AP Micro Unit 3 - Production, Cost, and the Perfect Competition Model
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
Production
* The process by which a producer takes inputs (factors of production) and creates an output
2
New cards
Fixed Costs
* The costs that aren’t affected by the quantity produced
* Examples:
* Rent
* Examples:
* Rent
3
New cards
Variable Costs
* The costs that are affected by the quantity produced
* Examples:
* Tomatoes to make pizza sauce
* Examples:
* Tomatoes to make pizza sauce
4
New cards
Total Revenue
* Total amount of money a firm brings in
* TR = P \* Q
* TR = P \* Q
5
New cards
Accounting Profit
* The amount of money a business makes
* Just explicit costs
* Just explicit costs
6
New cards
Economic Profit
* Profit, including the opportunity cost
* Explicit and implicit costs
* Explicit and implicit costs
7
New cards
Total Product (TP)
* How much a firm outputs in total
* Example: 2 workers produce 50 units, total is 50
* Example: 2 workers produce 50 units, total is 50
8
New cards
Average Product (AP)
* Divides total product by number of inputs
* Example: 2 workers produce 50 units, average is 25
* Example: 2 workers produce 50 units, average is 25
9
New cards
Marginal Product (MP)
* Additional output from adding one more input
* Helps us determine when we should stop adding more inputs - zero or negative, we stop
* Example: 2 workers produce 50 units, 3 workers produce 60 units - the 3rd worker’s MP was 10 units
* Helps us determine when we should stop adding more inputs - zero or negative, we stop
* Example: 2 workers produce 50 units, 3 workers produce 60 units - the 3rd worker’s MP was 10 units
10
New cards
Law of Diminishing Marginal Product
* As we add more inputs, the additional product produced we get from each input will eventually diminish
11
New cards
Returns to Scale
* Proportional increase in output from an increase in inputs
* Production doubles when input doubles
* Production doubles when input doubles
12
New cards
Increasing Returns to Scale
* Production more than doubles with doubled input
13
New cards
Decreasing Returns to Scale
* Production less than doubles with doubled input
14
New cards
Short-Run
* Period of time where at least one input is fixed and cannot change
15
New cards
Long-Run
* Period of time where no variables are fixed
16
New cards
Accounting Costs
* Explicit costs paid by firms to use resources during the production process
17
New cards
Economic Costs
* Sum of both the implicit costs (opportunity costs) and explicit costs of production
18
New cards
Total Cost
* Total cost of producing some quantity of output
* Sum of the variable and fixed costs
* TC = VC + FC
* Sum of the variable and fixed costs
* TC = VC + FC
19
New cards
Cost Curves Graph
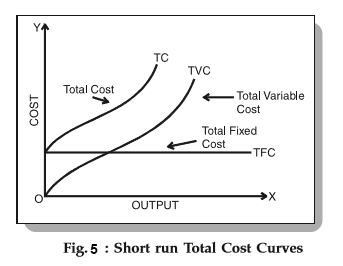
20
New cards
Profit
* Difference of revenue and costs
* Profit = TR - TC
* Profit = TR - TC
21
New cards
Average Total Cost (ATC) Equation
* TC / Q
* AFC + AVC
* AFC + AVC
22
New cards
Average Variable Cost (AVC) Equation
* VC / Q
* ATC - AFC
* ATC - AFC
23
New cards
Average Fixed Cost (AFC) Equation
* FC / Q
* ATC - AVC
* ATC - AVC
24
New cards
Marginal Cost
* Additional cost of producing one more unit
25
New cards
Total Cost, Variable Cost, Fixed Cost curves
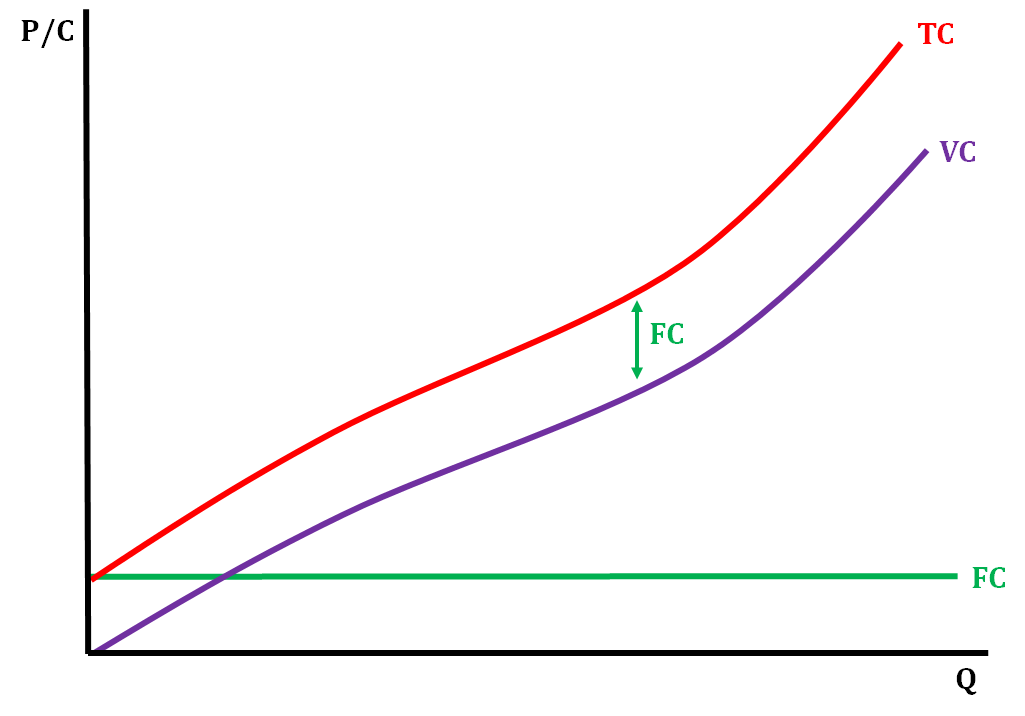
26
New cards
MC, ATC, AVC, AFC curves
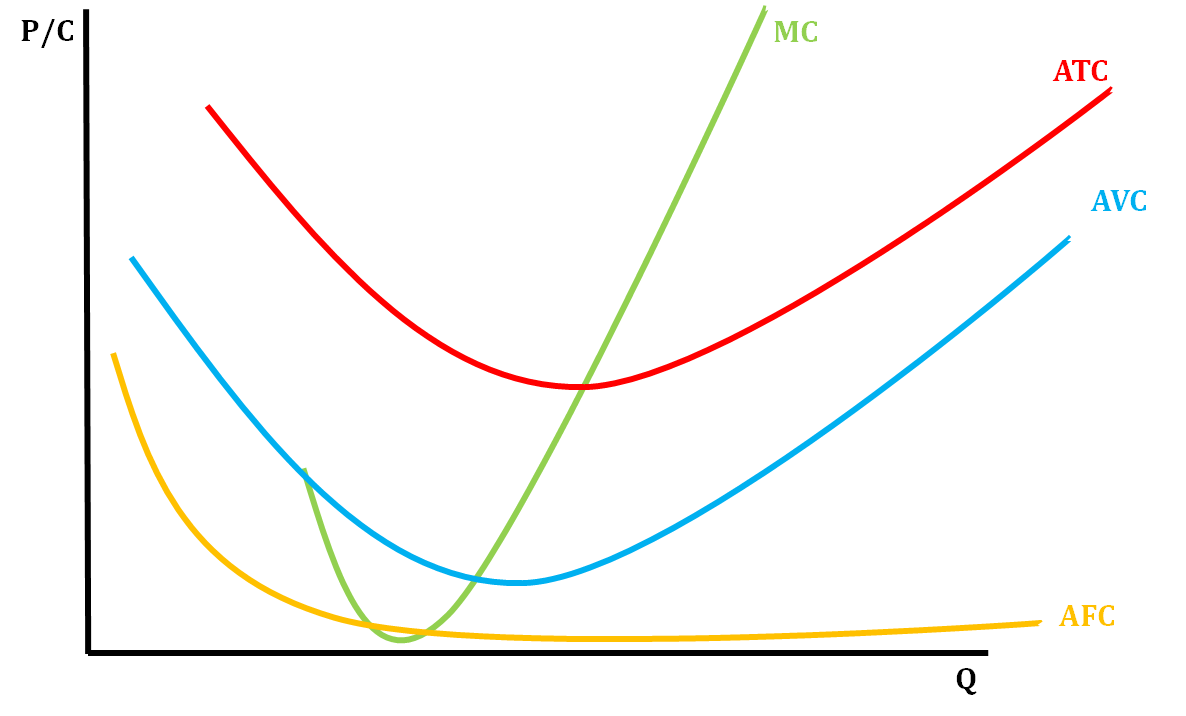
27
New cards
In the long run, all resources are…
flexible
28
New cards
Long Run ATC (LRATC) Curve
* Short Run Total Cost Curves will shift in the Long Run as more is produced
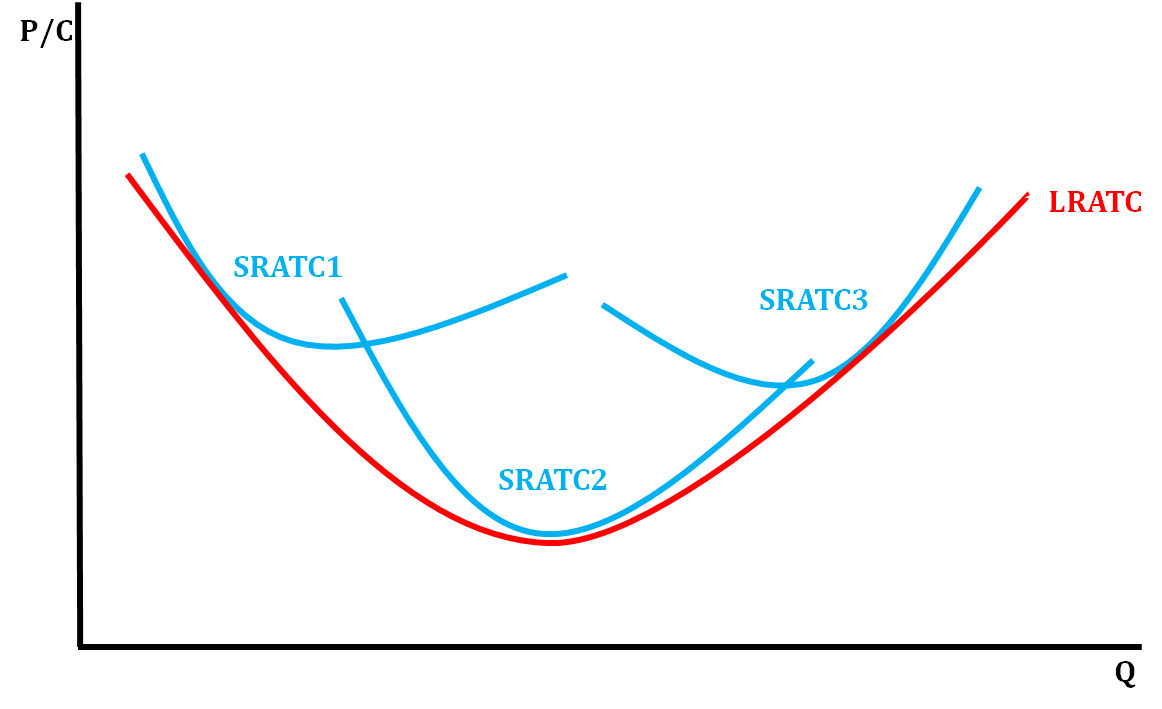
29
New cards
How do we find Long Run ATC (LRATC)?
* Take the lowest average total cost curve at each level of output (short run cost curves)
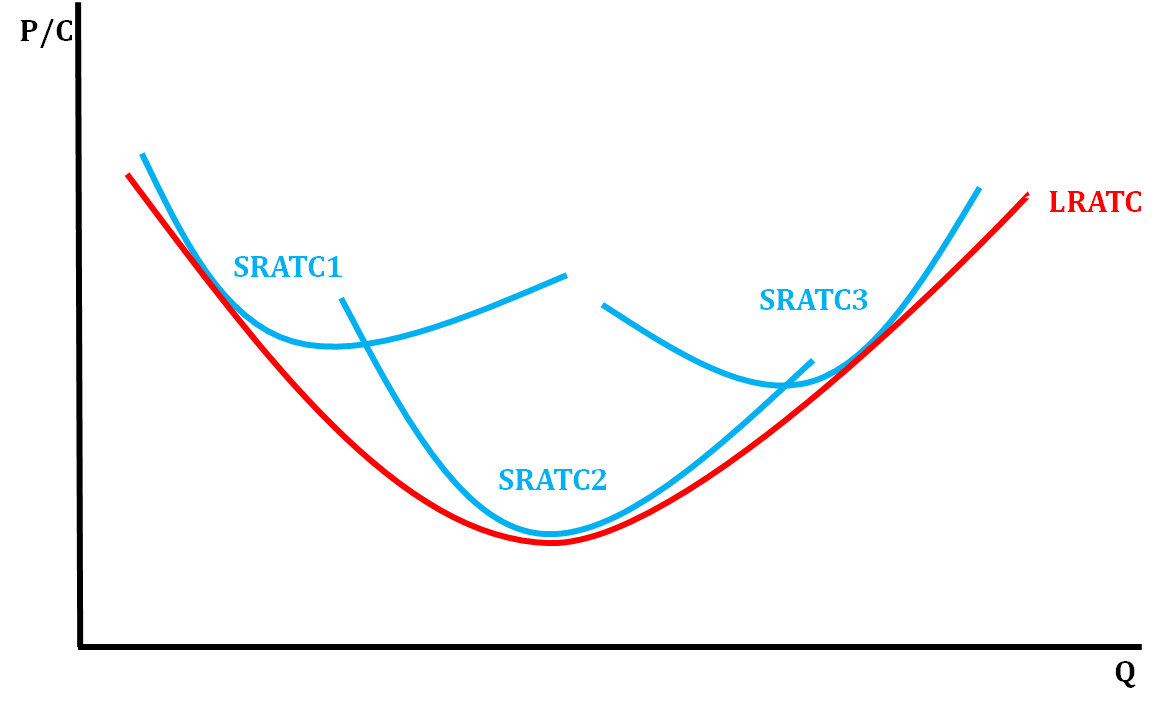
30
New cards
LR ATC Car Scenario (to help understand)
* In the beginning of production, a factory does not use it’s full plant capacity and mass production is difficult, so there is a high cost producing less quantity
* As the firm continues production, it expands in capacity and can mass produce, lowering ATC
* As the firm expands, its output becomes larger than its plant capacity and is too big to manage, so costs rise again
* As the firm continues production, it expands in capacity and can mass produce, lowering ATC
* As the firm expands, its output becomes larger than its plant capacity and is too big to manage, so costs rise again
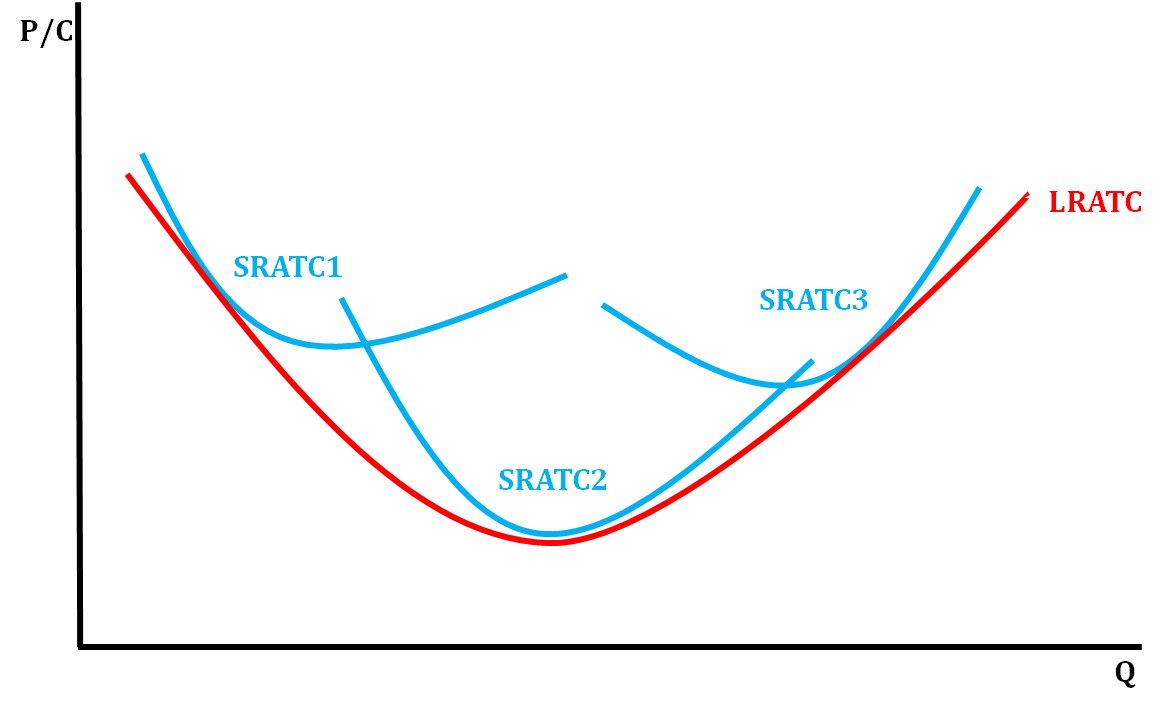
31
New cards
Economies of Scale
* Refers to the reduction in total cost-per-unit as a firm increases its production
* In this phase, the firm can reduce the total cost-per-unit by boosting its plant capacity and output
* In this phase, the firm can reduce the total cost-per-unit by boosting its plant capacity and output
32
New cards
Diseconomies of Scale
* Refers to the rise in total cost-per-unit as the firm increases its production
* In this phase, the firm would be better off reducing its plant capacity and output to lower per-unit costs
* In this phase, the firm would be better off reducing its plant capacity and output to lower per-unit costs
33
New cards
Constant Returns to Scale
* Between Economies of Scale and Diseconomies of Scale
* In this phase, when the firm increases production, costs stay the same
* ATC is at its lowest
* In this phase, when the firm increases production, costs stay the same
* ATC is at its lowest
34
New cards
Economies/Diseconomies of Scale
* Blue is Economies of Scale
* Green is Diseconomies of Scale
* Yellow is Constant Returns to Scale
* Green is Diseconomies of Scale
* Yellow is Constant Returns to Scale
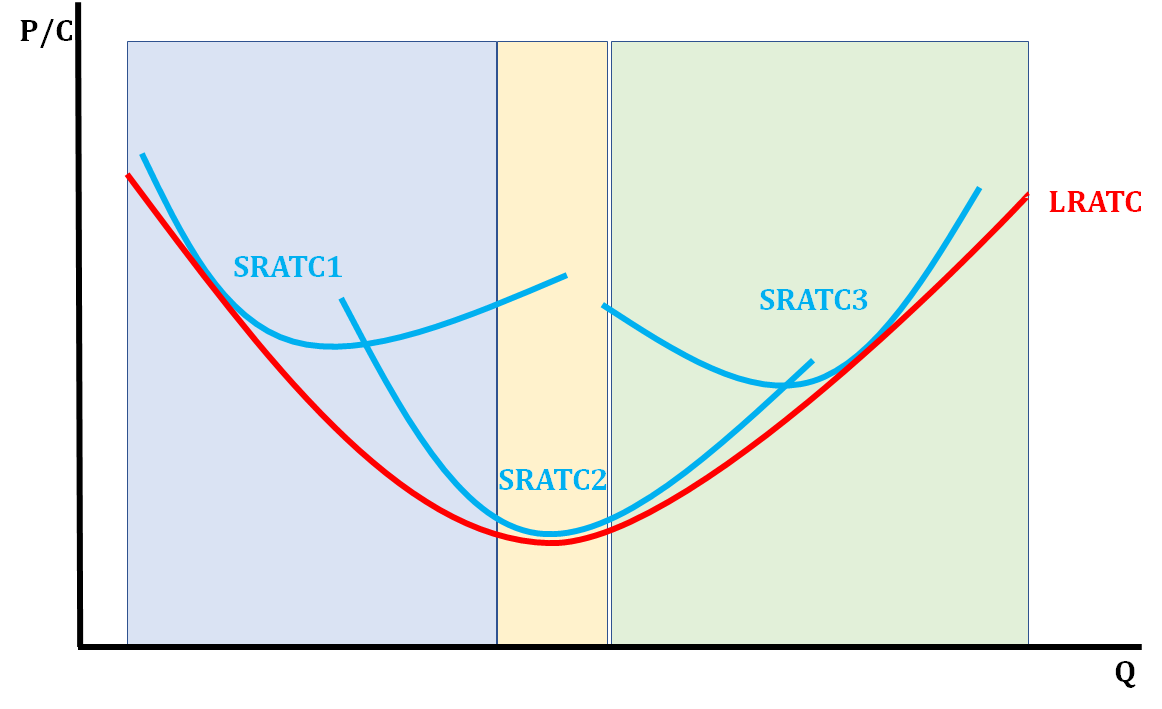
35
New cards
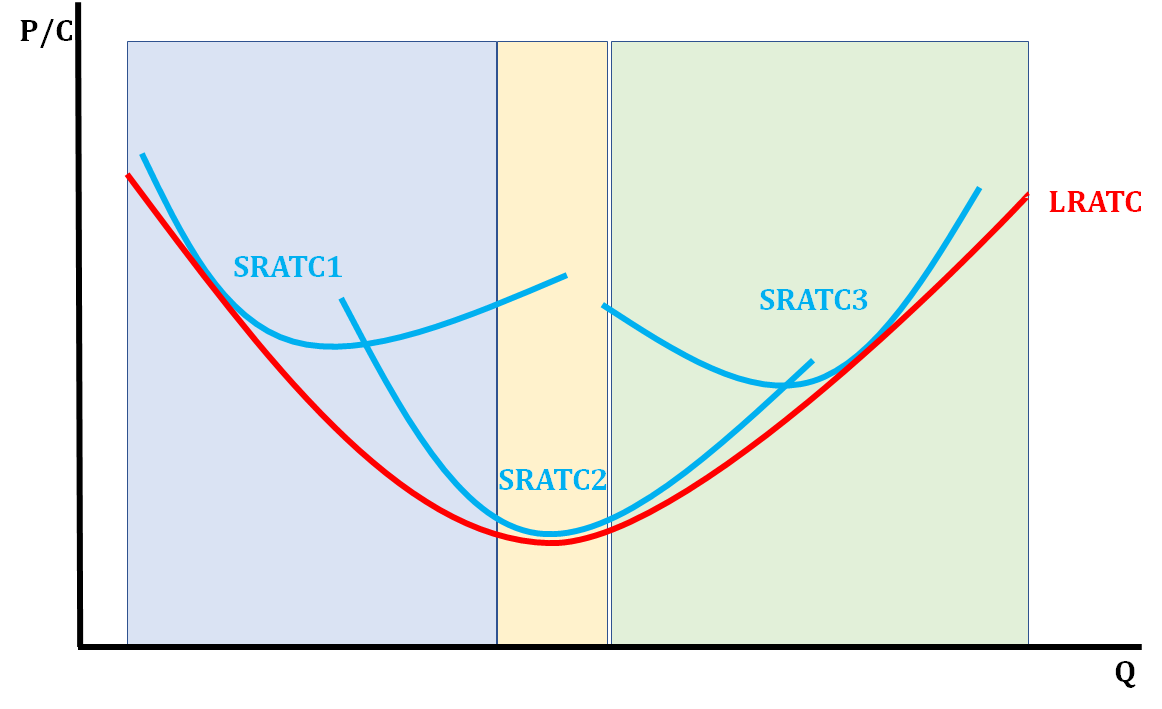
What does each color represent in the graph:
* Blue
* Yellow
* Green
* Blue
* Yellow
* Green
* Blue = Economies of Scale
* Yellow = Constant Returns to Scale
* Green = Diseconomies of Scale
* Yellow = Constant Returns to Scale
* Green = Diseconomies of Scale
36
New cards
Normal Profit
* When economic profit is zero - breaking even
* Our accounting profit is positive
* Our accounting profit is positive
37
New cards
Economic losses
* When revenue is less than costs
38
New cards
Supernormal profit
* When a firm experiences economic profits in the long run
39
New cards
Theory of the Firm
* The primary goal of any firm, regardless of market structure, is to maximize profits
40
New cards
Profit Maximizing Rule
* MR=MC
41
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
* Many, small firms in the industry
* Firms are price takers, and have no control over the price of the goods they sell in the market
* Market is impacted when firms enter or exit
* Low barriers to entry
* Firms break even in the long run
* Products sold are identical
* No non-price competition
* All products are identical, so no need for advertising
* Firms are perfectly efficient in the long-run
* Firms are price takers, and have no control over the price of the goods they sell in the market
* Market is impacted when firms enter or exit
* Low barriers to entry
* Firms break even in the long run
* Products sold are identical
* No non-price competition
* All products are identical, so no need for advertising
* Firms are perfectly efficient in the long-run
42
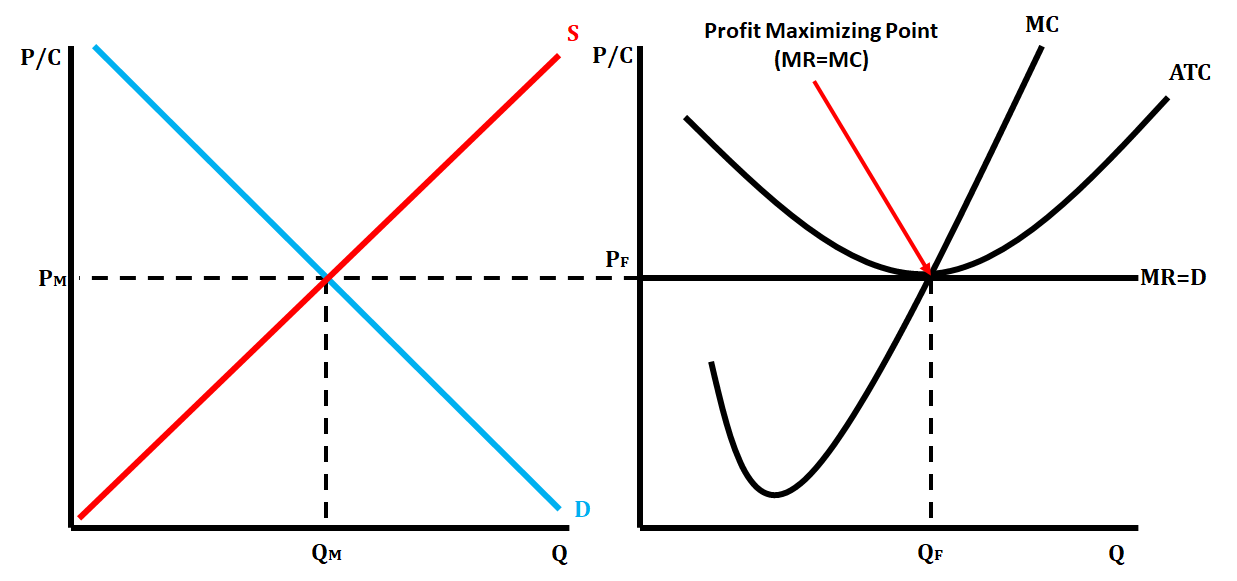
New cards
Perfect Competition Side by Side Graphs
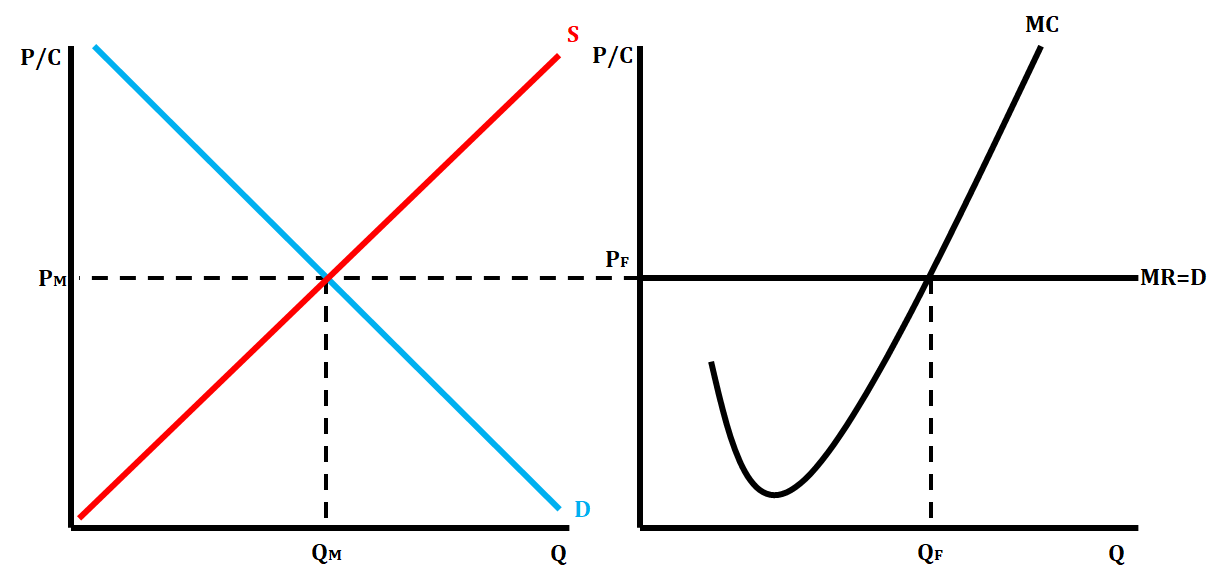
43
New cards
Perfect Competition Short Run Profit
* ATC and AVC curves are below MR=MC
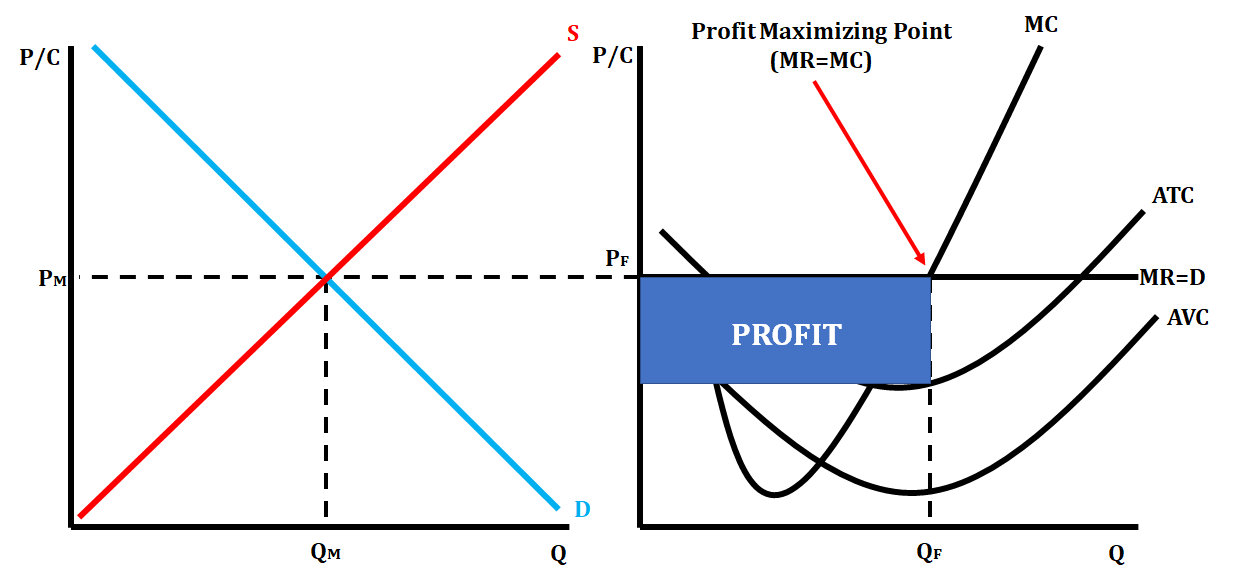
44
New cards
Perfect Competition Short Run Loss
* ATC curve is above MR=MC, and AVC curve is below MR=MC
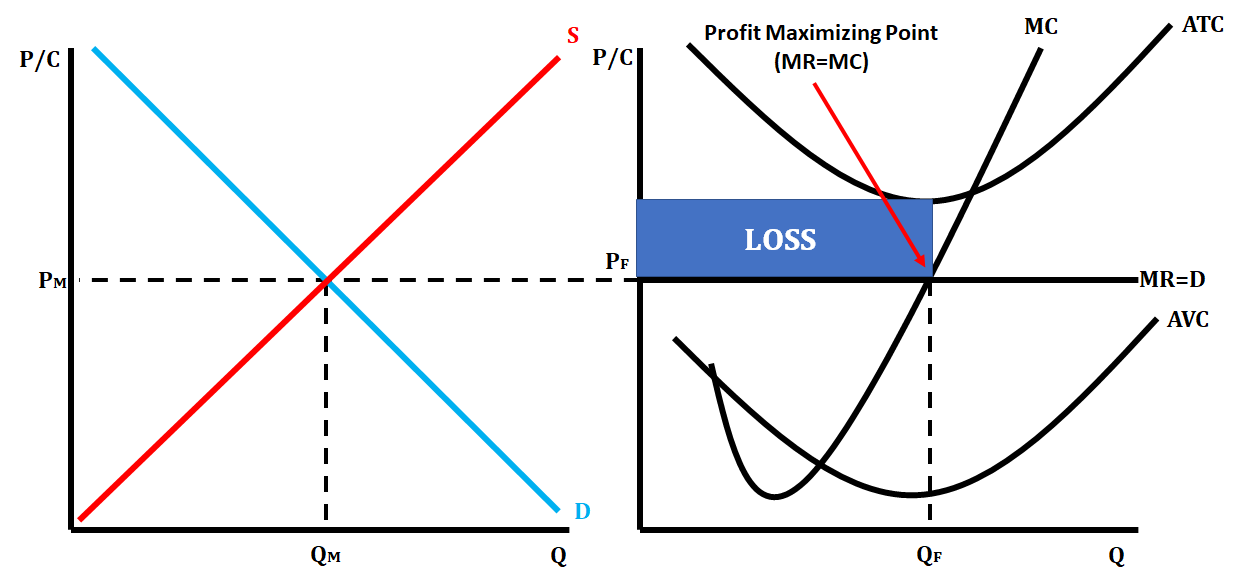
45
New cards
Perfect Competition Short Run Shut Down
* ATC and AVC curves are above MR=MC
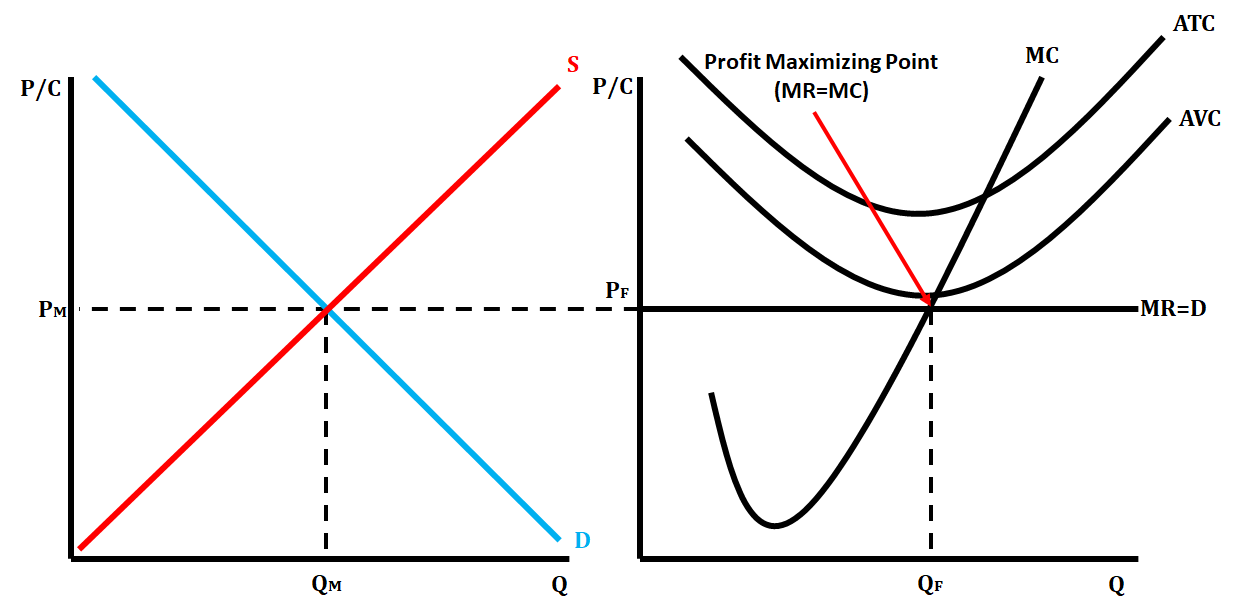
46
New cards
Perfect Competition Long Run Equilibrium
* ATC Curve is tangent to MR=DARP where MR=MC
* It is allocatively and productively efficient - perfectly efficient
* It is allocatively and productively efficient - perfectly efficient
47
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
Short Run Shut Down Rule
Short Run Shut Down Rule
* The firm should continue to operate as long as the price is equal to or above AVC
48
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
When firms are earning economic loss in the short run, in the long run firms will…
When firms are earning economic loss in the short run, in the long run firms will…
leave the industry due to the lack of profit available
49
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
When firms are earning economic profit in the short run, in the long run firms will…
When firms are earning economic profit in the short run, in the long run firms will…
enter the industry due to the potential profit available
50
New cards
What is MR DARP?
MR = D = AR = P
* Market equilibrium is equal to marginal revenue
* Market equilibrium is equal to marginal revenue
51
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
When a firm enters the market, what will happen?
When a firm enters the market, what will happen?
* Supply will shift right
* This will decrease price, driving MR DARP down
* This will decrease price, driving MR DARP down
52
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
When a firm leaves the market, what will happen?
When a firm leaves the market, what will happen?
* Supply will shift left
* This will increase price, raising MR DARP up
* This will increase price, raising MR DARP up
53
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Market
In the long run, the market will shift towards…
In the long run, the market will shift towards…
equilibrium, or normal profits