Kinetics
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Factors Affecting Rate
state of reactants; temperature; concentration; use of catalyst
What does a change in the state of reactants affect?
Increase in surface area increases rate (smaller particle size = bigger surface area)
What does temperature affect?
Increases in temp increases rate
What does concentration affect?
Increase in concentration increases frequency of collisions
Collision Theory
Reactants must collide in the correct orientation and with sufficient energy to react
Change in number of collisions causes
reaction rate to change
Rate Law
Rate = k[A]ᵐ[B]ⁿ
Rate law is only written with
reactants
Zero order
[ ] over time
Slope of zero order
-k
First order
ln[ ] over time
Slope of first order
-k
Second order
1/[ ] over time
Slope of second order
+k
Half-life of first order reaction
remains constant
Successful collisions need
enough energy to overcome Eₐ & proper orientation to break bonds
Mechanisms
Rate law of any elementary reaction can be written from its stoichiometry
Overall rate law is determined by
the slowest step
Larger rate constants leads to
larger % of moles having successful collisions
Rate law formula includes
catalysts (element goes from reactant → product)
Enzymes
Type of catalyst
Rate law formula does not include
intermediates (element goes from product → reactant)
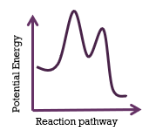
This energy profiles represents a reaction that is
exothermic; 2-step mechanism; slow 1st step
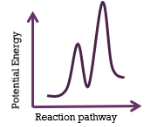
This energy profiles represents a reaction that is
endothermic; 2-step mechanism; slow 2nd step
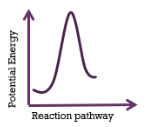
This energy profiles represents a reaction that is
endothermic; 1-step mechanism
To find ΔH from bond rates
broken bonds — formed bonds
(reactants — products)
When ΔH is negative
reaction is exothermic
When ΔH is postive
reaction is endothermic