robotics final
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1. A coordinate frame is defined by
A. A single point in space
B. Three orthogonal unit vectors
C. A set of Euler angles
D. A single rotation matrix
B: Explanation: A coordinate frame is defined by three mutually perpendicular unit vectors, which specify the orientation of the frame
2. A vector’s value changes when
A. The coordinate frame changes
B. The vector’s magnitude changes
C. The vector’s direction changes
D. All of the above
( D )Explanation: When the coordinate frame changes, or when the vector’s magnitude or
direction changes, its numerical representation will also be diƯerent
3. A transformation between two frames expresses:
A. The shape of the object
B. The relationship between the frames
C. The object’s mass distribution
D. The time evolution of motion
B
4. An orthonormal basis satisfies:
A. 𝐢 ⋅ 𝐣 = 1
B. ∣ 𝐢 ∣= 2
C. 𝐢 ⋅ 𝐣 = 0, ∣ 𝐢 ∣= 1
D. None of the above
C
5. A rotation matrix is:
A. Any 3×3 matrix
B. A 3×3 matrix with orthogonal columns of unit length
C. A symmetric matrix
D. A diagonal matrix
B
6. For a valid rotation matrix 𝑅:
A. 𝑅் 𝑅 = 𝐼 and det (𝑅) = 1
B. 𝑅் 𝑅 = 0
C. 𝑅ି ଵ = −𝑅்
D. det (𝑅) = −1
A
7. The inverse of a rotation matrix equals:
A. Its determinant
B. Its transpose
C. Its negative
D. None
B
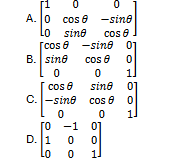
8. The standard rotation matrix about the z-axis by angle θ is:
B
9. The result of successive rotations is obtained by:
A. Adding the rotation angles
B. Multiplying rotation matrices in order
C. Subtracting the rotation matrices
D. Averaging the rotation matrices
B
10. Rotating a coordinate frame vs rotating a vector leads to:
A. The same mathematical operation
B. The transpose operation
C. No difference
D. A translation
B
11. A position vector represents:
A. Orientation only
B. Distance between two points
C. The location of a point relative to a reference frame
D. A direction only
C
12. Rigid body motion preserves:
A. Distances between points
B. Angles between lines
C. Both A and B
D. Neither
C
13. Rigid body motion is described by:
A. A rotation and a translation
B. A scaling factor
C. A shear transformation
D. None
A
14. The composition of two rigid transformations is:
A. Not a rigid transformation
B. A scaling
C. Another rigid transformation
D. Undefined
C
15. The homogeneous transformation matrix has size:
A. 3×3
B. 4×4
C. 2×2
D. 5×5
B
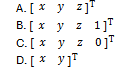
16. A 3D point in homogeneous coordinates is represented as:
B
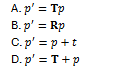
17. The point transformation in homogeneous form is:
B
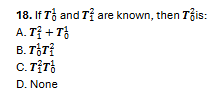
B

C

20. The Denavit–Hartenberg (DH) method is primarily used to:
B

B

B

D
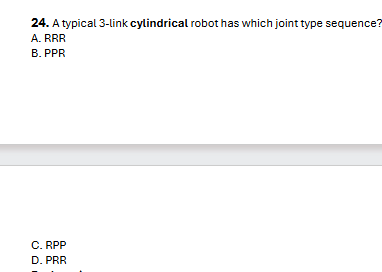
C

C
26. A spherical wrist allows:
A. Linear motion in three directions
B. Pure translational movement
C. Orientation control independent of position
D. Force amplification
C

B
28. Forward kinematics determines:
A. Joint variables from a desired end-effector pose
B. End-effector pose from given joint variables
C. Forces from torques
D. Velocities from accelerations
B
29. Forward kinematics is computed by:
A. Numerical iteration
B. Successive multiplication of link transformation matrices
C. Differentiation of joint angles
D. Integration of velocities
B
30. Inverse kinematics involves:
A. Finding joint variables for a desired end-effector pose
B. Determining link masses from torques
C. Computing inertia tensors
D. Calculating dynamic force
A

C
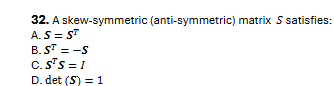
B

C
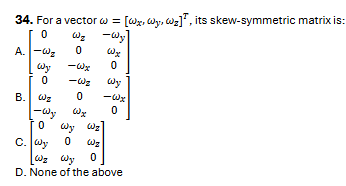
B
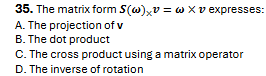
C
36. Angular velocity describes:
A. Change in position over time
B. Rate of change of orientation over time
C. The curvature of a path
D. The speed of linear translation
B

B
38. The matrix 𝑆(𝜔) represents:
A. Linear velocity
B. Rotational acceleration
C. The instantaneous rate of rotation (angular velocity)
D. A scaling transformation
C
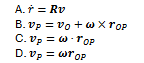
39. For a point 𝑃 at position vector 𝒓, its linear velocity is:
B
C
41. The Jacobian matrix relates:
A. Forces and torques
B. Joint velocities and end-effector velocities
C. Joint positions and accelerations
D. End-effector forces and displacements
B

C

A
44. Each column of the Jacobian corresponds to:
A. A Cartesian axis
B. The effect of one joint’s motion on the end-effector velocity
C. A transformation matrix
D. A torque vector
B
45. The Jacobian represents:
A. The gradient of energy
B. The instantaneous velocity mapping between joint space and task space
C. The potential field
D. The control gain matrix
B