Macromolecule Comparison Chart
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to macromolecules, their monomers, bonding types, and functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Carbohydrate: monomer, linkages, and function
A macromolecule made up of monosaccharides,
Linked by glycosidic linkages,
Used primarily for energy storage and structure, and makes up parts of other molecules and serves as a building block.
Carbohydrate: functional groups and structure
Atoms are in ratio of 1:2:1 with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Many -OH groups, A carbonyl group (C=O), Multiple carbon-hydrogen bonds
Usually in a ring structure
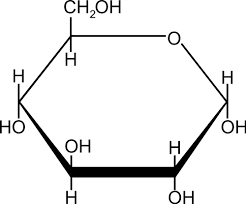
Carbohydrate: examples and naming
Glucose, frutose, cellulose, starch, glycogen
-ose ending to most carbs
Protein: monomer, linkages, and function
Amino acid
Peptide bond
Structural support, transport, and catalysis
Protein: examples and naming
Lactase, collagen, and hemoglobin
-ase ending for enzymes
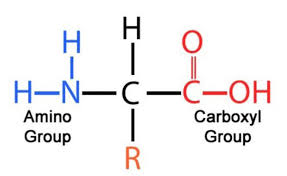
Protein: functional groups
For each amino acid there are four components around a central carbon: an amine group (N), a hydrogen, C = O or carboxyl group (depending on if the amino acid is part of a polypeptide) and a variable R group.
4 Main Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Protein
Nucleic Acid
Lipid
Nucleic Acid: monomer, linkages, and function
Nucleotide
Phosphodiester linkage
Storage and transmission of traits (DNA)
Involved in making proteins and catalysis of some reactions (RNA)
Nucleic Acid: examples
DNA, RNA, ATP
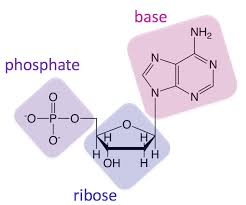
Nucleic Acid: functional groups and structure
For each nucleotide there are three basic components: phosphate group, 5-carbon sugar,
nitrogenous base (ring structure with nitrogens)
The nitrogenous base is made of adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
Lipid: examples
Triglycerides/fat, phospholipids, and steroids
Lipids: function
Energy storage
Cell membranes
Cell signaling (hormones)
Lipids: structure
Many carbons and hydrogens, few other types of atoms
May have fatty acids as part of its structure
Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids have different structures
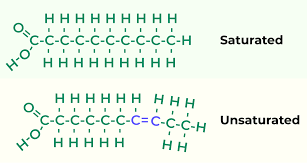
How does the amino acid sequence of a protein affect its function?
Each amino acid has an R-group that has different chemical properties. Some R-groups are non-polar, some are
charged, some are small, some are large. The interactions between the R-groups in a protein are important in
determining its three-dimensional shape
There are three main structural differences between DNA and RNA. List the ways RNA is unique:
Ribose is the 5-carbon sugar in RNA, deoxyribose is found in DNA. The difference between the two is that
ribose has an -OH group that deoxyribose does not
RNA has uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)
RNA is usually single-stranded, DNA is usually double-stranded
Saturated fatty acids have _________________ than unsaturated fatty acids, which is why they exist as a
____________ at room temperature
fewer double bonds; solid
Living things are characterized by five characteristics that they all share:
Composed of cells
Reproduction
Processing/responding to information
Energy
Evolution
Theories
Like hypotheses in that they must be testable and falsifiable, but they are MUCH more supported by evidence than are hypotheses (so, much less likely to be thrown out/changed) and
More broad in scope
Hypotheses
Must be testable and falsifiable and are tentative explanations of observations.
Generally, hypotheses are written in present tense
Predictions
Outline how to test the hypothesis, including what is being manipulated by the
experimenter (independent variable) and what is expected to change (dependent variable).
Generally, predictions are in future tense and contain more specifics than hypotheses
How are pH and Acidity related
Inversely so increase in pH = decrease in acidity
What chemical bonds store the most energy
Nonpolar bonds store more energy than polar bonds
Macromolecules
Large molecules that often consist of several smaller subunits (called
monomers) bound together
Why are monosaccharides important in carbohydrates?
The digestive system cannot absorb carbohydrates larger than a monosaccharide (larger molecules must be broken down before absorbed)
Monosaccharides (especially glucose) are used in cellular respiration
Disaccharides
Are carbohydrates that consist of two monosaccharides
Polysaccharides: denfintion + examples
Are many monosaccharides covalently linked
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose
Why is cellulose used by plants and not able to be digested by humans?
This is caused due to the use of β-glucose in cellulose’s structure.
4 levels of protein structures
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Enzymes
Are proteins that catalyze/speed up chemical reactions – often building or
breaking down other molecules
How to differentiate between DNA (deoxyribose) and RNA (ribose)
Deoxyribose contains one less oxygen than ribose does
DNA is double stranded
ATP
An activated nucleotide that is the most commonly-used direct source of energy for cells
Directionality of nucleic acid strands
5’ to 3’
Function of RNA
RNA has a much wider variety of uses.
One of the most important is that it is used as an intermediate between DNA and protein during protein synthesis
What makes lipid different from other marcomolecules?
Are characterized by not dissolving well in water (unlike other macromolecules, they don’t have monomers that characterize them
Triglycerides/fat function
Extremely non-polar lipids that are used as long-term energy storage
Saturated fats
Have no double bonds; usually solid at room temperature because the straight
structure packs well; often found in animal-based foods
Unsaturated fats
Have double bonds; usually liquid at room temperature because the double bonds form kinks; often found in vegetable oils and fish oils
Trans fat
Have double bonds, but are solid at room temperature because the double bond doesn’t form a kink; unnatural (found in highly-processed food) and hard to digest; indicated by “partially hydrogenated vegetable oil” labels
Steroids
Are lipids composed of four linked carbon/hydrogen rings
The most common steroid is cholesterol, which is a component of cell membranes and is used to make steroid hormones
Amphipathic molecules
Have polar/hydrophilic and non-polar/hydrophobic regions. They naturally form membranes because of this
Lipid bilayers: what molecules get through and what doesn’t
Are selectively permeable – only let certain molecules cross
Only small and non-polar molecules easily pass through the non-polar region of the bilayer
Charged ions almost never get through, even if they are small, unless they can go through a protein channel