Enzymes and Metabolism Chapter 6
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Catabolic
breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones, release energy,
Anabolic
building up, require energy, synthesizes larger molecules
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is transformed, the quantity of energy remains the same, but its ability to do work diminishes (transferred energy is not completely efficient ---> energy is always lost usually in form of heat)
What is entropy?
A measure of disorder or randomness.
How does entropy differ between gases, liquids, and solids?
Gases have higher entropy than liquids, and liquids have higher entropy than solids.
Gibs free energy
amount of energy available to do work (usable energy)
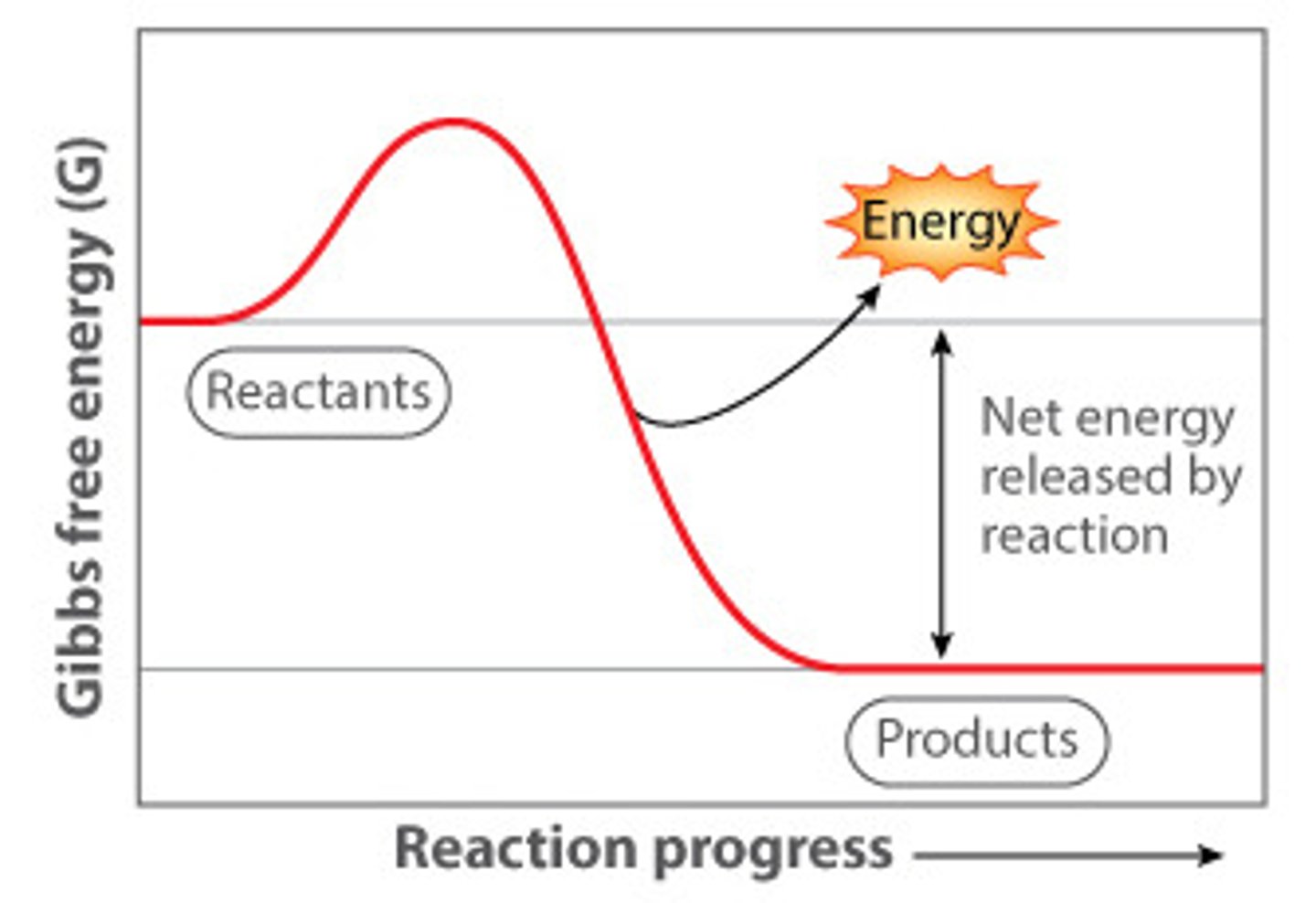
Exergonic
releases energy (think exits), delta G is negative
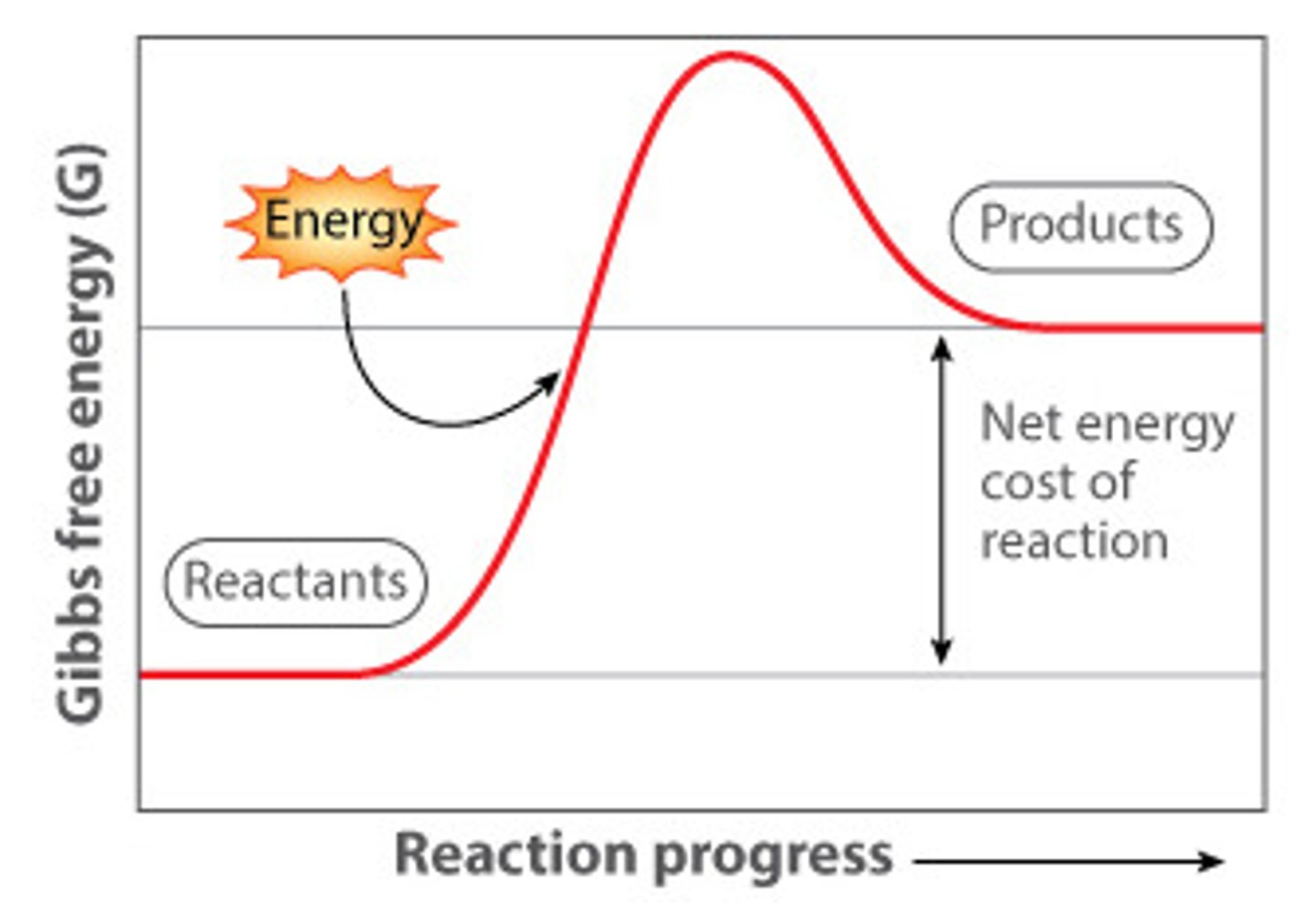
Endergonic
requires energy, delta G is positive
activation energy
energy required for a reaction to proceed, difference between reactants and transition state
Transition State
high-energy, unstable state, heat helps reactants reach their transition state, once in transition state reaction occurs fast
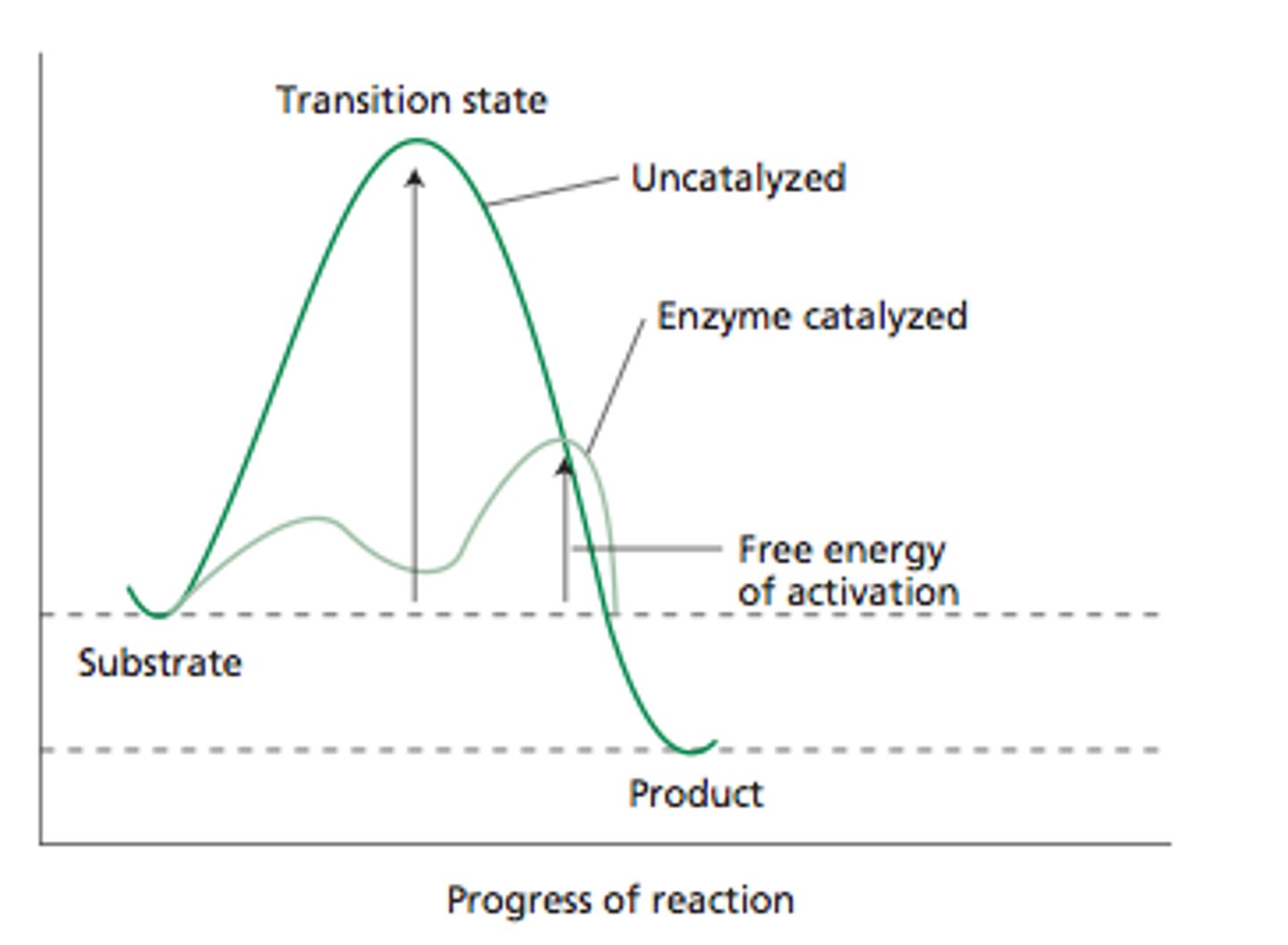
Catalysts LOWER activation energy in a cell therefore
speeds up reactions
What is the role of ATP in energy coupling?
ATP transfers energy from exergonic to endergonic reactions (exergonic to drive endergonic)
How is most energy coupling mediated?
Most energy coupling is mediated by ATP hydrolysis
What is the general function of enzymes?
Enzymes are usually catalytic proteins that speed up reactions. ually a catalytic protein (speeds up reactions) exception- riboenzymes
what is the function of enzymes f?
change the shape of substrate molecules.
Active Site
the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
induced fit model
enzyme model where the substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape slightly so it fits better
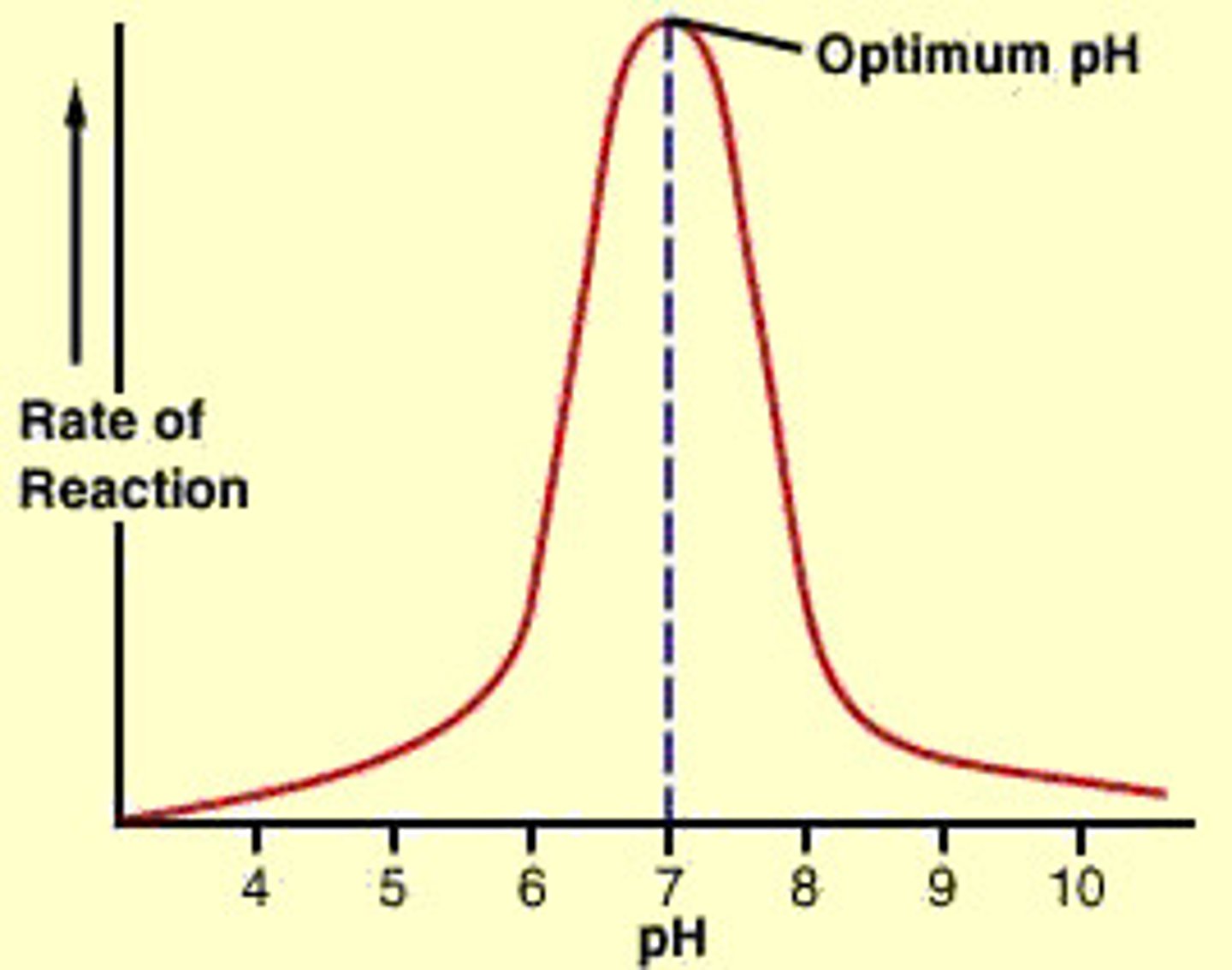
optimum pH and temperature for enzymes
temp can denature and cause enzyme to loss shape
pH can reduce substrate enzyme binding
Competitive inhibitors
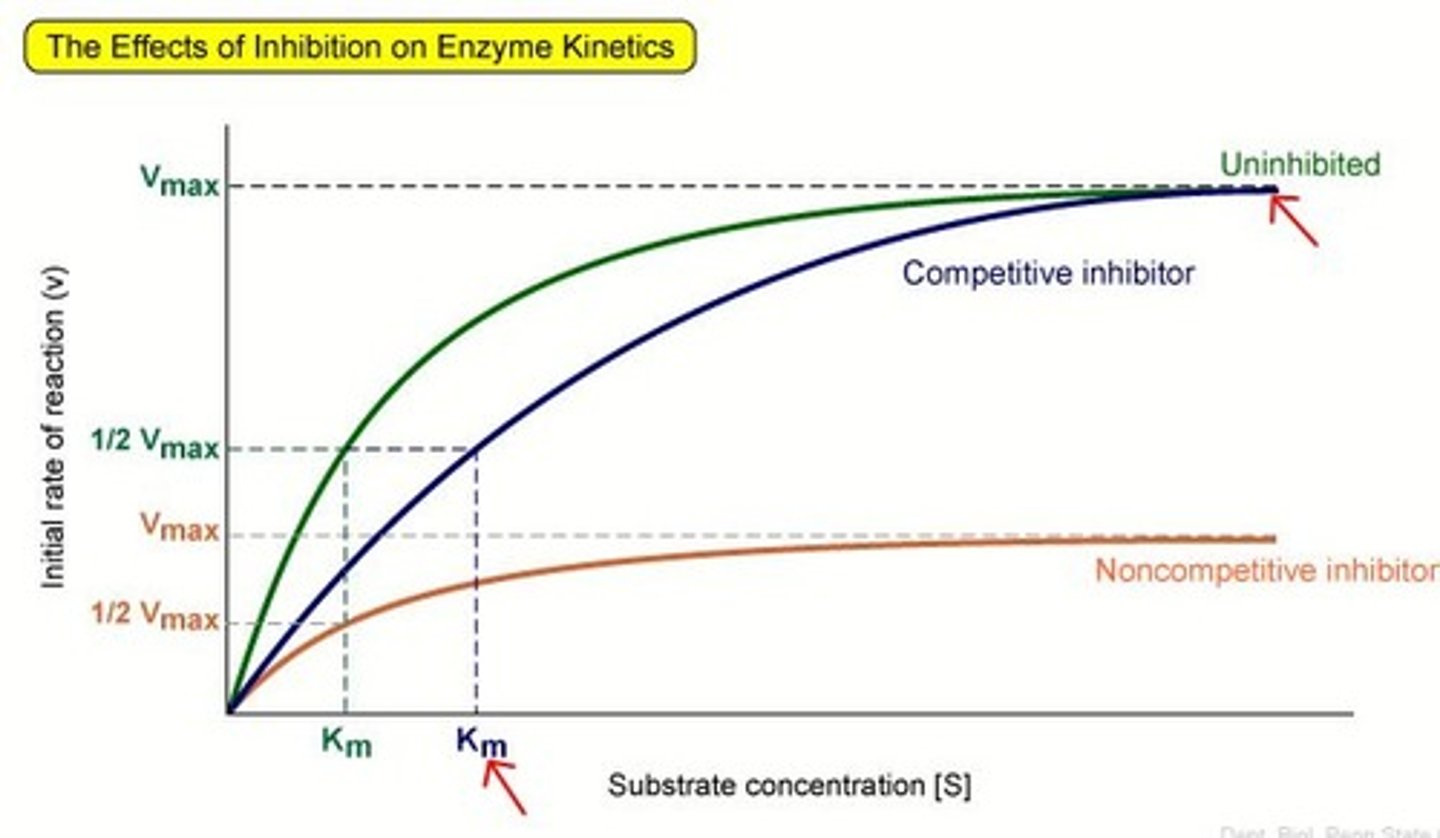
bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate, (slows reaction rates but doesn't effect maximal rate --> just takes more time)
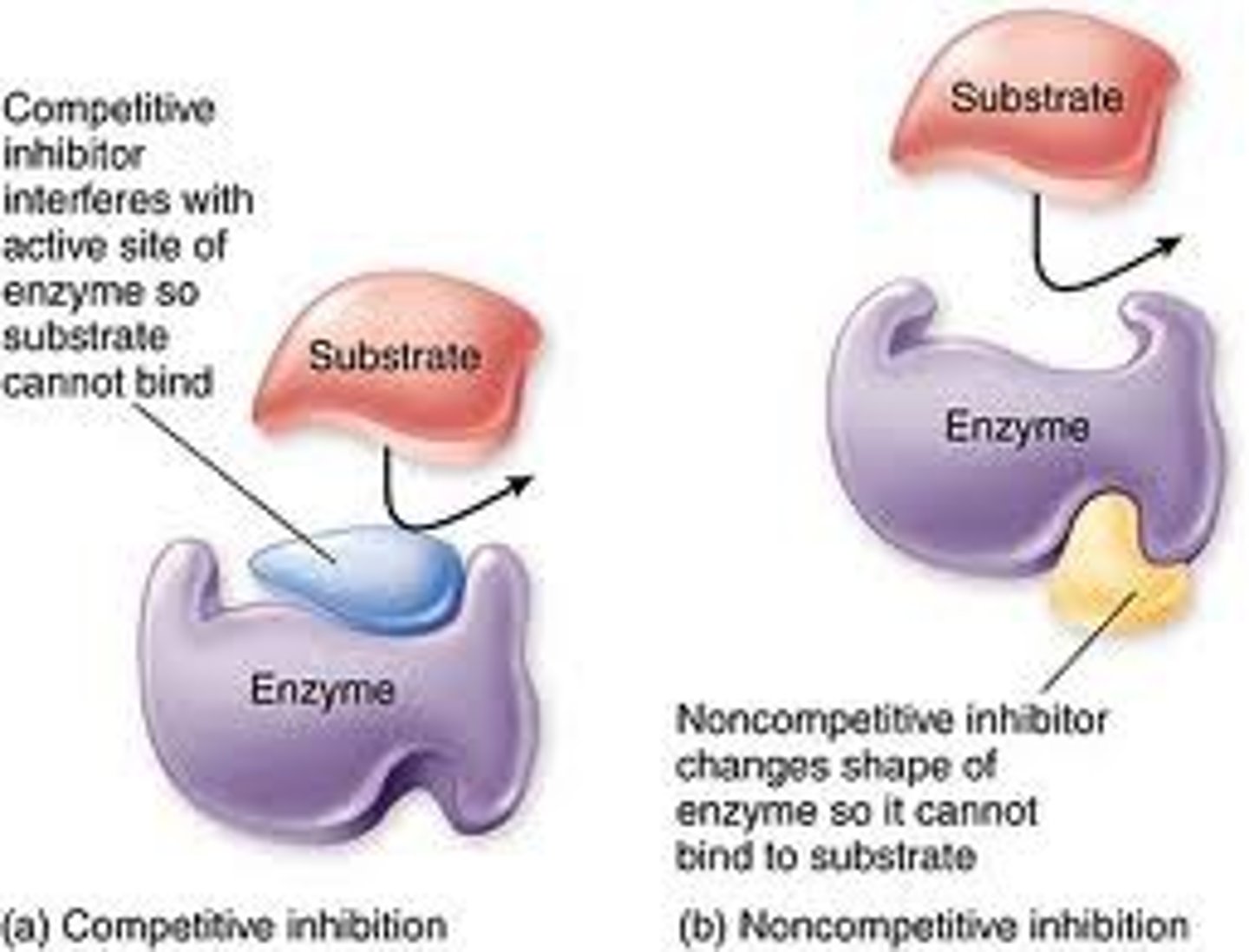
Noncompetitive Inhibitors
bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective (slows rates and reduce the maximal rate)
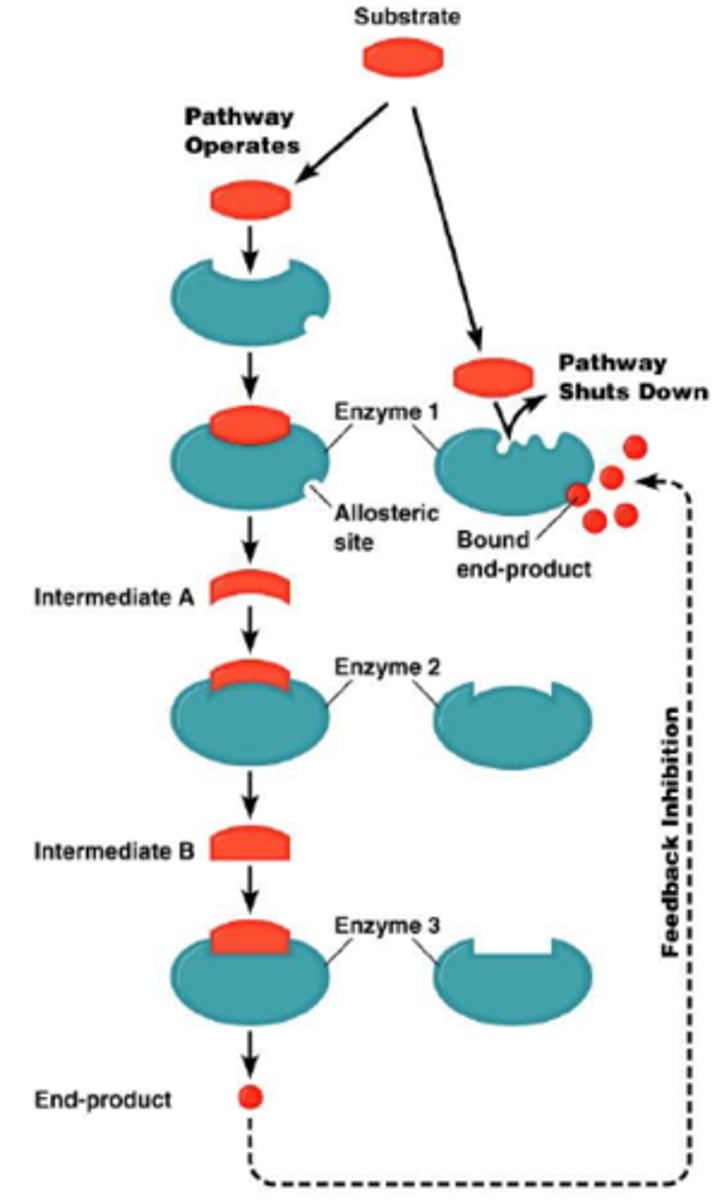
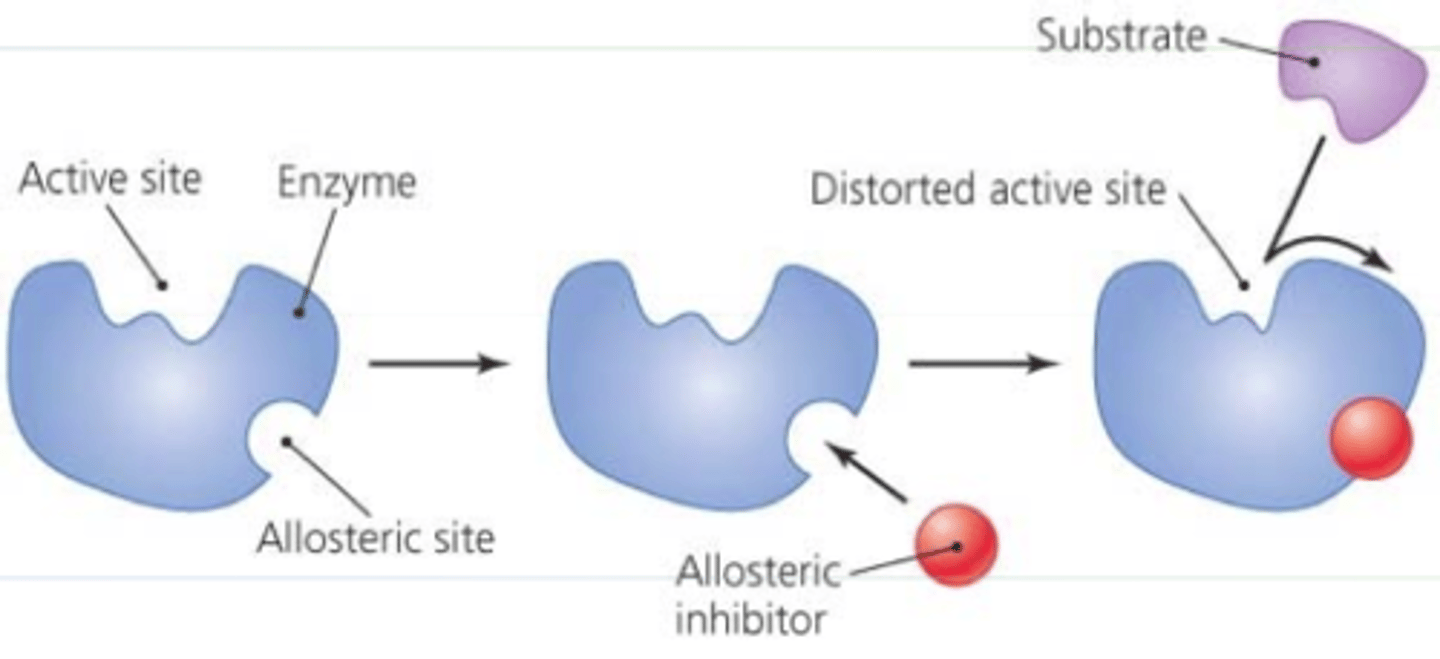
Allosteric inhibitors
modify the active site of the enzyme so that substrate binding is reduced or prevented
Allosteric activators
modify the active site of the enzyme so that the likelihood for the substrate increases
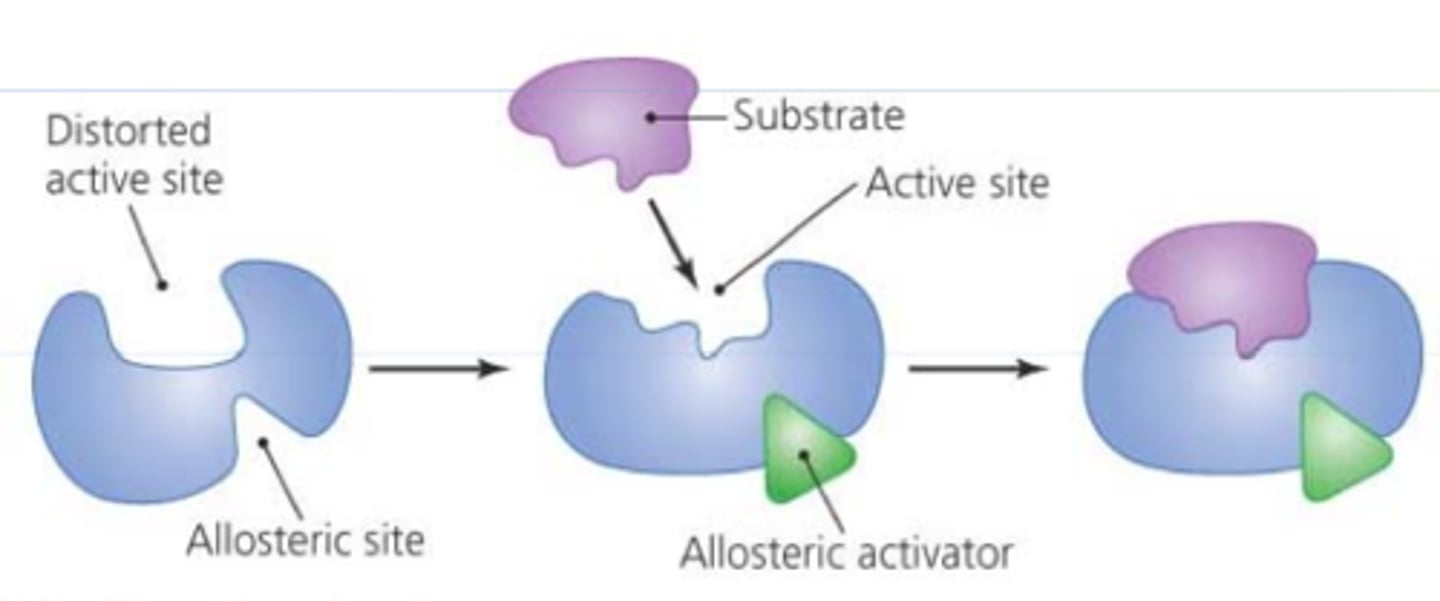
feedback inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.