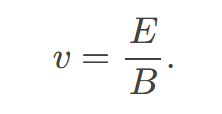Chapter 22: Magnetism
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Ampere’s Law
the physical law that states that the magnetic field around an electric current is proportional to the current; each segment of current produces a magnetic field like that of a long straight wire, and the total field of any shape current is the vector sum of the fields due to each segment
B-Field
another term for magnetic field
Biot-Savart Law
a physical law that describes the magnetic field generated by an electric current in terms of a specific equation
Curie Temperature
the temperature above which a ferromagnetic material cannot be magnetized
Direction of magnetic field lines
the direction that the north end of a compass needle points
domains
regions within a material that behave like small bar magnets
electromagnet
an object that is temporarily magnetic when an electrical current is passed through it
electromagnetism
the use of electrical currents to induce magnetism
ferromagnetic
materials, such as iron, cobalt, nickel, and gadolinium, that exhibit strong magnetic effects
gauss
G, the unit of the magnetic field strength; 1G=10–4T
Hall effect
the creation of voltage across a current-carrying conductor by a magnetic field
Hall emf
the electromotive force created by a current-carrying conductor by a magnetic field, 𝜀=Blv

Lorentz Force
the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field
magnetic field
the representation of magnetic forces

magnetic field lines
the pictorial representation of the strength and the direction of a magnetic field
magnetic field strength (magnitude) produced by a long straight current-carrying wire
defined as 𝐵=𝜇0𝐼2𝜋𝑟, where 𝐼 is the current, 𝑟 is the shortest distance to the wire, and 𝜇0 is the permeability of free space
magnetic field strength at the center of a circular loop
defined as 𝐵=𝜇0𝐼2𝑅 where 𝑅 is the radius of the loop
magnetic field strength inside a solenoid
defined as 𝐵=𝜇0𝑛𝐼 where 𝑛 is the number of loops per unit length of the solenoid (𝑛=𝑁/𝑙, with 𝑁 being the number of loops and 𝑙 the length)
magnetic force
the force on a charge produced by its motion through a magnetic field; the Lorentz force
magnetic monopoles
an isolated magnetic pole; a south pole without a north pole, or vice versa (no magnetic monopole has ever been observed)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
a medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields create detailed images of internal tissues and organs
Magnetized
to be turned into a magnet; to be induced to be magnetic
magnetocardiogram (MCG)
a recording of the heart’s magnetic field as it beats
magnetoencephalogram (MEG)
a measurement of the brain’s magnetic field
Maxwell’s equations
a set of four equations that describe electromagnetic phenomena
meter
common application of magnetic torque on a current-carrying loop that is very similar in construction to a motor; by design, the torque is proportional to 𝐼 and not 𝜃, so the needle deflection is proportional to the current
motor
loop of wire in a magnetic field; when current is passed through the loops, the magnetic field exerts torque on the loops, which rotates a shaft; electrical energy is converted to mechanical work in the process
north magnetic pole
the end or the side of a magnet that is attracted toward Earth’s geographic north pole
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
a phenomenon in which an externally applied magnetic field interacts with the nuclei of certain atoms
Permeability of free space
the measure of the ability of a material, in this case free space, to support a magnetic field; the constant 𝜇0=4π×10−7T⋅m/A
Right Hand Rule 1 (RHR-1)
the rule to determine the direction of the magnetic force on a positive moving charge: when the thumb of the right hand points in the direction of the charge’s velocity 𝐯 and the fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field 𝐁, then the force on the charge is perpendicular and away from the palm; the force on a negative charge is perpendicular and into the palm
Right Hand Rule 2 (RHR-2)
a rule to determine the direction of the magnetic field induced by a current-carrying wire: Point the thumb of the right hand in the direction of current, and the fingers curl in the direction of the magnetic field loops
Solenoid
a thin wire wound into a coil that produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it
South magnetic pole
the end or the side of a magnet that is attracted toward Earth’s geographic south pole
tesla
T, the SI unit of the magnetic field strength; 1T=1NA⋅m
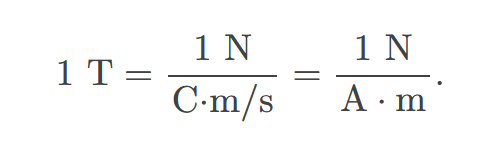
Magnetic Force (Circular Motion)
Magnetic force can supply centripetal force and cause a charged particle to move in a circular path of radius
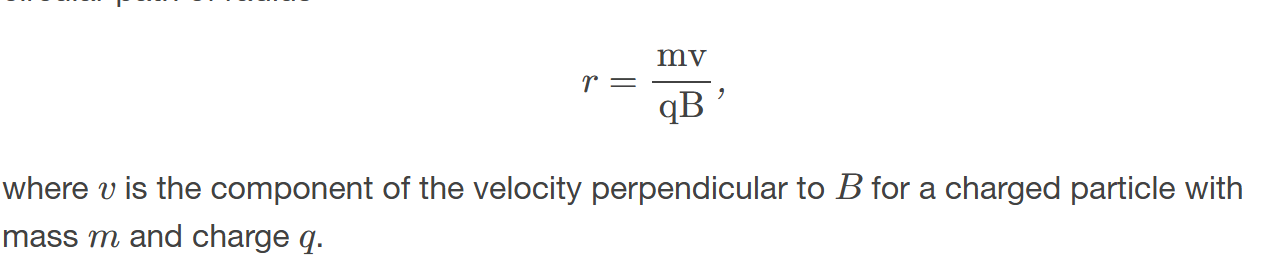
Magnetic force on current-carrying conductors
is the force experienced by a conductor carrying an electric current in a magnetic field, resulting in motion perpendicular to both the current and the magnetic field direction.

The torque 𝜏 on a current-carrying loop of any shape in a uniform magnetic field.
is the measure of the tendency of the loop to rotate due to the magnetic field, dependent on the current, area of the loop, and the strength of the magnetic field.
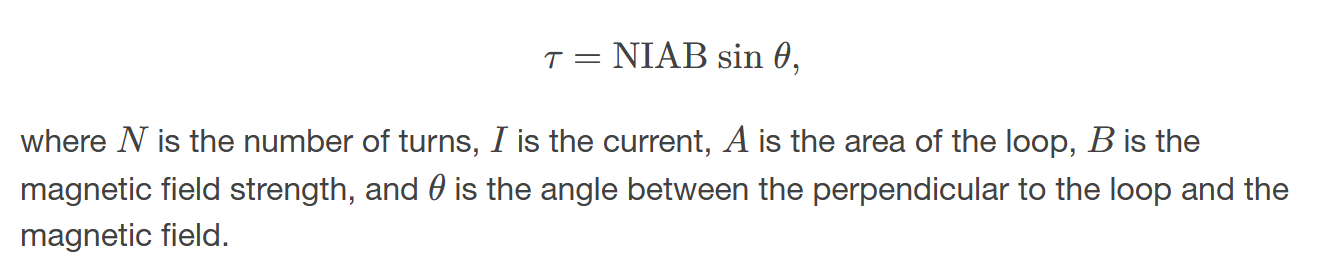
The force between two parallel currents 𝐼1 and 𝐼2, separated by a distance 𝑟, has a magnitude per unit length
equal to (\frac{{\mu0 I1 I_2}}{{2\pi r}}) in a vacuum.
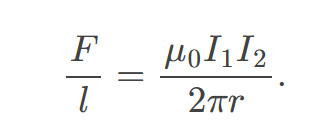
velocity filter of crossed electric and magnetic fields
is a device that uses electric and magnetic fields to select charged particles based on their velocity, allowing only those with a specific speed to pass through while filtering out others.