Physics : P5
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Define a force.
A push or pull acting upon an object: caused by it interacting with something
What are the contact and non-contact forces?
Contact = normal contact force, friction, tension, air resistance
Non-contact = gravity, electrostatic, magnetic
Define a vector and give examples
A quantity with a magnitude (size) and direction
Force, velocity, momentum, displacement and acceleration
Define a scalar and give examples
A physical quantity with a magnitude and no direction
Temperature, mass, time, distance, speed
What is an interaction pair?
A pair of forces that are equal and opposite and act on two interacting objects
Define acceleration
How quickly the velocity (speed or direction) is changing.
What is the formula for acceleration and deacceleration?
Acceleration = change in velocity/time taken
M/s(squared) = (m/s) / (s)
A = △v/t
(DEACCELERATION IS THE SAME BUT THE ANSWER WILL BE A NEGATIVE)
Define uniform acceleration
Consistent, not changing velocity
Acceleration due to gravity on Earth is…
9.8 m/s(squared)
Define resultant force
The overall force acting upon an object
What is the equation for resultant force?
Resultant force = biggest force - other forces
What does the resultant force determine? What if its 0?
The direction an object moves
The object us at constant velocity
Define acceleration and deacceleration
Acceleration = velocity increasing
Deaccleration = velocity decreasing
Define mass and its units
A measure of the number of atoms in an object
Kg
Define weight and its units
A force called by the pull of gravity on mass
Newtons (N)
Define gravitational field strength
Acceleration of an object caused by gravity (9.8 N/Kg on Earth)
Define gravity
A force of attraction between masses determined by mass and distance
What is the formula for weight?
Weight = mass x gravitational field strength
N = Kg x N/Kg
Define displacement and an example
A vector quantity which measures distance and direction in a straight line from start to end point.
E.g. if you work 5m north then 5m south, displacement = 0m, direction = 10m
Define speed and how it is calculated
A measure of how far an object travels in a given time
Speed = distance/time
What is the speed of someone walking, running and cycling?
Walking = 1.5 m/s
Running = 3 m/s
Cycling = 6 m/s
What is the speed of a car, train, plane?
Car = 25 m/s
Train = 30 m/s
Plane = 250 m/s
Define work done and how it is calculated
When energy is transferred and a resultant force moves an object, it is only done when a force is applied.
Work done = force x distance
J = N x m
1J of work done equates to…
1J of work done is when a force of 1N causes an object to move by 1m
Define terminal velocity
When the frictional and accelerating force are equal terminal velocity is reached and the object falls at a steady speed.
What 2 factors impact terminal velocity?
Less streamlined = lower TV
Large SA = lower TV
What is Newton’s first law?
Objects at rest and objects in motion remain in motion in a straight line, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
What is Newton’s second law?
Forcé = Mass x acceleration
What is Newton’s third law?
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Define inertia
An object continuing in the same state of motion
Define inertial mass
How difficult it is for an object to change its velocity
Define momentum and its formula
A property of moving objects. The greater the mass and velocity of an object the greater the momentum/
Momentum = mass x velocity
P = m x v
(Kg m/s) = (Kg) x *m/s)
What is conservation of momentum?
In a closed system the total momentum before an event (collision) is equal to the total momentum after the event.
What is the formula for total momentum?
M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
Mass object 1 x velocity object 1 = mass object 2 x velocity object 2
Kg x m/s = Kg x m/s
What is the equation that links initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and distance?
Final velocity² - initial velocity² = 2 x acceleration x distance
V² - u² = 2 x a x s
M/s - m/s = 2 x m/s² x m
If initial velocity is not given use..
0: the object starts stationary
What is the formula for reaction time?
Reaction time = √2 x acceleration x distance / acceleration
T = √2as / a
S = √2 x m/s x m / m/s²
Define friction? What does it cause?
A resistive force that slows things down and tries to stop objects sliding past each other, acting in the opposite direction to an objects moving.
It causes the wearing down of surfaces due to the release of thermal energy.
Define lubricants
Used to reduce friction in machinery and protect surfaces
Define air resistance
Friction caused by an object moving through the air
Define drag
Friction caused by an object moving through liquid
Define stopping distance and how its calculated
The total distance covered in the time taken from a driver seeing a hazard to stopping
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
Define thinking distance
The distance the vehicle travels during the drivers reaction time from the spotting of a threat
Define braking distance
The distance a vehicle travels once brakes are pressed
What factors impact thinking distance?
Reaction time, drugs, alcohol, speed, velocity
What factors impact braking distance?
Tyre conditions, speed, weather, brake conditions
As speed doubles breaking distance….
As speed trebles breaking distance…
Increases by + 2²
Increases by + 3²
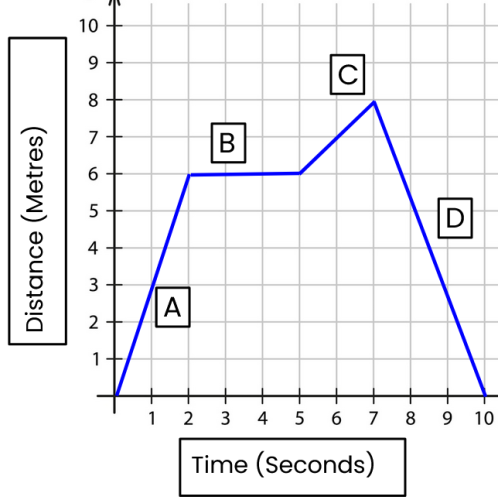
Label each point on the distance, time graph
A = constant speed
B = stationary
C = faster constant speed
D = constant speed (return)
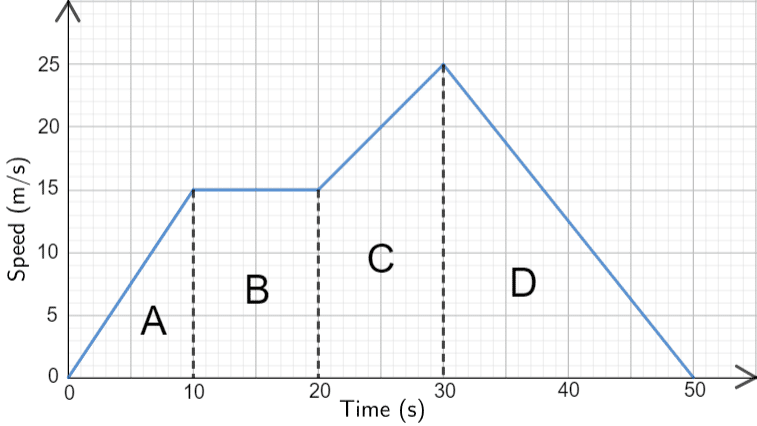
Label each point on the speed/velocity , time graph
A = gradual acceleration
B = steady speed
C = steady acceleration
D = steady deacceleration
Define elastic deformation
When an object goes back to its original shape and length after the force has been removed. Epe —> Ke
Elastic deformation can only happen when…
An object has energy in its elastic potential store
Define inelastic deformation
When an object can not return back to its original shape due to the force applied.
What formula links force, spring constant and extension?
Forcé = spring constant x extension
N = N/m x m
What is the formula for elastic potential energy?
Epe = ½ x spring constant x extension²
J = ½ x N/m x m²
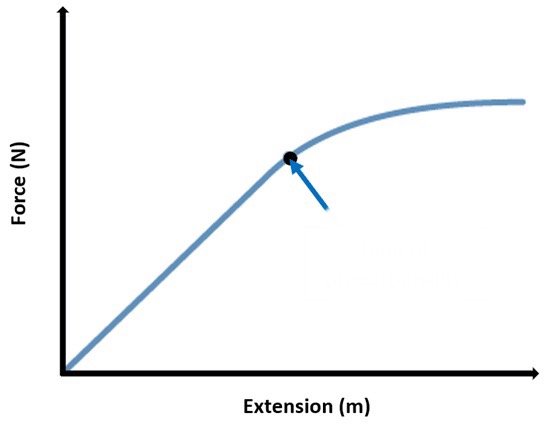
What does the curve represent?
Limit of proportionality, elastic limit: object is inelastically deformed