C18 Summary
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
zoonosis
disease transmitted from a vertebrae animal to human
e.g. ebola, salmonellosis, rabies
e.g. ebola, salmonellosis, rabies
2
New cards
arbovirus
distinct group of unrelated viruses that infect arthropod vectors
e.g. mosquitoes, ticks
e.g. mosquitoes, ticks
3
New cards
causative agents of malaria
Plasmodium falciparum = most common, malignant tertiary fever (36-48hr)
Plasmodium ovale
Plasmodium vivax
= tertian fever (48hr)
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium knowlesi
= quotidian fever (72hr)
Plasmodium ovale
Plasmodium vivax
= tertian fever (48hr)
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium knowlesi
= quotidian fever (72hr)
4
New cards
replication + transmission of malaria
via female Anopheles spp. mosquito
sporozoites in to human when infected mosquito bites
gametocytes out of human (pass on to mosquito when taking blood meal)
in human, exo-erythrocytic cycle in liver makes a schizont which ruptures -> blood
in blood, erythrocytic cycle makes mature trophozoite -> schizont which ruptures and gametocytes
in mosquito, microgamete enters macrogamete and ookinete -> oocyst forms, which ruptures to release sporozoites
can also be transmitted via transfusion, congenital and needle stick injury
sporozoites in to human when infected mosquito bites
gametocytes out of human (pass on to mosquito when taking blood meal)
in human, exo-erythrocytic cycle in liver makes a schizont which ruptures -> blood
in blood, erythrocytic cycle makes mature trophozoite -> schizont which ruptures and gametocytes
in mosquito, microgamete enters macrogamete and ookinete -> oocyst forms, which ruptures to release sporozoites
can also be transmitted via transfusion, congenital and needle stick injury
5
New cards
clinical features malaria
general = headaches, lethargy, ischaemia, N+V, diarrhoea, anaemia
cyclical paroxysms = chills -> fevers -> sweats
complicated malaria:
P. falciparum (36-48hr fever) = coma, pulmonary oedema, renal failure, shock, lactic acidosis, splenomegaly, death
P. vivax/ovale (48hr fever) = splenic rupture
P. malariae (72hr fever) = glomerulonephritis and immune complexes
cyclical paroxysms = chills -> fevers -> sweats
complicated malaria:
P. falciparum (36-48hr fever) = coma, pulmonary oedema, renal failure, shock, lactic acidosis, splenomegaly, death
P. vivax/ovale (48hr fever) = splenic rupture
P. malariae (72hr fever) = glomerulonephritis and immune complexes
6
New cards
malaria treatment
ACT = artemisinin combination therapy
e.g. artemisinin + chloroquine
falciparum malaria:
- IV ACT (artesunate) until oral can be tolerated
- artemether with lumefantrine
- quinine
- WHO says no monotherapy to prevent resistance
e.g. artemisinin + chloroquine
falciparum malaria:
- IV ACT (artesunate) until oral can be tolerated
- artemether with lumefantrine
- quinine
- WHO says no monotherapy to prevent resistance
7
New cards
malaria prevention
Mosquirix vaccination prevent liver infection, but poor efficacy and wanes after 4yrs
insecticide impregnated mosquito nets
removal of standing water
release of sterile male mosquitoes
prophylaxis in endemic areas
for adults in areas of chloroquine-resistant P falciparum: mefloquine, doxycycline etc. used
for children chloroquine, proguanil, mefloquine used
insecticide impregnated mosquito nets
removal of standing water
release of sterile male mosquitoes
prophylaxis in endemic areas
for adults in areas of chloroquine-resistant P falciparum: mefloquine, doxycycline etc. used
for children chloroquine, proguanil, mefloquine used
8
New cards
malaria diagnosis
gold standard = blood smear
thick smear for detection of parasitaemia (% of infected RBCs)
thin smear for identification of species
thick smear for detection of parasitaemia (% of infected RBCs)
thin smear for identification of species
9
New cards
artemisinin MOA
catalyses heme-iron which releases radicals which kills parasite
10
New cards
artesunate MOA
binds multiple target but MOA not understood
11
New cards
chloroquine MOA
interferes with parasite's ability to used Hb as nutrient
causes build up of toxic by product -> kills parasite
resistance common
causes build up of toxic by product -> kills parasite
resistance common
12
New cards
quinine
used in areas of chloroquine resistance
MOA not fully understood
MOA not fully understood
13
New cards
primaquine
used for treatment of dormant P. vivax/ovale
thought to inhibit respiratory chain
thought to inhibit respiratory chain
14
New cards
african trypanosomiasis causative agents
african trypanosomiasis = sleeping sickness
spread by Tsetse fly (Glossina spp.)
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense = 10%, very quick + acute onset, "East African", wild animals/livestock thought to be primary reservoir
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense = 90%, slow + insidious, "West African", humans thought to be primary reservoir
spread by Tsetse fly (Glossina spp.)
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense = 10%, very quick + acute onset, "East African", wild animals/livestock thought to be primary reservoir
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense = 90%, slow + insidious, "West African", humans thought to be primary reservoir
15
New cards
sleeping sickness stage I
haemolymphatic phase
trypanosomes multiply in skin + lymph nodes
fever
headaches
lymphadenopathy (Winterbottom's sign)
itchy skin
trypanosomes multiply in skin + lymph nodes
fever
headaches
lymphadenopathy (Winterbottom's sign)
itchy skin
16
New cards
sleeping sickness stage II
neurological phase
trypanosomes cross the BBB into the CNS
confusion
change in personality
sleep disturbance
coma
death
trypanosomes cross the BBB into the CNS
confusion
change in personality
sleep disturbance
coma
death
17
New cards
african trypanosomiasis transmission + lifecycle
extracellular
infected Tsetes fly (genus Glossina) injects metacyclic trypomastigotes into skin tissue
parasites enter lymphatic system -> bloodstream
in host they become trypomastigotes and carried around body
tsetes fly takes blood meal and ingests trypomastigotes, cycle in fly takes around 3 weeks
rarely gambiense can be acquired congenitally
infected Tsetes fly (genus Glossina) injects metacyclic trypomastigotes into skin tissue
parasites enter lymphatic system -> bloodstream
in host they become trypomastigotes and carried around body
tsetes fly takes blood meal and ingests trypomastigotes, cycle in fly takes around 3 weeks
rarely gambiense can be acquired congenitally
18
New cards
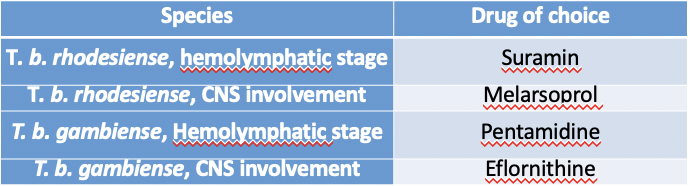
sleeping sickness diagnosis + treatment
needs definitive diagnosis by microscopy + stage of infection
complex dosing regimens if CNS involvement
drugs have adverse side effects
stage I = fexinidazole (first line) pentamidine, suramin
stage II = melarsoprol, eflornithine, fexinidazole (non-severe first line)
complex dosing regimens if CNS involvement
drugs have adverse side effects
stage I = fexinidazole (first line) pentamidine, suramin
stage II = melarsoprol, eflornithine, fexinidazole (non-severe first line)
19
New cards
chaga's disease causative agent
trypanosoma cruzi
spread by triatomine "kissing" bugs - defecate into bite wounds
can also be via transplant, oral and congenital
predominantly found in S America, but hotspots in regions of migration
spread by triatomine "kissing" bugs - defecate into bite wounds
can also be via transplant, oral and congenital
predominantly found in S America, but hotspots in regions of migration
20
New cards
phases of chaga's
acute phase = Romana sign - unilateral, painless periorbital swelling
indeterminate phase = asymptomatic
chronic (20-30%) =
cardiac form - pseudocysts cause massive infiltration + cardiomegaly
GI form - infiltrates megaoesophagus + megacolon
indeterminate phase = asymptomatic
chronic (20-30%) =
cardiac form - pseudocysts cause massive infiltration + cardiomegaly
GI form - infiltrates megaoesophagus + megacolon
21
New cards
triatomine bug lifecycle
blood meal, faeces containing trypomastigotes enter bite wound
at wound site, become amastigotes
amastigotes multiply by binary fission in cells, transform into trypomastigotes then burst out of cell into bloodstream
triatomic bug takes blood meal, multiply in midgut back into trypomastigotes
at wound site, become amastigotes
amastigotes multiply by binary fission in cells, transform into trypomastigotes then burst out of cell into bloodstream
triatomic bug takes blood meal, multiply in midgut back into trypomastigotes
22
New cards
chaga's treatment
NECT = nifurtimox-elfornithine combination therapy
benznidazole
benznidazole
23
New cards
leishmaniasis causative agent
Leishmania spp.
vector = phlebotomine sandflies
only infects phagocytic cells
avoids immune surveillance, inhibits innate immune response
primary replication in neutrophils, "hides" in macrophages, releases LCF to attract more neutrophils
distribution in Americas, N Africa, Middle East
vector = phlebotomine sandflies
only infects phagocytic cells
avoids immune surveillance, inhibits innate immune response
primary replication in neutrophils, "hides" in macrophages, releases LCF to attract more neutrophils
distribution in Americas, N Africa, Middle East
24
New cards
leishmaniasis cutaneous form
most common, sub clinical
non-ulcerating lesions -> ulcerating lesions + scarring
caused by L. tropica, L. aethiopica and L. mexicana
most common is Oriental sore
diffuse cutaneous = anergic, widespread non-ulcerating nodules
non-ulcerating lesions -> ulcerating lesions + scarring
caused by L. tropica, L. aethiopica and L. mexicana
most common is Oriental sore
diffuse cutaneous = anergic, widespread non-ulcerating nodules
25
New cards
leishmaniasis muco-cutaenous
S America
reaction at bite, metastasises to mucous membranes
chronic non-healing ulcers that destroy tissues + cartilage
pathogen = L. braziliensis
reaction at bite, metastasises to mucous membranes
chronic non-healing ulcers that destroy tissues + cartilage
pathogen = L. braziliensis
26
New cards
visceral leishmaniasis
a.k.a Kala-azar
pathogens = L. donovani, L. infantum, L. chagasi
fatal untreated
incubation of 1-2months -> 10 yrs
low grade fever, progressive hepatosplenomegaly, anaemia, wasting
PKDL = post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (pigmentation changes and extensive facial lesions)
pathogens = L. donovani, L. infantum, L. chagasi
fatal untreated
incubation of 1-2months -> 10 yrs
low grade fever, progressive hepatosplenomegaly, anaemia, wasting
PKDL = post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (pigmentation changes and extensive facial lesions)
27
New cards
leishmaniasis lifecycle
sandfly takes blood meal, injects promastigotes
promastigotes phagocytosed, become amastigotes
amastigotes multiply in cells and infect other cells
sandfly ingests infected macrophages from human
transform from amastigotes back into promastigotes
promastigotes phagocytosed, become amastigotes
amastigotes multiply in cells and infect other cells
sandfly ingests infected macrophages from human
transform from amastigotes back into promastigotes
28
New cards
leishmaniasis treatment
mainly for visceral, useful to know species + type of infection
visceral = liposomal amphotericin B
all forms = miltefosine
visceral = liposomal amphotericin B
all forms = miltefosine
29
New cards
dengue cause
dsRNA flavivirus
vector = Aedes spp. mosquito
4 serotypes
adapted to urban areas, prevention measures such as larvicide, no standing water, fogging and nets useful
vector = Aedes spp. mosquito
4 serotypes
adapted to urban areas, prevention measures such as larvicide, no standing water, fogging and nets useful
30
New cards
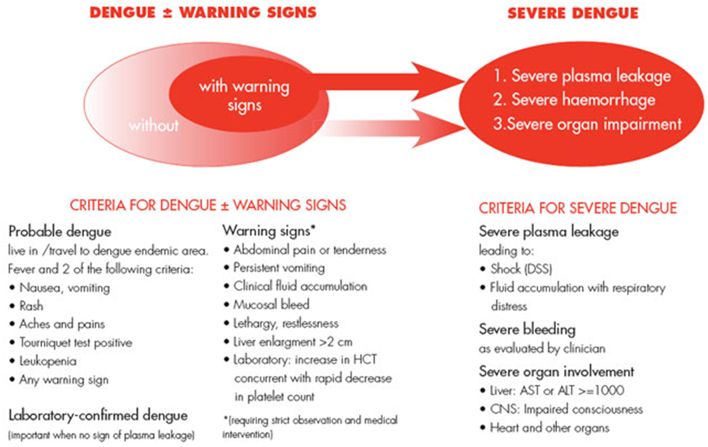
dengue clinical features
25% get sick
mild dengue = fever, N+V, rash, peri-orbital pain, aches
warning signs = severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, rapid breathing, fatigue, hepatomegaly, blood in vomit/stool, bleeding gums or nose
severe dengue = 3-7 days after onset
severe plasma leakage (shock + resp. distress)
severe bleeding/haemorrhage
severe organ involvement (liver, CNS, heart)
mild dengue = fever, N+V, rash, peri-orbital pain, aches
warning signs = severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, rapid breathing, fatigue, hepatomegaly, blood in vomit/stool, bleeding gums or nose
severe dengue = 3-7 days after onset
severe plasma leakage (shock + resp. distress)
severe bleeding/haemorrhage
severe organ involvement (liver, CNS, heart)
31
New cards
dengue diagnosis
less than 5 days post fever = viral RNA
5+ days post fever = IgM (recent) or IgG (lifetime)
5+ days post fever = IgM (recent) or IgG (lifetime)
32
New cards
dengue treatment + prevention
supportive care only
severe = emergency, fluid replacement needed
infection provides immunity for specific serotype, but re-infection can increase risk of severe + further increased if different serotype
prevention = avoiding bites, larval source management
vaccine available, but only after infection (antibody-dependent enhancement)
severe = emergency, fluid replacement needed
infection provides immunity for specific serotype, but re-infection can increase risk of severe + further increased if different serotype
prevention = avoiding bites, larval source management
vaccine available, but only after infection (antibody-dependent enhancement)
33
New cards
yellow fever cause
acute viral haemorrhagic disease
primary reservoir thought to be monkeys
human-human transmission via Aedes aegyptii mosquito
periodic outbreaks when infection introduced to urban area with little immunity and high mosquito density
seen in Africa and C + S America (tropical)
primary reservoir thought to be monkeys
human-human transmission via Aedes aegyptii mosquito
periodic outbreaks when infection introduced to urban area with little immunity and high mosquito density
seen in Africa and C + S America (tropical)
34
New cards
yellow fever clinical features
incubation = 3-6 days
mild = fever, muscle pain, headache, N+V
will resolve 3-4 days later
15% progress to severe 24hrs after initial resolution
severe = high fever, jaundice, renal failure, bleeding from mouth, nose, eyes, GI tract
mild = fever, muscle pain, headache, N+V
will resolve 3-4 days later
15% progress to severe 24hrs after initial resolution
severe = high fever, jaundice, renal failure, bleeding from mouth, nose, eyes, GI tract
35
New cards
yellow fever diagnosis + treatment
early diagnosis = RT-PCR blood/urine test
can also look for virus-specific IgM ELISA
differentials = malaria, viral hepatitis (fulminant), dengue etc.
supportive management
vaccine = life attenuated, effective, recommended in endemic areas
and prevention of vector
can also look for virus-specific IgM ELISA
differentials = malaria, viral hepatitis (fulminant), dengue etc.
supportive management
vaccine = life attenuated, effective, recommended in endemic areas
and prevention of vector
36
New cards
JEV cause + epidemiology
culex spp. mosquito
main cause of encephalitis in Asia, 1 in 250 progress into severe disease
differentials = meningitis, encephalitis
main cause of encephalitis in Asia, 1 in 250 progress into severe disease
differentials = meningitis, encephalitis
37
New cards
JEV clinical features
incubation = 5-15 days (very few get ill)
mild = fever, headache, vomiting
severe = neurological Sx, high fever, stiff neck, seizures, coma, 30% death, 30-50% permanent neurological/psych issues
mild = fever, headache, vomiting
severe = neurological Sx, high fever, stiff neck, seizures, coma, 30% death, 30-50% permanent neurological/psych issues
38
New cards
JEV diagnosis + management
CSF for virus-specific IgM antibodies
supportive treatment only
vaccine available, over 90% effective, good for 3yrs
supportive treatment only
vaccine available, over 90% effective, good for 3yrs
39
New cards
zika cause
vector = Aedes agyptii
two lineages: African + Asian
two lineages: African + Asian
40
New cards
zika clinical features
incubation = 3-10 days
mostly asymptomatic, may have: fever, rash, malaise, joint pain, headache
complications = Guillan-Barre syndrome (acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy), myelitis
presenting with paraesthesia, muscle weakness, pain
in pregnancy can lead to microencephaly, congenital zika syndrome (malformations) or miscarriage/preterm
mostly asymptomatic, may have: fever, rash, malaise, joint pain, headache
complications = Guillan-Barre syndrome (acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy), myelitis
presenting with paraesthesia, muscle weakness, pain
in pregnancy can lead to microencephaly, congenital zika syndrome (malformations) or miscarriage/preterm
41
New cards
zika treatment
supportive management
no vaccine
vector control, barrier contraception if at risk (avoid congenital)
no vaccine
vector control, barrier contraception if at risk (avoid congenital)
42
New cards
helminths
broad term for parasitic worms which invade body
series of eukaryotic multi-cellular macro-parasites, many of which reside in GI tract or invade blood/ lymph vessels
3 groupings:
nematodes (roundworms)
trematodes (flukes)
cestodes (tapeworms
series of eukaryotic multi-cellular macro-parasites, many of which reside in GI tract or invade blood/ lymph vessels
3 groupings:
nematodes (roundworms)
trematodes (flukes)
cestodes (tapeworms
43
New cards
ascariasis cause + epidemiology
nematode - creamy white round worm
13-35cm long
Ascaris lumbricoides
effects up to 1 billion people a year
13-35cm long
Ascaris lumbricoides
effects up to 1 billion people a year
44
New cards
ascariasis migratory phase
eosinophilia (high level)
pneumonitis
Loffler's syndrome (rare, self-limiting, benign pulmonary oedema)
pneumonitis
Loffler's syndrome (rare, self-limiting, benign pulmonary oedema)
45
New cards
ascariasis intestinal phase
can be asymptomatic
obstruction
perforation
anaemia
failure to thrive
obstruction
perforation
anaemia
failure to thrive
46
New cards
ascariasis hepatobiliary/pancreatic phase
due to migration into biliary tree
47
New cards
ascariasis lifecycle + transmission
faecal-oral route
ingestion of embryonated eggs, resistant to stomach acid
eggs hatch in gut lumen, larvae penetrate into circulatory system
migrate to lungs, further development, coughed up and re-enter GI tract
further mature to adult form in gut, produce eggs which are passed in faeces
unfertilised = not infective
fertilised eggs develop to infectivity after 18 days depending on conditions
ingestion of embryonated eggs, resistant to stomach acid
eggs hatch in gut lumen, larvae penetrate into circulatory system
migrate to lungs, further development, coughed up and re-enter GI tract
further mature to adult form in gut, produce eggs which are passed in faeces
unfertilised = not infective
fertilised eggs develop to infectivity after 18 days depending on conditions
48
New cards
ascariasis treatment
49
New cards
hookworm cause + epidemiology
nematode
Necator americanus = affects 80% of the world
Ancylostoma duodenale = "old world"
Ancylostoma carinum = infects dogs, not adapted to humans but can cause skin manifestations
Necator americanus = affects 80% of the world
Ancylostoma duodenale = "old world"
Ancylostoma carinum = infects dogs, not adapted to humans but can cause skin manifestations
50
New cards
hookworm presentation
ground itch or cutaneous larva migrans = blister-like eruption + itch at site of entry
often asymptomatic but can attach to gut causing blood, protein + fluid loss:
failure to thrive/malnutrition
anaemia
hypoproteinaemia
enteritis
eosinophilia
can cause cardiac, resp + GI complications
often asymptomatic but can attach to gut causing blood, protein + fluid loss:
failure to thrive/malnutrition
anaemia
hypoproteinaemia
enteritis
eosinophilia
can cause cardiac, resp + GI complications
51
New cards
hookworm lifecycle
infected individual defecates eggs which hatch in soil
motile filariform larvae after 5-10 days = infective, are chemoattracted to host
infect by burrowing through skin into circulatory system
migrate to lungs + develop, ascend to pharynx and are swallowed
mature in jejunum, release eggs into faeces
motile filariform larvae after 5-10 days = infective, are chemoattracted to host
infect by burrowing through skin into circulatory system
migrate to lungs + develop, ascend to pharynx and are swallowed
mature in jejunum, release eggs into faeces
52
New cards
hookworm treatment
53
New cards
schistosomiasis cause + epidemiology
trematode/fluke
genera Schistosome
most prevalent in Africa
S. haematobium = urogenital
S. mansoni + S. japonicum = intestinal + hepatic
genera Schistosome
most prevalent in Africa
S. haematobium = urogenital
S. mansoni + S. japonicum = intestinal + hepatic
54
New cards
schistosomiasis presentation
"Swimmer's itch" = inflammation, itching at source
acute = Katayama syndrome (nocturnal fever, cough, myalgia, headache + abdo tenderness)
chronic = hepatosplenomegaly, fibrosis, haematuria, haemospermia, miscarriage, infertility, cancer, portal hypertension, ascites
dependent on organism
rarely migrate to CNS causing seizures/paralysis/inflammation
acute = Katayama syndrome (nocturnal fever, cough, myalgia, headache + abdo tenderness)
chronic = hepatosplenomegaly, fibrosis, haematuria, haemospermia, miscarriage, infertility, cancer, portal hypertension, ascites
dependent on organism
rarely migrate to CNS causing seizures/paralysis/inflammation
55
New cards
schistosomiasis lifecycle
infected human sheds eggs into environment (water)
eggs hatch + parasites infect freshwater snail (intermediate hosts)
parasite matures into sporocysts within snail + released into water again
free-swimming cericariae penetrate host skin into circulation (as schistosomulae)
migrate to liver where they develop + mature
in S. haematobium migrate to venous plexus of bladder, secrete eggs -> released in urine
in S. mansoni + S. japonicum migrate to mesenteric veins of intestine + secrete eggs into GI tract -> faeces
eggs hatch + parasites infect freshwater snail (intermediate hosts)
parasite matures into sporocysts within snail + released into water again
free-swimming cericariae penetrate host skin into circulation (as schistosomulae)
migrate to liver where they develop + mature
in S. haematobium migrate to venous plexus of bladder, secrete eggs -> released in urine
in S. mansoni + S. japonicum migrate to mesenteric veins of intestine + secrete eggs into GI tract -> faeces
56
New cards
schistosomiasis diagnosis + treatment
57
New cards
hydatid disease cause
cestode
human echinococcosis
causative agents = Echinococcus granulises + multiocularis
dog/fox are definitive hosts, humans are intermediates
cystic + alveolar forms
human echinococcosis
causative agents = Echinococcus granulises + multiocularis
dog/fox are definitive hosts, humans are intermediates
cystic + alveolar forms
58
New cards
hydatid presentation
5-15yrs incubation
commonly affects lungs (chronic cough, chest pain, SOB) + liver (abdo pain, N+V)
alveolar is more fatal, signs include weight loss, hepatic failure, abdo pain as usually liver lesion
larvae may spread to lymph + blood
diagnosis usually incidental
commonly affects lungs (chronic cough, chest pain, SOB) + liver (abdo pain, N+V)
alveolar is more fatal, signs include weight loss, hepatic failure, abdo pain as usually liver lesion
larvae may spread to lymph + blood
diagnosis usually incidental
59
New cards
hydatid lifecyle
ingested eggs, oncospheres released in gut
spreads via circulation, cysts in organs
humans = dead end host
spreads via circulation, cysts in organs
humans = dead end host
60
New cards
hydatid treatment
61
New cards
taeniasis forms + causes
human tapeworm, cestode
taenia saginata = beef, ingestion of contaminated + undercooked meat
taenia solium = pork, ingestion of contaminated + undercooked meats + eggs
taenia asiatica
humans definitive host
taenia saginata = beef, ingestion of contaminated + undercooked meat
taenia solium = pork, ingestion of contaminated + undercooked meats + eggs
taenia asiatica
humans definitive host
62
New cards
taeniasis presentation
intestinal: fullness, anaemia, weight loss, B12 deficiency, nausea, abdominal pain
cysticercosis (PORK) = cysts cause inflammation, scarring etc., can die + calcify, can also infect CNS
neurocysticercosis = headaches, seizures, muscle weakness, confusion, blindness, meningitis
cysticercosis (PORK) = cysts cause inflammation, scarring etc., can die + calcify, can also infect CNS
neurocysticercosis = headaches, seizures, muscle weakness, confusion, blindness, meningitis
63
New cards
taeniasis lifecycle
eggs in faeces ingested by cattle or pigs
in animal intestine oncospheres hatch, invade wall, migrate to muscle where they become cysticerci
humans ingest infected meat
in intestine cysticercus develops over 2 months into adult, reside in small intestine
produce proglottids which mature, detach and are passed in faeces
in animal intestine oncospheres hatch, invade wall, migrate to muscle where they become cysticerci
humans ingest infected meat
in intestine cysticercus develops over 2 months into adult, reside in small intestine
produce proglottids which mature, detach and are passed in faeces
64
New cards
helminths diagnosis
microscopy of urine/faeces for most + serological testing
schistosomiasis = kato katz stool microscopy, urine, ELISA, PCR
hydatid = scans + surgical exploration
schistosomiasis = kato katz stool microscopy, urine, ELISA, PCR
hydatid = scans + surgical exploration
65
New cards
niclosamide
first line for tapeworms/taeniasis
MOA = blocks glucose uptake, oxidative phosphorylation + anaerobic metabolism in tapeworm
may cause mild GI Sx
MOA = blocks glucose uptake, oxidative phosphorylation + anaerobic metabolism in tapeworm
may cause mild GI Sx
66
New cards
mebendazole
for ascariasis and hookworm
also for pinworms, whipworms, cutaneous larva migrans
MOA = selectively inhibits synthesis of microtubules - blocks polymerisation of tubulin
contraindicated in pregnancy
SE include dizziness, neutropenia, alopecia, skin reactions
also need to treat any underlying anaemia etc.
also for pinworms, whipworms, cutaneous larva migrans
MOA = selectively inhibits synthesis of microtubules - blocks polymerisation of tubulin
contraindicated in pregnancy
SE include dizziness, neutropenia, alopecia, skin reactions
also need to treat any underlying anaemia etc.
67
New cards
albendazole
similar to mebendazole so used in ascariasis, hookworm, hydatid, taeniasis
prevents glucose uptake like mebendazole
prevents glucose uptake like mebendazole
68
New cards
praziquantel
first line for schistosomiasis
also used for taeniasis
single dose, 40mg/kg
MOA = paralysis of larvae + adult worms
SE include nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, headache
also used for taeniasis
single dose, 40mg/kg
MOA = paralysis of larvae + adult worms
SE include nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, headache
69
New cards
levisamole
used for ascariasis and hookworms
MOA = nicotinic ACh receptor agonist, paralyses helminth
MOA = nicotinic ACh receptor agonist, paralyses helminth
70
New cards
hydatid treatment
surgical removal of cysts
albendazole as cover
or mebendazole/praziquantel
albendazole as cover
or mebendazole/praziquantel
71
New cards
elephantiasis
also known as lymphatic filariasis, nematodes
obstruction of lymphatic system
diethylcarbamazine treatment
obstruction of lymphatic system
diethylcarbamazine treatment
72
New cards
onchocerciasis
river blindness
filarial worm Onchocerca volvulus - but transmitted by black flies
treatment = ivermectin
filarial worm Onchocerca volvulus - but transmitted by black flies
treatment = ivermectin
73
New cards
helminths summary flashcard
see image :)
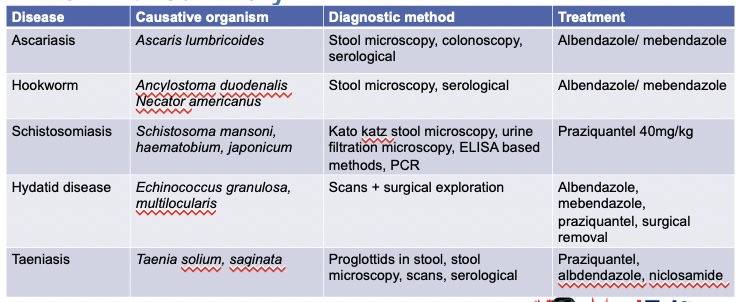
74
New cards
amoebiasis
amoebic dysentry
caused by ingestion of mature cysts, cysts + trophozoites passed in faeces
Entamoeba histolytica
presents as diarrhoea (+/- blood and mucus), abdominal pain
amoebic liver abscess (ALA) = URQ pain, clay colour stool, dark urine, fever, chills, night sweats
symptomatic treatment = metronidazole, tinidazole, omidazole
asymptomatic treatment. = diloxanide furoate
caused by ingestion of mature cysts, cysts + trophozoites passed in faeces
Entamoeba histolytica
presents as diarrhoea (+/- blood and mucus), abdominal pain
amoebic liver abscess (ALA) = URQ pain, clay colour stool, dark urine, fever, chills, night sweats
symptomatic treatment = metronidazole, tinidazole, omidazole
asymptomatic treatment. = diloxanide furoate
75
New cards
giardiasis
caused by Giardia duodenal
asymptomatic, or acute presentation of gassy diarrhoea, greasy floating stool, stomach cramps, N+V
treated with metronidazole, tinidazole or nitazoxanide
asymptomatic, or acute presentation of gassy diarrhoea, greasy floating stool, stomach cramps, N+V
treated with metronidazole, tinidazole or nitazoxanide
76
New cards
metronidazole
treatment for amoebic dysentry + giardiasis
77
New cards
nitazoxanide
used if needed in cryptosporidiosis and for giardiasis
MOA = disrupts metabolism + induces lesions in cell membranes
MOA = disrupts metabolism + induces lesions in cell membranes
78
New cards
cryptosporidiosis
caused by Cryptosporidium hominis + parvum
presents as asymptomatic in immunocompetent
immunosuppressed = diarrhoea, vomiting, stomach cramps
treatment = rehydration, Nitazoxanide if needed
presents as asymptomatic in immunocompetent
immunosuppressed = diarrhoea, vomiting, stomach cramps
treatment = rehydration, Nitazoxanide if needed
79
New cards
prevention + control of vector borne diseases
insecticide impregnated nets
indoor residual spraying, outdoor fogging
larvicide
tsetse fly traps
mass drug administration
water treatment
indoor residual spraying, outdoor fogging
larvicide
tsetse fly traps
mass drug administration
water treatment
80
New cards
ADR definition
NICE: response to medicinal product which is noxious + unintended
relationship between medicinal product + adverse event is either known or strongly suspected
relationship between medicinal product + adverse event is either known or strongly suspected
81
New cards
pharmacodynamic ADR
= what drug does to body
drug effect scaled up or down
e.g propanolol reducing effects of salbutamol
drug effect scaled up or down
e.g propanolol reducing effects of salbutamol
82
New cards
pharmacokinetic ADR
= ADME, what body does to drug
changes in ADME alter effect of drug
e.g. NSAIDs reduce antihypertensive action of diuretics by reducing renal blood flow
changes in ADME alter effect of drug
e.g. NSAIDs reduce antihypertensive action of diuretics by reducing renal blood flow
83
New cards
adherence
extent to which patient's actions match agreed recommendations (shared plan)
e.g. doctor prescribes, instructs only to take when in pain, so patient does this
enhancing adherence = key to patient safety
5 dimensions: socioeconomic, therapy related factors, patient related factors, condition related factors, health system factors
adherence = (no. of doses taken/no. of prescribed doses) x 100
e.g. doctor prescribes, instructs only to take when in pain, so patient does this
enhancing adherence = key to patient safety
5 dimensions: socioeconomic, therapy related factors, patient related factors, condition related factors, health system factors
adherence = (no. of doses taken/no. of prescribed doses) x 100
84
New cards
compliance
act of following a medical regime or schedule correctly and consistently
"do as I say"
e.g. doctor prescribes, patient takes even if not sure why
"do as I say"
e.g. doctor prescribes, patient takes even if not sure why
85
New cards
concordance
joint agreement about medication plan
"do you agree to do as I say?"
e.g. patient needs meds, doesn't want tablets, injections done instead
"do you agree to do as I say?"
e.g. patient needs meds, doesn't want tablets, injections done instead
86
New cards
ABCDEF classification of ADRs
Augmented = dose related, common, exaggeration of normal action, toxic + side effects
e.g. bleeding due to warfarin
Bizarre = non-dose related, unexpected, immunological/hypersensitivity/idiosyncratic
e.g. anaphylaxis to penicillin
Chronic = dose (cumulative) + time related, uncommon, persists
e.g. HPT suppression by corticosteroids
Delayed = time-related, take time to become apparent, uncommon
e.g. tardive dyskinesia, leucopenia
End of Use = withdrawal, uncommon
e.g. insomnia + anxiety after bento withdrawal
Failure = drug not working, dose-related, often due to DDIs
e.g. bleeding due to warfarin
Bizarre = non-dose related, unexpected, immunological/hypersensitivity/idiosyncratic
e.g. anaphylaxis to penicillin
Chronic = dose (cumulative) + time related, uncommon, persists
e.g. HPT suppression by corticosteroids
Delayed = time-related, take time to become apparent, uncommon
e.g. tardive dyskinesia, leucopenia
End of Use = withdrawal, uncommon
e.g. insomnia + anxiety after bento withdrawal
Failure = drug not working, dose-related, often due to DDIs
87
New cards
DoTS classification of ADRs
Do = Dose
supra-therapeutic dose (toxic effects)
standard therapeutic dose (collateral effects)
sub-therapeutic dose (hypersensitivity in susceptible patients)
T = Timing
will be time independent or time dependent
S = Susceptibility
age, gender, disease states, pregnancy, ethnicity, poly pharmacy
supra-therapeutic dose (toxic effects)
standard therapeutic dose (collateral effects)
sub-therapeutic dose (hypersensitivity in susceptible patients)
T = Timing
will be time independent or time dependent
S = Susceptibility
age, gender, disease states, pregnancy, ethnicity, poly pharmacy
88
New cards
explain how all drugs have both beneficial and adverse effects
no drug is 100% specific for 1 receptor subtype, will always be a knock-on effect
also, not all tissue perfect
TD50 = dose of drug causing toxicity in 50% of population
ED50 = dose of drug effective in 50% of population
therapeutic index = TD50/ED50
larger TI = safer
also, not all tissue perfect
TD50 = dose of drug causing toxicity in 50% of population
ED50 = dose of drug effective in 50% of population
therapeutic index = TD50/ED50
larger TI = safer