The photoelectric effect
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All knowledge needed for AS-level physics; Electromagnetic waves and quantum phenomena
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is an electronvolt?
The energy gained by an electron travelling through a potential difference of one volt
A unit to express very small energies <1J
eV x 1.6×10-19 = J
How is eV related to Ek?
When a charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference, it gains kinetic energy. If an electron accelerates from rest, an electronvolt is equal to the kinetic energy gained.
eV = ½ mv²
What is the photoelectric effect?
The phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal upon the absorption of electromagnetic radiation above the threshold frequency.
the electrons removed are photoelectrons
What does the photoelectric effect prove?
Provides evidence that light behaves as a particle. Light is quantised/carried in discrete packets. Shown by the fact that each electron only absorbs a single photon.
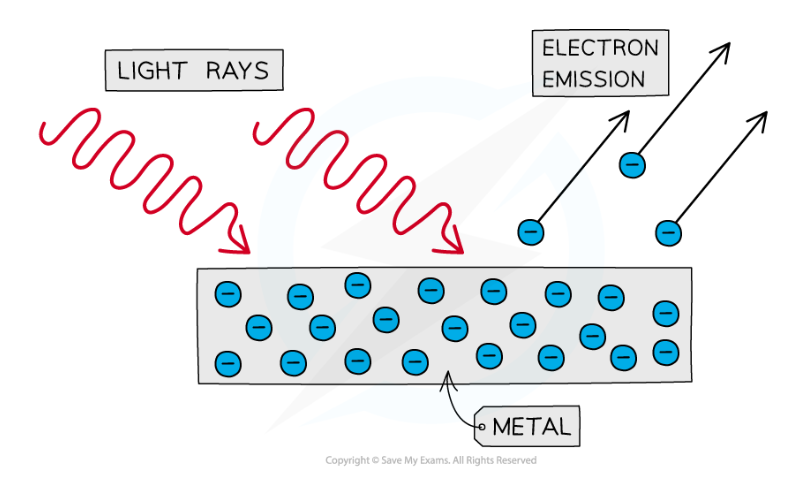
What is the threshold frequency?
The minimum frequency of incident electromagnetic radiation required to remove a photoelectron from a metal plate.
What is the threshold wavelength?
The longest wavelength of incident electromagnetic radiation that would remove a photoelectron from a metal plate.
What is the work function?
Also known as the threshold energy, the minimum energy required to release a photoelectron from a metal plate.
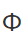
What is stopping potential?
The potential difference required to stop photoelectron emission from occurring
What does increasing the light intensity do in the photoelectric effect?
Increases the number of electrons emitted from the metal surface. Because increasing light intensity results in a larger number of photons being emitted from the EM source.
What is the kinetic energy of an emitted electron related to?
The frequency of the EM radiation source. Higher the frequency (above threshold), the more kinetic energy the electron has. If f = threshold then the electron will only be released from the metal plate.
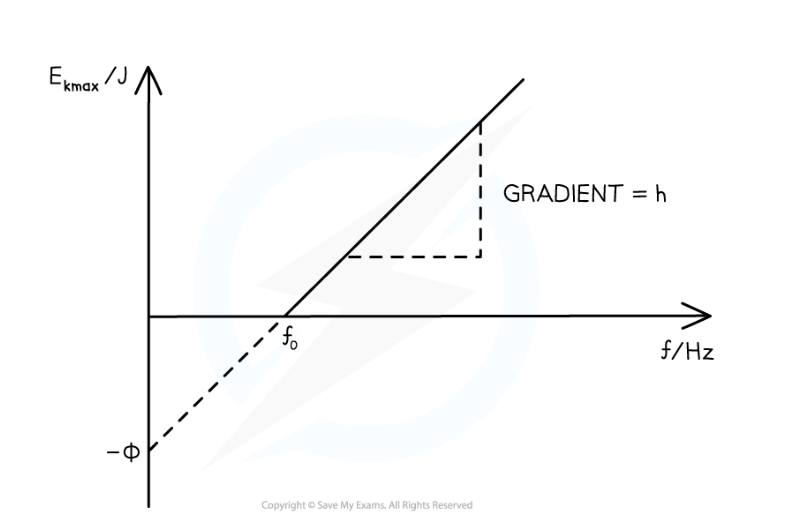
Interpret this graph.
The work function Φ is the y-intercept
The threshold frequency f0 is the x-intercept
The gradient is equal to Planck's constant h
There are no electrons emitted below the threshold frequency f0
equation: Ek(max) = hf - Φ
How many photons can each electron absorb?
ONE
What is intensity?
Rate of energy transferred per unit area, related to the number of electrons emitted from the metal plate.
Why is Ek the maximum?
Each electron in the metal acquires the same amount of energy from the photons in the incident radiation for any given frequency. The energy required to remove an electron from the metal varies due to electrons being at depths in the metals. Electrons with Ek max will be on the surface.
What is the photoelectric current?
A measure of the number of photoelectrons emitted per second, calculated by the number of electrons emitted multiplied by 1e
Photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation incident on the surface of the metal