Kaarten: Introduction to English Linguistics and Grammar: Phonetics and Phonology | Quizlet
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Phones
speech sounds
Phonetics
study of speech sounds (physical aspect)
articulatory phonetics
the study of the way speech sounds are produced by the vocal organs of the speaker
acoustic phonetics
the study of the physical properties of speech sounds i.e. their transmission as sound waves through the air
auditory phonetics
the studyy of the way speech sounds are picked up and identified by the listener's auditory apparatus
Bilabial
contact between upper and lower lips [w m b p]
labio-dental
lower lips touching the upper teeth [f v]
(Inter)dental
tongue tip between upper and lower teeth or close to upper teeth [θ ð]
alveolar
tongue blade close to the alveolar ridge [l n s t d z]
post-alveolar
tongue tip close to just behind the alveolar ridge /r/
retroflex
tongue tip curled back to well behind the alveolar ridge /r/
palato-alveolar
tongue blade close to alveolar ridge, with simultaneous raising of the front of the tongue towards the hard palate [ ʃ ʒ]
palatal
front of the tongue close to the hard palate [j]
velar
back of the rongue raised against the velum [k g ŋ]
glottal
using the glottis to make audible friction [h]
plosive or stop
The airstream is completely blocked off at some point in the vocal tract, causing air pressure to build up behind the closure which, when suddenly released, causes the air to explode outwards. The velum is raised to prevent the air from escaping through the nose. [p b t d k g]
nasal
The velum is lowered while the oral cavity is momentarily blocked off completely at some point in the vocal tract, causing the air to be channeled through the nose. [ n m ŋ]
affricate
The airstream is completely blocked off at some point in the vocal tract, causing air pressure to build up behind the closure which is then released relatively slowly with friction. The velum is raised to prevent air from escaping through the nose [tʃ dʒ]
lateral (only type of partial closure in RP)
Made by the blade of the tongue touching the alveolar ridge, the air being free to flow along one or both sides of the contact [l]
fricative
the vocal tract is narrowed at some point to such a degree that friction is produced as the air escapes [f v s z θ ð ʃ ʒ h]
approximant
the articulation involves a light contact or near-contact at some point in the vocal tract to the extent that very little or no friction is produced (even in case of light contact). [w j r]
liquids
the air flows around an obstruction caused by the tongue [l] and retroflex /r/
Semi-vowels / semi-consonants / glides
the phones have properties of both vowels and consonants [j w]
sibilants/stridents
consonants with a sharp hissing sound caused by a narrow groove in the tongue [s z ʃ ʒ tʃ dʒ]
tongue height (vowels)
the degree of raising/lowering of the tongue in the oral cavity and the resulting degree of openness of the oral cavity (high/close, mid-high/half-close, mid-low/half-open, low/open)
part of tongue (vowels)
the part of the tongue that is raised or lowered (front, central, back)
cardinal vowel system
schematic representation of the oral cavity in terms of two dimensions
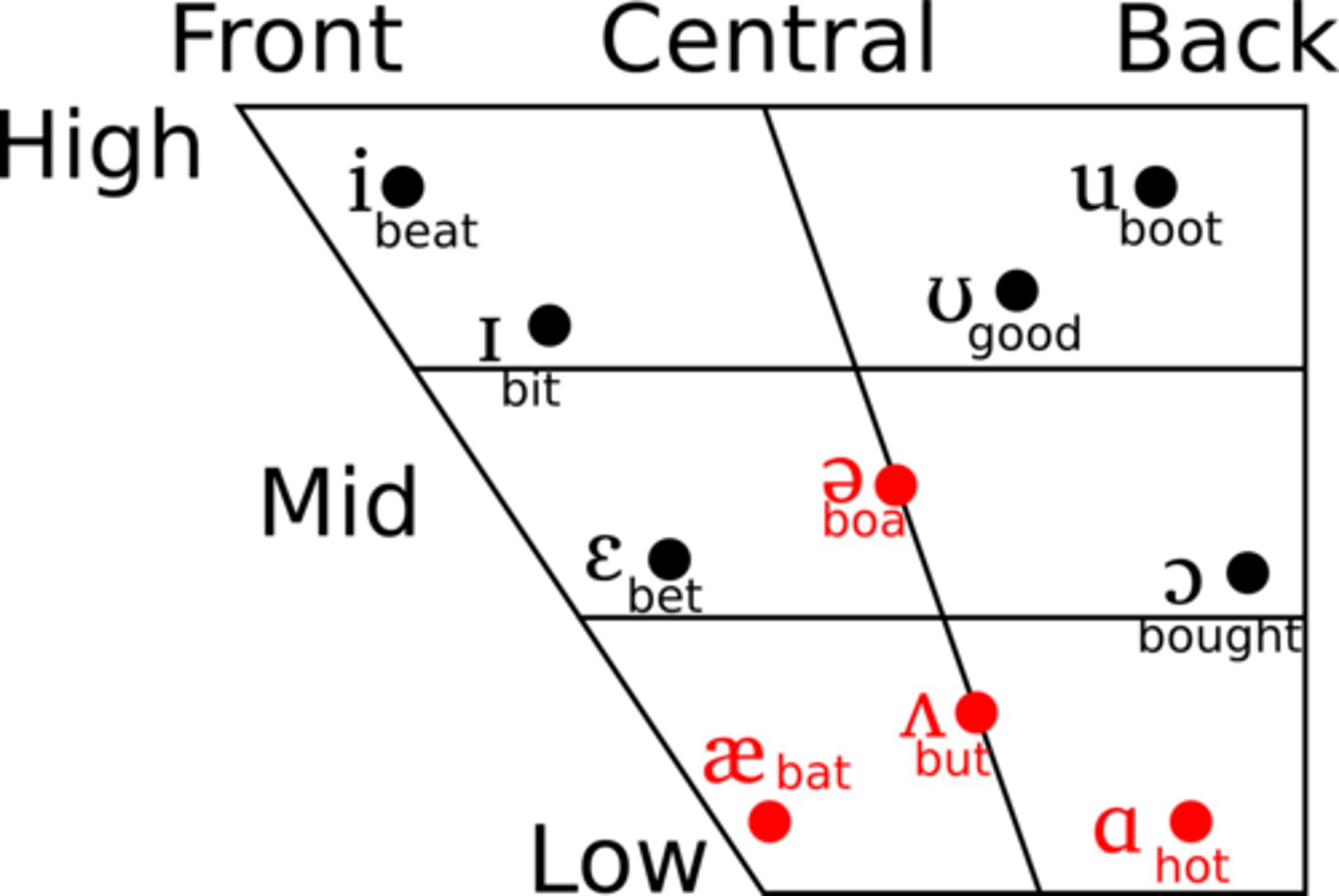
Monophthongs
They are made by moving the tongue towards one particular position in the oral cavity. They maintain their basic quality throughout their articulation.
diphthongs
Complex vowel sounds with diffrent beginnings and endings as the tongue glides from one point of articulation to another point without interruption. Two distinct vowel sounds can be perceived. (They still count as one phone)
Rounded position (lips)
the lips are pushed forwards in the shape of a circle [ɒ ɔː ʊ uː]
unrounded position (lips)
the lips are either spread, with the corners being moved away from each other [iː ɪ e æ], or in neutral position [ɜː ə ʌ ɑː]
vowel length
relative duration of the vowel. Indicated by diacritic lenghtening marker with monophthongs [ː] => long vowels. All diphthongs are long vowels.
nasality
refers to the absence or presence of nasal resonance in the production of a speech sound. RP does not have these kind of vowels.
Phonology
the study of speech sounds (abstract sound systems)
Phonemes
any sound which brings about a diffrence in sound
contrastive
two sounds are ... if changing one sound in a word to the other changes the meaning of the word.
minimal pairs
two words in the language with diffrent meanings which differ only in one sound.
Allophones
positional variants of a phoneme
aspiration
produced with a forceful puff of air
non-releasing of plosives
unreleased stops, happens when the burst of air after a complete closure (like for /p/, /t/, /k/) isn't heard, common at the end of words or before other stops
nasalization
when certain vowels and consonants precede a nasal consonant they may assume a slight nasal quality.
syllable
the smallest possible systematic cluster of phonemes in a language
phonotactics
sub-field of phonology which studies the pinciples that determine the permissible and non-permissible phoneme sequences.
stress
refers to the relative muscalar force and resulting amount of breath with which a speech segment is articulated.
intonation
refers to variations in pitch and stress that are related to diffrences in sentence meaning.
assimilation
process wherreby adjacent sounds influence each other so that they become more alike
anticipatory (or regressive) assimilation
the articulation of a given sound is influenced by the articulation of the following sound.
progressive assimilation
the articulation of a given sound is influenced by the articulation of the preceding sound.
coalescence
two adjacent sounds fuse into a new single element
elision
non-articulation or omission of a phoneme in rapid speech. This is for both vowels and consonants
gradation
a small set of grammatical function words can have a strong and a weak pronounciation depending on the degree of force or stress with which they are articulated. The strong form is used when the word is pronounced in isolation or or with emphasis. In all other instances, the weak variant is more common.
Liaison
articulation of an otherwise silent or non-occurring sound in between words to help them run more smoothly.
Nog leren (7)
Je hebt een begin gemaakt met het leren van deze termen. Hou vol!