AP Micro Unit 5 - Factor Markets
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:44 AM on 2/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
Factor Market
* Where the factors of production are sold by households to businesses
* Factors are:
* Land
* Labor
* Capital
* Entrepreneurship
* Factors are:
* Land
* Labor
* Capital
* Entrepreneurship
2
New cards
Derived Demand
* Demand for resources is determined/derived by the products they help to produce
* If demand for one thing increases, it will consequently increase demand for something else
* If demand for one thing increases, it will consequently increase demand for something else
3
New cards
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
* As variable resources are added to fixed resources, the additional output produced from each new input will eventually fall
4
New cards
Marginal Resource Cost (MRC)
* The cost of buying one additional unit of a factor (usually hiring a worker)
* For hiring a worker, this would wage rate
* For hiring a worker, this would wage rate
5
New cards
Marginal Product (MP)
* The additional product produced by hiring one more worker
6
New cards
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
* The additional revenue generated by hiring one more worker
* Marginal Product x Price
* MP x P
* Marginal Product x Price
* MP x P
7
New cards
Profit Maximization
* MRP = MRC
8
New cards
Firms should continue to hire workers until…
they’re no longer profit off of their worker (when MRP = MRC)
9
New cards
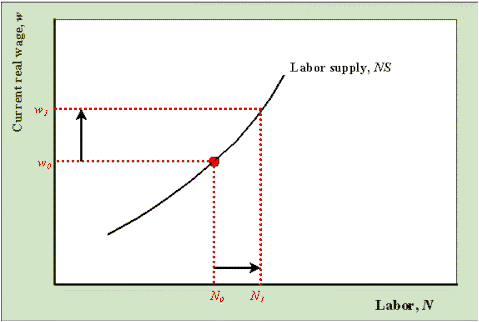
Factor Supply
* AKA Labor Supply
* Upward sloping curve
* Non-firm side of the factor market
* Curve represents the lowest willingness and ability to sell one’s labor to a firm
* As wage increases, quantity of labor available increases
* Upward sloping curve
* Non-firm side of the factor market
* Curve represents the lowest willingness and ability to sell one’s labor to a firm
* As wage increases, quantity of labor available increases
10
New cards
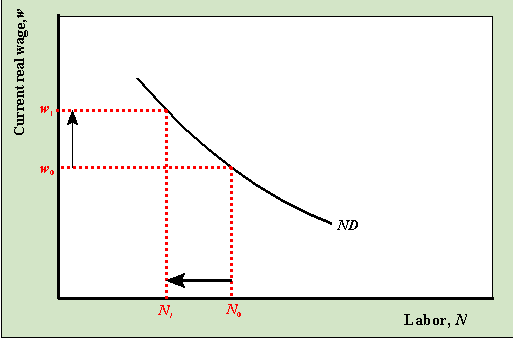
Factor Demand
* Downward sloping curve
* At a high wage, firms are not willing or able to buy much labor
* At a low wage, firms are willing to buy more labor
* At a high wage, firms are not willing or able to buy much labor
* At a low wage, firms are willing to buy more labor
11
New cards
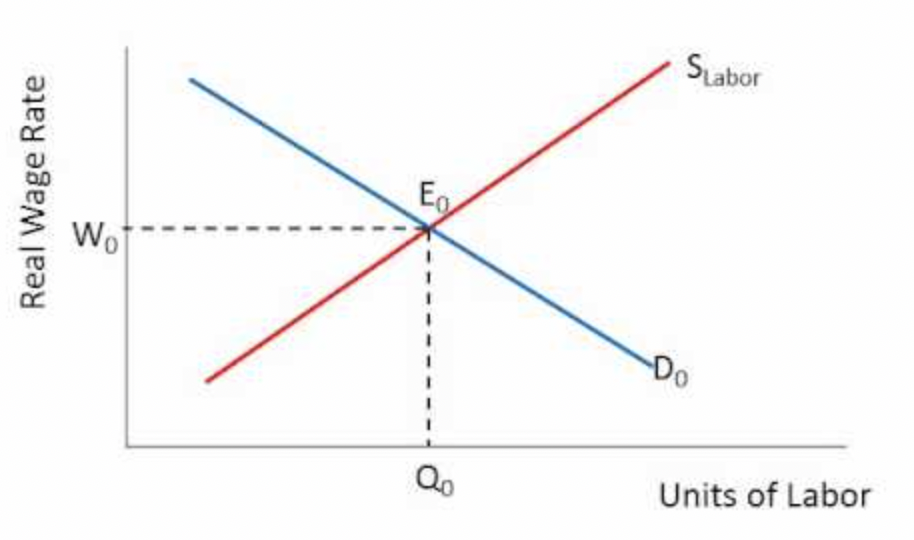
Factor Market Equilibrium
* Market labor and wage rate is set at where quantity of labor equals quantity of labor demanded
* Where Factor Demand and Factor Supply intersect
* No shortages or surpluses of labor
* Where Factor Demand and Factor Supply intersect
* No shortages or surpluses of labor
12
New cards
Determinants of Factor Demand
* Price of Related Input
* Changes in Productivity
* Product Demand
* Changes in Productivity
* Product Demand
13
New cards
First Determinant of Factor Demand
Price of Related Input
Price of Related Input
* Substitute resources and complementary resources that are used in the production of goods and services
* If the price of one resource becomes more expensive, the firm will increase their demand for the substitute resource
* If the price of one resource becomes more expensive, the firm will increase their demand for the substitute resource
14
New cards
Second Determinant of Factor Demand
Changes in Productivity
Changes in Productivity
* Say there’s a new technique that cuts production time in half, increasing productivity and now each worker can produce more in the same amount of time
* This will lead to each worker’s value increasing, leading to an increased demand in labor
* This will lead to each worker’s value increasing, leading to an increased demand in labor
15
New cards
Third Determinant of Factor Demand
Product Demand
Product Demand
* A change in the demand for the good or service
* If there’s an increased demand for a good, the resources required to make that good/service will increase
* Resource Demand can also by determined by a change in prices
* If there’s an increased demand for a good, the resources required to make that good/service will increase
* Resource Demand can also by determined by a change in prices
16
New cards
Determinants of Factor Supply
* Number of Qualified Workers
* Can be influenced by migration, immigration, education, training, and abilities
* Government Regulations
* Example: Laws about certification requirements, etc.
* Personal Values
* Personal values about leisure time and societal roles
* Wealth Effect
* Can be influenced by migration, immigration, education, training, and abilities
* Government Regulations
* Example: Laws about certification requirements, etc.
* Personal Values
* Personal values about leisure time and societal roles
* Wealth Effect
17
New cards
Wealth Effect
* If long-term wealth increases, fewer people will supply labor at all wages, meaning supply shifts left, and vice-versa
18
New cards
Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Labor (Factor) Markets
* Many, small firms hiring workers
* Firms are “wage takers”
* Skill level of workers is identical (workers are perfect substitutes)
* Firms can hire as many workers they want or need at the set wage in the market
* Firms will hire workers as long as MRP > MRC or until MRP = MRC
* Firms will profit maximize
* Firms are “wage takers”
* Skill level of workers is identical (workers are perfect substitutes)
* Firms can hire as many workers they want or need at the set wage in the market
* Firms will hire workers as long as MRP > MRC or until MRP = MRC
* Firms will profit maximize
19
New cards
Perfectly Competitive Labor (Factor) Market Graph
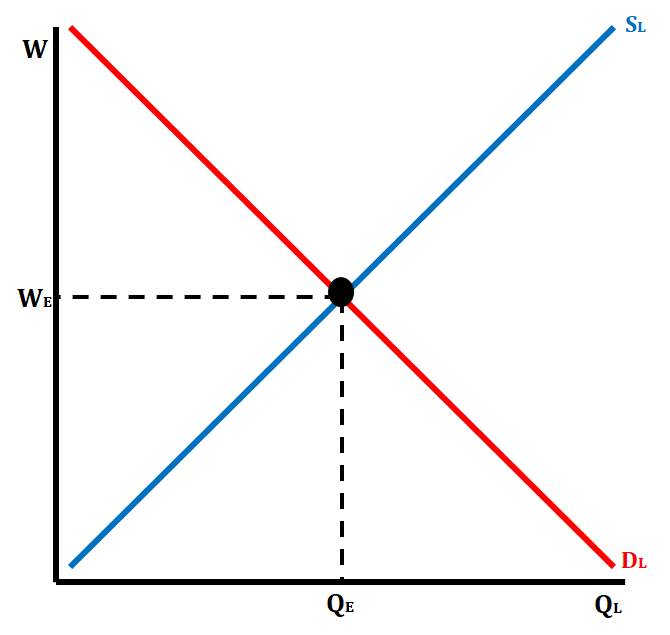
20
New cards
Firm Graph in a Perfectly Competitive Labor Market
* The supply of labor is perfectly elastic because firms are “wage takers”
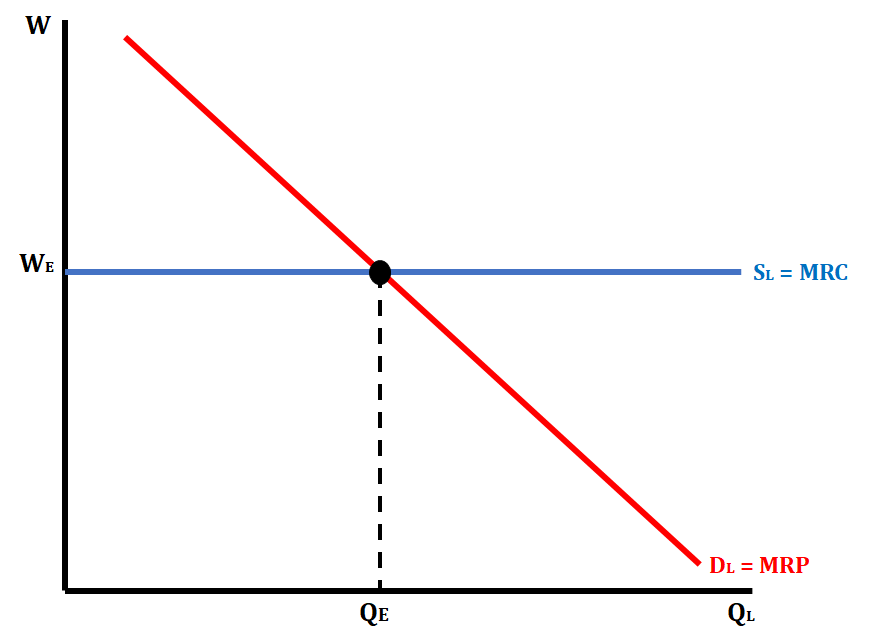
21
New cards
Side-by-Side Graphs in a Perfectly Competitive Labor Market
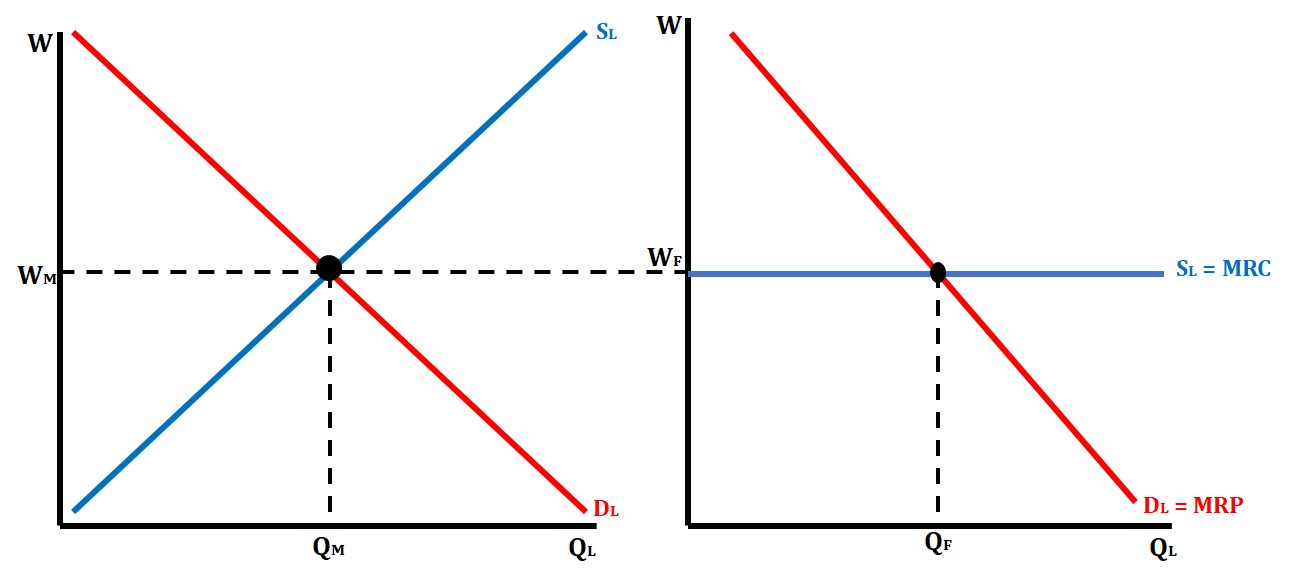
22
New cards
Cost Minimizing Combination of Resources
Least-Cost Rule
Least-Cost Rule
* (MPx/Px) = (MPy/Py)
* MP - Marginal Product
* P - Price
* MP - Marginal Product
* P - Price
23
New cards
Profit Maximizing Combination of Resources
* (MRPx/MRCx) = (MRPy/MRCy) = 1
* Firms is hiring where MRP = MRC for each resource
* Firms is hiring where MRP = MRC for each resource
24
New cards
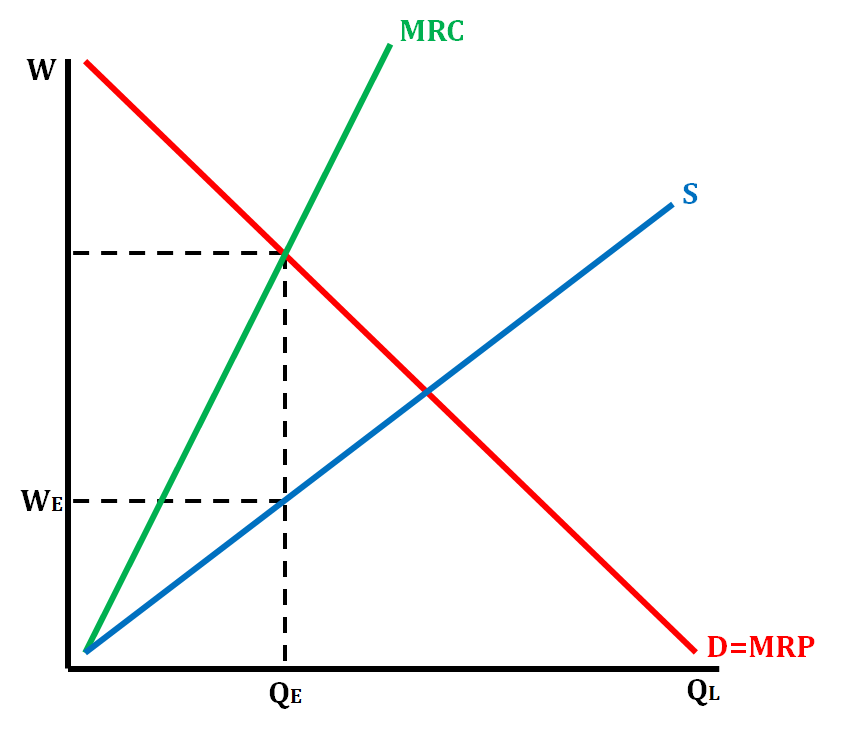
Monopsony
* An imperfectly competitive factor market where only one firm buys resources
* A market with one buyer and many sellers
* A market with one buyer and many sellers
25
New cards
Characteristics of a Monopsony
* One, large firm hires all laborers in a single labor market
* Imperfectly competitive market
* Firm is a wage maker
* MRC > Supply
* When you hire an additional worker, you must pay them a higher wage, but you cannot price discriminate so you take the cost of the additional worker and raising the wages of all previous workers
* Firm will hire Quantity of Labor at MRP = MRC
* Firm will pay workers a wage they are willing and able to work for below their MRP
* Imperfectly competitive market
* Firm is a wage maker
* MRC > Supply
* When you hire an additional worker, you must pay them a higher wage, but you cannot price discriminate so you take the cost of the additional worker and raising the wages of all previous workers
* Firm will hire Quantity of Labor at MRP = MRC
* Firm will pay workers a wage they are willing and able to work for below their MRP
26
New cards
Graph of a Monopsony
* D = MRP