17 - Endocrine
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Glucocorticoids
Keep blood glucose levels relatively constant
Maintain blood pressure by increasing action of vasoconstrictors
Cortisol (hydrocortisone)
Only one in significant amounts in humans
Cortisone
Corticosterone
Cortisol
a Glucocorticoids
Released in response to ACTH, patterns of eating and activity, and stress
Prime metabolic effect is gluconeogenesis— formation of glucose from fats and proteins
Promotes rises in blood glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids
“Saves" glucose for brain
Enhances vasoconstriction → rise in blood pressure to quickly distribute nutrients to cells
Inhibit inflammation, depress immune system
Homeostatic Imbalances of Glucocorticoids
Hypersecretion—Cushing's syndrome/disease
Hyposecretion—Addison's disease
Cushing's syndrome/disease
Hypersecretion of Glucocorticoids
Depresses cartilage and bone formation
Inhibits inflammation
Depresses immune system
Disrupts cardiovascular, neural, and gastrointestinal function
Addison's disease
Hyposecretion of Glucocorticoids
Also involves deficits in mineralocorticoids
Decrease in glucose and Na+ levels
Weight loss, severe dehydration, and hypotension
Gonadocorticoids
Sex Hormones
Most weak androgens (male sex hormones) converted to testosterone in tissue cells, some to estrogens
May contribute to
Onset of puberty
Appearance of secondary sex characteristics
Sex drive
Estrogens in postmenopausal women
Gonadocorticoids Homeostatic Imbalance
Hypersecretion
Adrenogenital syndrome (masculinization)
Not noticeable in adult males
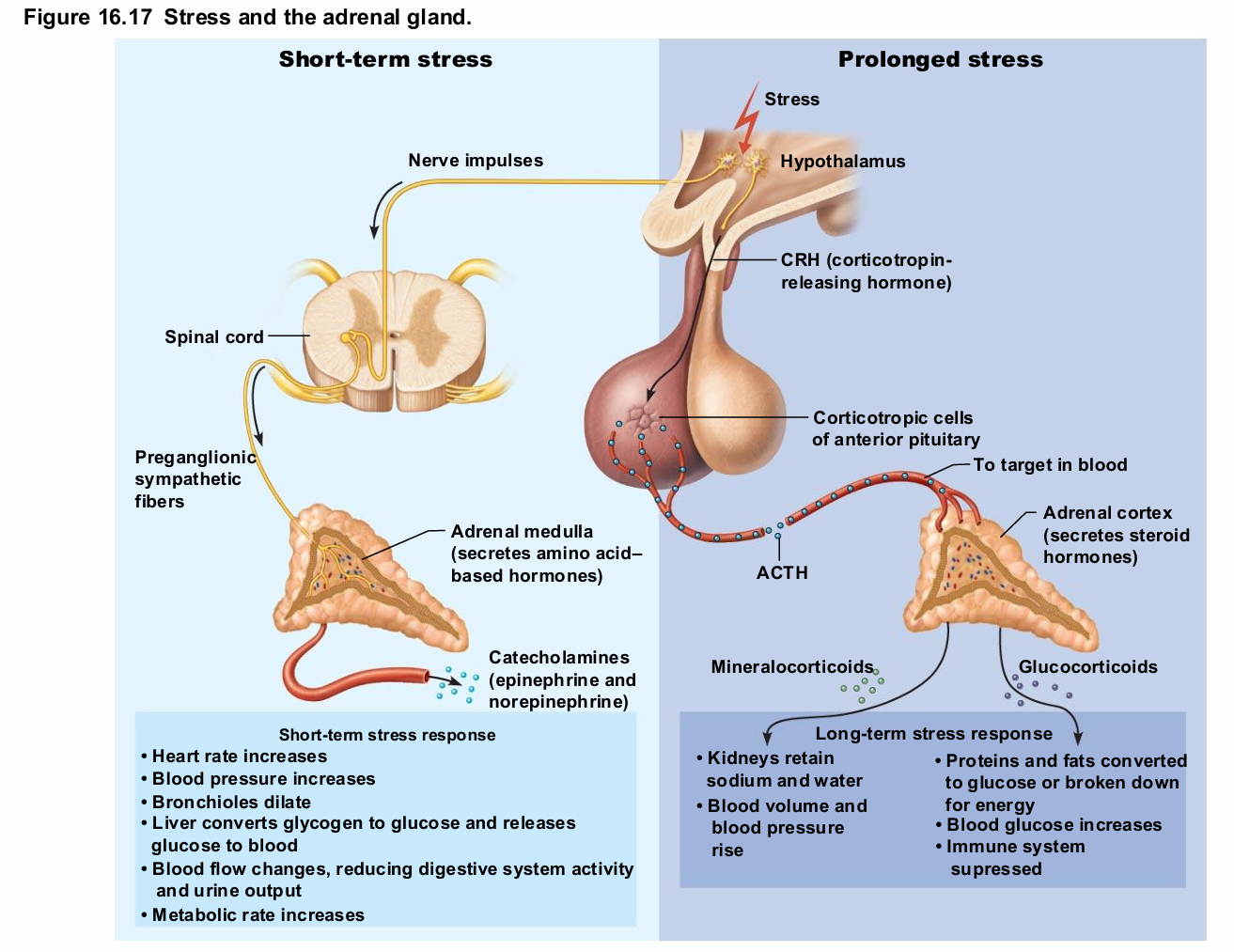
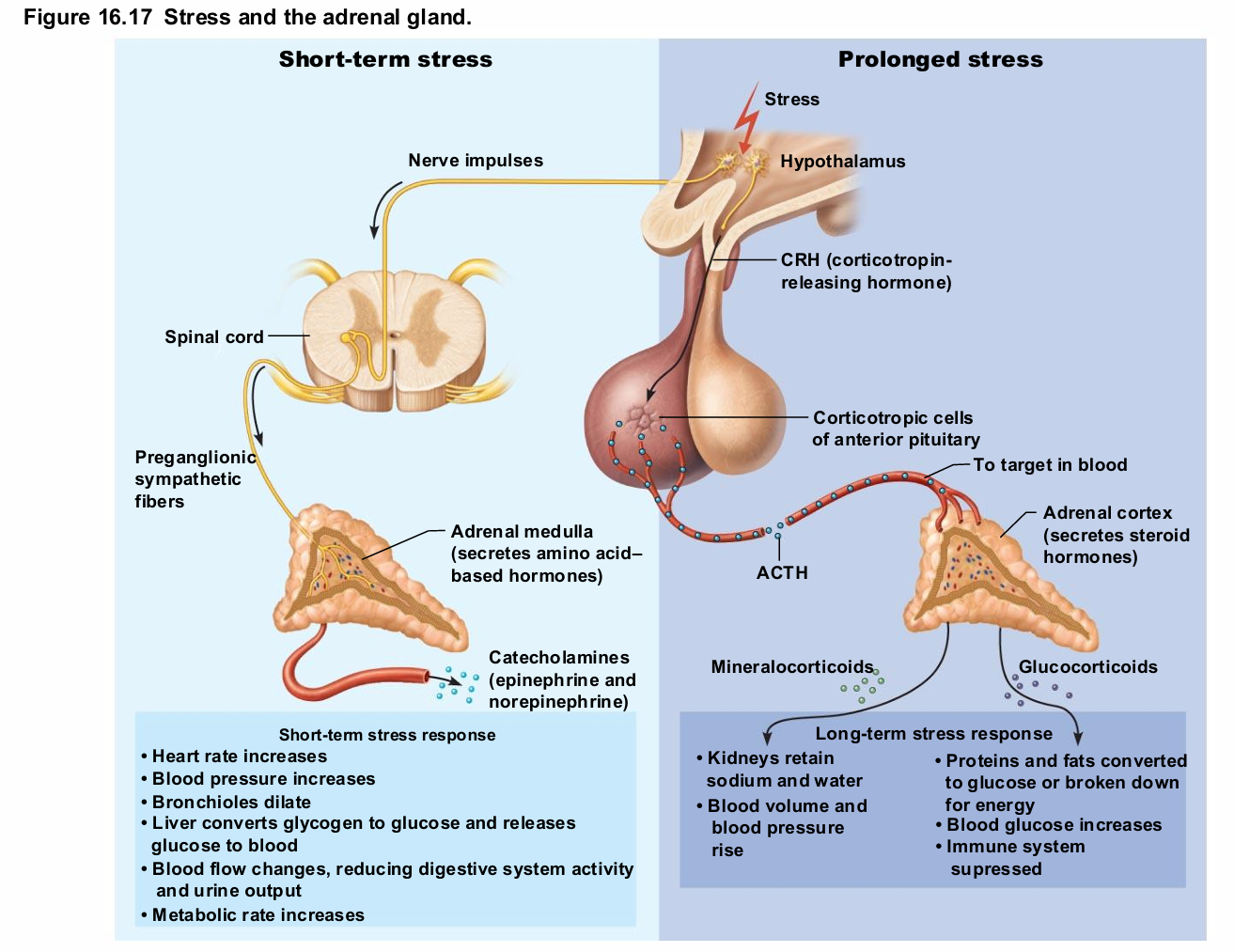
Adrenal Medulla Causes
Responses brief
Epinephrine stimulates metabolic activities, bronchial dilation, and blood flow to skeletal muscles and heart
Norepinephrine influences peripheral vasoconstriction and blood pressure
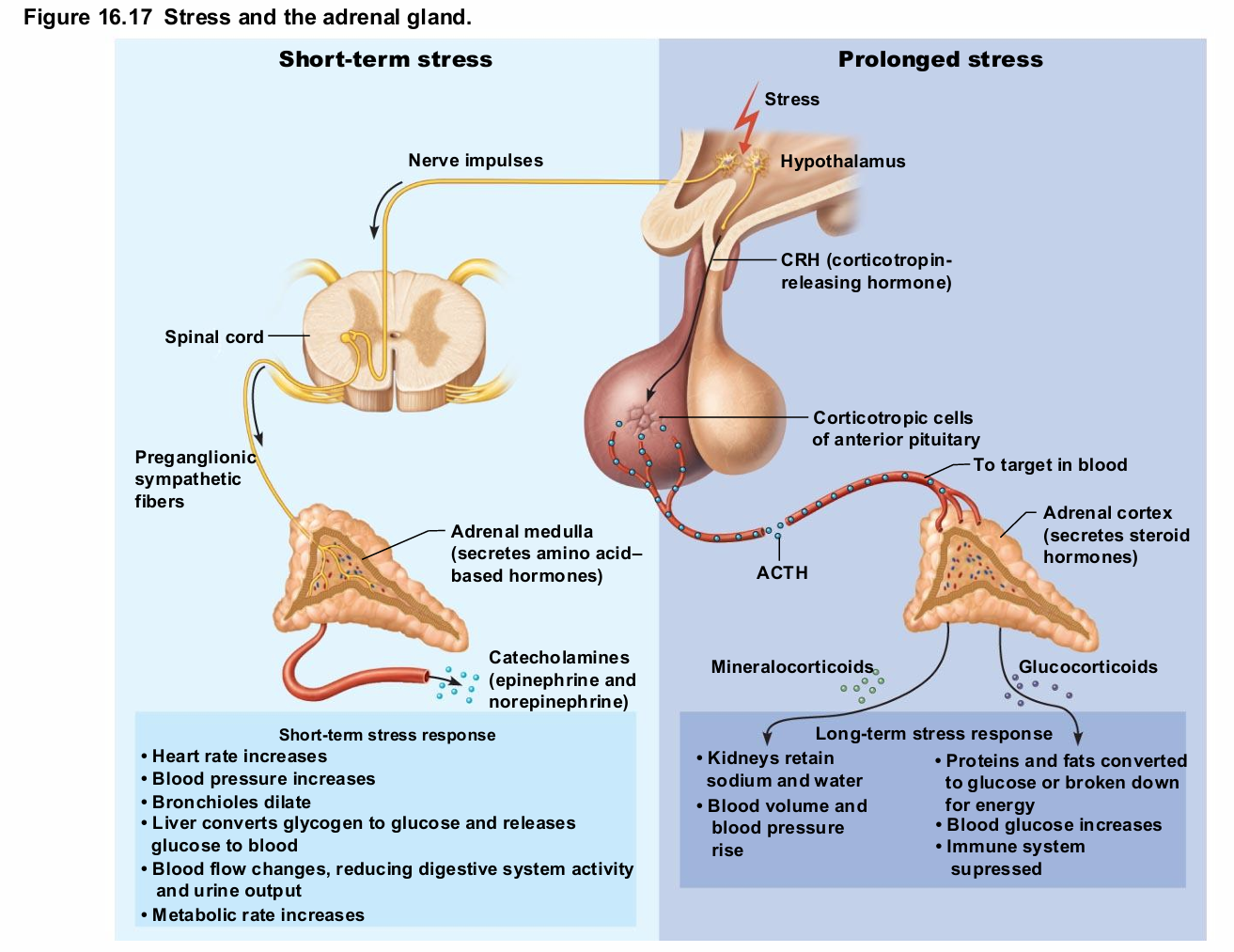
Adrenal Medulla
Medullary chromaffin cells synthesize epinephrine (80%) and norepinephrine (20%)
Effects
Vasoconstriction
Increased heart rate
Increased blood glucose levels
Blood diverted to brain, heart, and skeletal muscle
Adrenal Medulla homeostatic imbalances
Hypersecretion
Hyperglycemia, increased metabolic rate, rapid heartbeat and palpitations, hypertension, intense nervousness, sweating
Hyposecretion
Not problematic
Adrenal catecholamines not essential to life
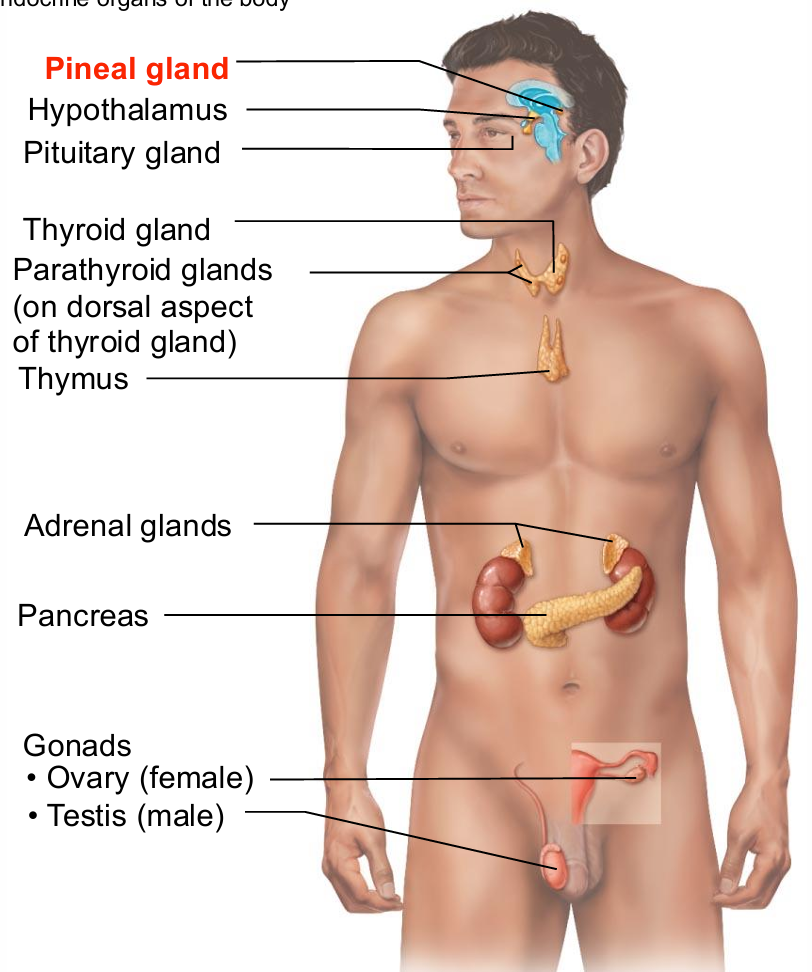
Pineal Gland
Small gland hanging from roof of third ventricle
Pinealocytes secrete melatonin, derived from serotonin
Melatonin may affect
Timing of sexual maturation and puberty
Day/night cycles
Physiological processes that show rhythmic variations (body temperature, sleep, appetite)
Production of antioxidant and detoxification molecules in cells
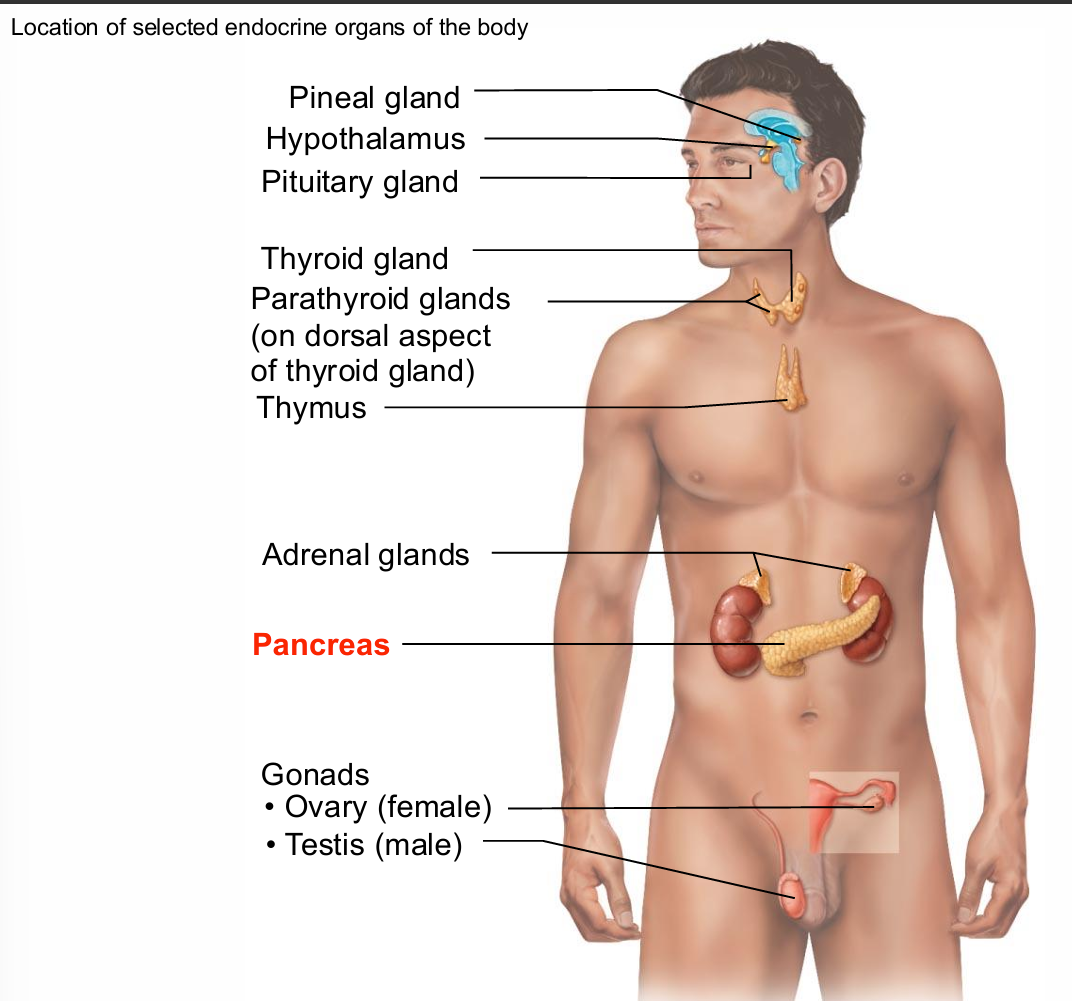
Pancreas
Triangular gland partially behind stomach
Has both exocrine and endocrine cells
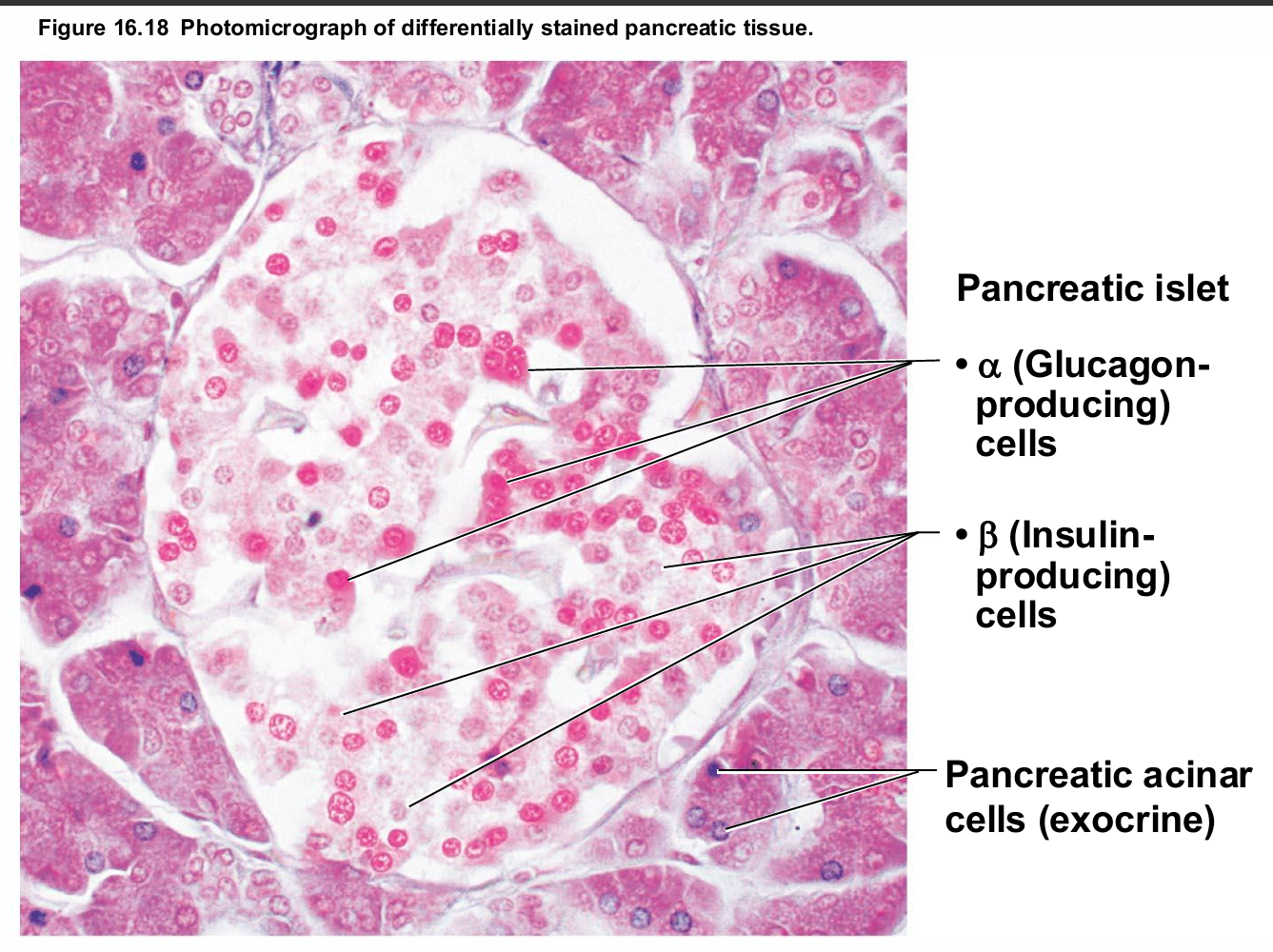
Type of Cells in Pancreas
Has both exocrine and endocrine cells
Acinar cells (exocrine) produce enzyme-rich juice for digestion
Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) contain endocrine cells
Alpha (α) cells produce glucagon (hyperglycemic hormone)
Beta (β) cells produce insulin (hypoglycemic hormone
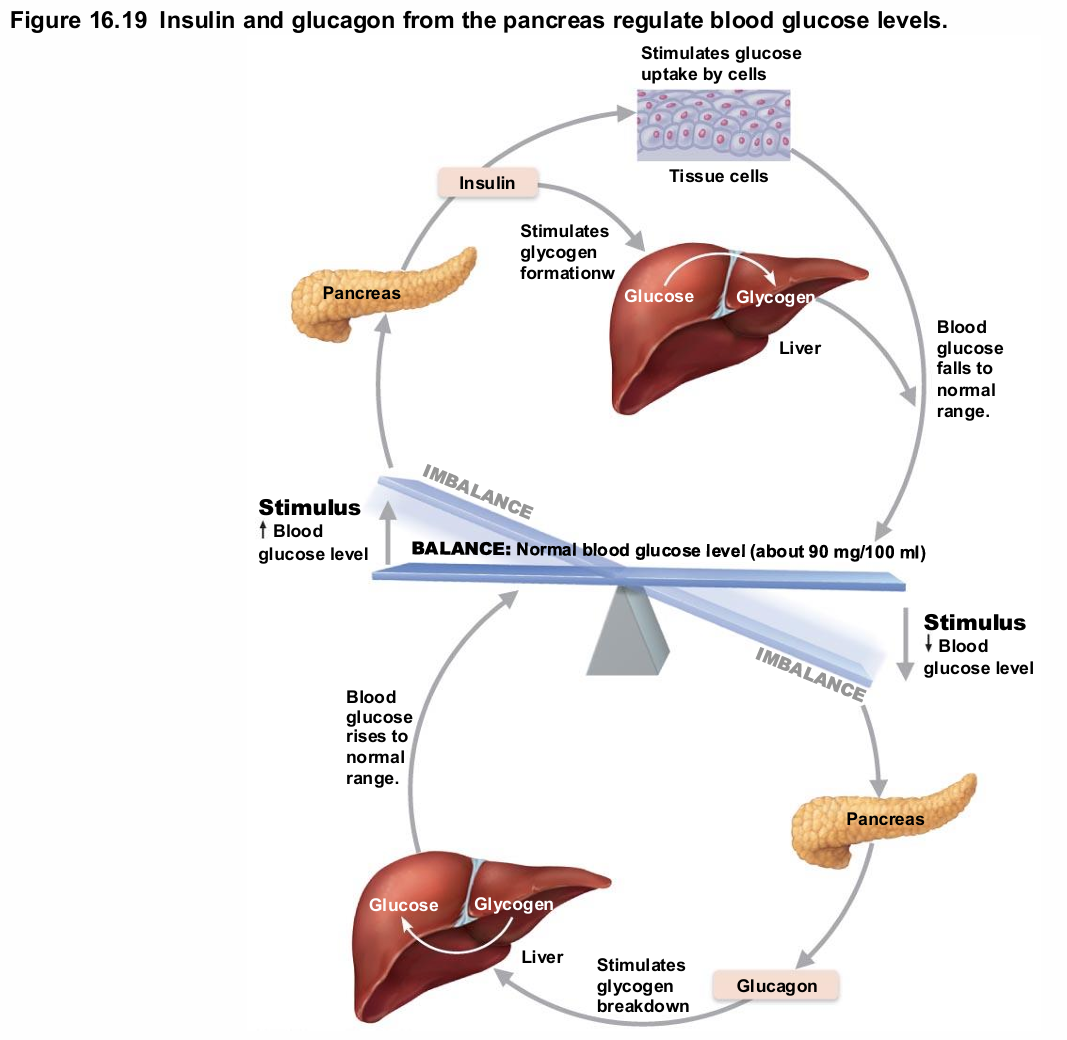
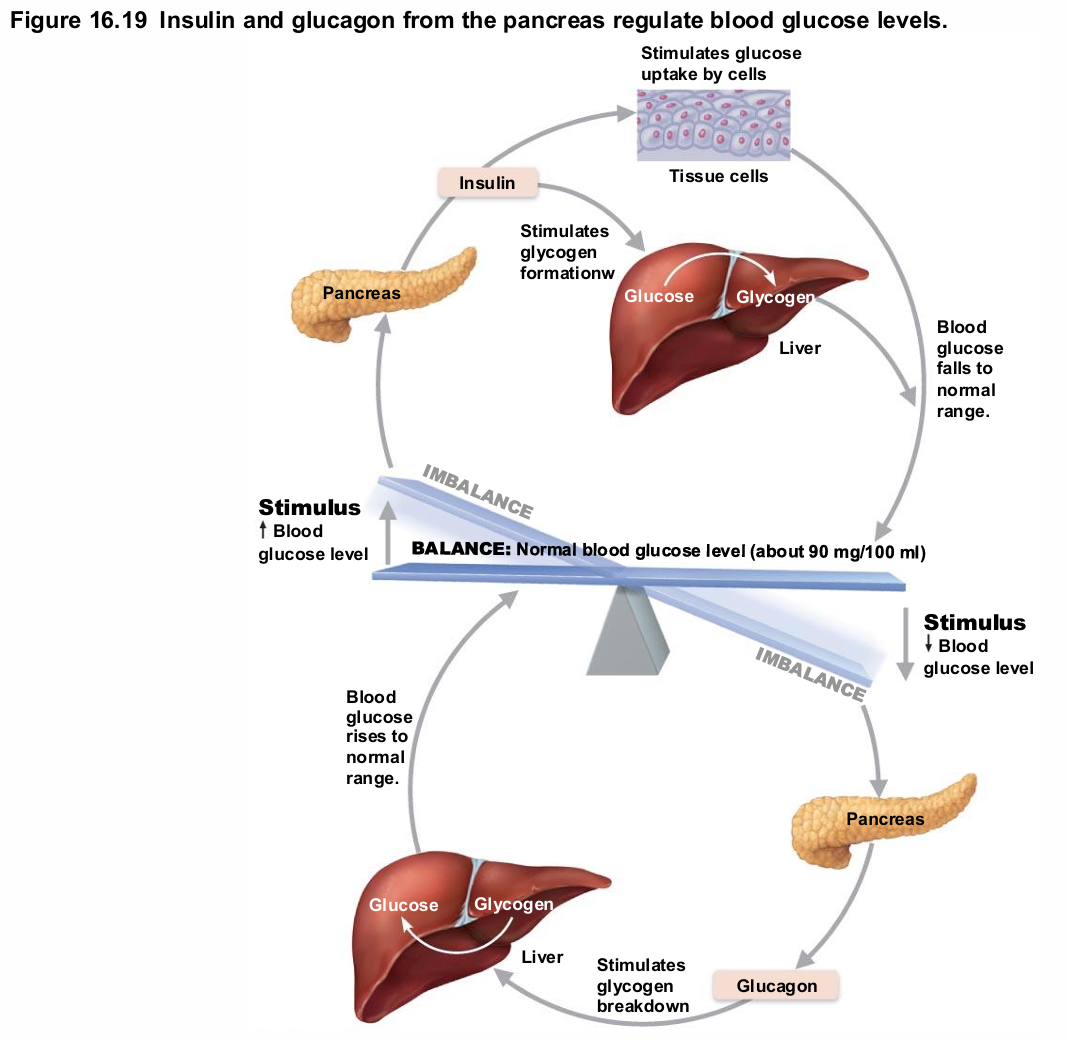
Glucagon
Major target—liver
Causes increased blood glucose levels
Effects
Glycogenolysis: breakdown of glycogen to glucose
Gluconeogenesis: synthesis of glucose from lactic acid and noncarbohydrates
Release of glucose to blood
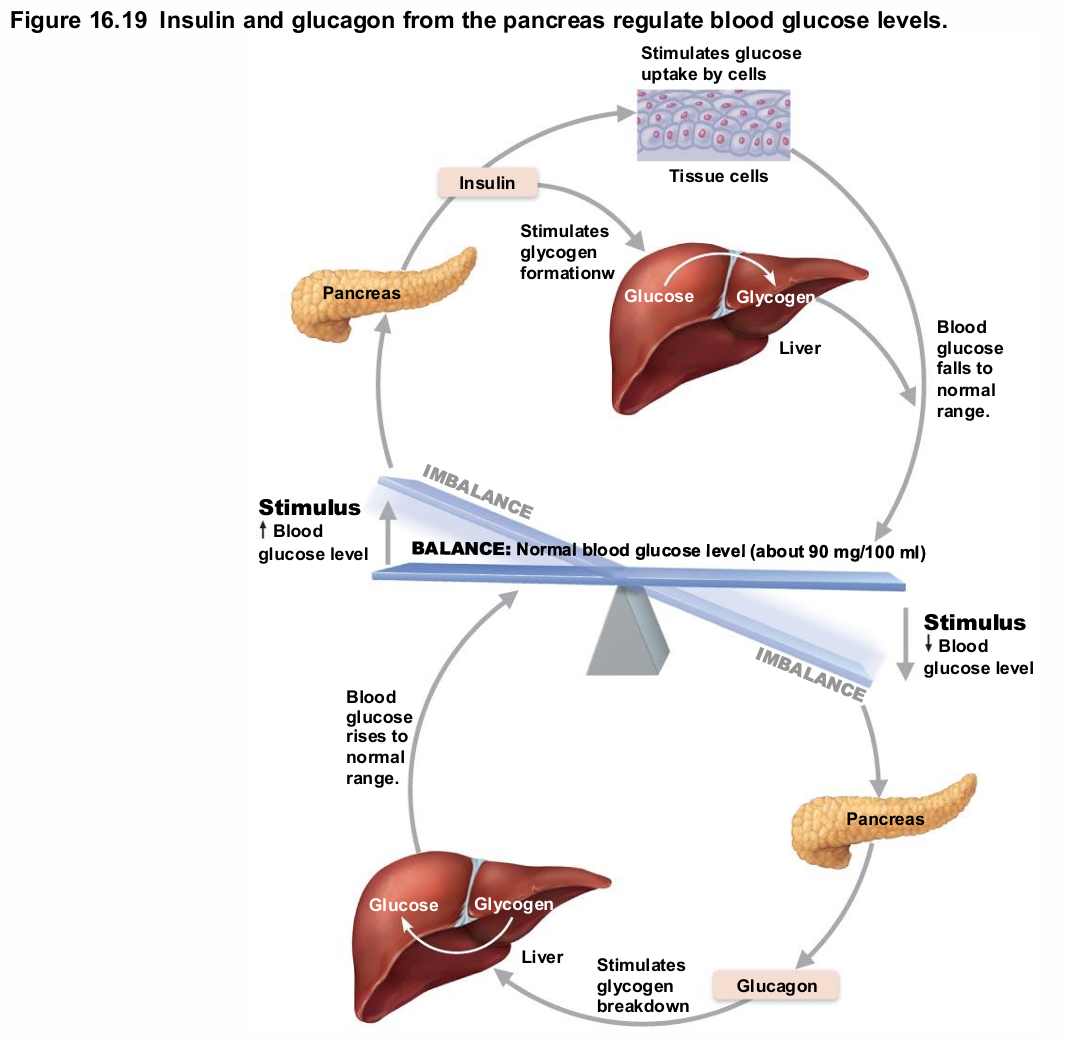
Effects of insulin
Lowers blood glucose levels
Enhances membrane transport of glucose into fat and muscle cells
Inhibits glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
Participates in neuronal development and learning and memory
Not needed for glucose uptake in liver, kidney or brain
Insulin Action on Cells
Activates tyrosine kinase enzyme receptor
Cascade → increased glucose uptake
Triggers enzymes to
Catalyze oxidation of glucose for ATP production – first priority
Polymerize glucose to form glycogen
Convert glucose to fat (particularly in adipose tissue)
Factors that Influence Insulin Release
Elevated blood glucose levels – primary stimulus
Rising blood levels of amino acids and fatty acids
Release of acetylcholine by parasympathetic nerve fibers
Hormones glucagon, epinephrine, growth hormone, thyroxine, glucocorticoids
Homeostatic Imbalances of Insulin
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Hyperinsulinism
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
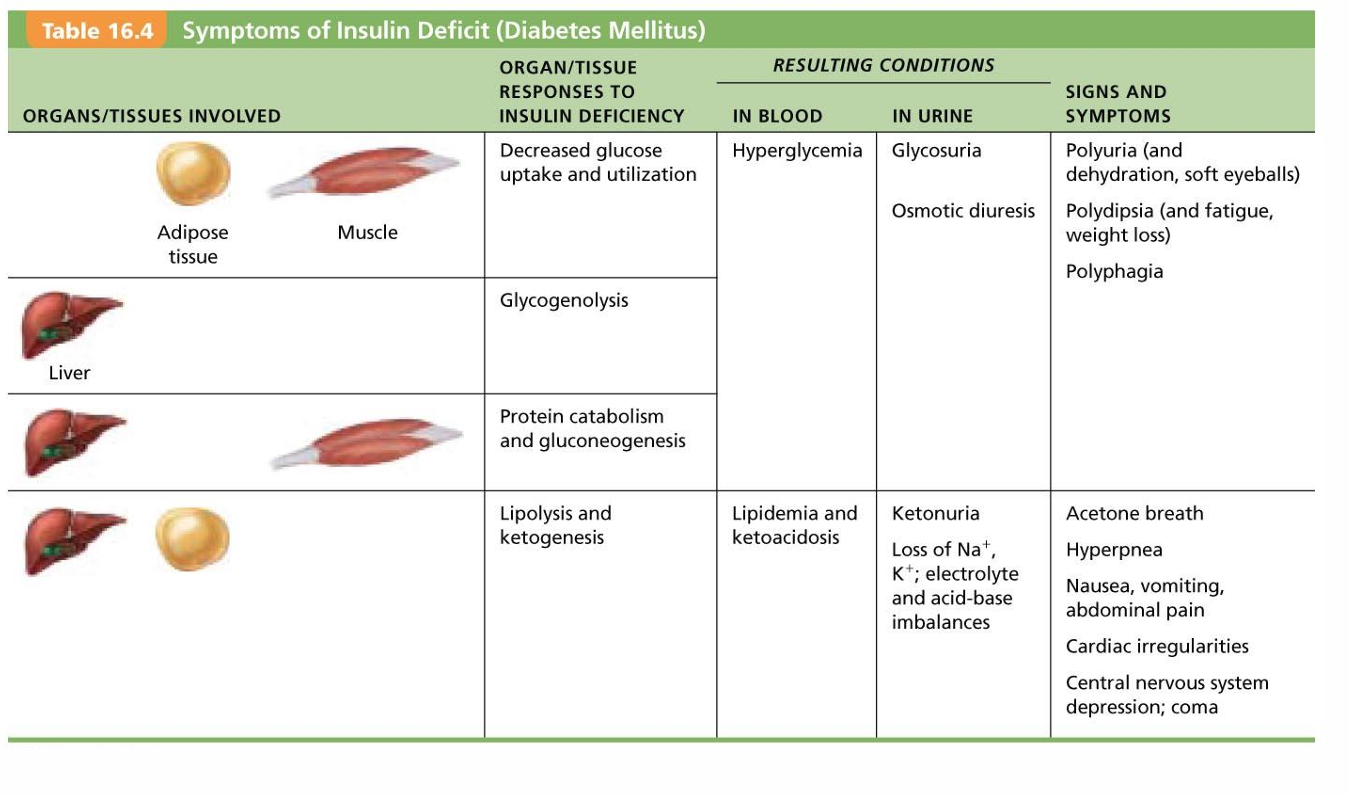
Due to hyposecretion (type 1) or hypoactivity (type 2) of insulin
Blood glucose levels remain high → nausea → higher blood glucose levels (fight or flight response)
Glycosuria – glucose spilled into urine
Fats used for cellular fuel → lipidemia; if severe → ketones (ketone bodies) from fatty acid metabolism → ketonuria and ketoacidosis
Untreated ketoacidosis → hyperpnea; disrupted heart activity and O2 transport; depression of nervous system → coma and death possible
Diabetes Mellitus: Signs
cardinal signs of DM
Polyuria—huge urine output
Glucose acts as osmotic diuretic
Polydipsia—excessive thirst
From water loss due to polyuria
Polyphagia—excessive hunger and food consumption
Cells cannot take up glucose; are "starving"
Hyperinsulinism
Excessive insulin secretion
Causes hypoglycemia
Low blood glucose levels
Anxiety, nervousness, disorientation, unconsciousness, even death
Treated by sugar ingestion
Ovaries and Placenta
Gonads produce steroid sex hormones
Same as those of adrenal cortex
Ovaries produce estrogens and progesterone
Estrogen
Maturation of reproductive organs
Appearance of secondary sexual characteristics
With progesterone, causes breast development and cyclic changes in uterine mucosa
Placenta secretes estrogens, progesterone, and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG
Pregnancy hormone (what tests test for)
Testes
produce testosterone
Initiates maturation of male reproductive organs
Causes appearance of male secondary sexual characteristics and sex drive
Necessary for normal sperm production
Maintains reproductive organs in functional state
Other Hormone-producing Structures
Adipose tissue
Enteroendocrine cells of gastrointestinal tract
Heart
Kidneys
Skeleton (osteoblasts)
Skin
Thymus
Adipose tissue Hormone-producing Structure
Leptin – appetite control; stimulates increased energy expenditure
Resistin – insulin antagonist
Adiponectin – enhances sensitivity to insulin
Enteroendocrine cells of gastrointestinal tract as Hormone-producing Structure
Gastrin stimulates release of HCl
Secretin stimulates liver and pancreas
Cholecystokinin stimulates pancreas, gallbladder, and hepatopancreatic sphincter
Serotonin acts as paracrine
Heart as Hormone-producing Structure
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) decreases blood Na+ concentration, therefore blood pressure and blood volume
Kidneys as Hormone-producing Structure
Erythropoietin signals production of red blood cells
Renin initiates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism
Skeleton (osteoblasts) as Hormone-producing Structure
Osteocalcin
Prods pancreas to secrete more insulin; restricts fat storage; improves glucose handling; reduces body fat
Activated by insulin
Low levels of osteocalcin in type 2 diabetes – perhaps increasing levels may be new treatment
Skin as Hormone-producing Structure
Cholecalciferol, precursor of vitamin D
Thymus as Hormone-producing Structure
Large in infants and children; shrinks as age
Thymulin, thymopoietins, and thymosins
May be involved in normal development of T lymphocytes in immune response
Classified as hormones; act as paracrines
Overall Layout of the Cardiovascular System
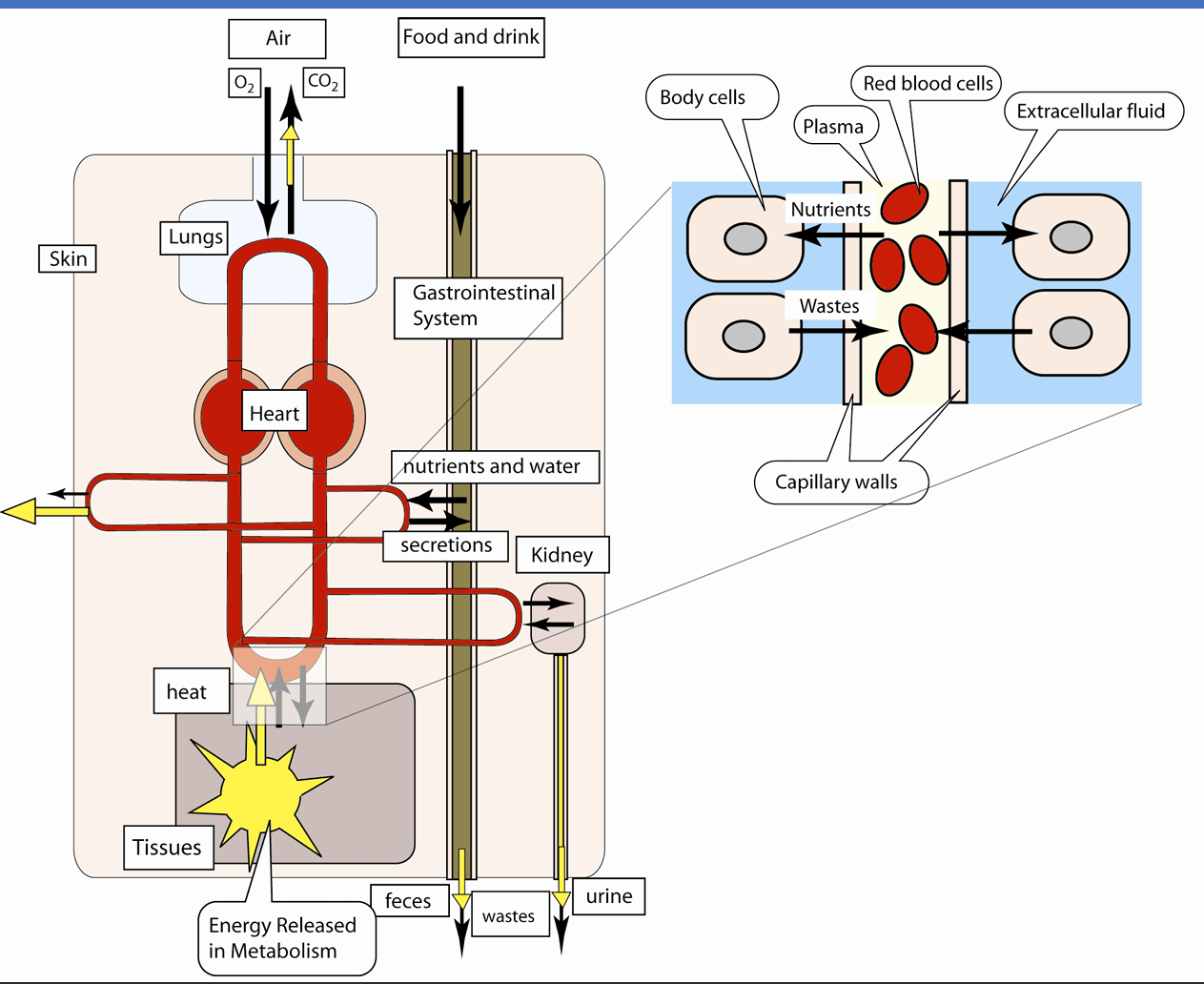
The circulation is necessary because diffusion to and from the environment is ____
too slow
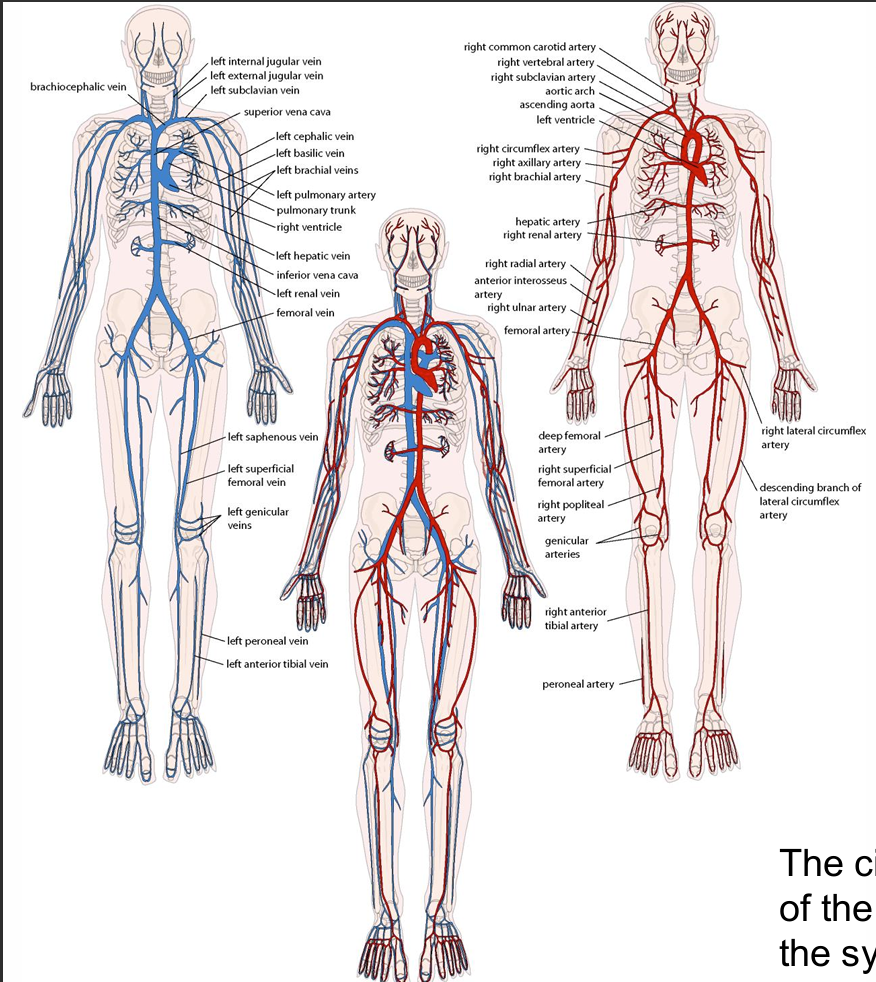
Anatomy of the CV system
The circulatory system consists of the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation
General Layout of the Circulation System
Most circulatory beds are arranged in parallel
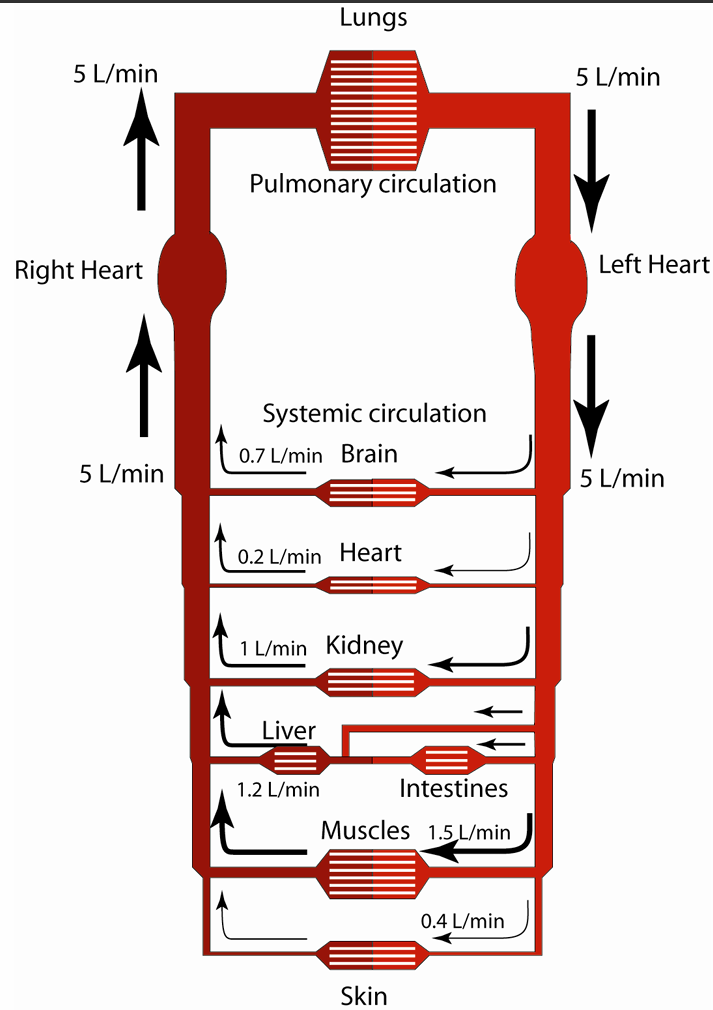
Flow through the CV system
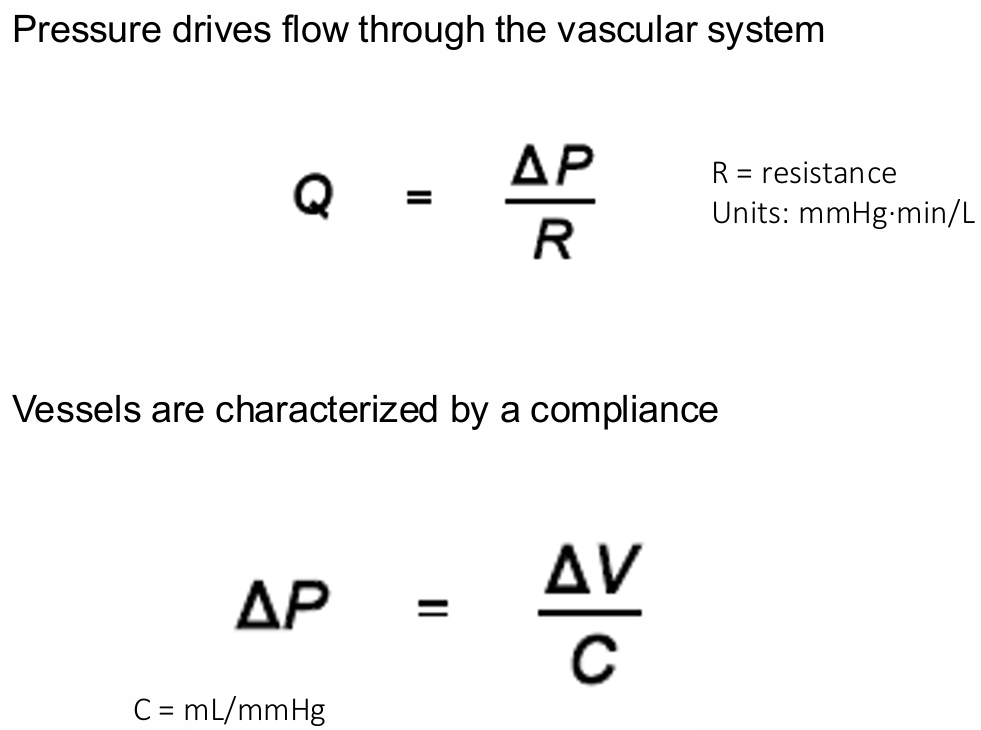
Pressure drives flow through the vascular system
Vessels are characterized by a compliance
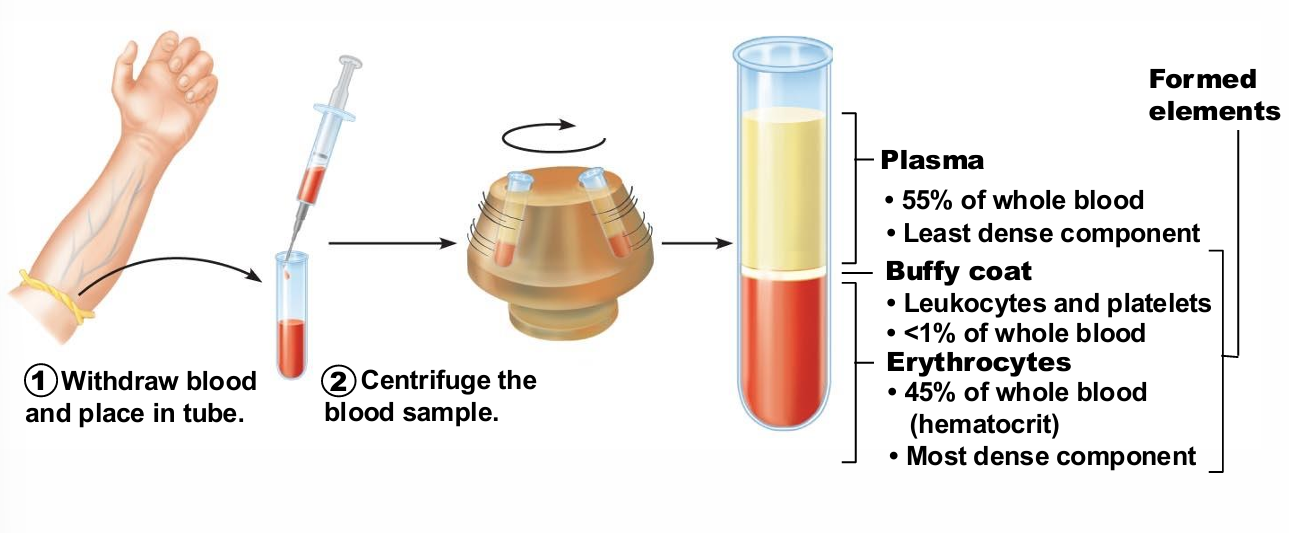
Blood Composition
Fluid connective tissue
Plasma – non-living fluid matrix
Formed elements – living blood "cells" suspended in plasma
Erythrocytes (red blood cells, or RBCs)
Leukocytes (white blood cells, or WBCs)
Platelets
Spun tube of blood yields
three layers
Plasma on top (~55%)
Erythrocytes on bottom (~45%)
WBCs and platelets in Buffy coat (< 1%)
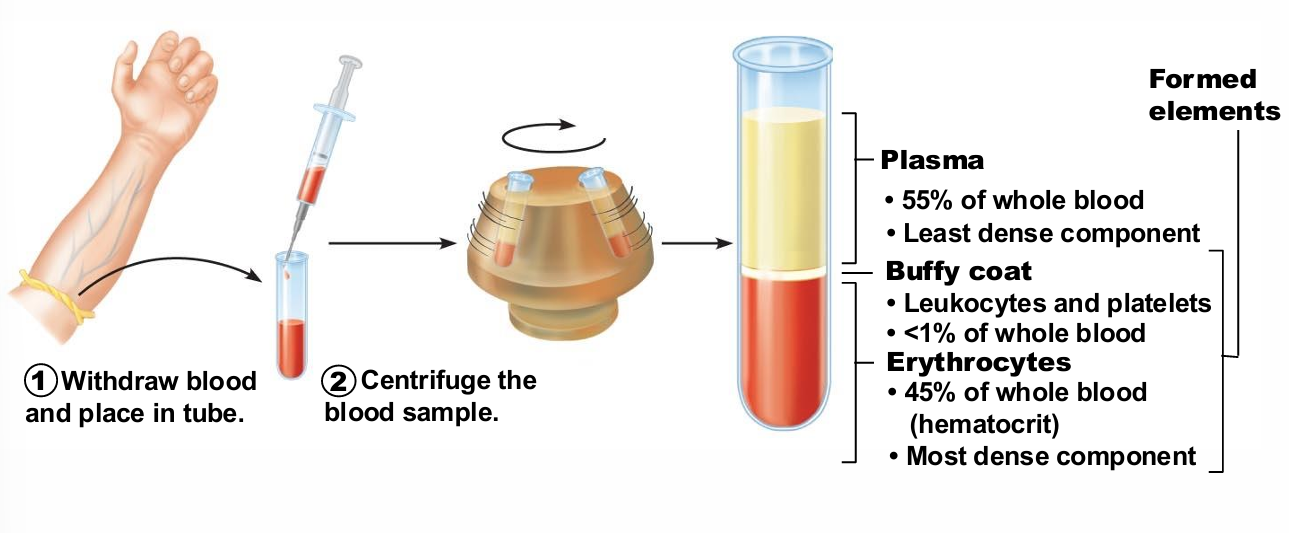
Hematocrit
Percent of blood volume that is RBCs
Physical Characteristics of Blood
Sticky, opaque fluid with metallic taste
Color varies with O2 content
High O2 - scarlet; Low O2 - dark red
pH 7.35–7.45
~8% of body weight
Average volume
Functions of Blood
Distributing substances
Regulating blood levels of substances
Protection
Distribution Functions of Blood
Delivering O2 and nutrients to body cells
Transporting metabolic wastes to lungs and kidneys for elimination
Transporting hormones from endocrine organs to target organs
Regulation Functions
Maintaining body temperature by absorbing and distributing heat
Maintaining normal pH using buffers; alkaline reserve of bicarbonate ions
Maintaining adequate fluid volume in circulatory system
Protective Functions of blood
Preventing blood loss
Plasma proteins and platelets initiate clot formation
Preventing infection
Antibodies
Complement proteins
WBCs
Blood Plasma
90% water
Over 100 dissolved solutes
Nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes, proteins, inorganic ions
Plasma proteins most abundant solutes
Remain in blood; not taken up by cells
Proteins produced mostly by liver
60% albumin; 36% globulins; 4% fibrinogen
Plasma proteins and ions buffer changes in plasma _
pH
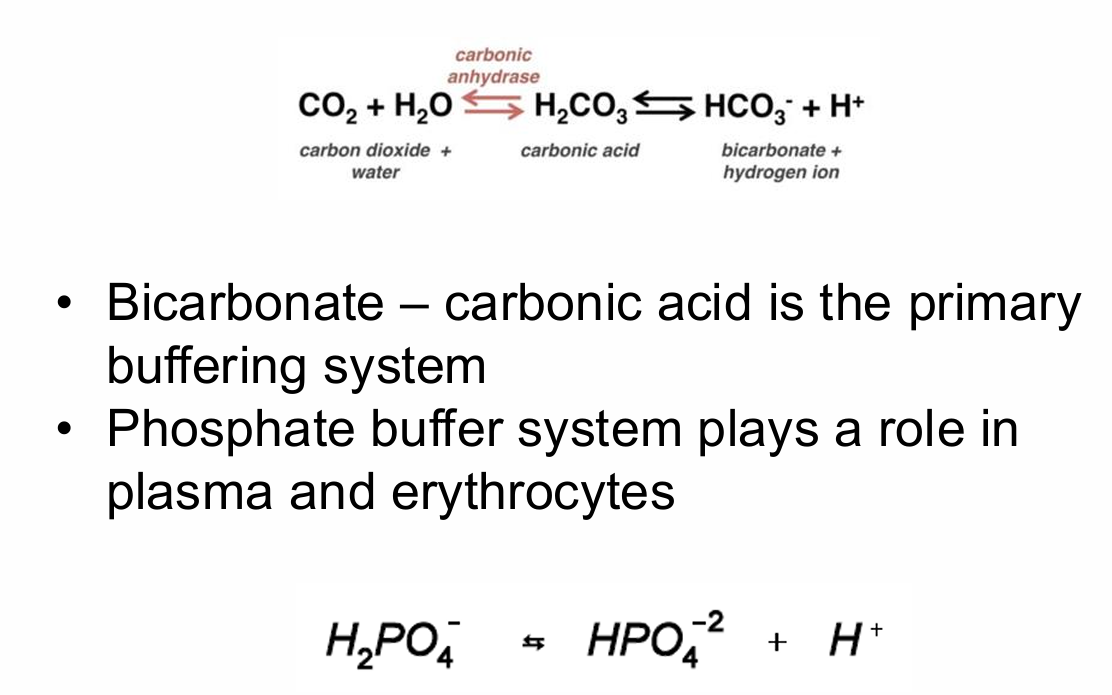
Bicarbonate – carbonic acid is the primary buffering system
Phosphate buffer system plays a role in plasma and erythrocytes
Albumin
60% of plasma protein
Functions
Substance carrier
Blood buffer
Major contributor of plasma osmotic pressure
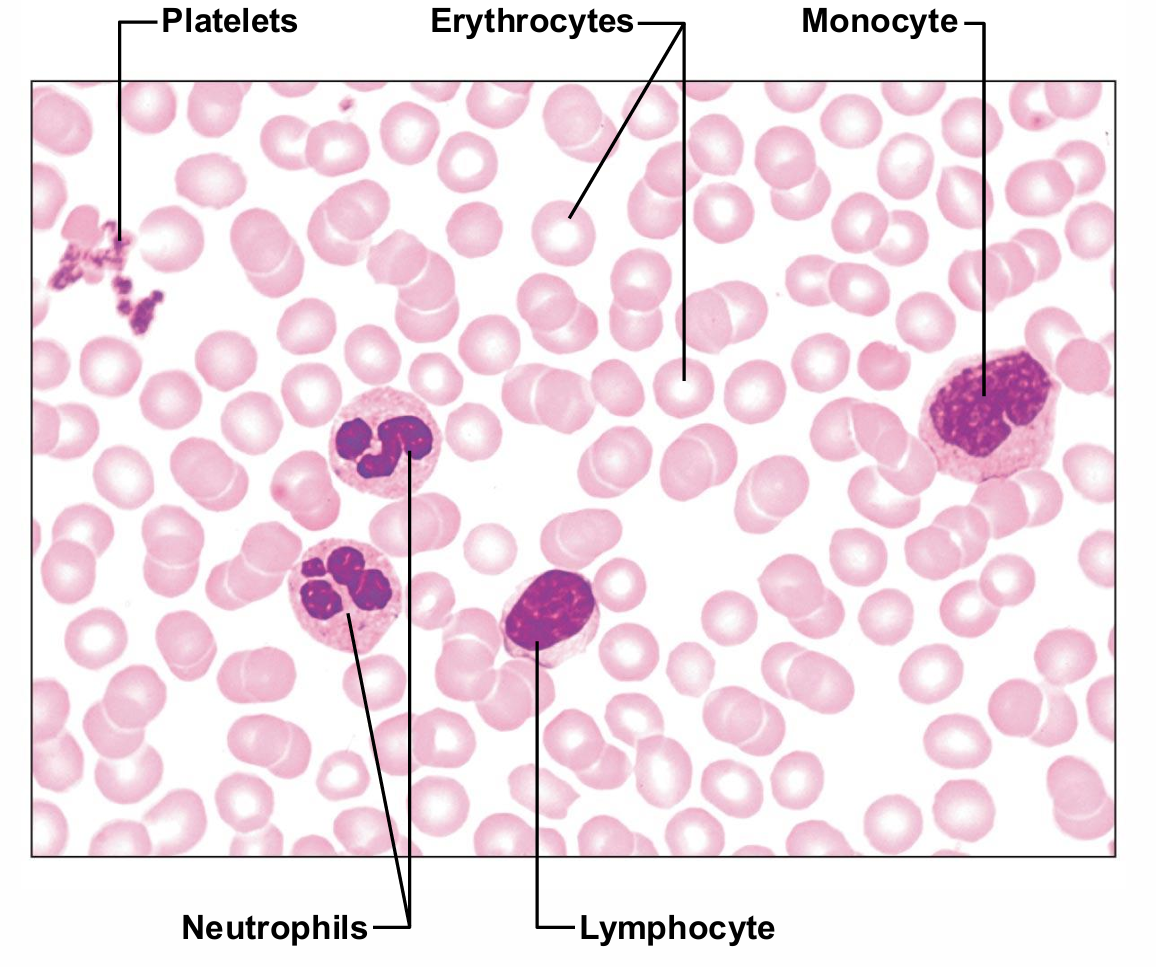
Formed Elements
Only WBCs are complete cells
• RBCs have no nuclei or other organelles
• Platelets are cell fragments
• Most formed elements survive in bloodstream only few days
• Most blood cells originate in bone marrow and do not divide
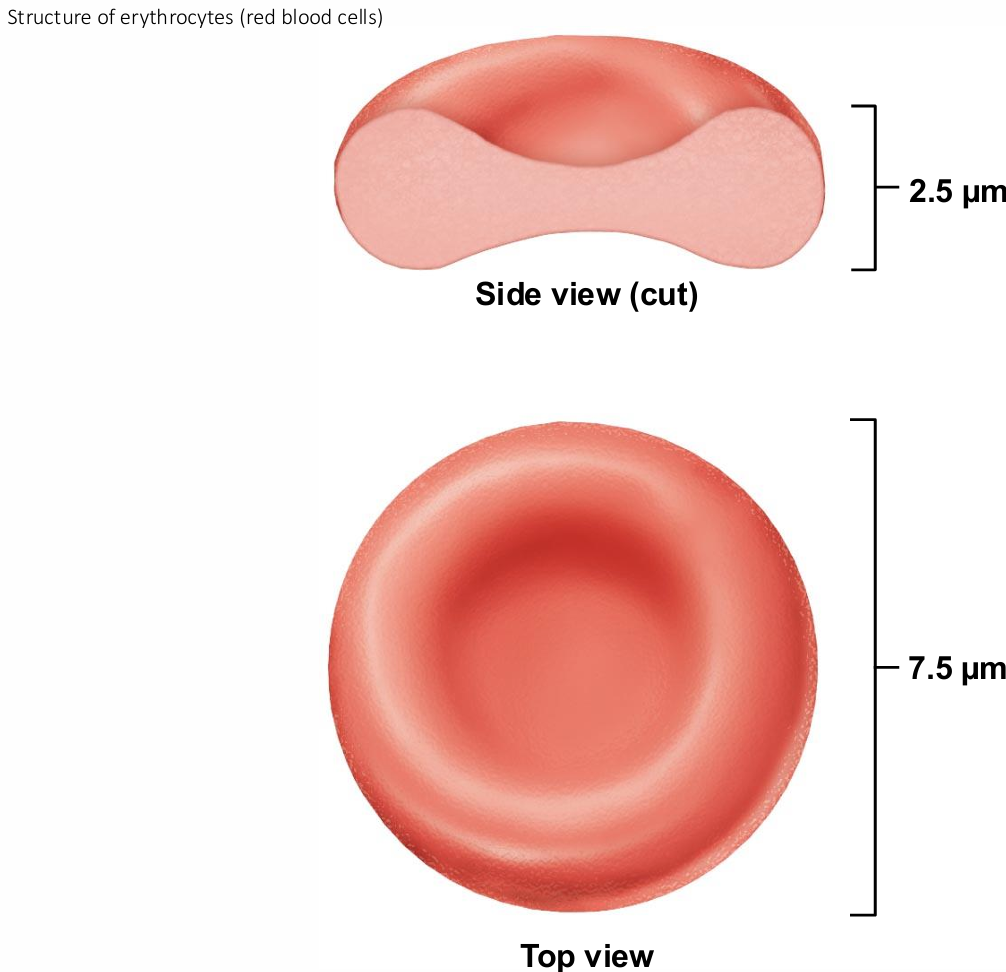
Erythrocytes
Biconcave discs, anucleate, essentially no organelles
Diameters larger than some capillaries
Filled with hemoglobin (Hb) for gas transport
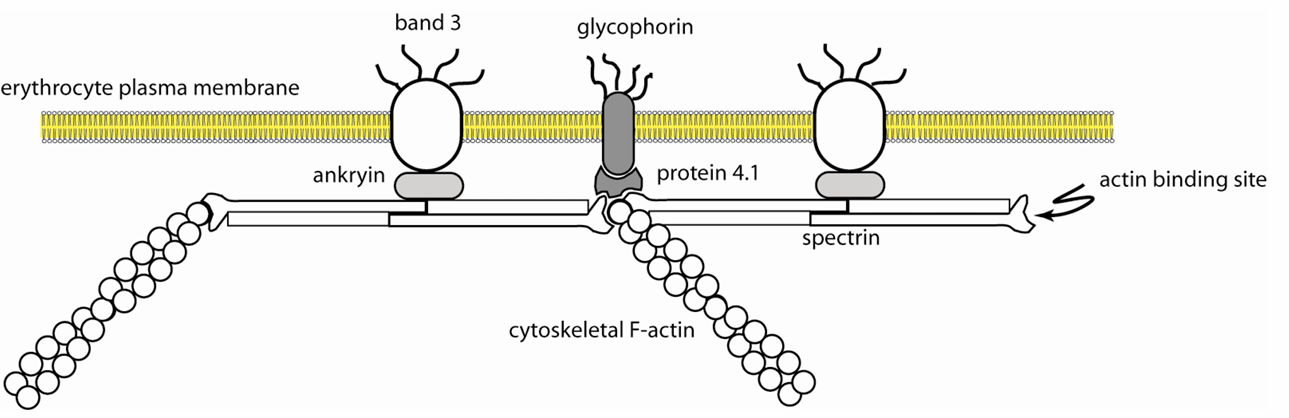
Contain plasma membrane protein spectrin and other proteins
Spectrin provides flexibility to change shape
Major factor contributing to blood viscosity
Erythrocytes Structural characteristics
contribute to gas transport
Biconcave shape—huge surface area relative to volume
>97% hemoglobin (not counting water)
No mitochondria; ATP production anaerobic; do not consume O2 they transport
Superb example of complementarity of structure and function
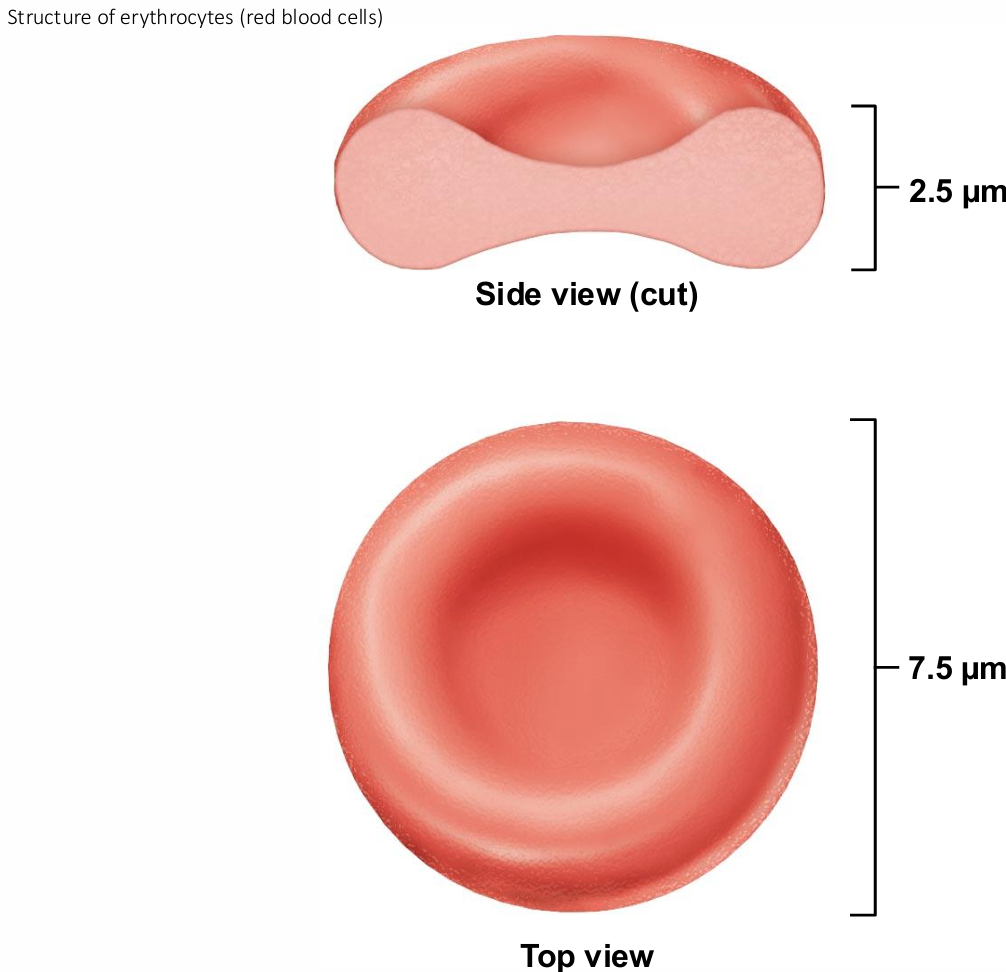
Cytoskeleton of erythrocytes
Erythrocyte Function
RBCs dedicated to respiratory gas transport
Hemoglobin binds reversibly with oxygen
Normal values
Males - 13–18g/100ml; Females - 12–16 g/100ml
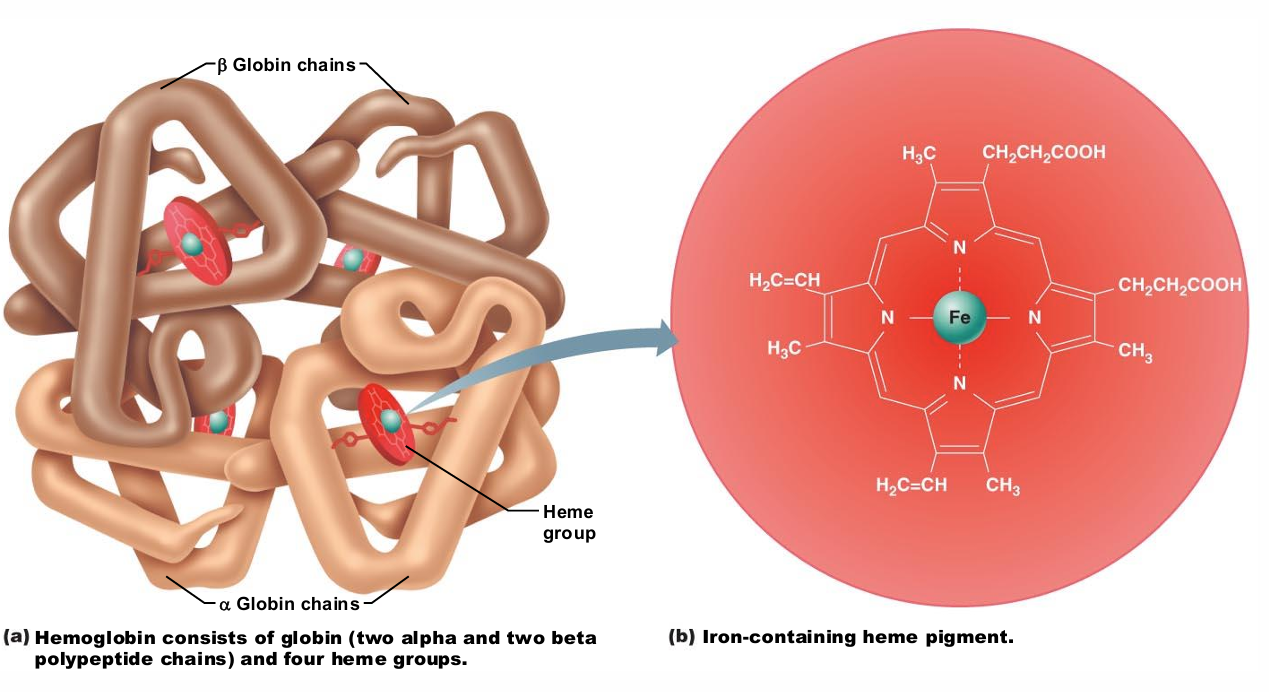
Hemaglobin Structure
Globin composed of 4 polypeptide chains
Two alpha and two beta chains
Heme pigment bonded to each globin chain
Gives blood red color
Heme's central iron atom binds one O2
Each Hb molecule can transport four O2
Each RBC contains 250 million Hb molecules
Hemaglobin Loading vs Unloading
O2 loading in lungs
Produces oxyhemoglobin (ruby red)
O2 unloading in tissues
Produces deoxyhemoglobin or reduced hemoglobin (dark red)
CO2 loading in tissues
20% of CO2 in blood binds to Hb → carbaminohemoglobin
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell formation in red bone marrow
Composed of reticular connective tissue and blood sinusoids
In adult, found in axial skeleton, girdles, and proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur