transport in plants
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
what is the xylem
transport system that transports water from roots to leaves
what is the xylem made of
dead, empty plant cells joined end by end
what is the phloem
transport system from leaves to around the plant
what is the phloem made of
living plant cells joined end to end
what does the xylem transport
water and mineral ions
what does the phloem transport
amino acid, sucrose and more
what is lignin
hard, strong waterproof substance that forms the walls of xylem vessels
what is a branching shape
structure or growth pattern where stems or roots spread out and form branches
why are branching shapes are important
increase surface area in relation to volume
what do you know about the cells regarding the plant branching shape
most cells are close to the surface
why is lignin strong
to keep the plant uprgith
what is wood entirely made of
lignin
which one does not have nuclei or cytoplasm
xylem
what is another reason why the xylem walls are strong
stop it from collapsing inwards
why does the xylem have a thin area of wall
help movement of water between adjacent xylem vessels
what supports the xylem
lignin
why do the xylem contain lignin
support great weight
why are the cells in a xylem dead
water can flow easily through the tube
why are there no cross walls between dead cells in xylem
makes a continues tube for water to flow all the way through
what is the diameter of the xylem vessel
between 15 to 200 micrometres
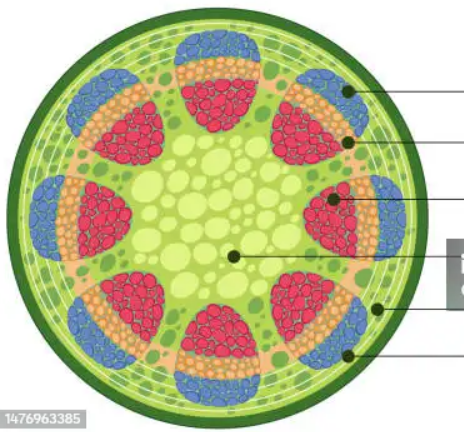
what is this
vascular bundle
how are the xylem and phloem places together in a vascular bundle
grouped or close together
where do you find vascular bundles
roots and stems and leaves
what takes up soil in a plant
the root hairs
what do you find at the tip of a root
protective gap and no root hairs
function of the root cap
protect growth through soil
why do root hairs not live long
get damaged by soil
function of root hair
absorb water and mineral ions
what do the root hair cells
higher surface area
why is a high surface area good from the root hair cells
increase uptake
how does water get into the root hair cell
diffusion
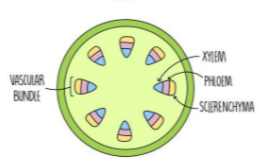
where can you find this vascular bundle in the plant
stem
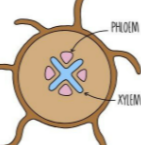
where can you find this vascular bundle in the plant
root
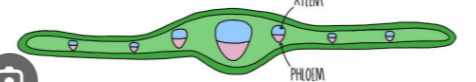
where can you find this vascular bundle in the plant
leaf
what is the first step of water going through a plant
water enters root hair cell
what is the second step of water going through a plant
water passes across the root from cell to cell
what is the third step of water going through a plant
water is drawn up xylem vessel
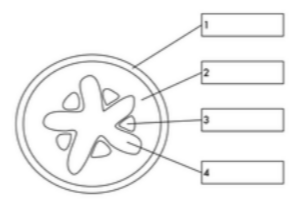
what is label 1
epidermis
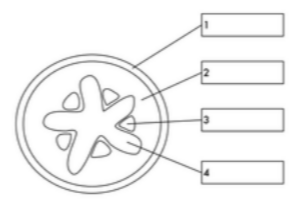
what is label 2
cortex
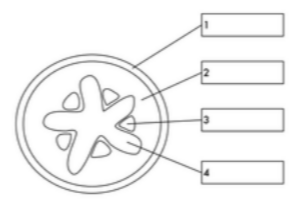
what is label 3
phloem
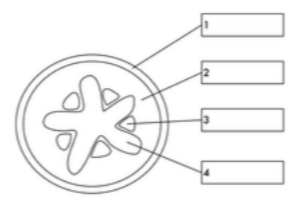
what is label 4
xylem
function of the cortex in the root
storage and support
why is the xylem larger in the roots than the stem
stem is for transport, root is to absorb large amounts
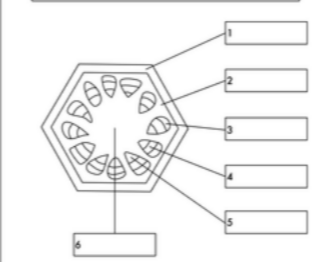
what is label 2
cortex
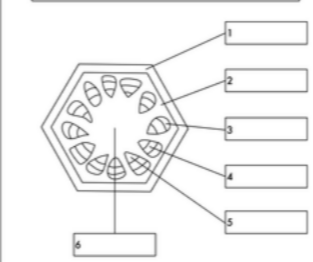
what is label 4
phloem
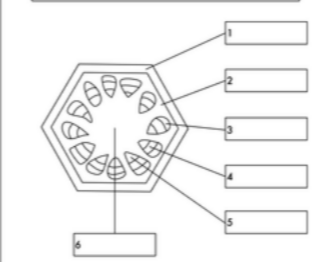
what is label 5
xylem
what is the cortex in a root
unspecialised cells lying between epidermis and vascular tissue
how does water move up a xylem
high pressure at the bottom and low pressure at the top
what is transpiration
loss of water vapour from leaves
what opening is on the leaves
stomata
where do you find most of the stomata
lower epidermis
how does water vapour leave the leaves
diffusion
where does water from xylem vessels go?
to mesophyll cells
how does water enter the mesophyll cells
osmosis
how does water leave the mesophyll cells
evaporation
what is the transpiration pull
a force produced by the loss of water vapour from a leaf
why does spongey mesophyll hold an important role in transpiration pull
combined large surface area helps keep water moving through
how does pressure get reduced in vessels
constant movement of water from xylem, mesophyll, and then air spaces
why do we say the xylem is like a straw
pressure higher at the bottom and lower at the top
what does a potometer do
measure transpiration rate
what condition affect transpiration rate
water, temperature, humidity
what can increase the transpiration rate
high temperature, quick winds, dry day
why does high temperature affect transpiration rate
more kinetic energy
why does a windy day affect transpiration rate
increases evaporation rate
how does high humidity affect transpiration rate
decreases speed
what happens to a plant when it has too high of a transpiration rate
it wilts
what is humidity
how much water vapour is present in the air
what is wilting
losing more water than it can take up causing cells to lose turgidity
how does low temperature affect transpiration rate
water evaporates slower
how does low wind speed affect transpiration rate
diffuses out leaf slower
how does low humidity affect transpiration rate
water leaves quicker
what is translocation
movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from sources to sinks
what is a source in a plant
part of a plant that releases sucrose or amino acids to be transported to other parts
what is a sink in a plant
part of the plant where sucrose and amino acids are transported to be stored
what happens during winter for plants regarding sources or sinks
leaves becomes sink and roots become source