C4.1 Populations and Communities
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Population
Group of same species organisms in an area.
Random Sampling
Techniques to estimate size of a population, ensuring equal chance of observation.
Quadrat Sampling
Method to estimate population of sessile organism
- A quadrant is placed over a section of habitat being studied, count organisms in frame

Transect Sampling
Sampling method along a linear path in ecosystems to study distribution
Capture-Mark-Release-Recapture
Method for estimating motile animal populations.
- Involved capturing a sample, mark each individual, & release them. After some time capture a 2nd sample and count the marked individuals.
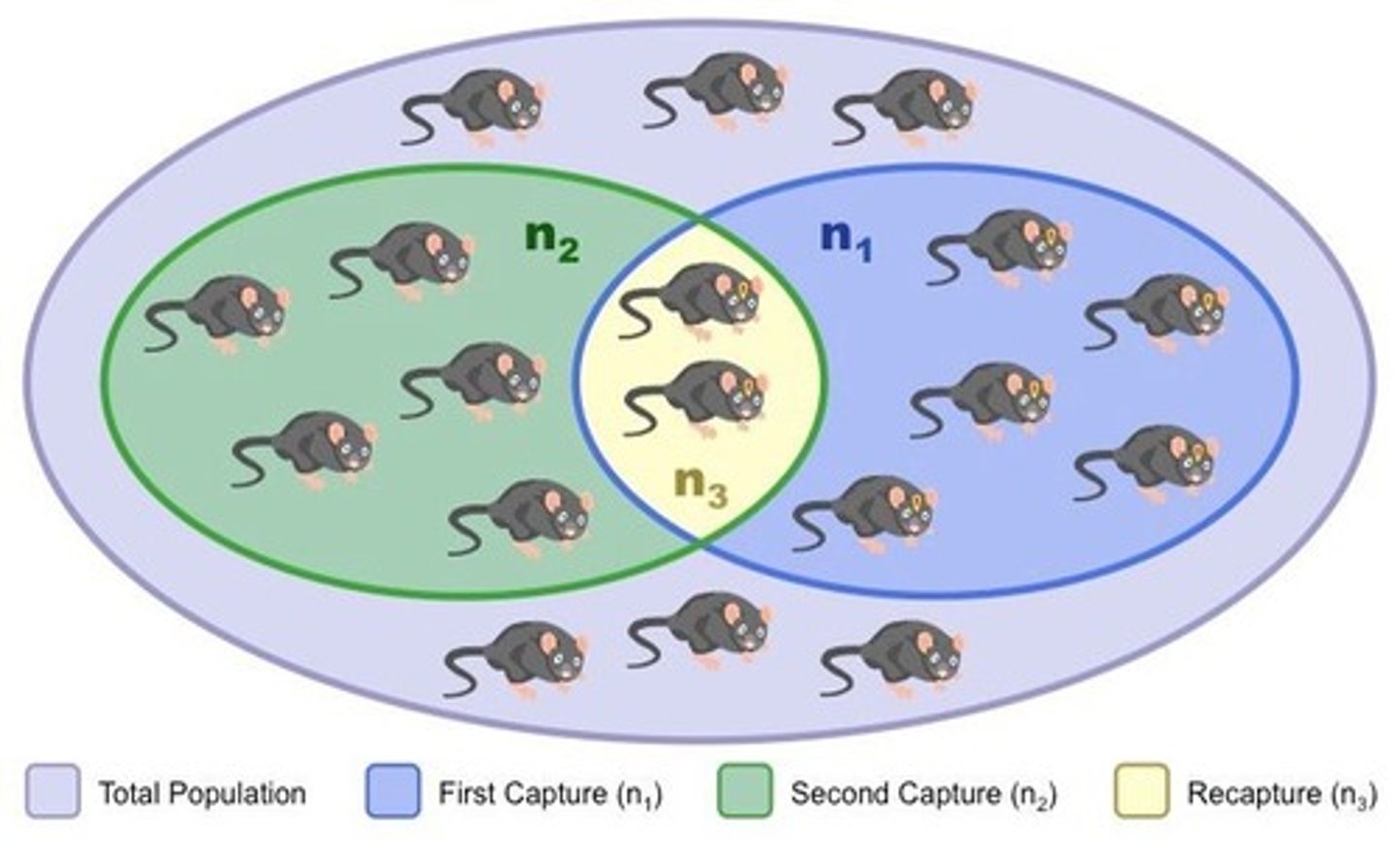
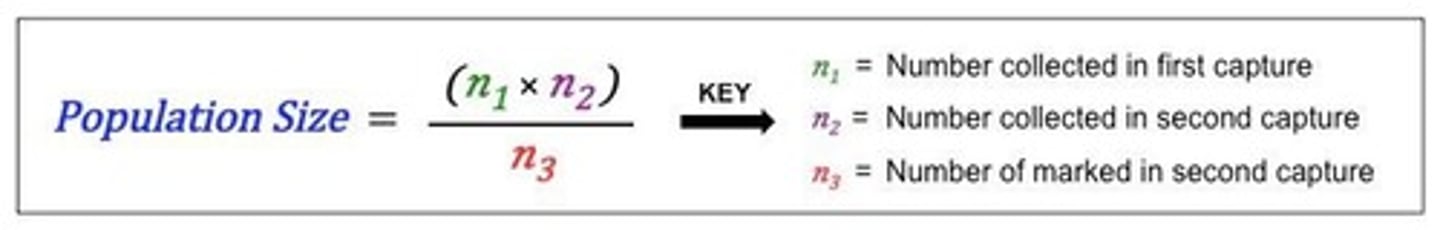
Lincoln Index
Formula using recapture data to estimate population size.
M*N/R
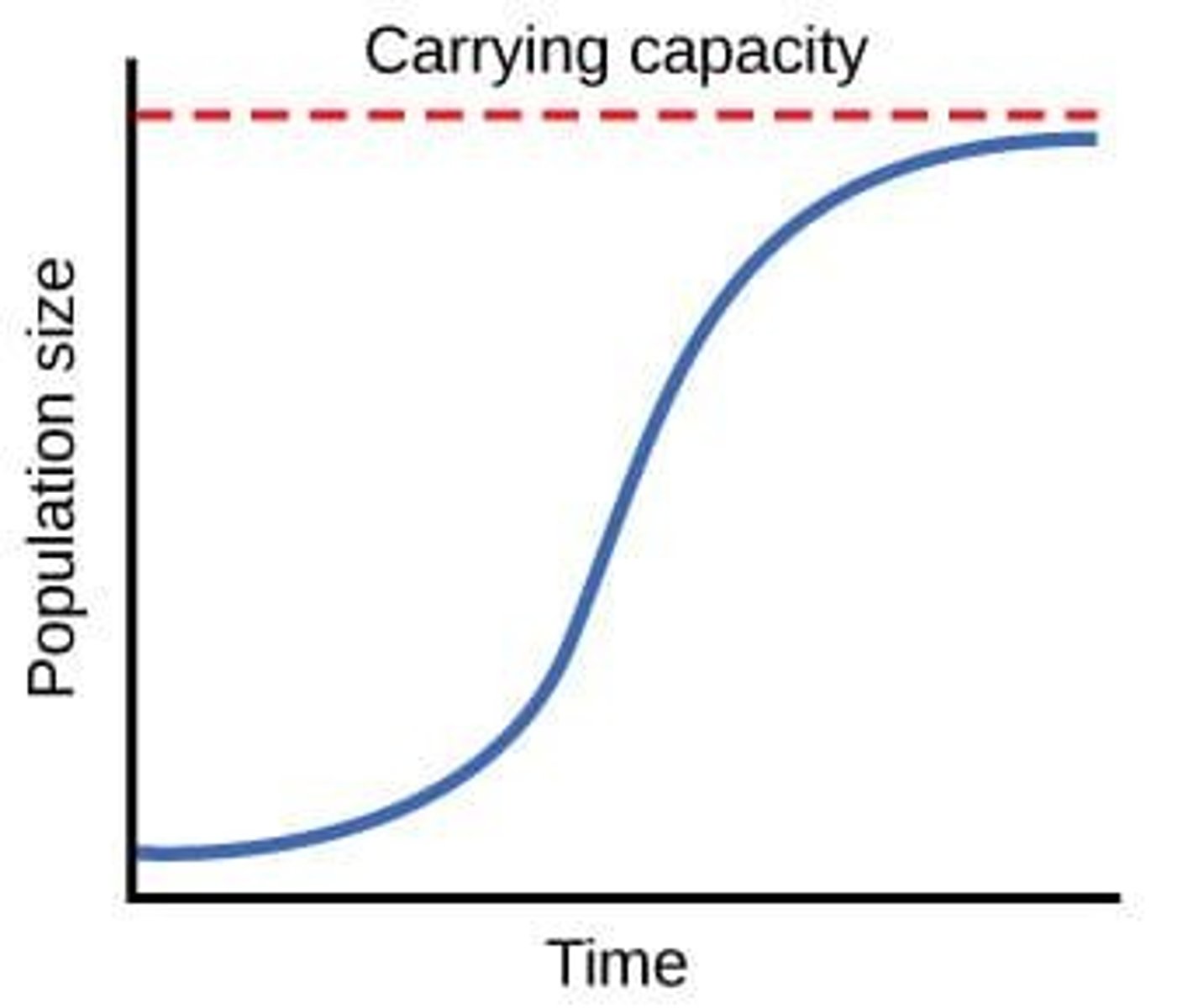
Carrying Capacity
Maximum individuals an environment can support.
Density-Independent Factors of Population density
Abiotic factors affecting all populations equally.
- Includes natural disturbances such as floods, droughts, hurricanes, anthropogenic events, climate change
Density-Dependent Factors
Biotic factors affecting populations based on size.
- Such as competition for resources, predation, disease, parasitism
- Biotic factors intensify when increased
Negative Feedback control of population size
Mechanism returning population to carrying capacity.
- Counters or reverses changes in a system to maintain stability
Natality
Rate of individuals born in a population.
Mortality
Rate of individuals dying in a population.
Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population.
Emigration
Departure of individuals from a population.
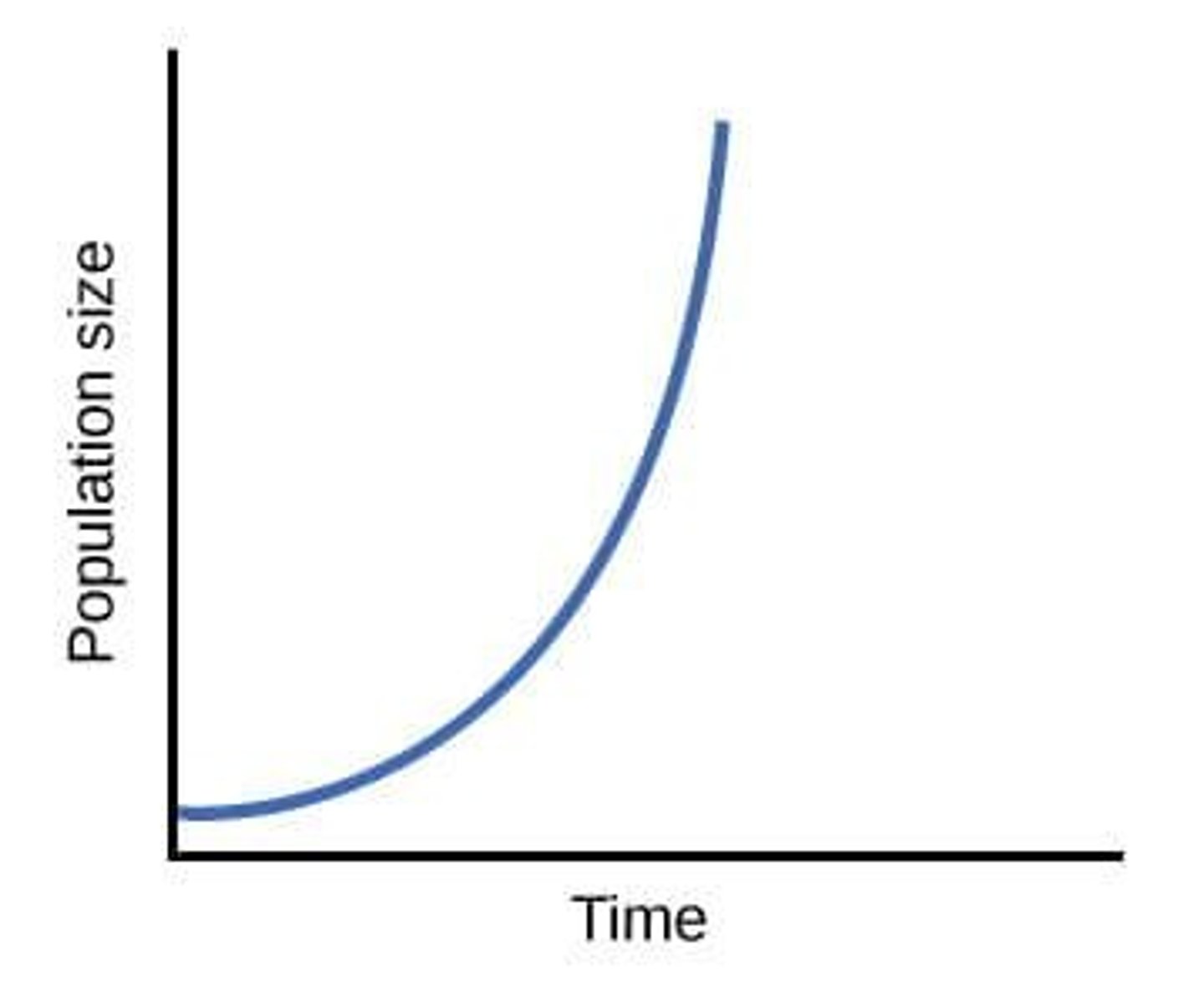
Exponential Growth
Population growth in ideal, unlimited environments.
- J shaped curve
- population experiences exponential growth when resources are abundant and competition is low
Abiotic Factors
Non-living environmental factors affecting populations.
Biotic Factors
Living components affecting population dynamics.
Predation
Interaction where one organism preys on another.
Intraspecific Relationships
Interactions among individuals of the same species.
- Includes competition and cooperation
Interspecific Relationships
Relationships between individuals of different species.
- Include herbivory, predation, interspecific competition, mutualism, parasitism, pathogenicity
Fertility
Ability of individuals to reproduce successfully.
Sigmoid Growth Curve
S-shaped graph representing population growth phases.
- Initially population has exponential growth, then density dependent factors come into play, limiting rate of population growth
- Carrying capacity is reached which leads to sigmoid population growth
Interspecific Relationships
Interactions between individuals of different species.
Mutualism
Relationship where both species benefit.
Parasitism
One organism benefits at the host's expense.
Pathogenicity
Ability of pathogens to cause disease.
Herbivory
Feeding relationship between herbivores and plants.
Alien Species
Species introduced by human activity.
Invasive Species
Rapidly increasing alien species harming native species.
Endemic Species
Species found only in a specific area.
Native Species
Species naturally found in an area.
Zooxanthellae
Algae living within coral cells, aiding photosynthesis.
Root Nodules
Plant structures housing nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Garlic Mustard
Invasive herb from Europe, disrupts native flora.
Competitive Exclusion
One species outcompetes another, leading to exclusion.
Fundamental Niche
Potential ecological role of a species without competition.
Realized Niche
Actual ecological role of a species with competition.
Chi-Square Test
Statistical test for association between species.
Degrees of Freedom
Calculated as (m-1)(n-1) in chi-square tests.
Predator-Prey Relationship
Interaction controlling population dynamics of species.
Top Down Control
Higher trophic levels influence lower levels via predation.
Bottom Up Control
Lower trophic levels affect higher levels through resources.
Allelopathy
Chemical inhibition of one plant by another.
Allelochemicals
Chemicals released by plants to suppress competitors.
Brassica Plants
Group of plants known for allelopathic properties.
Bracken Fern
Excludes other plants through allelopathic mechanisms.
Penicillin
First mass-produced antibiotic discovered by Fleming.
Contingency Table
Table used to calculate expected frequencies in chi-square.
Nutrient Competition
Plants compete for nutrients, affecting growth and survival.
Forest Invaders
Species that disrupt local ecosystems by outcompeting natives.
Field Manipulation
Experimental method involving removal of species.
Fungi Interference
Fungi essential for plant nutrient uptake can be disrupted.
Population Dynamics
Study of how populations change over time.
Germination Inhibitors
Chemicals that prevent seed sprouting in competing plants.
Trophic Levels
Hierarchical levels in an ecosystem based on energy flow.
Contaminated Dishes
Fleming's discovery of penicillin from mould contamination.
Ecological Models
Tools for understanding complex biological interactions.
Factors contributing to the overall size of a population over time
natality, mortality, immigration, emigration