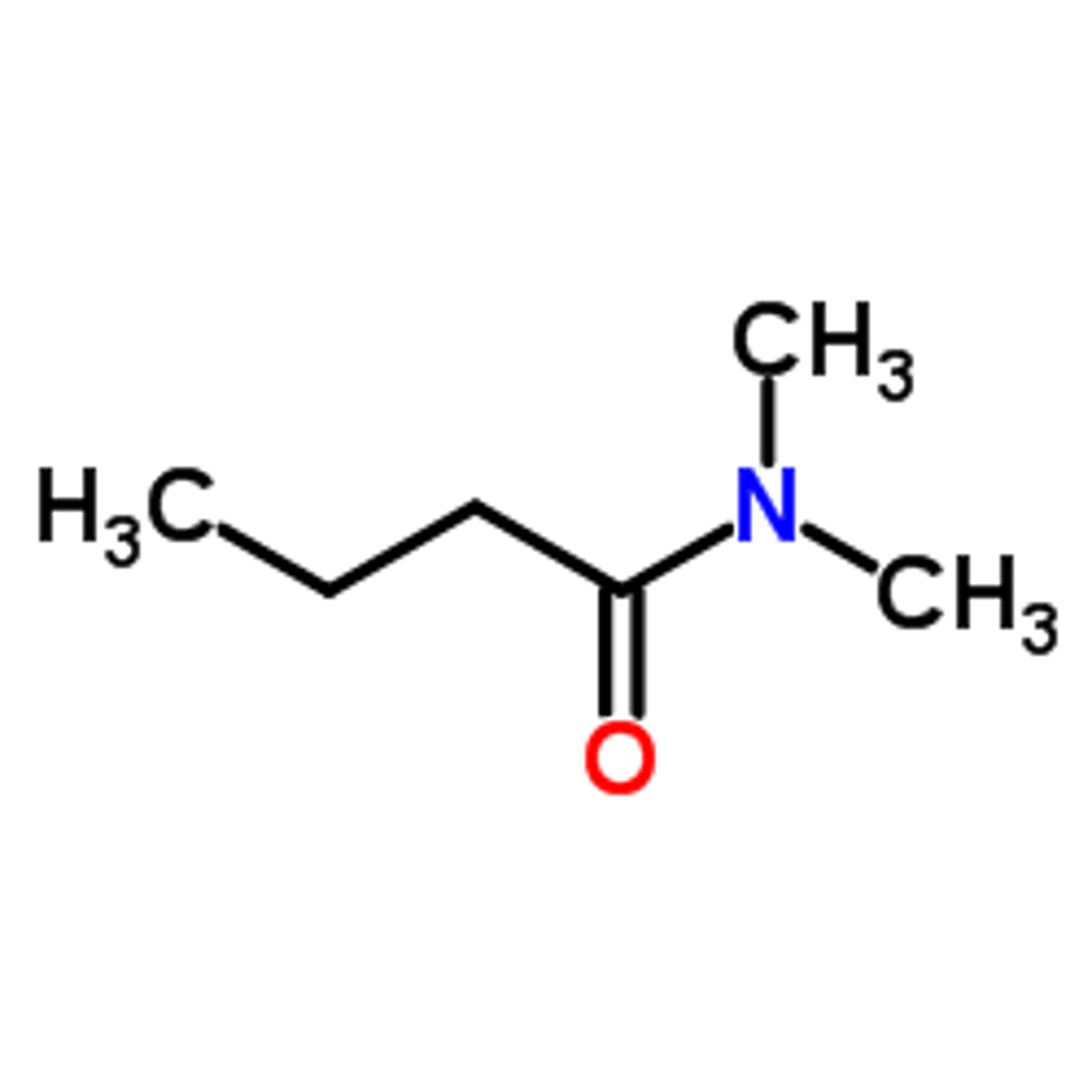
Draw N,4-dimethyl Benzamide
How does Induction relate to the reactivity of an Acetyl Chloride?
Induction is the withdrawing of electron density, which chloride does to the carbonyl carbon due to chloride's high electronegativity. This results in a more electrophilic alpha-carbon, making acetyl chlorides more reactive.
Why does resonance dominate induction in the case of an amide?
This is because nitrogen is not very electronegative, so it holds onto its electrons less tightly and will more readily donate them to form the resonance structure.
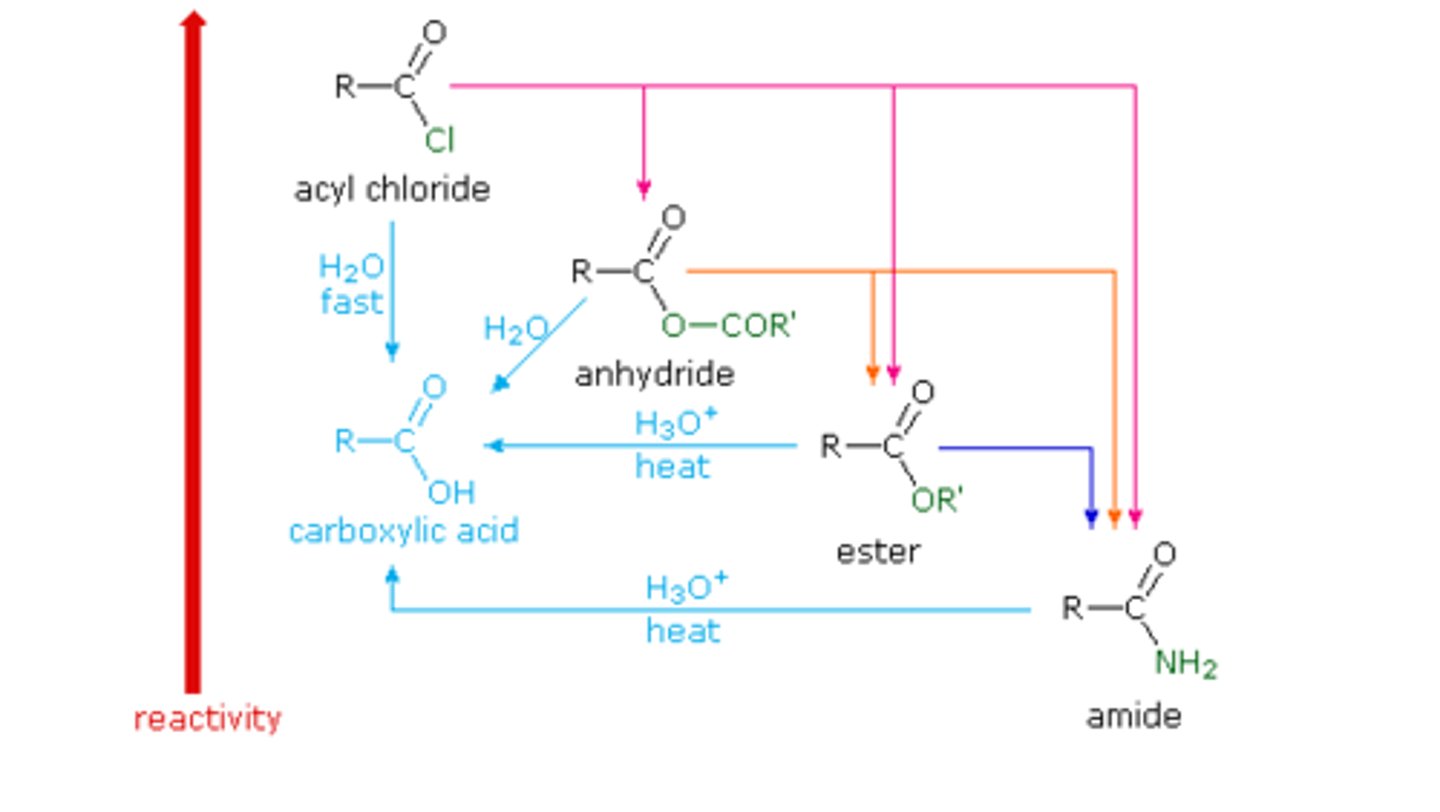
Order the following compounds in terms of increasing reactivity:
I. Acetic Anhydride
II. Acetamide
III. Methyl Acetate
IV. Acetyl Chloride
(A) II < III < I < IV
(B) II < I < III < IV
(C) IV < III < I < II
(D) IV < I < III < II
(A) II < III < I < IV
In terms of increasing reactivity: Acetamide < Methyl Acetate < Acetic Anhydride < Acetyl Chloride.
Draw the Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Mechanism.
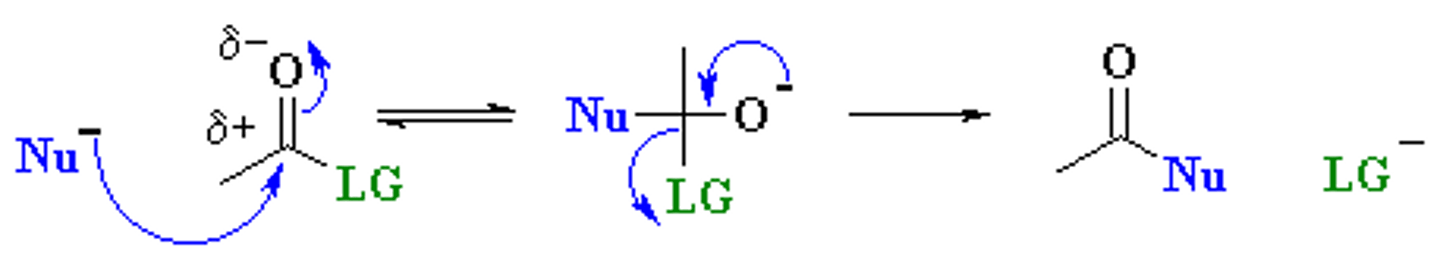
You have an Acetate Anion and Acetyl Chloride in solution. What product will result?
(A) Acetic Anhydride
(B) Acetamide
(C) Methyl Acetate
(D) Acetyl Chloride
(A) Acetic Anhydride
Acetic Anhydride is a more stable product than Acetyl Chloride; thus, its formation is favored.
You have Hydrochloric Acid and Methyl Acetate in solution. What product will result?
(A) Acetic Anhydride
(B) Acetamide
(C) Methyl Acetate
(D) Acetyl Chloride
(C) Methyl Acetate
Methyl Acetate is a more stable product than Acetyl Chloride, so the reaction will not proceed.
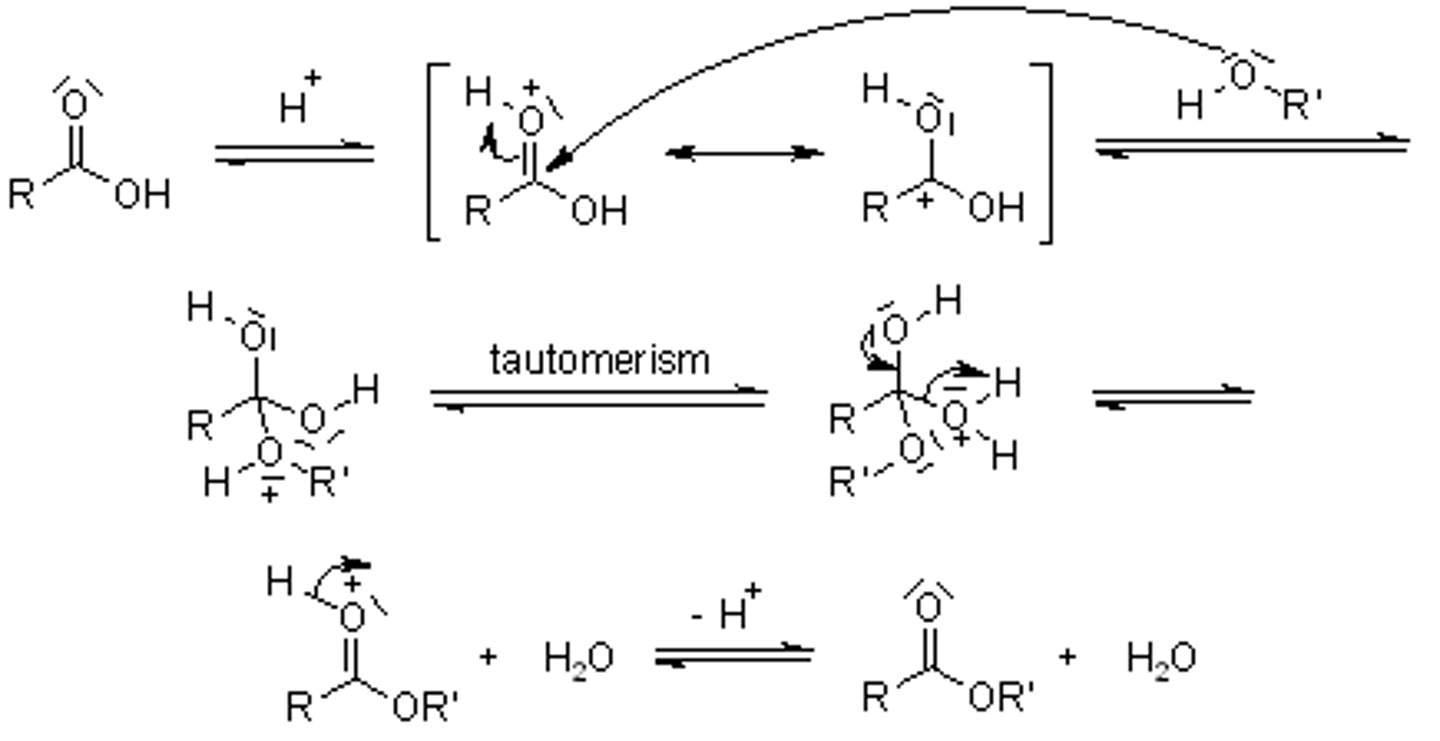
CRB Draw the mechanism for an acid-catalyzed esterification of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol.
CRB Under which of the following conditions will a Fischer Esterification occur?
I. Acidic conditions with carboxylic acids and alcohols
II. Basic conditions with lactones and alcohols
III. Acidic conditions with anhydrides and alcohols
(A) I only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and III only
A Fischer Esterification can occur in either of the following conditions:
I. Acidic conditions with carboxylic acids and alcohols
II. Acidic conditions with anhydrides and alcohols
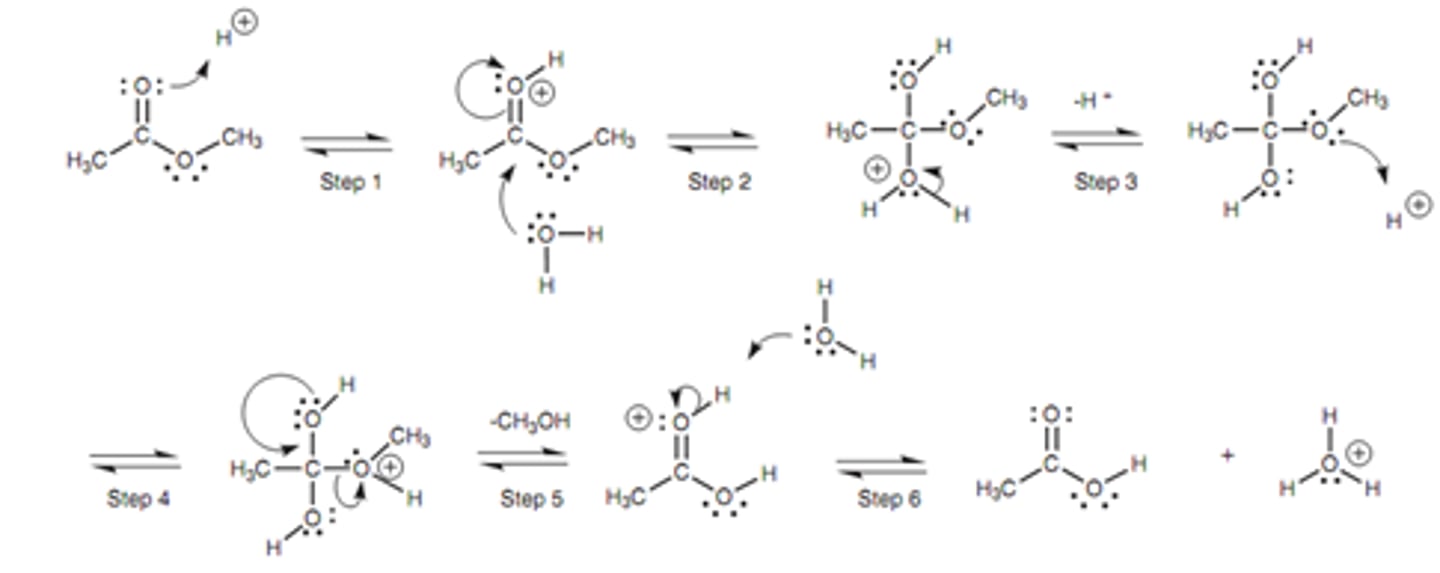
Draw the mechanism for Acid-catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis.
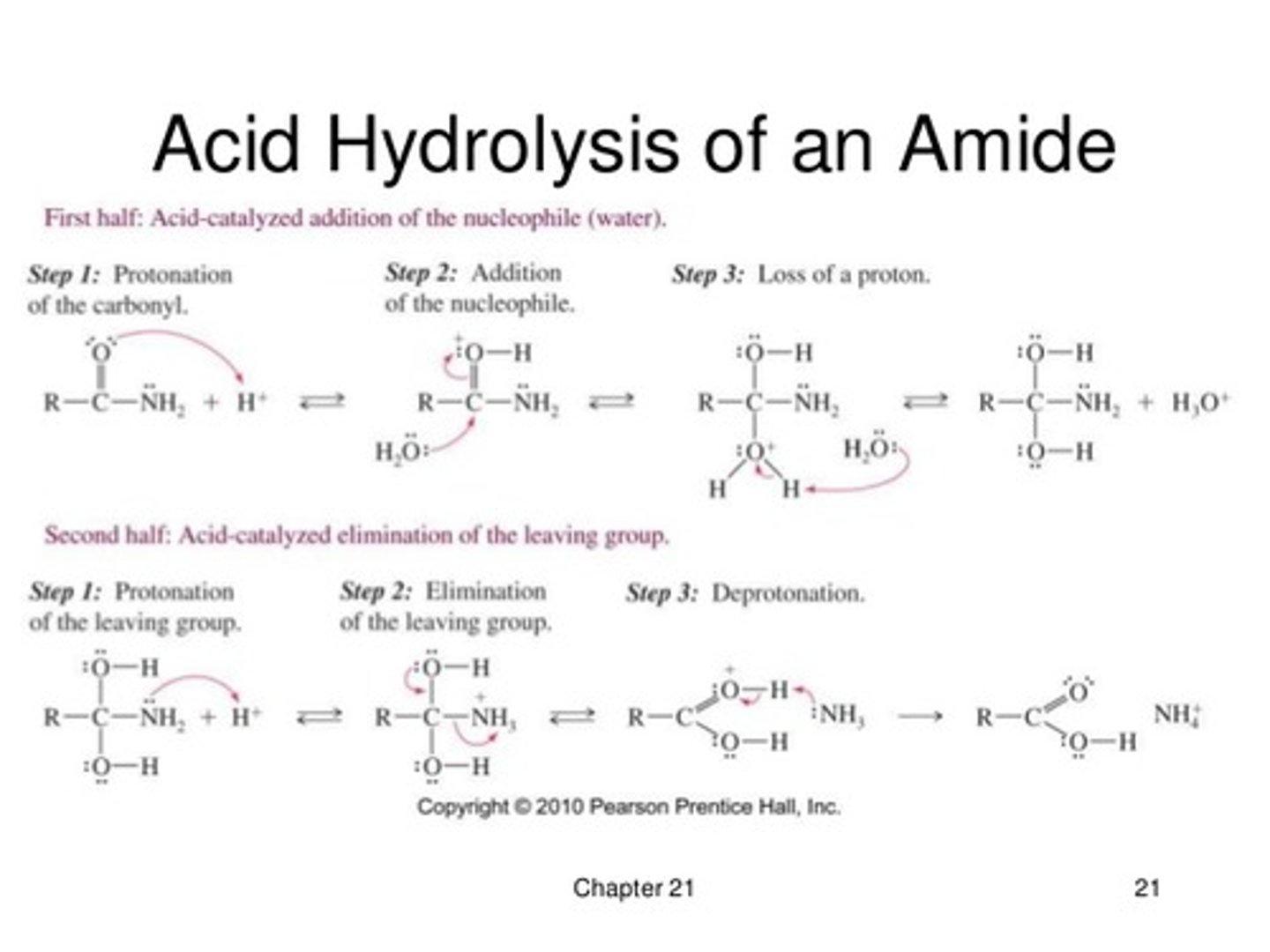
Draw the mechanism for Acid-catalyzed Hydrolysis of an Amide.
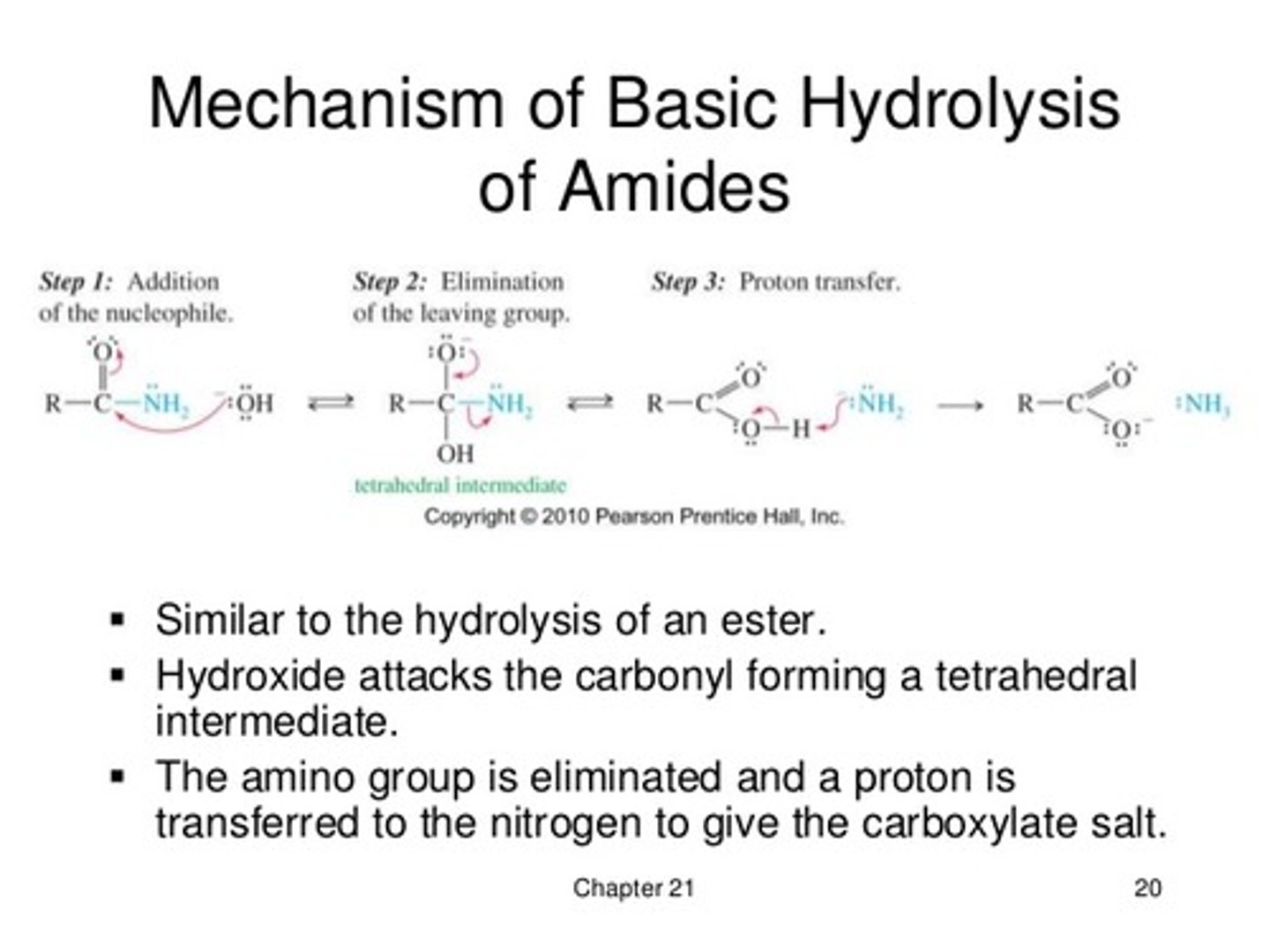
Draw the mechanism for Base-catalyzed Hydrolysis of an Amide.
Draw a β-lactam ring.
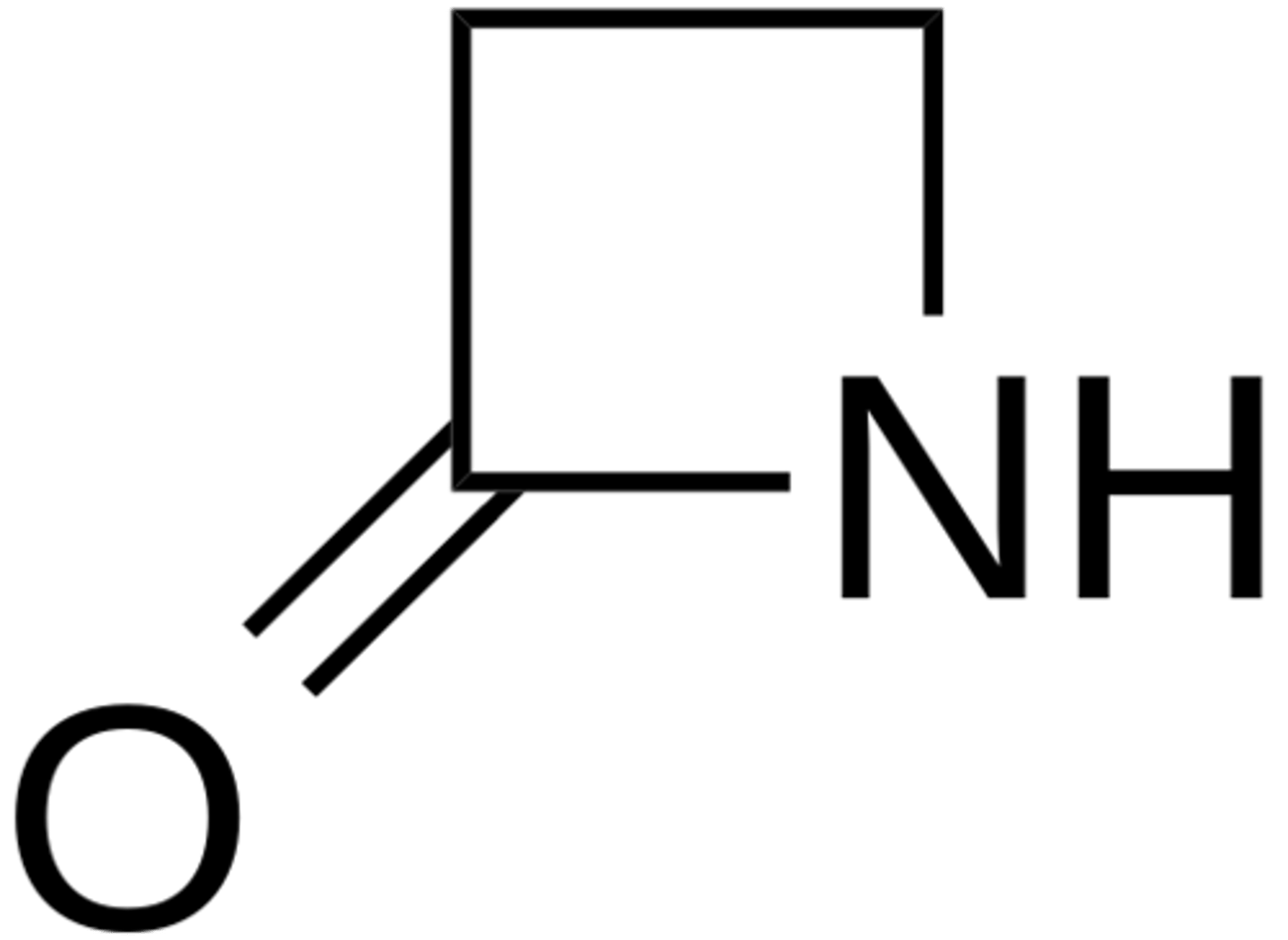
CRB When talking about Lactams (and their closely related Lactones), what do the greek letter (e.g. β) signify?
(A) Number of members in the ring
(B) Number of Carbons that are not part of the carboxylic acid derivative
(C) Number of Carbons including the carboxylic acid derivative
(D) Number of atoms bound together
(B) Number of Carbons that are not part of the carboxylic acid derivative
For example, that β-lactam has two carbons that aren't part of the carboxylic acid.
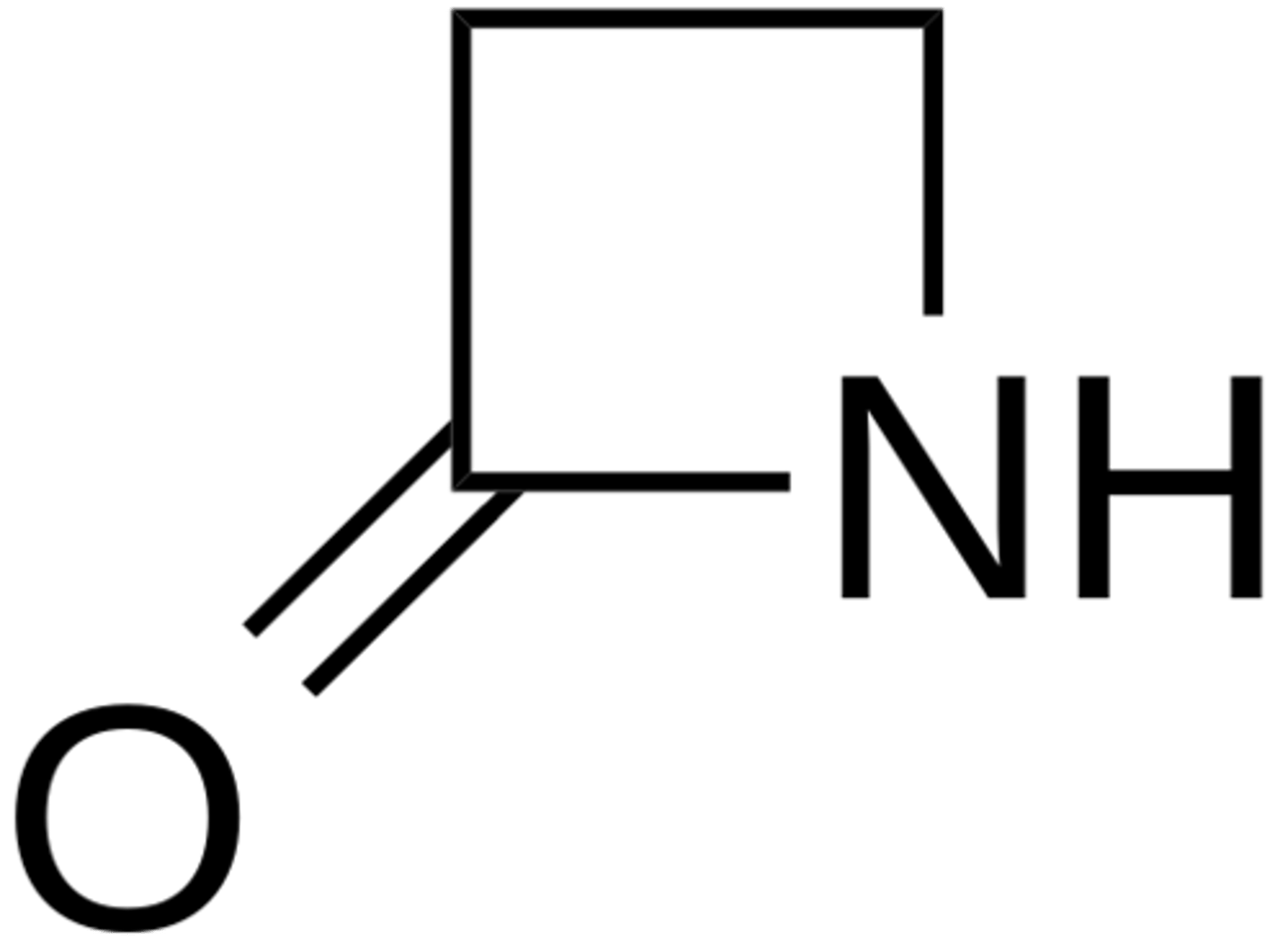
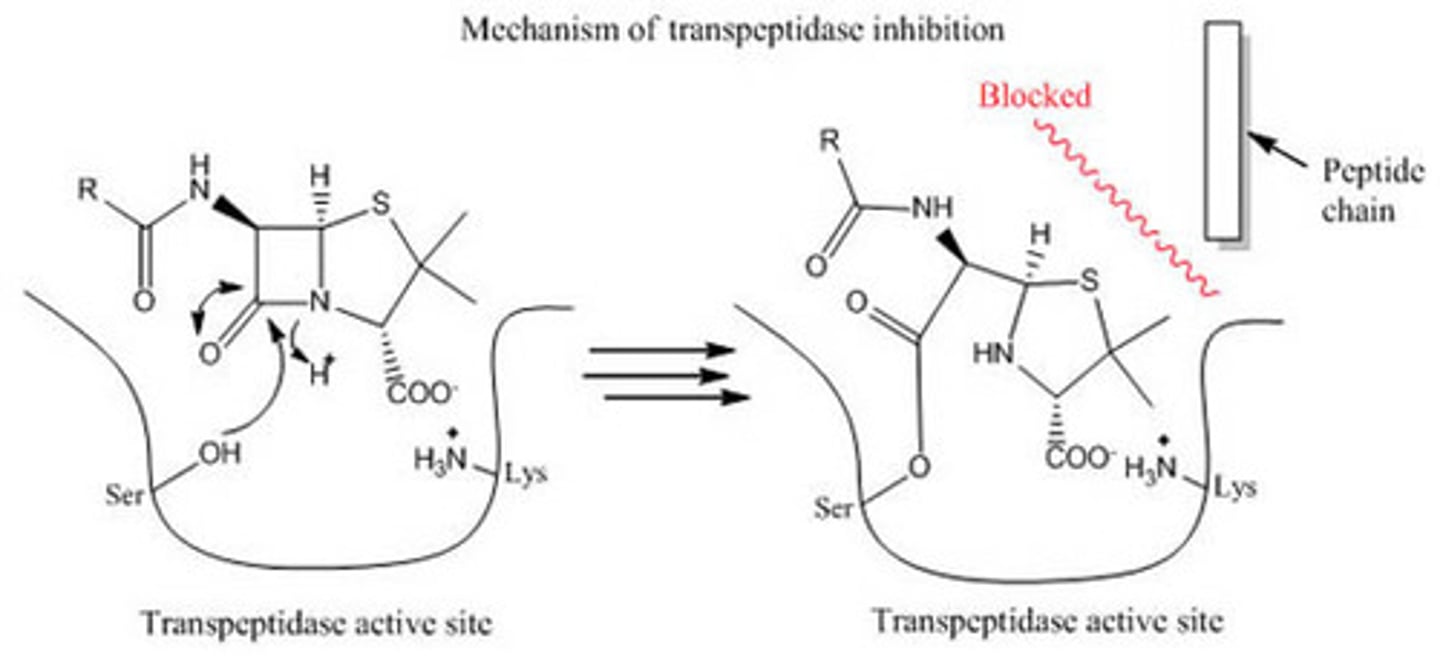
Penicillin has a β-lactam ring. Why is this essential in terms of the reactivity of Penicillin and its interaction with transpeptidase, the enzyme in bacteria responsible for building its cell wall?
The β-lactam ring results in a non-planar structure, which means nitrogen will donate less electron density to the carbonyl carbon, increasing its reactivity. The β-lactam ring also suffers from ring-strain, resulting in further reactivity. This way, transpeptidase is more inclined to attack penicillin's carbonyl carbon, resulting in transpeptidase getting disabled.