Psychology - Biopsychology
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the divisions of the nervous system
Nervous system
CNS
Peripheral nervous system
Autonomic and somatic nervous system
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
What are the functions of the nervous system
Consists of CNS and PNS and communicates via electrical signals.
fast acting and short term effects
Two roles:
Processes and responds to information from the environment
Coordinates the working of different glands and organs
What is the CNS
involves complex processing
consists of the brain (responsible for conscious and most unconscious processing)
consists of spinal cord (receives and transmits information and some reflex processing)
What is the PNS
neurones transmit impulses to and from CNS
sensory - to CNS
motor - away from CNS
What is autonomic nervous system
unconscious, involuntary system
governs vital functions in the body such as breathing and heart rate
What is somatic nervous system
conscious, voluntary system
governs muscle movement and receives information from sensory receptors
What is sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
S → increases bodily functions, releases adrenaline to prepare body for fight or flight, increases heart rate and breathing rate, dilates pupils and inhibits digestion and saliva production
PS → decreases bodily functions, decreases heart and breathing rate, contracts pupils and stimulates digestion and saliva production
What is the endocrine system
It instructs glands to release hormones which act on target cells
Communicates via chemicals
It acts slowly but has widespread and long-term effects
Outline the fight or flight response
The body senses a stressor and the amygdala reacts
The amygdala sends signals to the hypothalamus which activates the sympathetic nervous system, and the adrenal medulla releases adrenaline
Adrenaline induces sympathetic state which causes changes such as: increased heart and breathing rate, dilated pupils and inhibited digestion and saliva production
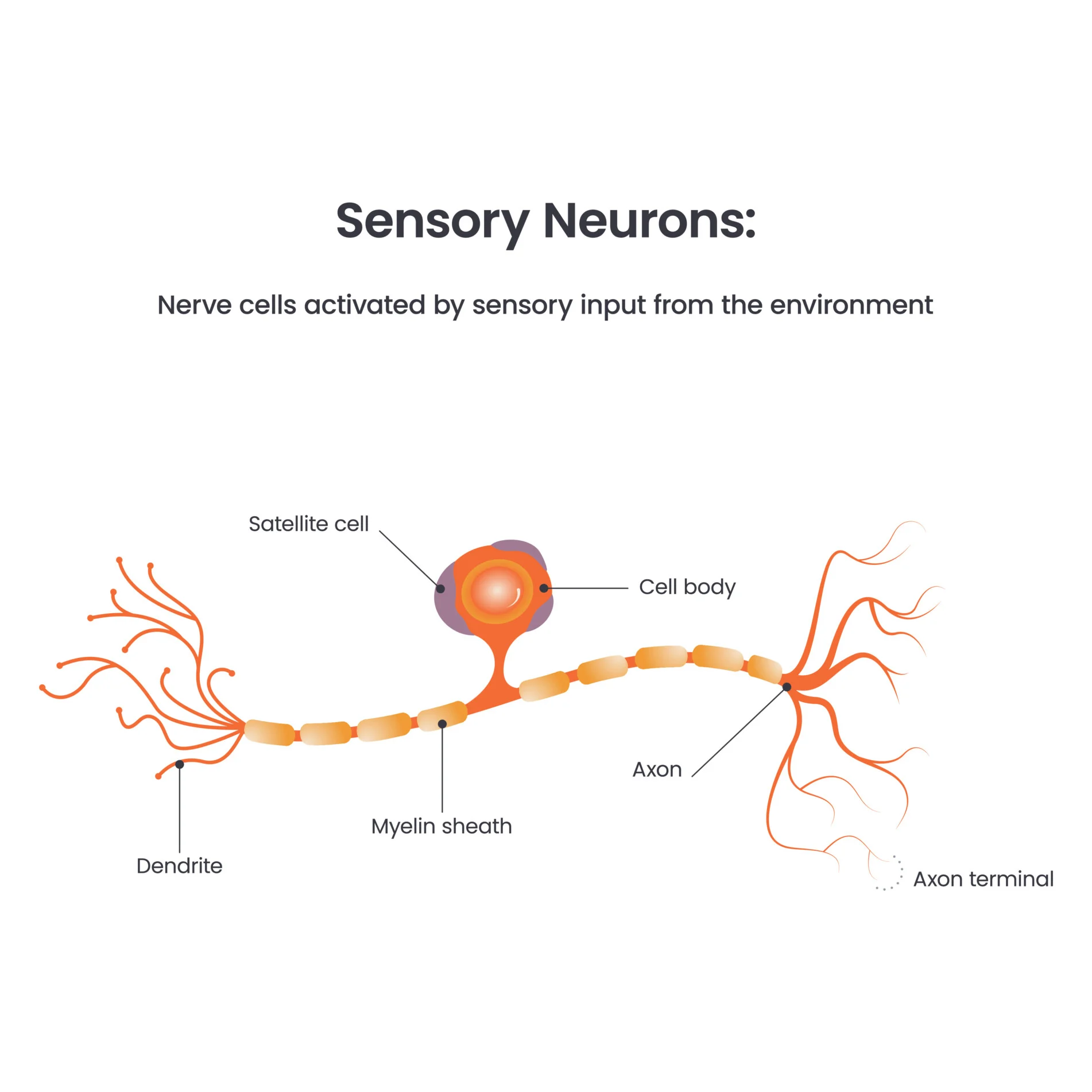
Structure and function of sensory neurone
long dendrites and short axon
unipolar → only one process extends from cell body
detects sensations from sensory site and sends action potential to CNS along myelinated axon
found in various locations around body
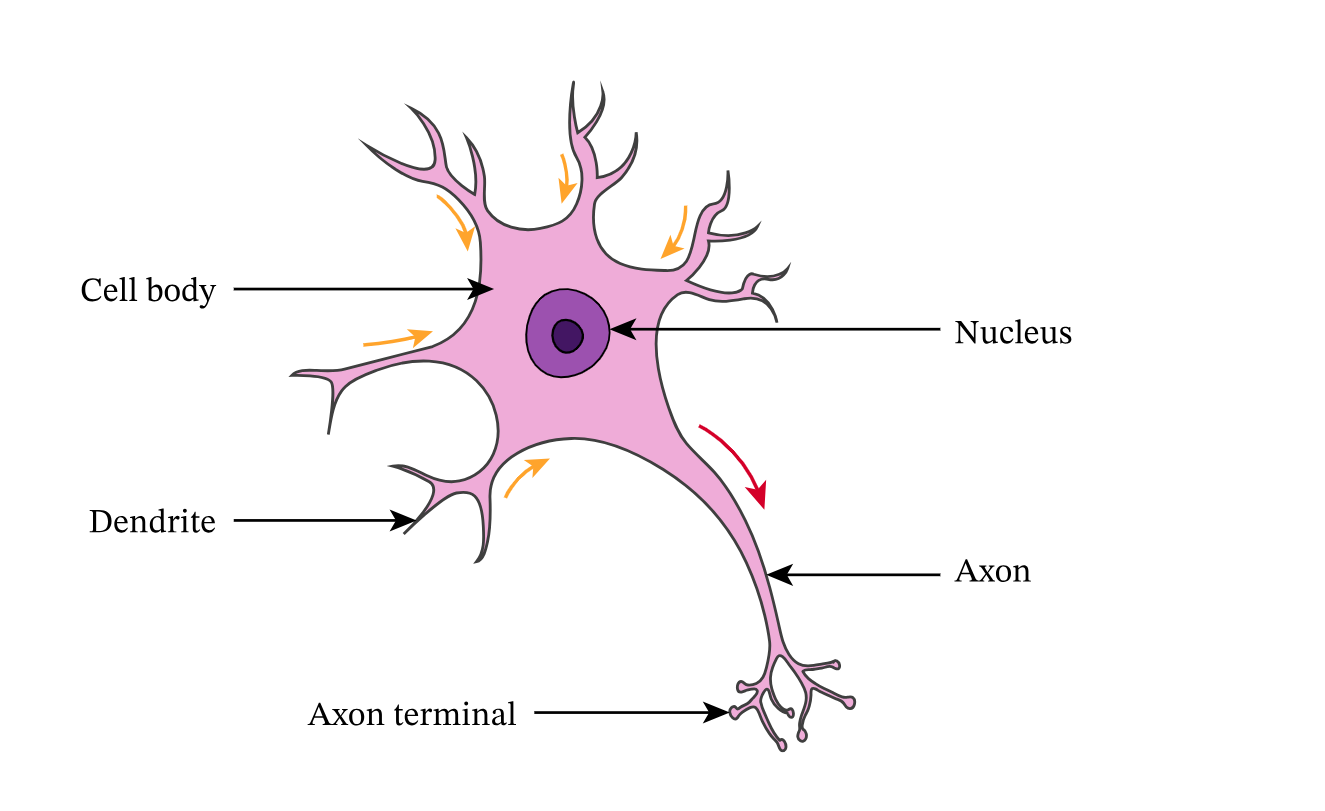
Structure and function of relay neurone
short dendrites and no myelinated sheath
found in CNS
communicator between sensory and motor neurone
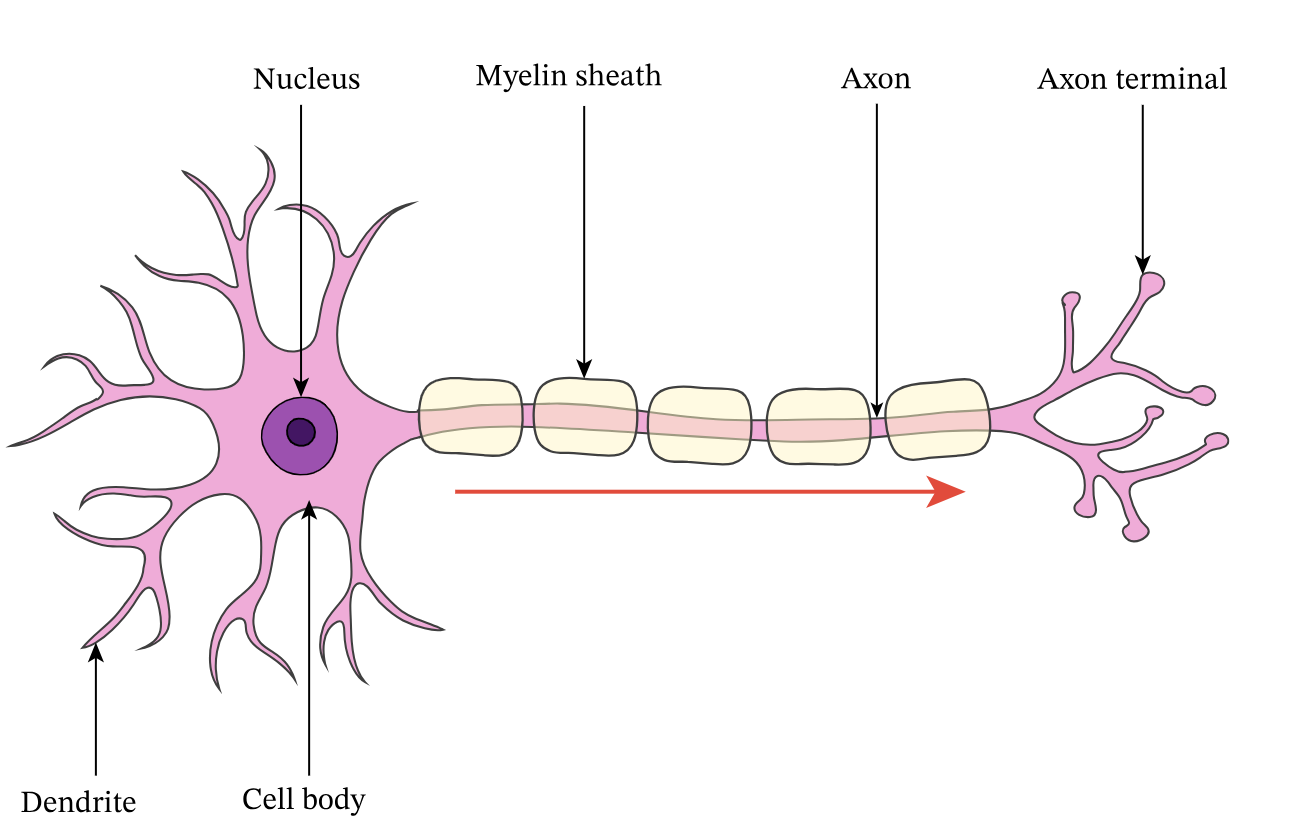
Structure and function of motor neurone
short dendrites and long axon
begins in CNS and projects to muscles
detects signal from relay neurone in CNS via synaptic transmission and sends to effector along myelinated axon to contract
Describe the structure and function of a neuron (6)
neurons enable communication within the nervous system
the soma in the cell body contains the genetic material
dendrites extend from cell body and receive information from other neurons
axons, which can be myelinated to increase speed of transmissions, carry messages away from cell body
axon terminals contain neurotransmitters
What is a synapse
junction where 2 neurons meet
What is a neurotransmitter + types
chemical messages released by neurones
excitatory → increases likelihood of neurone firing action potential
inhibitory → decreases likelihood of neurone firing action potential
Outline synaptic transmission
Action potential reaches presynaptic neurone, causing it to release vesicles containing neurotransmitters to synaptic gap
Neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic gap and bind to receptors on postsynaptic membrane
Postsynaptic neurone releases another impulse along axon
Neurotransmitters return to presynaptic neurone via transport proteins via reuptake
What is localisation
theory that specific areas of the brain are associated with certain physical and psychological functions
What lateralisation
theory that certain hemispheres control certain physical and psychological functions
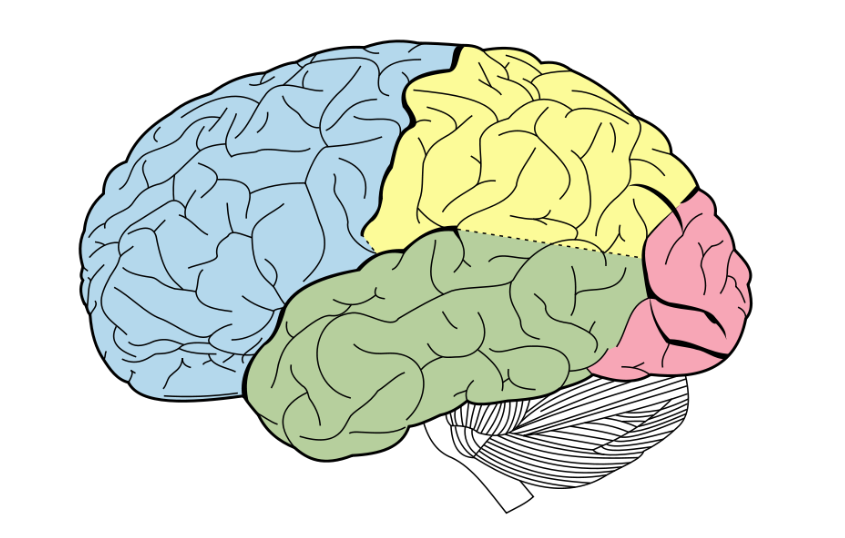
label ts
blue → frontal lobe
yellow → parietal lobe
green → temporal lobe
red → occipital lobe
Function of frontal lobe & area & cortex
controls cognitive activity
Broca’s area (in left frontal lobe) → language production, allows speech to be fluent
damage leads to Broca’s aphasia → difficulty producing speech
Motor cortex → controls voluntary movement
damage leads to loss of movement
Function of parietal lobe and cortex
processes sensory information and directs movement
Somatosensory cortex → processes sensory information from skin
Function of temporal lobe and area
processes auditory information and understanding speech
Wernicke’s area → language understanding, allows speech to be meaningful
damage leads to Wernicke’s aphasia → difficulty understanding language, but can produce it
Function of occipital lobe and cortex
processes visual information
Visual cortex → Each eye sends information from right visual field to left visual cortex and vice versa
AO3 for Localisation of function in the brain
✅Evidence from neurosurgery → cingulotomy isolates part of brain responsible for OCD
✅Evidence from brain scans → dual tasks show Broca and Wernicke’s areas are responsible for language during reading task and listening task
❌Language may not be localised to just Wernicke and Broca’s areas
❌Lateralisation is supported by case studies such as Phineas Gage
What is split brain research
the study of individuals whose corpus callosum have been severed