Topographic Anatomy and Osteology of Canine Skeletons
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
TOPOGRAPHIC ANATOMY
Relative positions of the various parts of the body are accurately determined.
APPLIED ANATOMY
Anatomical facts in relation to surgery, physical diagnosis, and other practical branches.
Morphology
Form and structure of an organism (shape, location, texture).
Greek word anatome
To cut into or to open a particular structure; the art of separating the parts of an organism in order to ascertain their position, relations, structure, and function.
MACROSCOPIC OR GROSS ANATOMY
Study of structure of the body (tissues and organs) with the naked eye.
COMPARATIVE ANATOMY
Study of structure of different animal species; focusing on the distinct anatomical differences and correlations between these differences.
MEDIAN PLANE
An imaginary plane passing through the body craniocaudally, dividing the body into equal right and left halves.
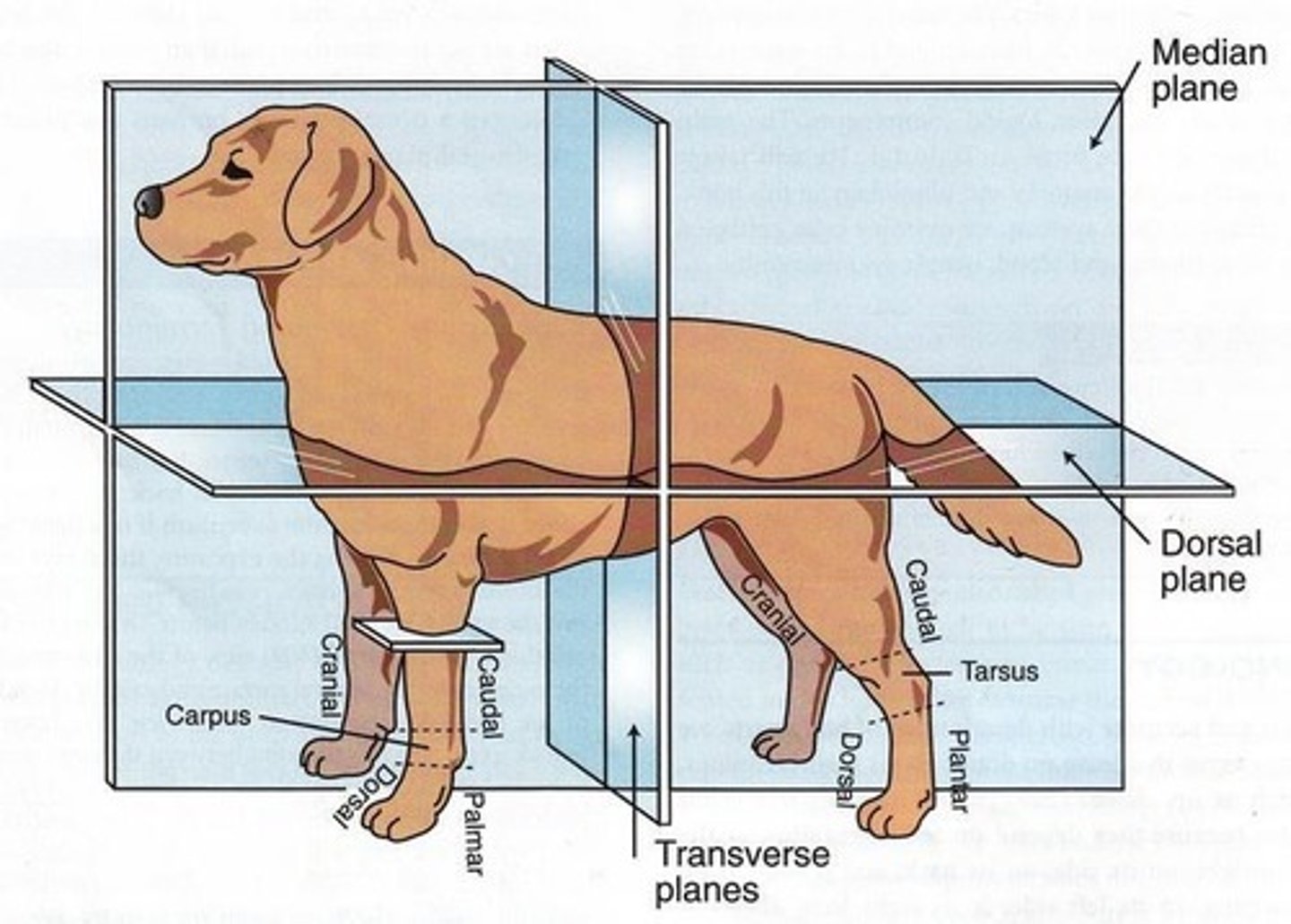
SAGITTAL /PARAMEDIAN PLANE
Any plane parallel to the median plane; the animal can have a lot of paramedian planes.
TRANSVERSE PLANE
Plane at right angles or perpendicular to the median plane, dividing the body into cranial and caudal parts.
DORSAL PLANE
Plane at right angles to both median and transverse plane, dividing the trunk into a dorsal and ventral part.
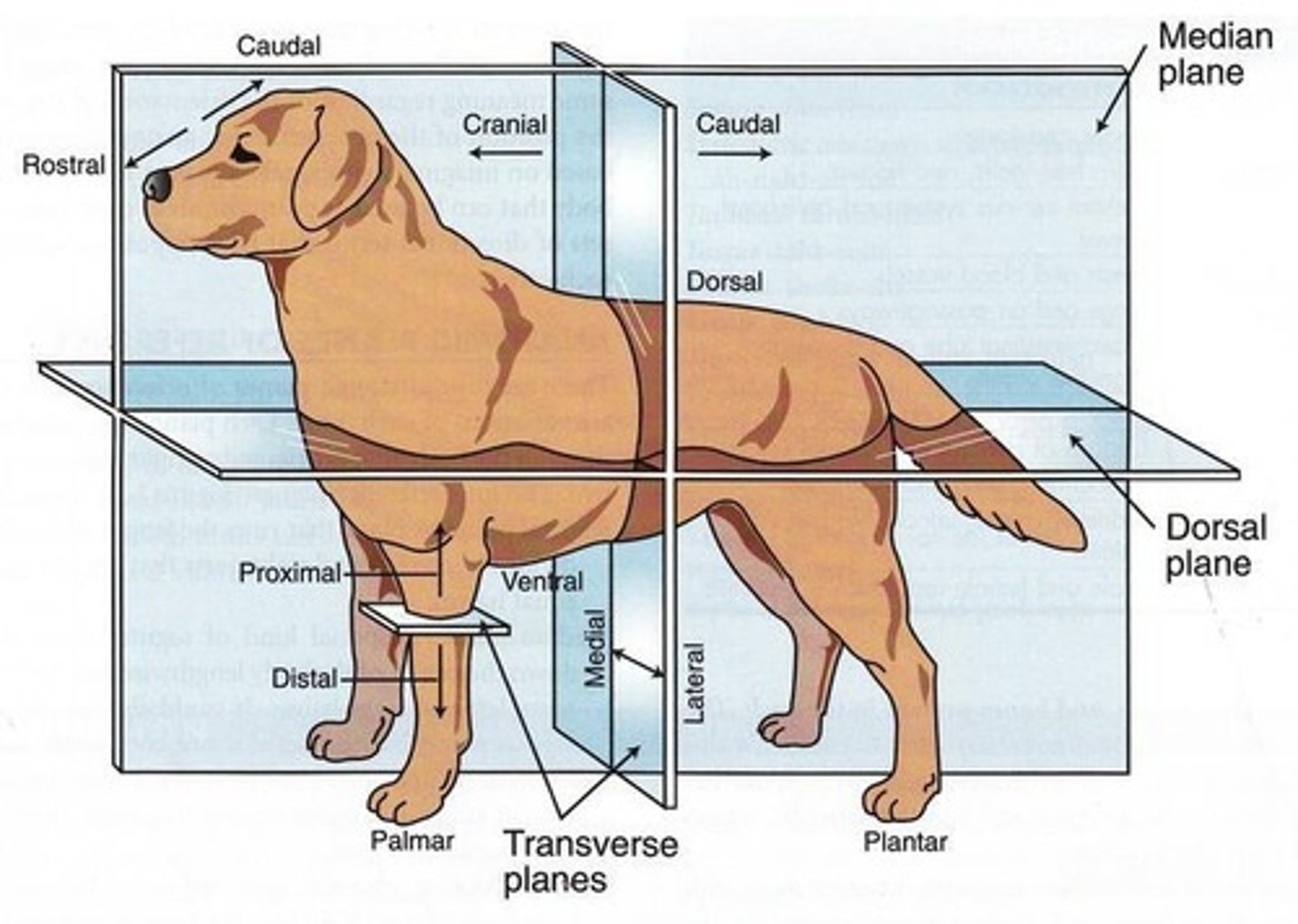
MEDIAL surface
The inner surface of the limb closer to the median plane.
LATERAL surface
The outer surface of the limb, meaning away from the median plane.
DORSAL
Means toward or beyond the vertebral column or backbone.
VENTRAL
Means away from the vertebral column, towards the mid-abdominal wall.
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY
Study of cells and structural organization of tissues, organs, and systems with the use of a microscope.
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CYTOLOGY
Study of ultrastructural feature of cells (very minute structural details cellular components) with the use of an electron microscope.
PATHOLOGIC ANATOMY
Study of organs functionally deviating from the normal.
EMBRYOLOGY
Study of the developmental anatomy (ontogenesis) from fertilization to birth of the offspring.
SYSTEMATIC APPROACH
The body is regarded as consisting of systems of organs which are similar in origin and structure and are associated in the performance of certain functions.
Skin
Dermatology.
Bones
Osteology.
Muscles
Myology.
Visceral
Splanchnology (visceral organs).
Nerves brain
Neurology.
Blood vessels and the heart
Angiology and cardiology.
Sensory organs
Esthesiology (anesthesia).
Ventral surface
Ilalim ng ulo ng aso, sa may chin part.
Palmar
Ventral surface ng fore paw (fore limb).
Plantar
Hind paw (hind limb).
Deep and Internal
Refer to closeness to the center of gravity or center of extremity.
Cranial and Anterior
Mean more towards or relatively closer to the head.
Superficial and External
Refer to proximity to skin or surface of body or surface of an extremity.
Caudal and Posterior
Mean more towards the tail.
Proximal
Means close to a given part usually body, vertebral column or center of gravity.
Rostral
Means toward or close to the nose (used only when referring to structures of the head).
Distal
Used for parts of the limb far from the vertebral column.
Medial
Means toward or close to the median plane.
Abduction
Movement away from the median plane.
Adduction
Movement towards the median plane.
Axial
Situated around, in the direction of, on, or along an axis.
Abaxial
Situated out of or directed away from the axis.
Dorsad
Movement towards the vertebral column.
Ventrad
Movement away from the vertebral column.
Caudad
Movement towards the tail.
Craniad
Movement towards the head.
Palmar/Volar
Flexion or caudal surface of forelimb below the elbow.
Prone/Pronate
Position in which the dorsal aspect or dorsum of body or extremity is uppermost.
Proximity
Malapit; Proximal = malapit sa body.
Distant
Malayo; Distal = malayo sa body.
Middle
Any other structures that are found in the middle of the superficial and deep.
SUPINE
Position in which the ventral aspect or dorsum of body (nakahiga), volar (forelimb) or plantar (hindlimb) part is uppermost.
Supination
Turning toward the supine position.
OSTEOLOGY
Study of bones.
OSTEO
Bones.
Organic component
Carbon atoms.
COLLAGENOUS MATRIX
Organic component of the bones, it is a matrix of tissue composed of collagen; a type of protein.
Inorganic component
No carbon atoms.
HYDROXYAPATITE CRYSTALS OF CALCIUM PHOSPHATES
Inorganic component of the bones.
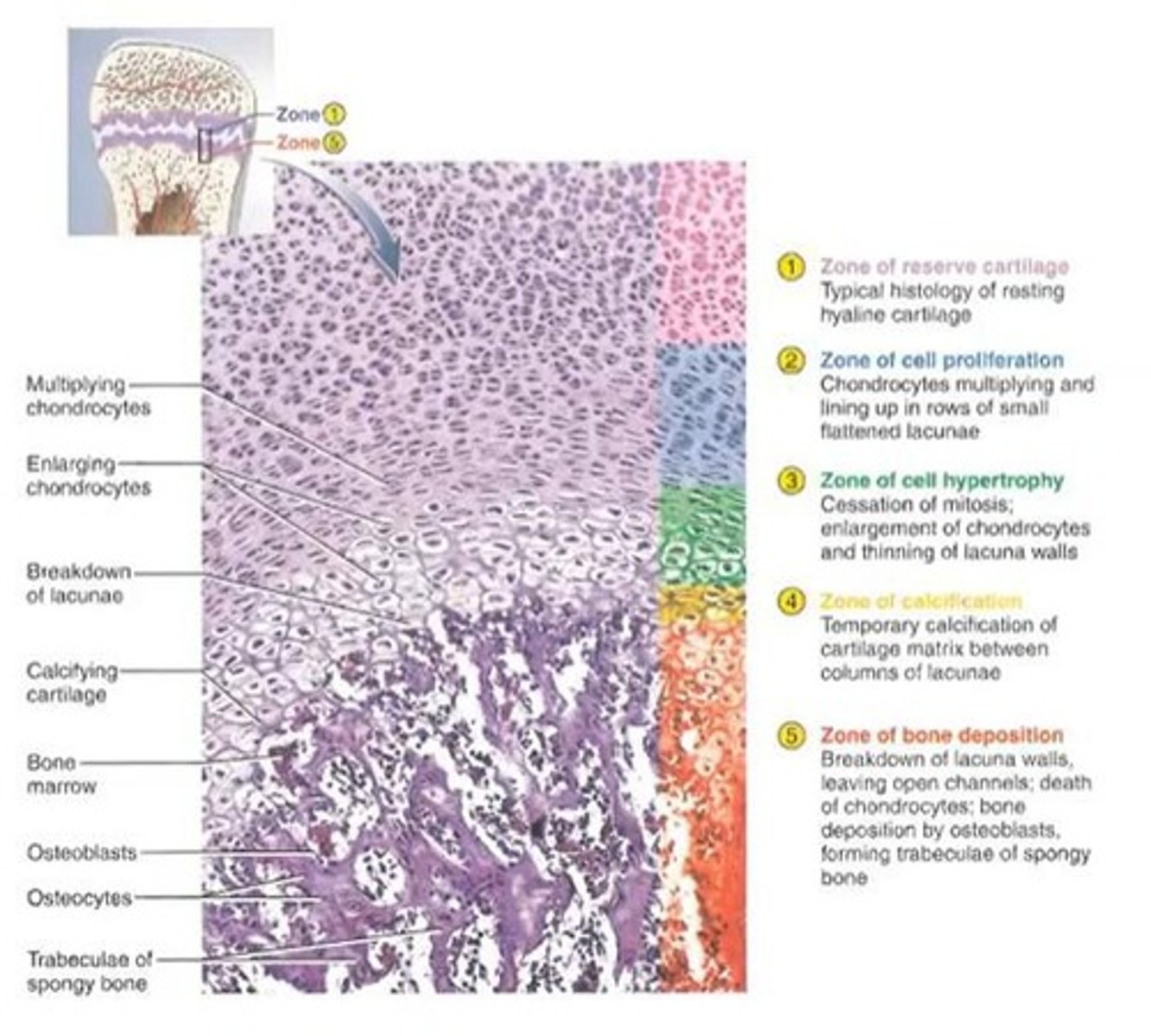
ZONE 1: Zone of reserved cartilage
This zone is still composed of pure cartilage.
ZONE 2: Zone of cell proliferation
This cartilage will proliferate or multiply greatly.
ZONE 3: Zone of cell hypertrophy
The cells will get bigger; they are still cartilage; they are called CHONDROCYTES.
OSTEOMALACIA
Bone softening; bumababa 'yung inorganic component ng bones.
OSTEOPOROSIS
Bone brittling; bumababa 'yung organic component sa bone.
FUNCTIONS OF THE BONE
1. Supporting and protecting framework of the body. 2. As levers for muscle action, to change position of force and fulcrum. 3. Storehouse for calcium, phosphorous and other elements in small amounts. 4. Blood cell formation.
INTRAMEMBRANOUS
Forms directly from the mesenchyme.
ENDOCHONDRAL BONE FORMATION
Forms from cartilage models.
EPIPHYSEAL PLATE
This is where the bone grows.
LONG BONES
Termed as 'ossa longga' - long bones.
SHORT BONES
Termed as 'ossa brevis' - compressed rods.
SESAMOID BONES
Termed as 'ossa sesamoida'; found near freely moving joints e.g. in tendons.
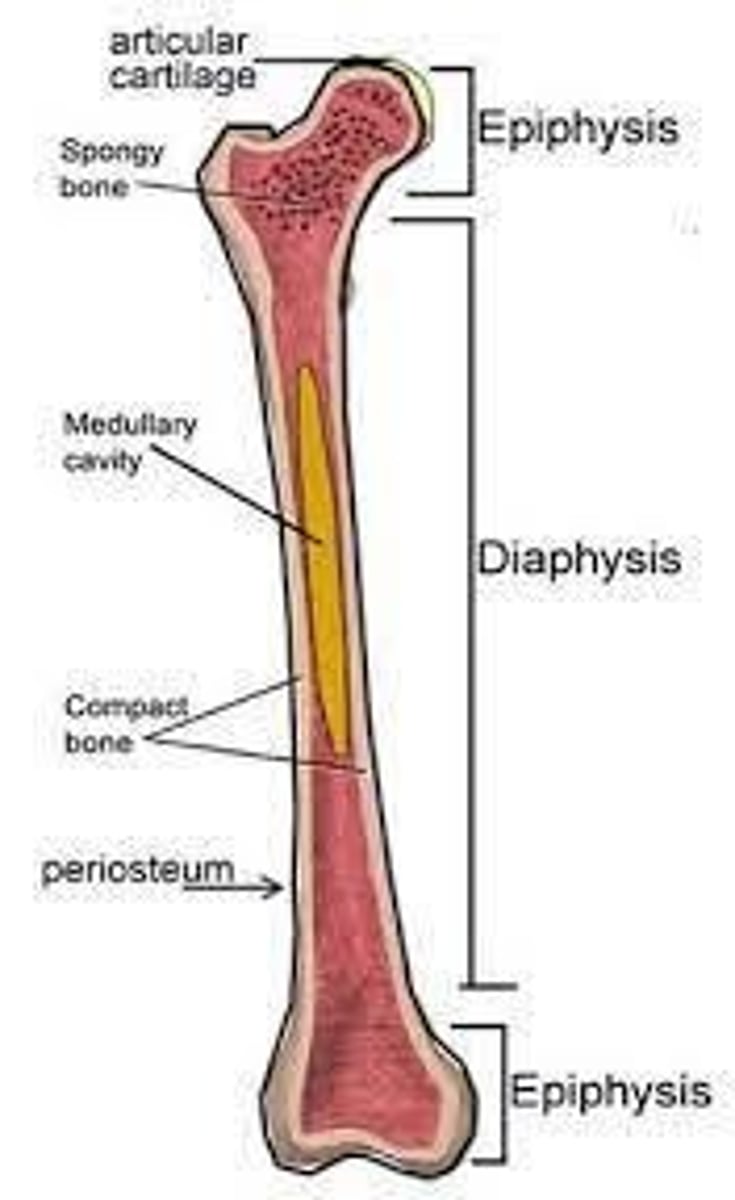
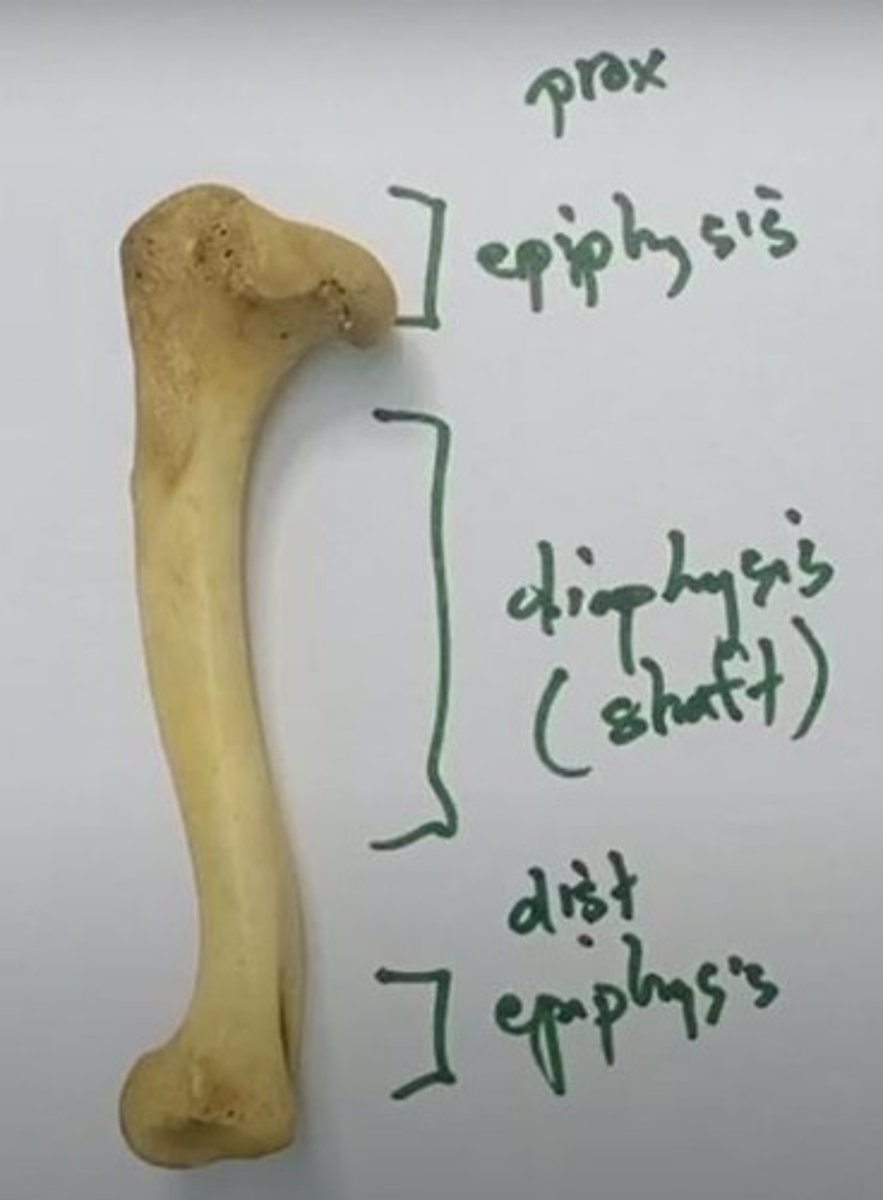
Parts of a Long bone
2 epiphyses (proximal and distal) and 1 diaphysis (shaft of the bone).

Tarsal bones
Ankle bones; cuboidal or irregularly compressed rods.
Epiphyses
Have rounded projections because they serve as the contact points of the joint.
Indentations
Produced by blood vessels, nerves, roughened elevations or depression produced by attachment of tendons and ligaments.
Calcium deposition
We will see the calcium deposition in between the epiphysis and the diaphysis known as the epiphyseal plate.
Patella
kneecap in humans

Rounded edges
The edges of the patella that are smooth and curved.
Convex on its dorsal side
The dorsal side of the patella is outwardly curved.
Concave on its ventral side
The ventral side of the patella is inwardly curved.
Rough portions on the bone
These serve as muscle or tendon attachments.
Freely movable joints
Joints that allow for a wide range of motion.
Embedded within the tendons
Sesamoid bones are located within tendons.
Function of sesamoid bones
To relieve the pressure from friction.
Frontal bone
A bone located in the forehead region.

Irregular bones
Bones with many jutting processes, termed 'ossa irregulare'.
Patella's location
The patella resides on the groove of the femur.
Flat bones
Bones that consist of outer and inner tables of compact bone and an intermediate uniting spongy bone, the diploe.
Muscular attachment
Flat bones surround and protect sense organs and brain.
Paranasal sinuses
Formed by growth of bone tables that subsequently invade the diploe.
Pneumatic bones
Bones that contain air cavities.
Ossa plata
Term used for flat bones.
Cortical bone
Compact, hard bone composed of concentric layers of tissue known as lamella/lamellae.
Functional unit of bone
Osteon, composed of concentric layers of lamellae.
Spongy/Trabecular bone
Bone composed of trabecula, which looks like a sponge.
Trabecula
A structural unit of spongy bone that has irregular deposition.
Axial skeleton
Group of bones found in the axis of the dog.
Appendicular skeleton
Bones that make up the limbs of the dog.
Heterotrophic bone
Bone found only in males, called os penis.
Compression strength
The strongest strength of a bone, which is strength against compressive strain.
Tensile strength
Half of compression strength; comparable to tendons and ligaments.