The Working Memory Model (WMM)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the Working Memory Model?
Proposed that short-term memory isn’t one store but a system of separate components (slave systems) that handle different types of information. It explains how we actively process information when doing tasks like problem-solving, reading, and mental calculations. By Baddeley & Hitch (1974).
Why did Baddeley and Hitch criticise the MSM?
They thought it was overly simplistic, particularly with regard to STM.
Draw a diagram of the WMM.
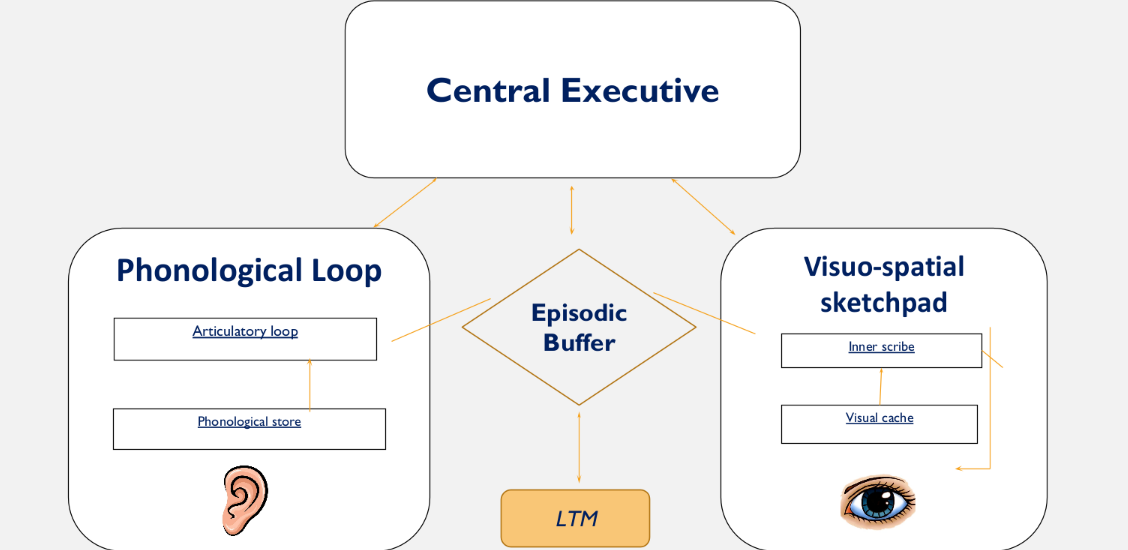
What are the four main components of the WMM?
Central Executive
Phonological Loop
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Episodic Buffer (added 2000)
What is the Central Executive?
Role is to focus attention to the most important tasks that need attending to in the current moment. The CE coordinates the three other components of the WMM (known as ‘slave systems’) by allocating them to different tasks.
Has limited capacity
Cannot store information
What is the Phonological Loop?
Responsible for coordinating auditory information. It preserves the order in which acoustic information is processed.
Coding: acoustically
Limited capacity: what can be said in 2 secs
There are two divisions of it:
The phonological store: this component stores spoken words (the inner ear)
The articulatory process: this component stores written words (the inner voice)
Uses maintenance rehearsal to keep words in STM, but this repetition doesn’t transfer information to LTM (unlike the MSM).
What is the Visuospatial Sketchpad?
The slave system responsible for storing visual and/or spatial (where things are and how they move in space) information.
Information in here is stored temporarily
Limited capacity: holds 3-4 objects at a time
There are two divisions of it:
The visual cache: this component stores visual data, e.g., colour, shape
The inner scribe: this component stores the arrangement of objects within the visual field of view
What is the Episodic Buffer?
It’s function is to receive information from the Central Executive, Phonological Loop and Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad and to integrate this information into 'episodes'.
Added in 2000
Records information (any type) as episodes, so that it is time-sequenced
Information is stored temporarily in it (sends info to the LTM)
Capacity: limited
Separate from LTM, but it forms an important stage in long-term episodic learning
What is the procedure of Baddeley & Hitch (1974) research supporting the WMM?
Lab experiment, repeated measures design
Participants were asked to do two tasks at the same time (dual task technique):
a) A digit span task (repeating a list of numbers – using the phonological loop)
b) A verbal reasoning task (answering true/false Qs – using the central executive)
This allowed researchers to see whether two tasks using different components could be done simultaneously.
What were the results of Baddeley & Hitch’s (1974) research supporting the WMM?
Participants were slower on the verbal reasoning task while repeating digits,
but their performance remained accurate
What did Baddeley & Hitch (1974) conclude from their research supporting the WMM?
Verbal reasoning task made use of the central executive & the digit span task made use of the phonological loop
It’s easier to do 2 tasks at the same time if they use different processing systems (verbal & visual) than if they use the same slave system
Supports the idea that working memory isn’t a single store - exactly what the WMM proposes
Who is KF?
Shallice and Warrington’s did a case study of KF, a man who had brain damage following a motorcycle accident which damaged his STM, but different parts of his memory were affected in different ways. His LTM was mostly intact.
His impairment was mainly for verbal information, his memory for visual information was largely unaffected (in the STM)
- e.g. his immediate recall of letters and digits were better when he read them (visual) than when they were read to him (acoustic)
How does the case of KF support the WMM?
It shows that STM isn’t a single store (like the MSM says).
Instead, KF’s damage was specifically to the phonological loop (verbal/auditory info), while his visuospatial sketchpad (visual info) was still functioning
This provides strong evidence for the idea that working memory has separate, specialised components
What are counterpoints of KF supporting the WMM?
KF had other cognitive impairments (apart from the damage to his phonological loop) which might have affected his performance on memory tasks. His injury may have caused multiple changes in the brain, not just a simple verbal-memory impairment
Some researchers argue KF may have had problems with auditory processing, not the phonological loop itself.
This means his poor verbal STM might not be about memory structure at all, but that he couldn’t accurately perceive what he was hearing
What was the procedure of Prabhakaran et al 2000 research in existence/location of episodic buffer?
Lab experiment, independent designs
Used brain imaging FMRI scans while participants completed tasks involving:
a) Integrated information (e.g. combining verbal + visual info)
b) Separate information (e.g. verbal alone or visual alone)
This let them see which brain areas were active when the brain needed to bind different types of information together
What were the results of Prabhakaran et al 2000 research in existence/location of episodic buffer?
Integrated tasks (verbal + visual together): activated the prefrontal cortex much more than tasks that only used one type of information
Separate information (e.g. verbal alone or visual alone): less prefrontal cortex activation
What did Prabhakaran et al conclude from their 2000 research in existence/location of episodic buffer?
Suggest Episodic Buffer exists and is in the prefrontal cortex when information integrated
A brain region specialised in the combination & temporary storage of visual & verbal information
Biological evidence for existence of EB
What was the procedure of Hunt’s (1980) research on the Central Executive?
Lab experiment, repeated measures design
Participants performed 2 tasks
a) Psychomotor task (moving lever with their hand)
b) Visual Intelligence task (solve visual reasoning problem, such as identifying patterns or relationships between shapes)
Tasks performed both, separately or at the same time (1 or 2 or both), to see whether doing two tasks together would overload the Central Executive
What were the results of Hunt’s (1980) research on the Central Executive?
When participants performed the visual reasoning task alone, they did well.
When the psychomotor + visual reasoning tasks were done together, performance got worse on the psychomotor task, showing the CE has limited capacity
As the visual problems got harder, performance on the psychomotor task deteriorated
This showed that the CE couldn’t coordinate both demanding tasks without a drop in performance.
What did Hunt (1980) conclude on his research on the Central Executive?
Proves central executive has limited capacity because performance declines when it has to coordinate two tasks that both require attention
Supports Baddeley & Hitch’s idea that the CE is the most important, but limited - “control centre” of working memory
What was the procedure of Baddeley et al (1975) research into the visuospatial sketchpad?
Lab experiment, independent measure, dual-task technique
Participants completed two tasks:
a) A visual tracking task (following spot of light w/ a pointer)
whilst simultaneously doing secondary visual imagery task
b) Two types of secondary tasks:
- Visual task → looking at and identifying the corners of a letter (also uses the VSS)
- Verbal task → listening to and answering questions (uses the -phonological loop
Participants did the visual-tracking task both on its own and alongside each secondary task
What were the results of Baddeley et al (1975) research into the visuospatial sketchpad?
Performance got worse when two visual tasks were done at the same time (visual tracking + letter corners)
Performance stayed good when a visual + verbal task were done together
What did Baddeley et al (1975) conclude from their research into the visuospatial sketchpad?
The visuospatial sketchpad has limited capacity, so doing two visual/spatial tasks at once overloads it
But doing a visual task with a verbal task is fine, because they use different components of working memory
This strongly supports the WMM idea that working memory has separate, specialised stores.
What was the procedure of Baddeley, Thompson & Buchanan’s (1975) research into the Phonological Loop?
Lab experiment, repeated measure
Participants were shown visually presented word lists that were briefly displayed on a screen. There were two types of word lists:
a) Mono-syllabic English words e.g. cat, with, twice
b) Polysyllabic English words e.g. university, organisation
Measure which condition led to better recall
After the brief exposure, participants had to recall the words in chorological order
This tests the phonological loop, especially the articulatory rehearsal process (inner voice)
What were the results of Baddeley, Thompson & Buchanan’s (1975) research into the Phonological Loop?
Over several trials participants recalled more monosyllabic (short) words than polysyllabic (long) words
Shows word length effect, short words are recalled better than long words in short-term memory tasks because of the articulatory rehearsal process (your “inner voice”)
What did Baddeley, Thompson & Buchanan (1975) conclude from their research into the Phonological Loop?
The phonological loop has a time-limited capacity (about 2 seconds of what you can rehearse)
Shorter words fit more easily into this rehearsal loop, so they are recalled better
Longer words take more time to articulate → they can’t be rehearsed quickly → they decay before recall
This strongly supports the idea that the phonological loop depends on subvocal rehearsal and has a time-based limit.
Why is the Central Executive considered vague?
Described as the “boss” that directs attention, but its exact processes are unclear (isn’t explain how or why it directs attention)
Difficult to measure or test directly in experiments
Lacks a clear, detailed structure compared to PL, VSS, and EB
Little direct research supporting exactly how it works - evidence mostly comes from indirect tasks (e.g., dual-task studies), so its processes remain unclear
What did Bertz (1995) criticise about the Working Memory Model?
Much of the supporting evidence for the Working Memory Model comes from dual-task research - that is, studies where participants do two tasks at once.
Why is it a problem that much of the evidence for the WMM comes from dual-task research?
Dual-task experiments are often:
Highly artificial
Lab-based
Not everyday memory situations
This means the findings may lack ecological validity.
What did Bertz (1995) argue about the validity of the WMM?
The tasks used to support the WMM (e.g., tracking lights, repeating digits, tapping sequences), don’t represent how working memory is used in real life (lack of mundane realism). Therefore, the WMM might not fully explain everyday memory functioning, because the evidence is based on tasks that are too controlled and too unrealistic.
What did Bertz (1995) conclude from his analysis on the research supporting the WMM?
He highlighted that although the WMM is supported by research, the nature of the evidence is limited, so we should be cautious about applying the model to real-world situations
What is a practical application of the WMM?
Helps support dementia sufferers (where area of their brain dies): they have difficulty doing dual tasks, so reducing info or slowing presentation helps if the CE is impaired
In education: teaching methods that split visual & auditory info can improve learning