Self-report techniques
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are self-report techniques?
Methods of gathering data where participants provide information about themselves without interference from the researcher. The participant gives information to the researcher/provides details of own feelings/thoughts/behaviour.
What is a Questionnaire?
A type of self report technique which involves a pre-set list of written questions (or items) that the participant responds to, they provide information about their thoughts, feelings and behaviours. They’re predetermined i.e. structured (all the questions are set in advance).
How can questionnaires be distributed?
Online (email, social media), paper based (in person or by post), in person (school, work etc.)
What are open questions?
Doesn’t have a fixed range of answers so it allows respondents to answer in any way they wish. They can state their attitudes and opinions, recall their experiences and more in their own words. This is useful if you want to capture new ideas from your participants. Produces qualitative data.
What are closed questions?
AKA fixed response questions. Offer the respondent a closed set of responses which they can choose from so it produces numerical data. This is only useful if you have a thorough understanding of the range of possible responses so that you can appropriately develop the answer choices but not as useful if you want to capture new ideas or thoughts from the respondent. Produces qualitative data.
What are the 3 different types of closed questions that can be used in questionnaires?
Likert scales
Rating scales
Fixed choice option
What is a Likert scale?
The respondent indicates their agreement or disagreement with a statement using a scale of usually 5 points. The scale ranges from strongly agree to strongly disagree.

What is a rating scale?
Works in a similar way to a Likert scale but gets respondents to identify a value that represents their strength of feeling about a particular topic.
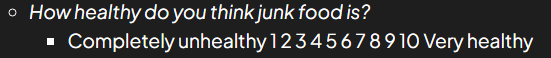
What is a fixed choice option?
Includes a list of possible options and respondents are required to indicate those that apply.

What is an interview?
A research method used to collect data by asking people questions face-to-face or over the phone. It’s often used to find out about people’s thoughts, feelings, attitudes, or experiences — things that might be hard to measure with numbers.
What are the 3 types of interviews?
Structured interviews
Unstructured interviews
Semi-structured interviews
What is a Structured interview?
Made up of a pre-determined set of questions that are asked in fixed order. Basically like a questionnaire but conducted face-to-face (or over the phone) i.e. the interview asks a question then waits for a response.
Semi-structured interviews?
Many interviews fall under this category. There’s a list of questions that have been worked out in advance, but the interviewers are also free to ask follow up questions when they feel it’s appropriate.
What is an Unstructured interview?
Works a lot like a conversation. There are no set questions, just a general aim that a certain topic will be discussed, and interaction tends to be free-flowing. The interviewee is encouraged to expand and elaborate their answers as prompted by the interviewer.
What is an interview schedule?
A list of questions that the interviewer intends to cover.
Why should an interview schedule be standardised?
To reduce interviewer bias.
How can an interview be recorded?
Audio recording, video recording (filming) or making written notes during the interview.
Identify 3 things that would be good practice when conducting interviews.
Conduct the interview in a quiet room, away from other participants
Begin the interview with some neutral questions to make the participant more relaxed and comfortable
Remind the interviewee on the several occasions that their answers will be kept private and confidential
What is interviewer bias?
Happens when the interviewer (researcher) influences the participant’s answers — intentionally or unintentionally — during an interview. This can affect the validity of the data because the results might reflect the interviewer’s expectations or behaviour, not the participant’s true thoughts.
E.g. Leading questions, tone of voice or facial expressions, body language, Interpretation bias (the interviewer interprets ambiguous answers in a way that fits their expectations)
What is a risk in self-report techniques?
Social desirability bias.
What is social desirability bias?
A form of demand characteristic. A tendency for respondents to answer questions in a way that will present them in a better light. Respondents may also not be honest when answering questions if they think someone will judge them or not agree with them. This may be particularly true with a sensitive topic such as views on racism or disability.
What are the strengths of a questionnaire?
They’re a quick, easy and convenient method of gathering data
Large samples can be reached via the use of electronic survey tools
Large samples produce reliable results as any anomalous results are averaged by the overall trend of the data
Questionnaires use standardised questions which means that they can be replicated to check for reliability
What are the limitations of a questionnaire?
There’s a tendency for people to under-report negative and over-report positive aspects of themselves when completing a questionnaire
This means that questionnaires can lead to participants succumbing to social desirability bias
Any form of bias in research impairs the validity of the findings
Questionnaires tend to under-utilise open questions which limits their usefulness
This means that they can show the 'what' of behaviour (e.g. people become more cautious with age) but not the 'why' of that behaviour (e.g. why do people become more cautious with age?)
What are the strengths of interviews?
What are the limitations of interviews?