Chapter 5- Chapter 6 (MC Graw Hill: Chemistry Matter and Change)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 5- 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Electro Magnetic Radiatiom
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space.
Characteristics of Waves
Wavelength, Frequency, Amplitude
Wavelength(λ)
the shortest distance between equivalent point on a continuous wave.Measured by crest to crest.
Wavelength are expressed in?
Meters, centimeters, and, nanometers
Frequency(v)
Is the number of waves that pass a given point per second.
Frequency is expressed in?
Hz, 1/s, s-1
Amplitude
is the wave’s height from the origin to the crest .
Electromagnetic Wave Relationship
c=λv
Speed of light
3.00×108
Wavelength and Frequency are(relationship)?
inversely related. Which means as one increases the other decreases
Visible Light
White Light
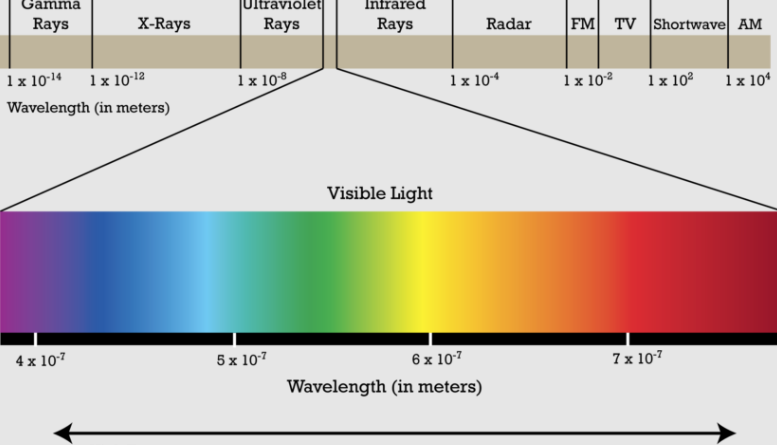
EM( Electro Magnetic Spectrum)
.
Temperature of an object
is a measure of average kinetic energy of its particles
Max Planck
Matter can gain or lose energy in small specific amounts called quanta
Quantum
is the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
Energy of a Quantum
E = hV
(E = energy, h = Planck's constant, V = frequency)
Planck’s Constant
6.626 × 10-34 J*s
Energy sign
J
Velocity
meters * second m/s
Photoelectric effect
electrons ,called photoelectrons, are emitted from from a metel’s surface when light of a certain frequency or higher shines on the surface.
Einstein dual light nature
a beam of light has wavelike and particle like properties.
Photon
is a massless particle that carries a quantum energy.
Energy of a photon
E = hv
E = energy of the photonh = Planck's constant (6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ J·s)v = frequency of the photon