chairside procedures test 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Dental Unit
A comprehensive setup used in dental procedures, which includes various components like handpieces, waterlines, and evacuation systems.
Handpiece
Formally known as a drill, it is a tool used in dental procedures for cutting and shaping teeth.
Front Delivery
A dental unit configuration positioned over the patient’s chest for easy access.
Side Delivery
A dental unit configuration positioned at either side of the patient’s chair for accessibility.
Rear Delivery
A dental unit configuration positioned behind the dental chair for operational efficiency.
Rheostat
A foot-operated control for handpieces that regulates speed and water flow.
Waterlines
Tubes in a dental unit that carry water for cooling and cleaning during procedures, requiring regular maintenance to prevent bacteria growth.
Air Water Syringe
Also known as a tri-syringe, it delivers water, air, or a combination of both during dental procedures.
Central Air Compressor
Provides compressed air for air-water syringe and air-driven handpieces
why is the air compressor placed far away from the clinical setting?
for safety reasons and the noise level
required maintenance for central air compressor is…
changing filters and occasionally checking for condensation in the lines
Operating Light
A light positioned to illuminate the oral cavity, requiring careful adjustment and cleaning after use.
where will the operating light be positioned?
on the patients chest approximately 25-30 inches below the patients chin. it is turned on and then slowly adjusted upward, straight, etc depending on what area of the oral cavity is being worked on.
operating light maintenance
light is only cleaned once bulb has cooled, halogen bulbs are to be replaced with a gloved hand.
Oral Evacuation System
A system for removing fluids (water, saliva, blood, etc) during procedures, including saliva ejectors and high-volume evacuators (HVE).
how often is the oral evacuation system cleaned?
disinfected between each patient
saliva ejector
provides removal of the patients excess fluids from the mouth
high volume evacuator (HVE)
more powerful than saliva ejector and helps to maintain a clear field.
Central Vacuum Compressor
Supplies suction for oral evacuation systems
2 parts of Central vacuum compressor
Compressor and vacuum tank
Compressor
provides air flow
vacuum tank
screens flow of air to create suction
how often should central vacuum compressor be maintained?
suction trap should be cleaned once a week, remove cap and take screen off. either clean trap or throw it out and replace with new one.
Curing Light
A light used to harden dental materials, requiring protective covers to prevent eye damage.
Amalgamator
An electrical device used to mix dental materials through vigorous shaking.
what is another name for amalgamator?
triturate
Dental Imaging Unit
A unit for taking radiographs, which can be left on throughout the day but requires disconnection for maintenance.
Another name for dental imaging unit
radiographic unit
Digital Imaging
A modern, safer, and more environmentally friendly method of capturing dental images.
Computer Monitor
An LCD screen used for patient records, treatment planning, and entertainment, requiring proper infection control.
Care of Dental Equipment
Emphasizes the importance of careful use and maintenance of expensive dental tools according to manufacturer instructions.
Team Dentistry
A collaborative approach involving the dentist and dental assistant, focusing on ergonomics and efficiency. four-handed dentistry
what is the correct working distance
12-14 inches between the patients and operators faces
eye level
4-6 inches above the eye level of the operator
how do you want your legs positioned
parallel with the patients chair
CLASS I
Movement of fingers only
CLASS II
Movement of fingers and wrist
CLASS III
Movement of fingers, wrist and elbow
CLASS IV
Use of the entire arm and shoulder (this should try and be limited)
CLASS V
Use of the entire upper torso (this should try to be limited)
What are the 4 types of “zones”
operators zone
transfer zone
assistants zone
static zone
operators zone
7-12 oclock
transfer zone
4-7 o’clock
assistants zone
2-4 o’clock
static zone
12-2 o’clock
what hand should dental assistants be transferring materials with?
left hand
what position are instruments transferred in?
position of use, place firmly in dentists hand
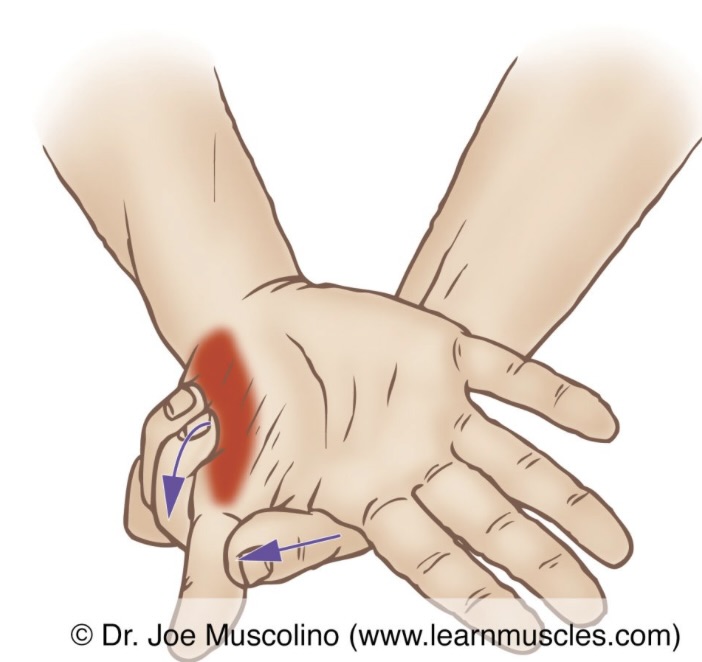
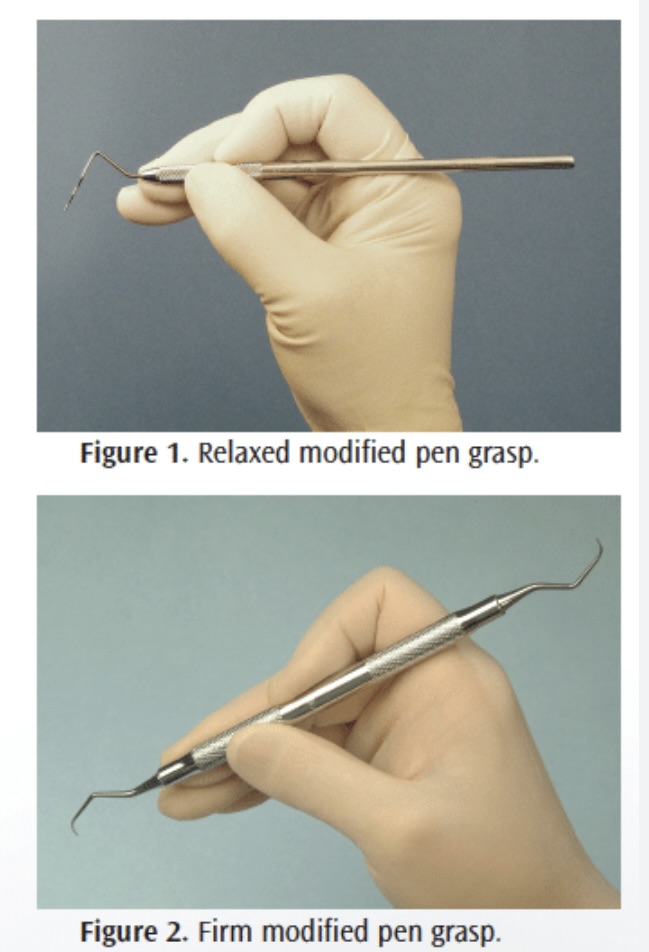
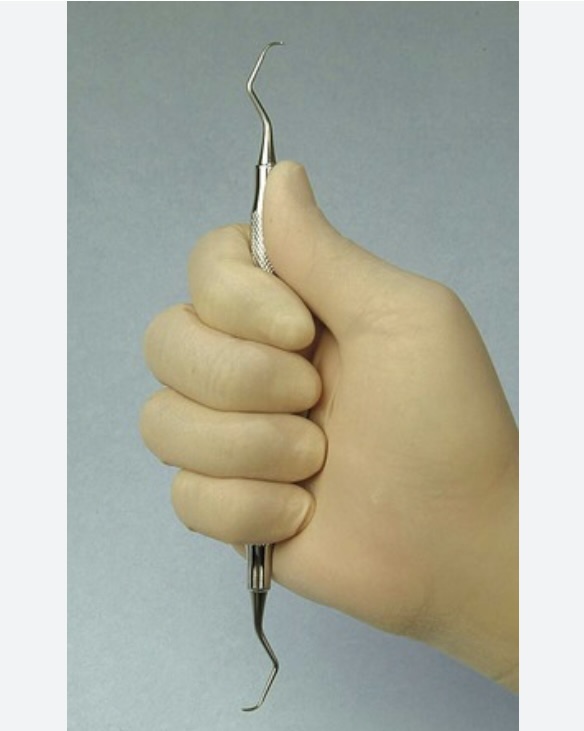
What are the 3 basic grasps?
pen grasp
palm grasp
palm-thumb grasp
pen grasp
self explanitory
palm grasp
the instrument is held securely in the palm of the hand

palm-thumb grasp
instrument is held in palm of hand and the thumb is used to stabilize and guide the instrument
when passing a mirror and explorer, the explorer goes into which hand of the doctor?
dominate hand of the doctor
how do you hand off dual ended instruments?
hand them the correct end they want to use.
direct supervision
The dentist must be in the same treatment area as the RDA for the assistant to perform the function
indirect supervision
The dentist must be in the dental office area but not necessarily be present in the same treatment room as the RDA
Ergonomics
The adaptation of the work environment to fit the human body, aiming to reduce fatigue and injury risk.
Risk Factors in the Workforce
Factors like posture that can lead to fatigue and conditions such as lower-back pain or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Fulcrum
A safety technique using a finger rest on a hard surface to stabilize hand movements during procedures.

Mirror Skills
can be indirect vision and looking through the mirror
Maintain posture, reduce eyestrain, and complete specific functions
Position yourself to gain a “straight-on” visual effect
Mirror must be kept parallel to the working surface
Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs)
Injuries resulting from repetitive strain, with carpal tunnel syndrome being a common example.
What is the most common CTD
CTS (carpal tunnel syndrome) there are 8 bones in this tunnel
how can you prevent CTS
resting hands frequently
what type of reach should air-water syringe, handpiece, saliva ejector and HVE be kept in?
normal horizontal reach
what type of reach should the operatory light be kept within?
maximum vertical reach
what type of reach should other supplies that are used less frequently be kept in?
maximum horizontal reach
waterline that functions in 3 ways
tri-syringe
what are the functions of the tri-syringe
delivers a water stream
delivers a stream of air
delivers a combo of air and water
thenar eminence
base of thumb