Psych 20 FINAL- Working Memory and executive function
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Recency effect
the ability to remember things better that were shown/said last (latest &short term)
Primacy Effect
The ability to remember things better that were said/shown first. (early on&long term)
Filled delay
waiting period after list that stops the recency effect from happening
Serial Position curve
states that primacy and recency will be the things most remembered
Anterograde amnesia
Inability to make new long term memory (stops primacy effect)
Bradley and Hitch model (1973)
working memory emphasizes the role of active maintenance and manipulation. Temporary workspace, highly integrated with sensory memory and attention
key components of cognitive abilities
Language, devious making, mental operations, Goal-directed behavior, consciousness
Span tests
used to test working memory (digit span)
Miller item capacity
7 (+/-) 2 items can be held in working memory at a time
Cowan Chunking Capacity
4(+/-)1 chunks (held in tong term memory) can be held at a time
Temporal grouping
spacing things out to make it more rhythmically memorable (Example: making it sound like a phone number )
Phonological loop
responsible for auditory information, including language
Word length effect
we recall fewer long words than short words in short term memory due to longer words taking longer to articulate and rehearse exhausting the loops 2 second capacity.
Visuospatial Sketchpad (VSSP)
responsible for visual and spatial information, (color, shape, location)
Chunking in VSWM
past experience and expertise helping us understand what we are looking at. (Example: Chess players remembering detailed chess positions)
Episodic buffer
temporary storehouse for audio/visual information, integrates info from Long term memory. (responsible for chunking)
central executive
responsible for coordinating systems, essentially deciding what to do with the information we are receiving. Also maintains rehearsal
homunculus argument
criticism of central executive: explaining something buy using that thing to explain it (its a fallacy)
Executive function
responsible for: willed attention, self regulation, sequence planning and executing sequential goal directed behavior, time management, impulse control (frontal cortex)
A-not-B error
showing kid that you are repeatedly putting a toy under a cloth, then suddenly show them you put it under another different cloth. If you ask the child where the toy is they will say the first one you showed them despite seeing that you put it under a new one.
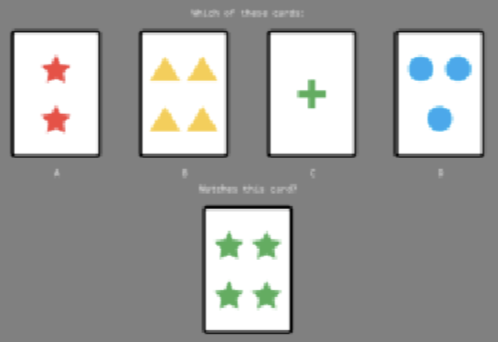
Wisconsin card sort test
Cards sorted into piles, rules are figured out through feedback, rules change without notice, we tend to keep using old rule despite us being told it no longer works
delaying gratification
related to executive function, need to inhibit behavior now fr better reward later (example: kids marshmallow test)
Poor working memory
Major depression, schizophrenia, Parkinson, dementia
Alcohol and executive function
Acts as a neural inhibitor, reduces activity in frontal cortex so it lowers EF abilities
IQ test
tested Working memory capacity
Engle (2004) factor analysis of Working memory
found genera fluid intelligence is a predictor of many other IQ test as well as academic performance (likely genetic component)
Improving intelligence
can brain train to increase WM capacity and focus HOWEVER only kinda works on general fluid intelligence.