Mock Exam 3
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
University of Cincinnati, BIO 1081, Dr. Mosley
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1. What structure is key for crossing over to happen during meiosis?
a. Synaptonemal complex
b. Sister chromosomes
c. Chiasmata
d. Centromere
a. Synaptonemal complex
1. In eukaryotes, genes can be found outside the nucleus in
a. Smooth ER
b. Golgi complex
c. Mitochondria
d. Genes are only found in the nucleus
c. Mitochondria
1. In the Calvin Cycle, which molecule is regenerated and used to capture carbon dioxide for the synthesis of sugars?
a. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)
b. Glucose
c. 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA)
d. ATP
a. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)
1. Which macromolecules make up the structure of chromosomes?
a. Proteins and lipids
b. Proteins only
c. Nucleic acids and proteins
d. Sugars and Phosphate Groups only
c. Nucleic acids and proteins
1. How do eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes in terms of their primary mode of reproduction?
a. Eukaryotes reproduce through binary fission
b. Eukaryotes reproduce through meiosis
c. Prokaryotes reproduce through mitosis
d. Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission
d. Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission
1. If a cell undergoes mitosis, and it starts with 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have?
a. 3
b. 6
c. 12
d. Not enough information because we don't know if it's mitosis 1 or mitosis 2
c. 12
1. What structure most likely provides the material for spindle formation during cell division?
a. Nucleus
b. Cytoskeleton
c. Sister chromatids
d. Ribosomes
e. Plasma Membrane
b. Cytoskeleton
1. Which of the following is NOT associated with prophase?
a. Fragmentation of the nuclear envelope
b. Disappearance of the nucleus
c. Separation of the sister chromatids
d. Visible chromosomes
c. Separation of the sister chromatids
1. The primary electron acceptor in photosynthesis during the light reactions is:
a. Water
b. NADP
c. Carbon dioxide
d. Chlorophyll a
b. NADP
1. Interphase is composed of which specific stages of cellular growth and division?
a. G1, G2, and M
b. G1, S, and G2
c. M, S, and G2
d. M, S, and G1
b. G1, S, and G2
1. An increase in cyclin levels at the end of metaphase is most likely to promote
a. Activation of the G2/S checkpoint
b. Cytokinesis
c. Formation of the mitotic spindle
d. Degradation of the centromere
d. Degradation of the centromere
1. What distinguishes cytokinesis in plant cells from that in animal cells?
a. Plant cell cytokinesis involves a cleavage furrow, whereas in animal cell cytokinesis, it forms a new plasma membrane and new cell walls between the cells.
b. Animal cell cytokinesis involves a cleavage furrow, whereas in plant cell cytokinesis, it forms a new plasma membrane and new cell walls between the cells.
c. Animal cytokinesis cell plates originate from microfilaments, whereas plant cytokinesis cell plates come from the Golgi.
d. There is no difference between the two.
b. Animal cell cytokinesis involves a cleavage furrow, whereas in plant cell cytokinesis, it forms a new plasma membrane and new cell walls between the cells.
1. Which statement about cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and cyclin is incorrect?
a. Different Cdks act at different points in the cell cycle.
b. A Cdk can catalyze the phosphorylation of other proteins.
c. Cdks use ATP as a substrate.
d. Cyclin is made continuously during the cell cycle.
c. Cdks use ATP as a substrate.
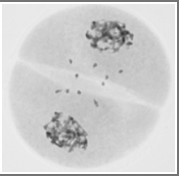
1. What stage is represented by this figure?
a. Prophase I
b. Metaphase I
c. Anaphase I
d. Metaphase II
e. Prophase II
e. Prophase II
1. Mutations in proto-oncogenes can lead to the formation of what type of cancer-causing agents?
a. Tumor suppressor genes
b. Malignant tumors
c. Stem cells
d. Oncogenes
e. P-53 never allows this to happen
d. Oncogenes
1. In an organism with a diploid number of 28 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each nucleus have after meiosis I, but before cytokinesis?
a. 7
b. 14
c. 28
d. 56
b. 14
1. A dihybrid test cross has a distribution of phenotypes with the ratio 9:3:4:1. This is the result of
a. Codominance
b. Epistasis
c. Hybridization
d. X inactivation
b. Epistasis
1. In an organism with a diploid number of 28 chromosomes, how many sister chromatids will the cell have after meiosis II, but before cytokinesis?
a. 56
b. 14
c. 28
d. None of the above
d. None of the above
1. What is the primary purpose of the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis?
a. To capture photons of light
b. To produce ATP and NADPH
c. To fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules
d. To generate glucose from carbon dioxide
c. To fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules
1. What defines members of a homologous pair of chromosomes?
a. Are identical in size and appearance
b. Contain identical genetic information
c. Separate to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis
d. Are present only after the S phase
b. Contain identical genetic information
1. In Mendel's Law of Segregation, what is the key principle?
a. Alleles of different genes segregate independently during gamete formation.
b. A progenitor passes on one randomly selected copy of a gene to its offspring.
c. Homologous chromosomes separate during meiosis.
d. Genes on the same chromosome are linked
a. Alleles of different genes segregate independently during gamete formation.
1. How do proto-oncogenes differ from tumor suppressor genes?
a. They both promote cell proliferation
b. Tumor suppressor genes inhibit cell growth, while proto-oncogenes promote it
c. They both lead to apoptosis initiation
Tumor suppressor genes stimulate cell differentiation, while proto-oncogenes inhibit it
b. Tumor suppressor genes inhibit cell growth, while proto-oncogenes promote it
1. What term refers to the alleles an individual receives at fertilization?
a. Genotype
b. Phenotype
c. Karyotype
d. Linotype
a. Genotype
1. In photosynthesis, what is the primary function of photosystem II (PSII)?
a. Absorbing photons of light
b. Splitting water to release oxygen
c. Pumping protons into the thylakoid space
d. Transferring electrons to NADP+ to produce NADPH
b. Splitting water to release oxygen
1. What does the presence of both A and B types of glycoproteins on the red blood cells of people with AB blood type represent?
a. Codominance
b. Polygenic inheritance
c. Autosomal recessiveness
d. Incomplete dominance
a. Codominance
1. Which of the following characterizes autosomal recessive disorders?
a. Heterozygotes with normal phenotypes
b. Affected parents always having affected children
c. Affected individuals with homozygous dominant mates having unaffected children
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
1. During the light reactions in photosynthesis, where are the protons being pump into?
a. To the intermembrane space
b. To the thylakoid lumen
c. To the cytoplasm
d. To the stroma
b. To the thylakoid lumen
1. What would be the best choice of parental genotypes for a test cross?
a. Aa x Aa
b. Aa x aa
c. AA x Aa
None of these
b. Aa x aa
1. Incomplete dominance results in a phenotype that is:
a. A blend of the two homozygous phenotypes.
b. Dominant over both homozygous phenotypes.
c. Recessive to both homozygous phenotypes.
d. Expressed only in heterozygous individuals.
a. A blend of the two homozygous phenotypes.
What does the G1/S checkpoint controls?
a. DNA integrity
b. Chromosomes correctly attached to the spindle
c. Size of the cell
d. Replication completion
c. Size of the cell
1. You cross a red flower with a white one and get offspring with the following phenotypic ratio: 25% Red, 50% Pink, and 25% White. What is going on here?
a. Epistasis
b. Codominance
c. Heterozygote advantage
d. Incomplete dominance
d. Incomplete dominance
1. Wee1 is a protein kinase that regulates the cell cycle by inactivating cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) through phosphorylation. It plays a crucial role in cell cycle control, specifically at the G2 checkpoint, where it helps regulate the transition from the G2 phase to the M phase and preventing premature entry into mitosis. What is a possible outcome of a mutation that prevents Wee1 from functioning properly.
a. The cell fails to divide
b. The cell will divide imperfectly but recover in the next phase
c. The cell will divide prematurely, resulting subsequently smaller cells
The cell cycle will correct for this, and division will proceed normally
c. The cell will divide prematurely, resulting subsequently smaller cells
1. If the parents are heterozygous for cystic fibrosis (Ff x Ff), then each offspring has what percent chance of having cystic fibrosis (consider the disease to be recessive)?
a. 2%
b. 25%
c. 25%, but it would go down with each child they have
d. 75%
b. 25%
1. Which of the following statements is true regarding C4 plants?
a. They fix carbon dioxide during the day.
b. They utilize PEP carboxylase for carbon fixation.
c. They do not undergo photosynthesis.
d. They produce a 3-carbon molecule as the first stable product.
b. They utilize PEP carboxylase for carbon fixation.
1. During the cell cycle, ____ levels rise and fall which stimulates ____ to phosphorylate key enzymes.
a. CDK, cyclins
b. Cyclin, CDKs
c. Cyclin, Wee1
d. CDK, P53
b. Cyclin, CDKs
1. Which genetic concept involves one gene influencing the expression of another gene?
a. Codominance
b. Epistasis
c. Pleiotropy
d. Polygenic inheritance
b. Epistasis
1. A genetic disease in which females can be unaffected carriers but males with a single allele will have the condition is most likely
a. Autosomal recessive
b. Sex-linked
c. A frameshift mutation
d. Due to X inactivation
b. Sex-linked
1. Where is chlorophyll “a” mainly located?
a. In the stroma of chloroplasts
b. In the thylakoid membrane
c. In the cytoplasm
d. In the mitochondria
b. In the thylakoid membrane
1. In the ABO blood typing system, what determines an individual's blood type?
a. The presence of white blood cells
b. The presence of platelets
c. The presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells
d. The number of red blood cells in the bloodstream
c. The presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells
1. In dogs, erect ears and barking while following a scent are due to dominant alleles; droopy ears and silence while following a scent are due to recessive alleles. A dog homozygous dominant for both traits mated to a droopy-eared, silent follower. The expected F1 phenotypic ratios should be:
a. 9:3:3:1
b. 8:8 (1:1)
c. 16:0
d. 4:8:4 (1:2:1)
e. None of the above
c. 16:0
1. When individuals make an abnormal form of the extracellular matrix protein, fibrillin, which affects many other traits, the inheritance is the result of:
a. Codominance
b. Multiple alleles
c. Simple dominance
d. Pleiotropy
d. Pleiotropy
1. If the allele for red petals is not completely dominant to the allele for white petals, when a true-breeding plant with red petals is crossed with a true breeding plant with white petals, the offspring will:
a. All have red petals
b. All have white petals
c. All have pink petals
d. All have red and white petals
c. All have pink petals
1. In sex-linked inheritance of a recessive gene:
a. Male offspring of a normal male and a heterozygous female carrier would show the trait.
b. Female offspring would be carriers.
c. Male offspring who receive the mutant X chromosome would show the trait.
d. Female offspring who receive the mutant X would show the trait
c. Male offspring who receive the mutant X chromosome would show the trait.
1. Y-linked genes include a gene that produces hairy pinnae (the external ear). A male with hairy pinnae will pass this trait:
a. To his sons and daughters
b. Only to his sons
c. Only to his daughters
d. To all his children if the mother is a carrier
b. Only to his sons
1. Cleft chin is a sex-linked dominant trait. A man with a cleft chin marries a woman with a round chin. What is the percent chance of their female progeny to show the cleft chin trait?
a. 0
b. 25
c. 50
d. 75
e. 100
e. 100
1. If the alleles for a white coat and a black coat are both completely dominant in cows, what color will the offspring be?
a. All will be white
b. All will be black
c. All will be gray
d. All will be white with black spots
d. All will be white with black spots