Tutorial #22: Energy (III)- Photosynthesis I (Light-dependent Reactions)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
photosynthesis
light energy is converted to chemical energy
how are chemoheterotrophs dependent on photoautotrophs?
dependent on photoautotroph's ability to transform light energy into chemical energy via photosynthesis
true or false: algae and phytoplankton produce as much, if not more, oxygen than plants.
true---algae and phytoplankton produce 90% of oxygen content in atmosphere
true/false: only plants & some protists can undergo photosynthesis
false--some bacteria can undergo photosynthesis
cellular respiration
(catabolic or anabolic)?
sugar + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy to do cellular work
(catabolic)

Photosynthesis equation
(catabolic or anabolic)?
light energy + carbon dioxide + water --> oxygen + sugar
(anabolic)
what do plants have that enable them to carry out photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
chloroplasts & mitochondria
true or false: plants undergo photosynthesis, but not cellular respiration--meaning that the majority of ATP is produced within the chloroplasts?
false--
photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts = glucose + O2
cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria O2 --> ATP
majority of ATP plant uses for growth & maintenance is produced by cellular respiration in mitochondria
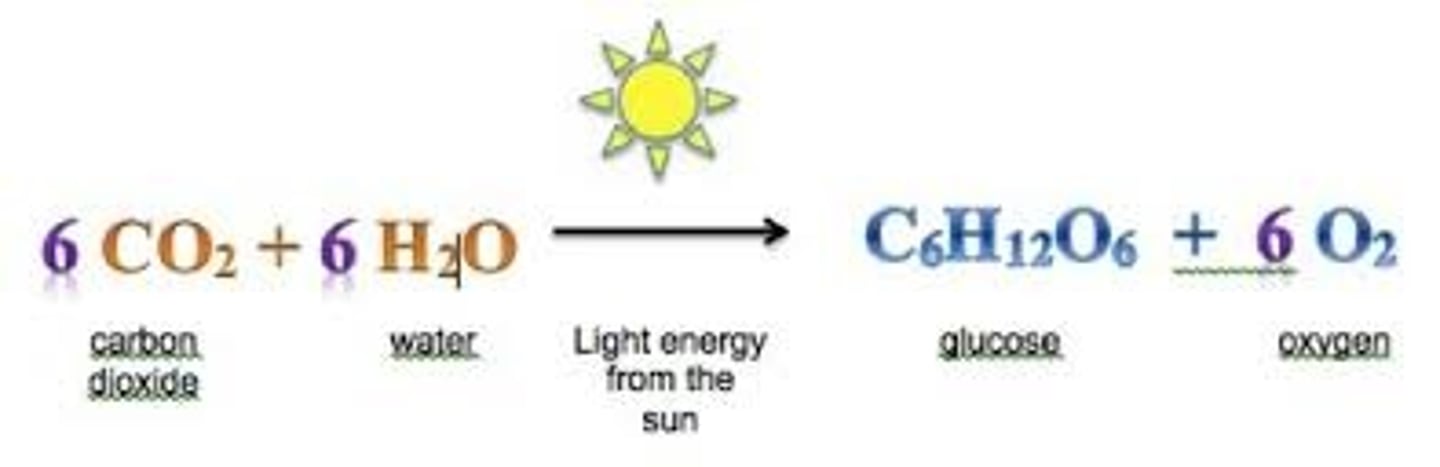
What is the result of photosynthesis in the form of an equation?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
in photosynthesis, what is being oxidized and what is being reduced?
oxidized: H2O --> O2
reduced: CO2 --> glucose
visible light
portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that has wavelengths detectable by the human eye (400-700nm)
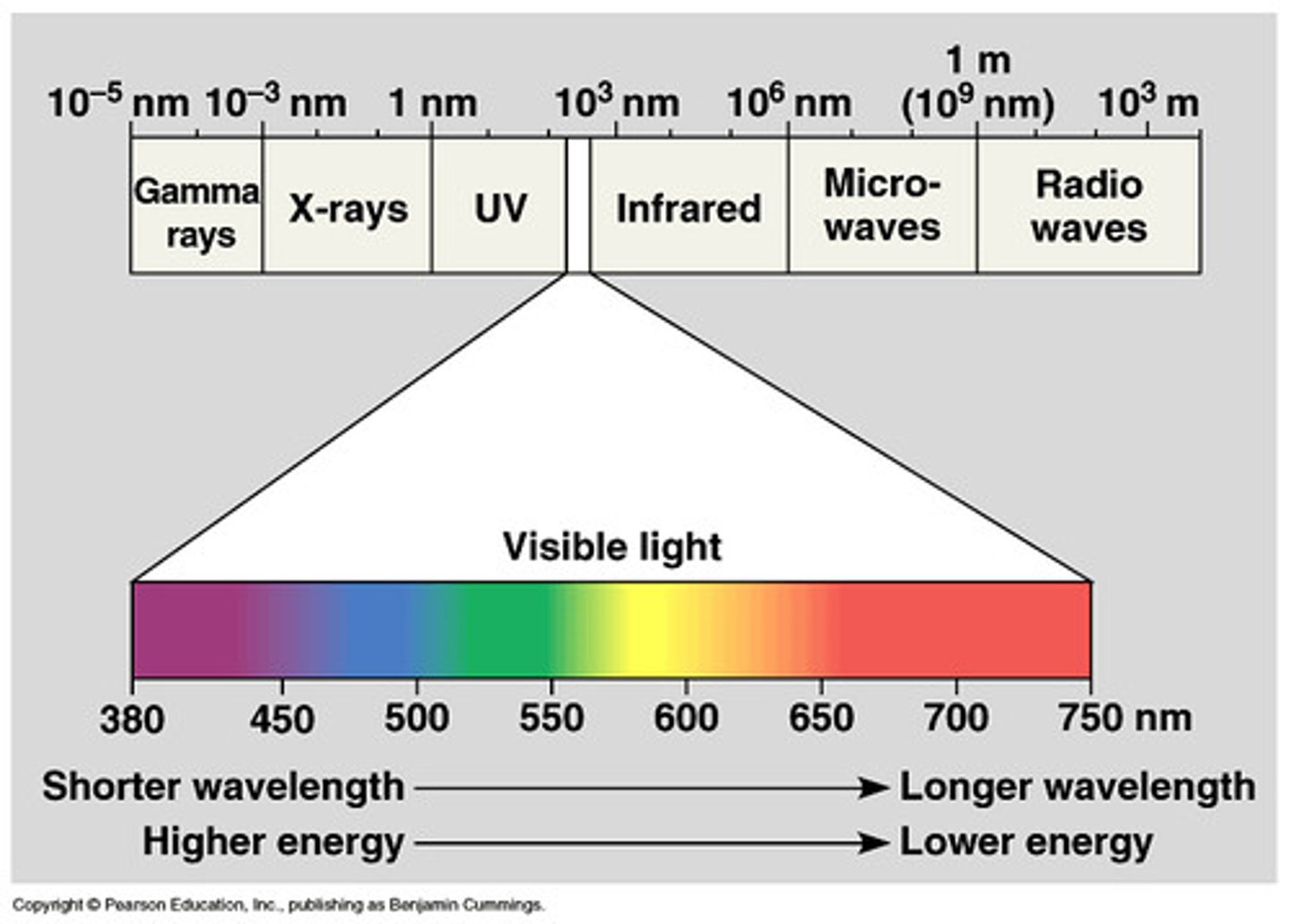
How does sunlight travel to a plant leaf?
sunlight travel through space as electromagnetic radiation (visible light)
light radiates to plant light through photons and reaches leaf's surface
light is absorbed by chlorophyll inside chloroplasts, wavelength of light will be reflected
how do plants use light as discrete packets of energy?
photons-- pigments absorb photons and excites electrons
electrons --> electron transport chain
make ATP, reduce NADP, power Calvin Cycle
which wavelengths have the lowest relative light absorbance for all pigments? why is this important in terms of visual appearance of a typical plant?
green pigments have the lowest relative light absorbance
- this is why leaves appear green because green light is mostly reflected, not absorbed
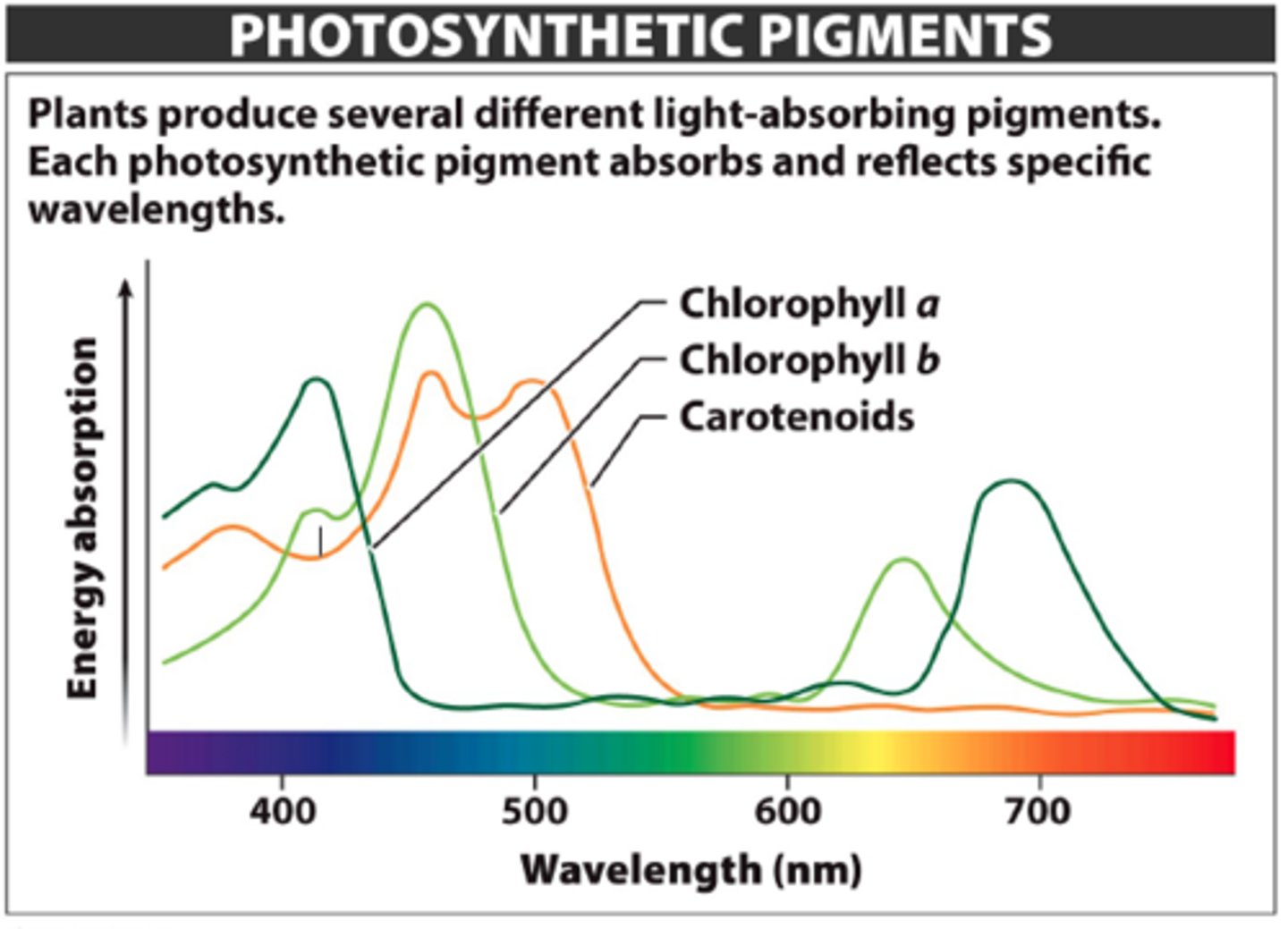
pigments
compounds that absorb light
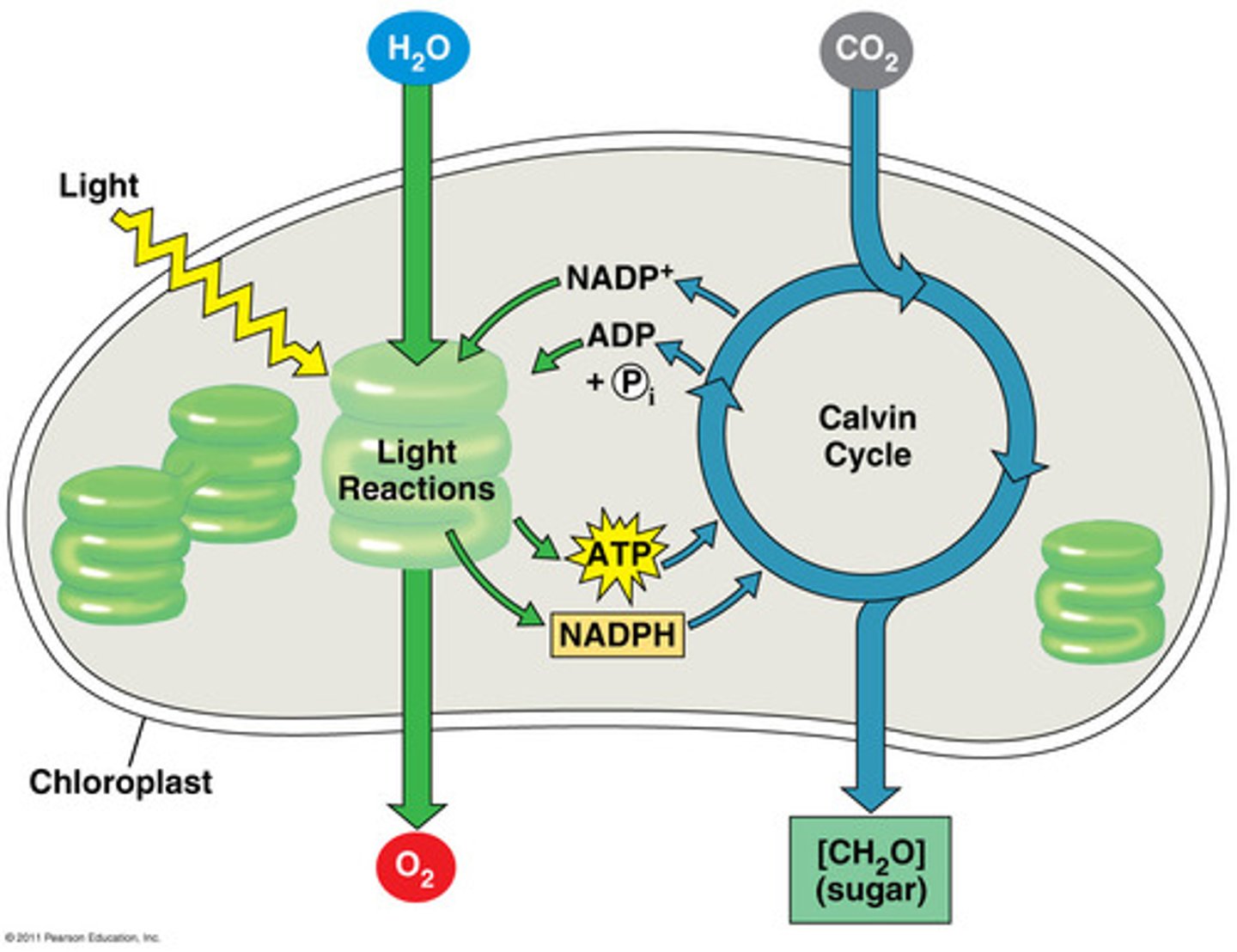
where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur?
thylakoids of chloroplasts
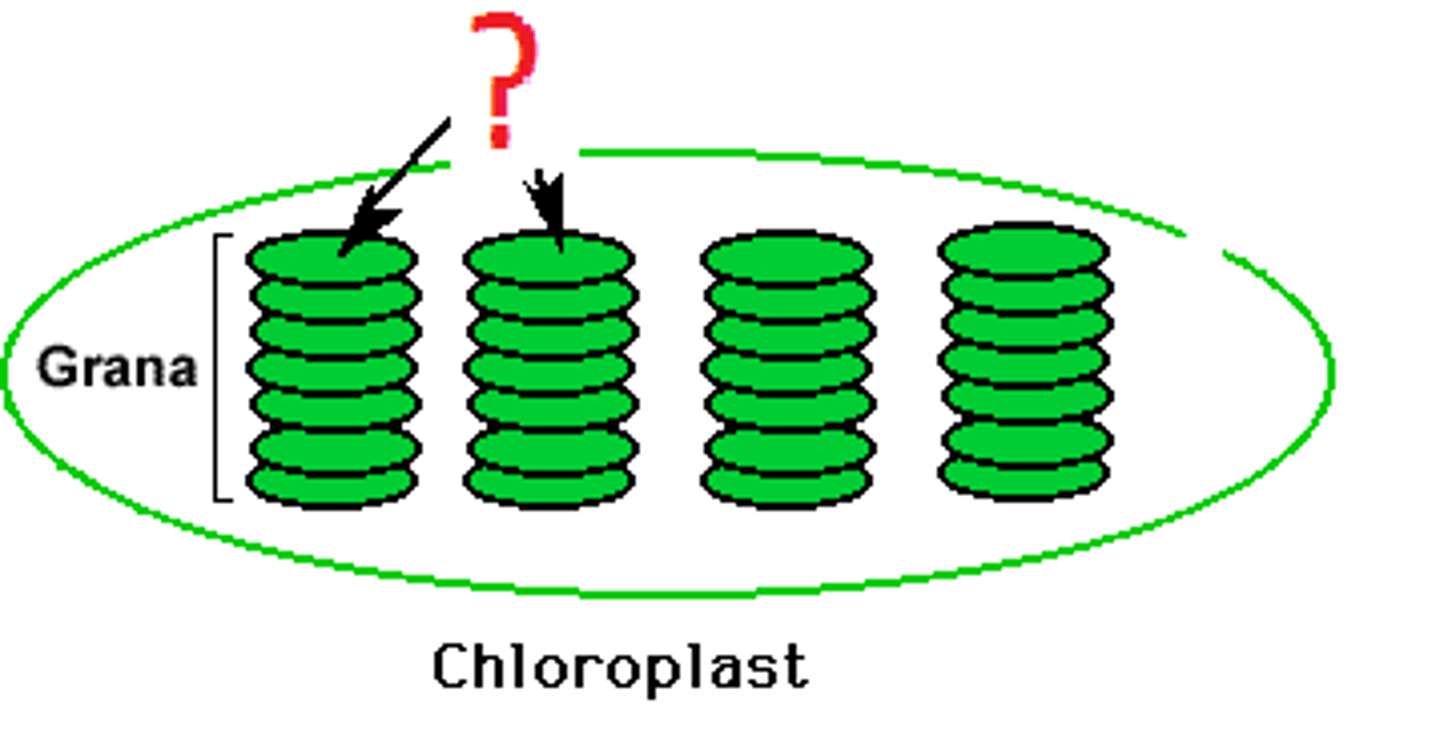
Thylakoids
saclike photosynthetic membranes
- contain essential components (pigments & electron transport chains) of light reactions of photosynthesis
photosystem
chemical system in plants and other photosynthetic organisms in which chlorophyll absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
photosystem I
Transfers electrons, makes NADPH
occurs after PSII
- does not produce oxygen
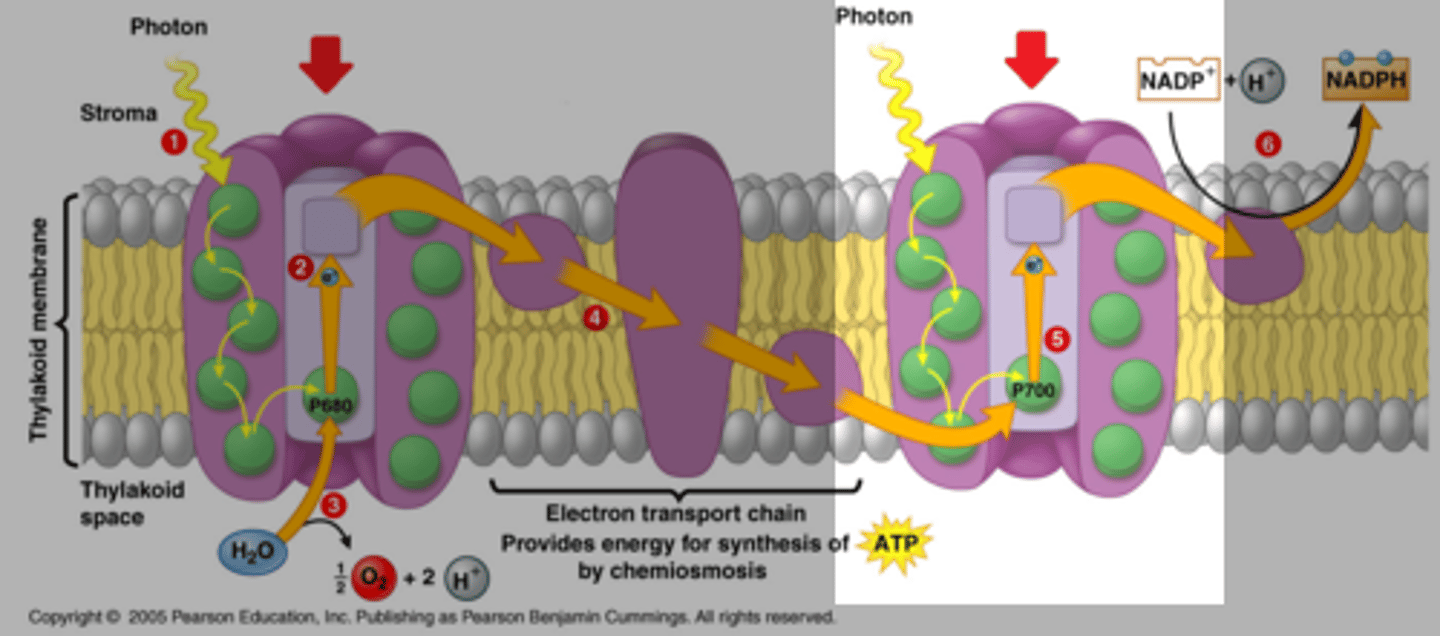
photosystem II
splits a water molecule to produce oxygen, electrons and hydrogen ions
- source of electrons come from water
products: ATP
- occurs first
how are PSI and PSII similar?
both absorb light and use it to excite electrons
- power light-dependent reactions
ATP + NADPH --> Calvin Cycle
z-scheme
a model depicting the series of energy changes of an electron during the light reactions of photosynthesis. The electron absorbs light energy twice, resulting in an energy curve with a zigzag shape (electrons excited to higher energy states, fall back down in energy, then excited again)
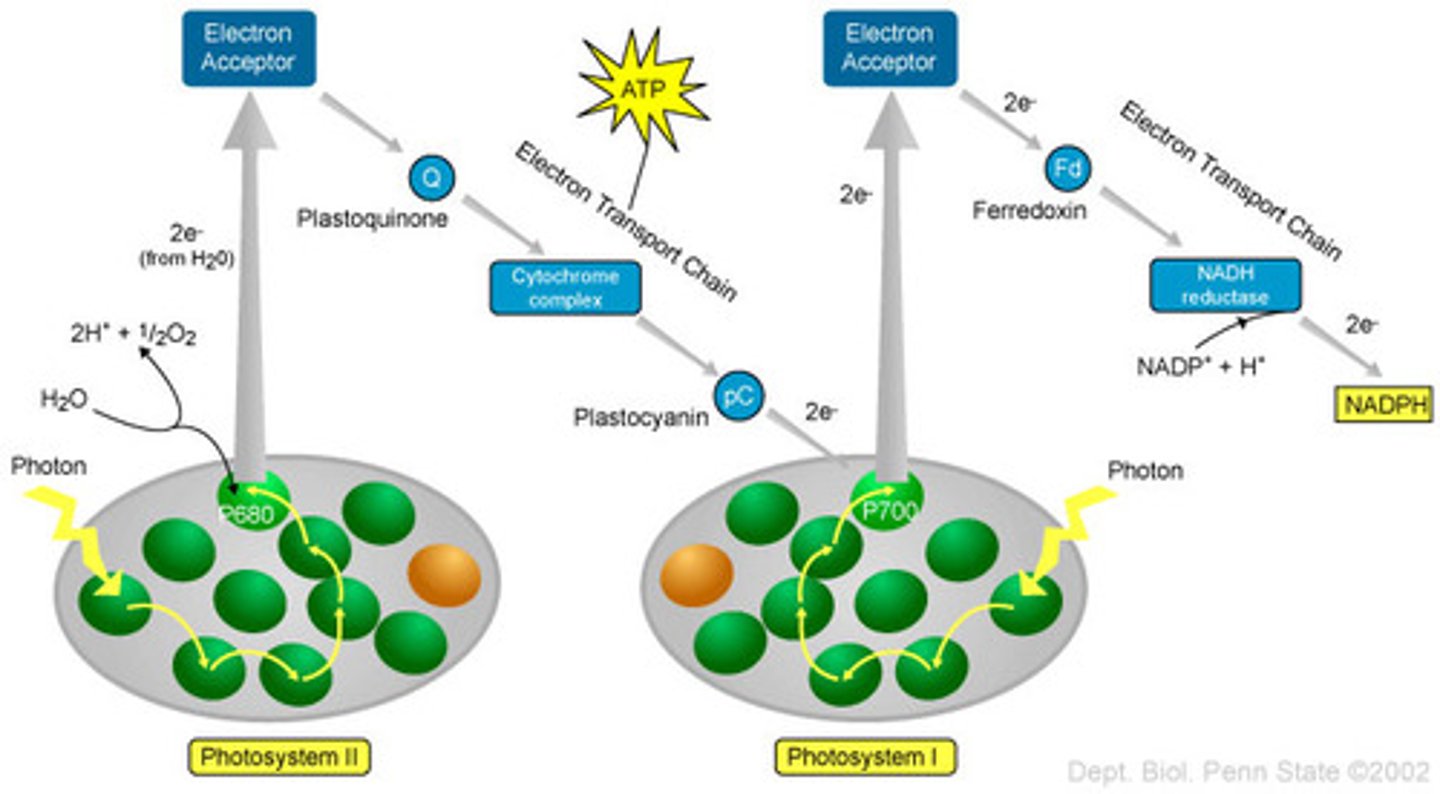
what is the source of electrons that move through the photosystems to NADPH?
water (PSII splits water & those electrons released enter ETC and generate proton gradient)
- electrons are transferred to NADP+ at PSI to form NADPH
what is the source of oxygen produced in photosynthesis?
water
2 H2O --> 4H+ + 4e- + O2
oxygen released as byproduct
summarize z scheme movement of electrons
H2O --> PSII --> ETC --> PSI --> NADP+ ---> NADPH (+ ATP & O2)
why do plants need water for photosynthesis?
as a source of electrons for the reduction of CO2 to sugar in Calvin Cycle
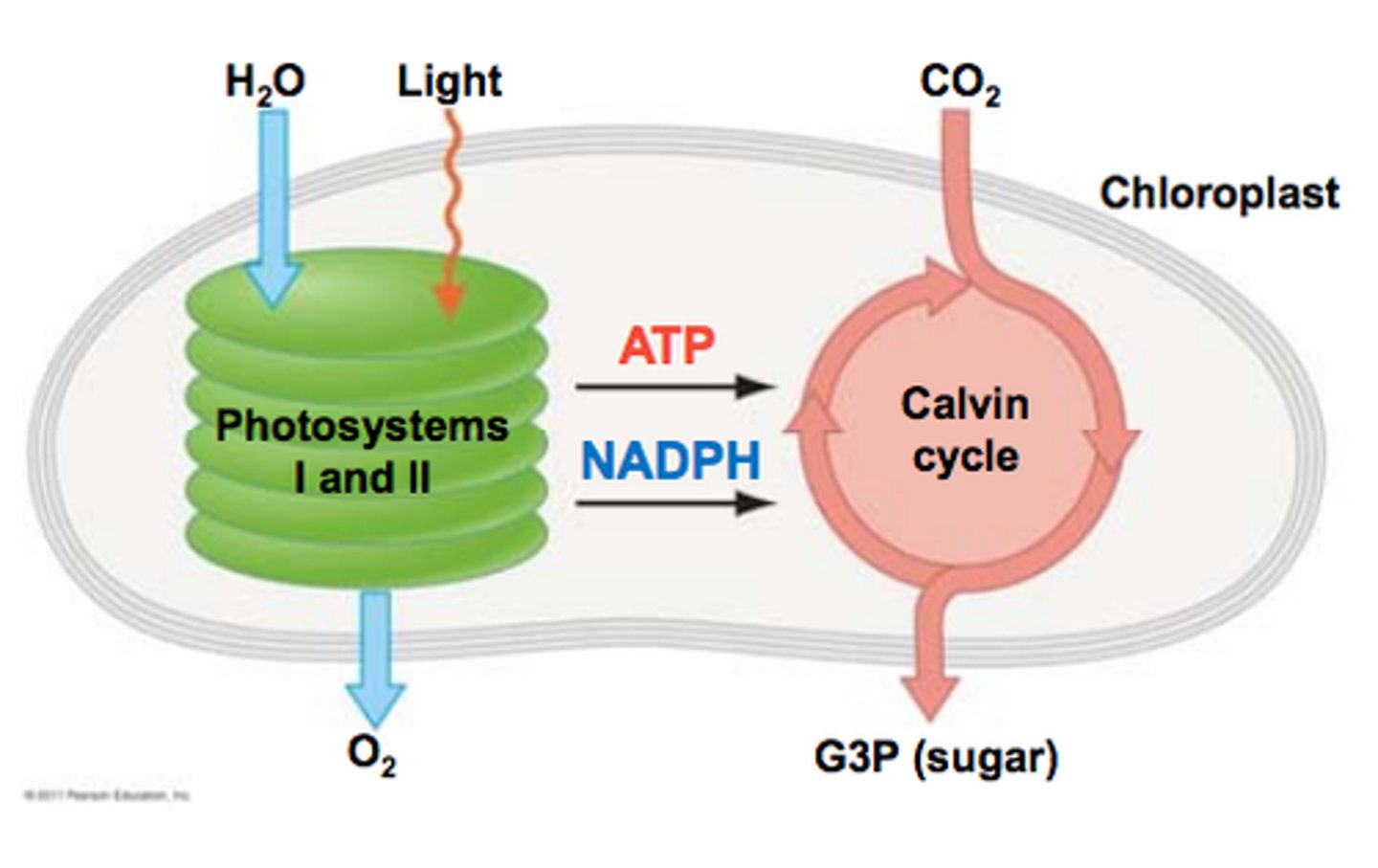
What is the function of NADPH and ATP in the process of photosynthesis?
used in light-independent reactions to make sugar and provide energy for chemical reactions
products of light-dependent reactions
ATP, NADPH, O2
Photophosphorylation
the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight
Does a plant cell use the ATP produced in the light-dependent reactions to drive metabolic processes outside of the chloroplasts?
No, ATP stays inside chloroplast and is used to power the calvin cycle
where is photosynthesis occurring in a plant?
in leaves
(all green parts of a plant contain chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll --a green pigment)
where do light dependent reactions occur?
thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Where do light independent reactions occur?
stroma of the chloroplast