Business Analytics terms
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
nominal scale
classifies data into distinct categories with no ranking
ordinal scale
classifies data into distinct categories with ranking
population
contains all of the items or individuals of interest that you seek to study
sample
contains only a portion of a population of interest
population parameter
a number that summarizes the value of a specific variable for a population
sample statistic
a number that summarizes the value of a specific variable for sample data
simple random sample
every individual or item from the frame has an equal chance of being selected
either with or without replacement
stratified sample
divide population into two or more subgroups (strata) according to some common characteristics
a simple random sample is selected from each subgroup, with sample sizes proportional to strata sizes
samples from subgroups are combined into one
even representation of population
cluster sample
divide population into several “clusters,” each representative of the population
select a simple random sample of clusters
summary table
tallies the frequencies or percentages of items in a set of categories so that you can see differences between categories
contingency table
helps organize multiple categorical variables
used to study patterns that may exist between the responses of two or more categorical variables
central tendency
the extent to which all the data values group around a typical or central value
mean
most common measure of central tendency
affected by outliers
median
middle number in an ordered array
less sensitive to outliers than mean
range
simplest variation measure
sensitive to outliers
= largest # - smallest #
sample variance
a measure of the degree to which the numbers in a list are spread out
sample standard deviation
most commonly used measure of variation
is square root of variance
Z-score (aka standard score)
gives you an idea of how far a data point is from the mean
data point is an extreme outlier if this is less than -3.0 or greater than +3.0
the larger the absolute value of this, the farther the data point is from the mean
left-skewed distribution
(median - smallest #) > (largest # - median)
(Q1 - smallest #) > (largest # - Q3)
(median - Q1) > (Q3 - median)
symmetric distribution
(median - smallest #) ≈ (largest # - median)
(Q1 - smallest #) ≈ (largest # - Q3)
(median - Q1) ≈ (Q3 - median)
right-skewed distribution
(median - smallest #) < (largest # - median)
(Q1 - smallest #) < (largest # - Q3)
(median - Q1) < (Q3 - median)
covariance
measures the direction of the linear relationship between two numerical variables
cov(X,Y) is positive: X and Y tend to move in the same direction
cov(X,Y) is negative: X and Y tend to move in opposite directions
cov(X,Y) = 0: No linear relationship between X and Y
coefficient of correlation
measures the relative strength and directoin of the linear relationship between two numerical variables
population variable: p
sample variable: r
closer to -1: stronger negative linear relationship
closer to 1: stronger positive linear relationship
closer to 0: weaker linear relationship
sample space
all possible outcomes of a variable
simple event
event with 1 characteristic
joint event
event with 2+ characteristics
complement
outcomes that are not part of an event
mutually exclusive events
events that cannot occur simultaneously
collectively exhaustive
a set of events is this if at least one of the events must occur
simple probability
the probability of a single event
joint probability
the probability of two or more events occurring simultaneously
marginal probability
consists of a set of joint probabilities while focusing on one variable
you want to find the probability of a certain event as unconditioned by any other event
general addition rule
used to find the probability of either A or B
conditional probability
the probability that event A happens given information about event B
P(A | B) = P(A and B) / P(B)
independent
events are this when the probability of one event is not affected by the fact that the other event has occurred
if and only if: P(A | B) = P(A)
multiplication rule
used to find the probability events A and B occurring
marginal probability with multiplication rule
used to find the unconditioned probability of an event when the given events are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive
counting rule 1
If any one of k different mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive events can occur on each of n trials, the number of possible outcomes is equal to k^n
ex.: rolling a die 3 times
6 sides
roll 3 times
6³ = 216 possible outcomes
counting rule 2
If there are k1 events on the first trial, k2 events on the second trial, … and kn events on the nth trial, the number of possible outcomes is (k1)(k2)…(kn)
ex.: you want to go to a park, eat at a restaurant, and see a movie. there are 3 parks, four restaurants, and 6 movie choices. how many diff possible combinations are there?
(3 parks)(4 restaurants)(6 movies) = 72 possible combinations
counting rule 3
the number of ways that n items can be arranged in order
n! = (n)(n-1)(n-2)…(1)
ex.: you have five books. how many diff ways can you place these books on the bookshelf?
5! = (5)(4)(3)(2)(1) = 120 possible orders
counting rule 4: permutations
the number of ways of arranging X objects selected from n objects in order
nPX = n! / (n-X)!
ex.: you have five books and are going to put three on a bookshelf. how many diff ways can the books be ordered on the bookshelf?
nPX = 5! / (5-3)! = [(5)(4)(3)(2)(1)] / (2) = 120 / 2 = 60
counting rule 5: combinations
the number of ways of selecting X objects from n objects regardless of order
nCX = n! / X!(n-X)!
ex.: you have five books and are going to select three to read. how many diff combinations are there, ignoring the order of selection?
nCX = 5! / [3!(5-3)! = 120 / [(6)(2)] = 10
discrete variable
comes from a counting process
ex.: number of classes you’re taking
continuous variable
comes from a measurement
ex.: annual salary; weight
probability distribution for a discrete variable
a mutually exclusive listing of all possible numerical outcomes for a variable and a probability occurence associated with each outcome
expected value of a discrete variable
weighted average of the possible values, each one weighted by its own probability
properties of binomial distribution
used when the discrete variable = the number of events of interest in a sample of n observations
sample consists of a fixed number of observations, n
each observation is either mutually exclusive or collectively exhaustive
the probability of an observation being classified as the event of interest, π, is constant from observation to observation → probability of an observation being classified as not the event of interest, 1 - π, is constant
binomial distribution
represents the probability for x successes in n trials, given a success probability p for each trial
Poisson distribution
used to find the number of times an event occurs in a given area of opportunity
area of opportunity - a continuous unit or interval of time, volume, or area in which more than one occurence of an event can occur
ex.: number of mosquito bites on a person
ex.: number of computer crashes in a day
when to apply Poisson distribution
you want to count the number of times an event occurs in a given area of opportunity
the probability that an event occurs in one area of opportunity is the same for all areas of opportunity
the number of events that occur in one area of opportunity is independent of the number of events that occur in the other areas of opportunity
the probability that two or more events occur in an area of opportunity approaches zero as the area of opportunity becomes smaller
the average number of events per unit is λ (lambda) (mean)
continuous random variable
a variable that can assume an uncountable number of values
ex.: thickness of an item
time required for a task
temperature
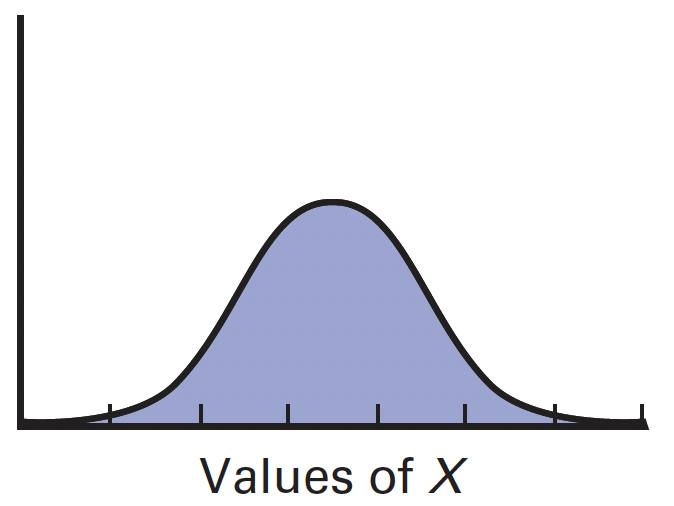
normal distribution
symmetrical bell-shape
ranges from negative to positive infinity
mean determines location
standard deviation determines spread
mean = median = mode
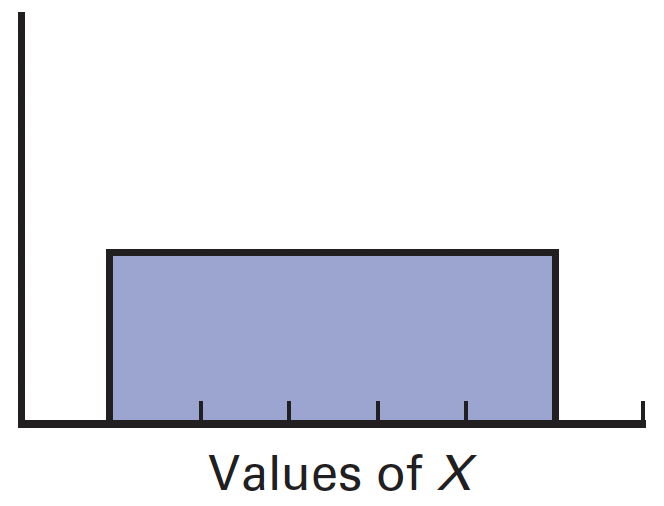
uniform (rectangular) distribution
all values are equally distributed
every value is equally likely
commonly used for completely random events
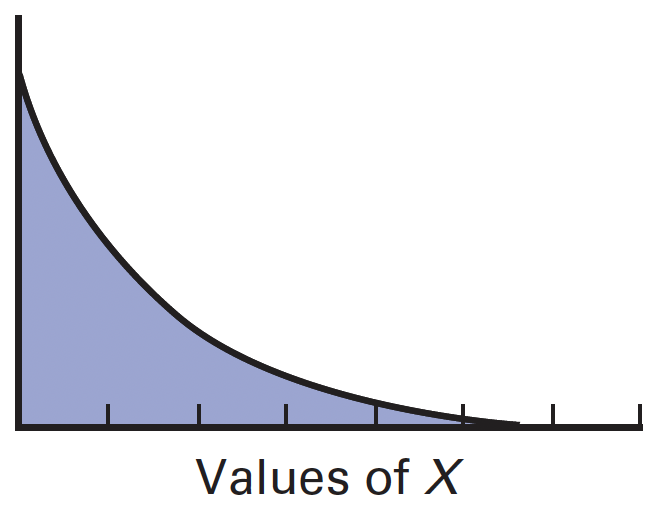
exponential distribution
contains values from zero to positive infinity
right-skewed: mean > median
probability density function
defines the distribution of the values for a continuous variable and can be used as the basis for calculations that determine the probability that a value will be within a certain range
represented by f(X)
standardized normal distribution (Z)
the normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1
Z score
tells us how many standard deviations from the mean each value lies