Neuro Block 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
1
New cards
reticular theory
nerves communicate through a continuous nerve net (protoplasmic links)
2
New cards
Golgi method
Silver solution that randomly stains about 1% of neurons in their entirety
3
New cards
Camillo Golgi
proponent of reticular theory
4
New cards
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
used Golgi method to provide evidence against reticular theory, no continuity between neurons
5
New cards
Neuron Doctrine
The hypothesis that the brain is composed of separate cells that are distinct structurally, metabolically, and functionally.
6
New cards
Ross Harrison
showed that neural processes (dendrites and axon) grow from the cell body when neurons are isolated in culture, axons can extend to target neurons or tissue
7
New cards
Brainbow
individual neurons stained using genetically encoded fluorescent proteins
8
New cards
neuron
basic unit of the nervous system; about 86 billion but only 1% work; specialized for reception, conduction, and transmission of electrochemical signals
9
New cards
dendrites
receive input from other neurons and carry messages towards cell (many per neuron)
10
New cards
soma
contains nucleus and machinery to maintain life
11
New cards
axon hillock
integration and initiation of new message; membrane potential here determines if an action potential will be fired
12
New cards
axon
carries new message away from cell body to another neuron (1 per neuron, but can branch to form axon collaterals)
13
New cards
terminal bouton
site of neurotransmitter release, "output"
14
New cards
principle of dynamic polarity
electrical signals within a neuron flow in one direction
15
New cards
potential
electrical impulse within neurons
16
New cards
chemical neurotransmitters
communication between a neuron and its target
17
New cards
sensory neurons
afferent; specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of sensory stimulation; conducts impulses from periphery to CNS; may be bipolar or pseudo-unipolar; soma in ganglia
18
New cards
interneurons
primary neurons of CNS; serve as relay or integration units between afferent and efferent; multipolar
19
New cards
motor neurons
efferent; receive signals from other neurons and conduct impulses to a muscle; multipolar; soma in spinal cord
20
New cards
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord; protected inside bone (skull and vertebral column)
21
New cards
glia
cells that aid and modulate neurons' activities
22
New cards
ventricles
series of interconnected, fluid filled spaces within the core of the CNS; filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) derived from ependymal cells in choroid plexus
23
New cards
choroid plexus
a network of blood vessels and cells in the ventricles of the brain; have cilia, which circulate CSF around the CNS
24
New cards
astrocytes
most abundant type of glia; structural support for neurons; synthesize and regulate NT levels; regulate Blood Brain Barrier (BBB); help maintain proper extracellular chemical environment for neural signaling; "endfeet" interact with capillary endothelial cells to maintain their tight junctions, which comprise BBB
25
New cards
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
limits what can get into brain; small, uncharged molecules pass with ease while big molecules have to be fat soluble or have a transporter
26
New cards
microglia
immune defense for CNS; change shape, proliferate, and move to site of problem; phagocytize debris, plaques, and pathogens; thought to be impacted in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Schizophrenia, + pain conditions
27
New cards
oligodendrocytes
myelinate axons in the CNS
28
New cards
myelin sheath
fatty tissue that covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
29
New cards
Schwann cells
myelinate axons in the PNS; facilitates repairs if PNS axons are damaged
30
New cards
nodes of Ranvier
unmyelinated sections between myelination on an axon
31
New cards
peripheral nervous system
extends beyond (or exists entirely outside of ) the bony skull and vertebral column, including cranial and spinal nerves
32
New cards
visceral stimuli
afferent, produced by internal organs
33
New cards
dorso-ventral axis
The axis in bilateral symmetry that defines the top of an organism from the bottom
34
New cards
rostro-caudal axis
(relative to forebrain) long head-tail axis; axis for brainstem is perpendicular to that of rest of brain, thus coordinates change accordingly
35
New cards
anterior-posterior axis
front to back axis
36
New cards
superior-inferior axis
up and down axis
37
New cards
proximal/medial
closer to body midline
38
New cards
distal/lateral
further from body midline
39
New cards
horizontal/axial
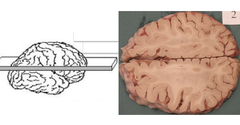
40
New cards
coronal
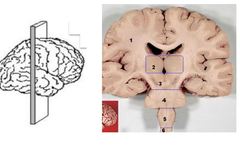
41
New cards
sagittal
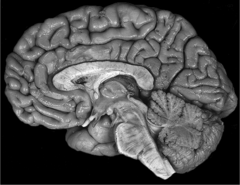
42
New cards
gray matter
made up of cell bodies and dendrites, color comes from nuclei
43
New cards
white matter
made up of myelinated axons
44
New cards
nuclei
bundles of gray matter in the CNS
45
New cards
tracts
bundles of white matter in the CNS
46
New cards
ganglia
groups of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
47
New cards
nerves
groups of axons in the PNS
48
New cards
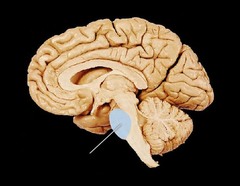
medulla
part of the brainstem that coordinates basic life functions and reflexes (breathing, heart rate, vomiting, salivation, coughing and sneezing)
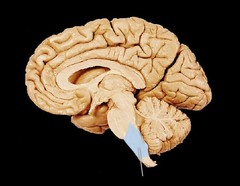
49
New cards
pons
part of the brainstem that includes axons that allow the cerebellum to communicate with the brainstem and cerebral cortex
50
New cards
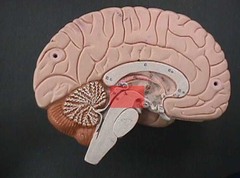
midbrain
part of the brain that contains structures involved in processing visual and auditory information
51
New cards
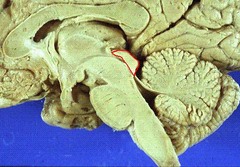
tectum
sensory region of midbrain; contains colliculi
52
New cards
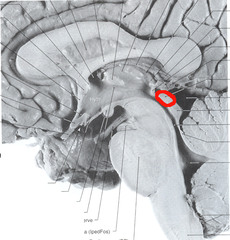
superior colliculus
part of the midbrain that receives visual sensory input
53
New cards
inferior colliculus
part of the midbrain involved in auditory processing
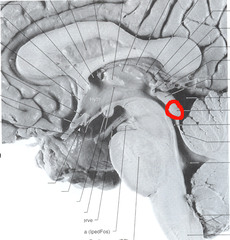
54
New cards
tegmentum
motor region of the midbrain; contains dopaminergic neurons
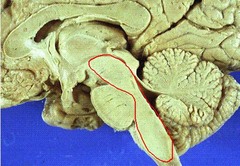
55
New cards
ventral tegmental area (VTA)
part of the midbrain associated with reward pathway + dopamine
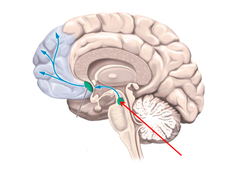
56
New cards
substantia nigra (SN)
part of midbrain that initiates movements; black substance
57
New cards
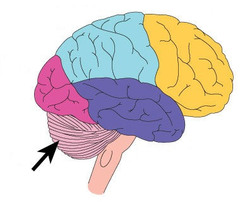
cerebellum
motor planning, motor learning, and balance
58
New cards
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
59
New cards
thalamus
relay for information going to and coming from the neocortex
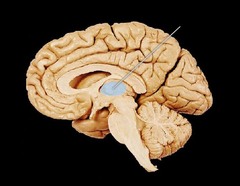
60
New cards
hypothalamus
regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior; regulates hormone release by coordinating with the pituitary
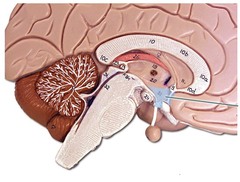
61
New cards
basal ganglia
group of interconnected structures that curve in a C shape around the thalamus that control planning and initiation of voluntary, smooth movement
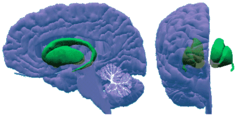
62
New cards
limbic system
group of interconnected structures related to emotions, motivation, aggression, memory; the 4 Fs- fleeing, feeding, fighting, sexual behavior
63
New cards
amygdala
emotions (fear, reward, anger, etc)
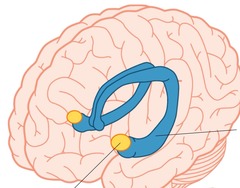
64
New cards
hippocampus
memory formation and storage
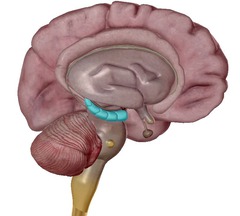
65
New cards
cerebral cortex (cerebrum)
80% of brain volume; higher order functions; expanded most in evolution
66
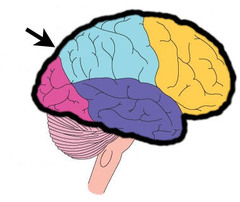
New cards
frontal lobe
motor control and executive functions (planning, inhibition of inappropriate behaviors, working memory)
67
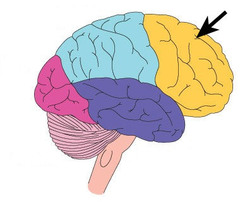
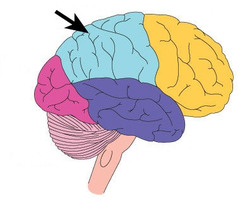
New cards
parietal lobe
somatosensory and tactile processing
68
New cards
temporal lobe
auditory processing, language and memory
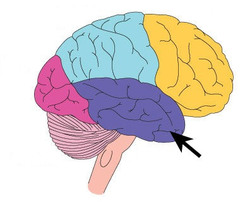
69
New cards
occipital lobe
visual processing
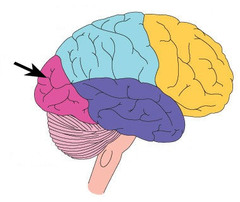
70
New cards
central sulcus
separates parietal and frontal lobes
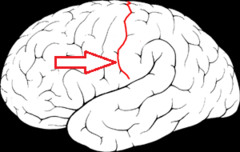
71
New cards
Sylvian fissure (lateral sulcus)
separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes
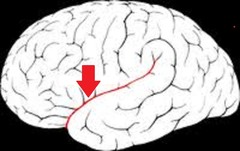
72
New cards
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
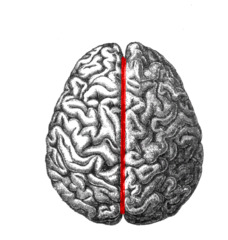
73
New cards
gyrus
ridge/bump
74
New cards
sulcus
groove/crack
75
New cards
fissure
infolding of gyrus/sulcus
76
New cards
postcentral gyrus
directly caudal to central sulcus; contains primary somatosensory cortex, which processes touch and pain information
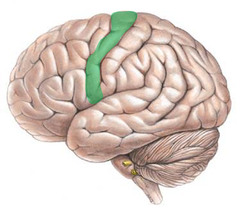
77
New cards
precentral gyrus
directly rostral to central sulcus; contains primary motor cortex, which helps plan movements and sends motor signals to spinal cord
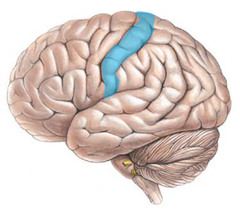
78
New cards
corpus callosum
where axons cross between brain hemispheres
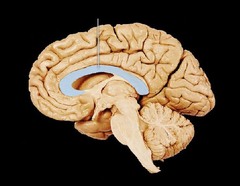
79
New cards
31
# of pairs of spinal nerves
80
New cards
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
81
New cards
dorsal horn
contains sensory axons (afferents) entering spinal cord
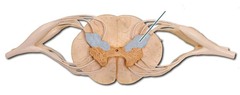
82
New cards
ventral horn
contains cell bodies of motor neurons (efferents)
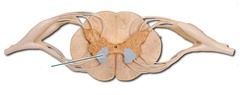
83
New cards
cranial nerves
send motor commands to and receive sensory information from the head and neck; emerge from the brain; 12 pairs
84
New cards
olfactory (I)
sensory nerve; sense of smell
85
New cards
optic (II)
sensory nerve; vision
86
New cards
oculomotor (III)
motor nerve; eye movement (papillary constriction/accommodation, eyelid muscles)
87
New cards
trochlear (IV)
motor nerve; eye movement (intorsion, downward gaze)
88
New cards
trigeminal (V)
sensory/motor nerve; somatic sensation of face, mouth, and cornea; muscles of mastication
89
New cards
abducens (VI)
motor nerve; eye movement (abduction or lateral movement)
90
New cards
facial (VII)
sensory/motor nerve; facial expressions; taste from anterior tongue; lacrimal and salivary glands
91
New cards
vestibulocochlear (VIII)
sensory nerve; hearing and balance
92
New cards
glossopharyngeal (IX)
sensory/motor nerve; sensation and taste of posterior tongue; carotid baroreceptors and chemoreceptors
93
New cards
vagus (X)
sensory/motor nerve; autonomic gut functions; larynx and pharynx sensation; vocal cord muscles; swallowing
94
New cards
spinal accessory (XI)
motor nerve; shoulder and neck muscles
95
New cards
hypoglossal (XII)
motor nerve; tongue movements
96
New cards
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
part of PNS that controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
97
New cards
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
part of PNS that controls involuntary bodily functions
98
New cards
sympathetic division
part of ANS that arouses the body to expend energy; fight or flight
99
New cards
parasympathetic division
part of ANS that calms body to conserve and maintain energy; rest and digest
100
New cards
preganglionic neurons
neurons involved in ANS that originate in CNS; cell bodies in lateral horn of spinal cord/brain stem; project to postganglionic neurons