electricity
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is charge(Q) measured in
coulombs (C)
what is current(I) measured in
amps/amere (A)
what is time(t) measured in
seconds (s)
what is resistance(R) measured in
ohms (Ω)
what is power(P) measured in
watts (w)
what is energy(E) measured in
joules (j)
what is potential difference(V) measured in
volts (v)
how to you calculate the resistance of components in series
R= R1+R2 etc.
how do you calculate the resistance of components in parallel
1/R= 1/R1+1/R2 = 2/R =R/2
what is current
current is a flow of charge
what is the e.m.f.
energy supplied or work done by a source, per unit of change, in a complete circuit
what is e.m.f. measured in
coulombs because it is the energy supplied
how do you calculated current
I=Q/t I=V/R
how do you calculate power
P=IV P=E/t
how do you calculate energy
E=IVt E=Pt
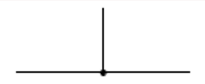
junction of conductors
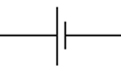
cell
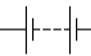
battery

power supply

switch

ammeter
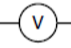
voltmeter
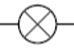
lamp

resistor
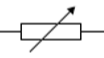
variable resistor
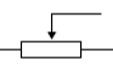
potential divider
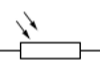
LDR
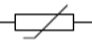
thermistor

fuse
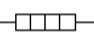
heater
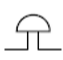
bell
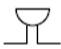
buzzer
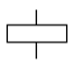
relay coil
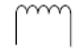
magnetism coil
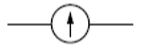
galvanometer
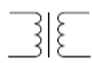
transformer
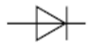
diode
what is potential difference
the energy or work done by a charge passing through a component
what is ohms law
current is proportional to potential difference at a constant temperature
is resistance proportional to length
yes
the longer the resister, the higher the resistance
is resistance proportional to the cross sectional area
no, it is inversely proportional
wider the cross sectional area, lower the resistance
LDR and resistance
the brighter, the lower the resistance
thermistor and resistance
the hotter, the lower the resistance
are all objects charged
yes, they are usually neutral
what charges can move
electrons (negative charges)
what is an electric field
region is space where an electric force can be felt
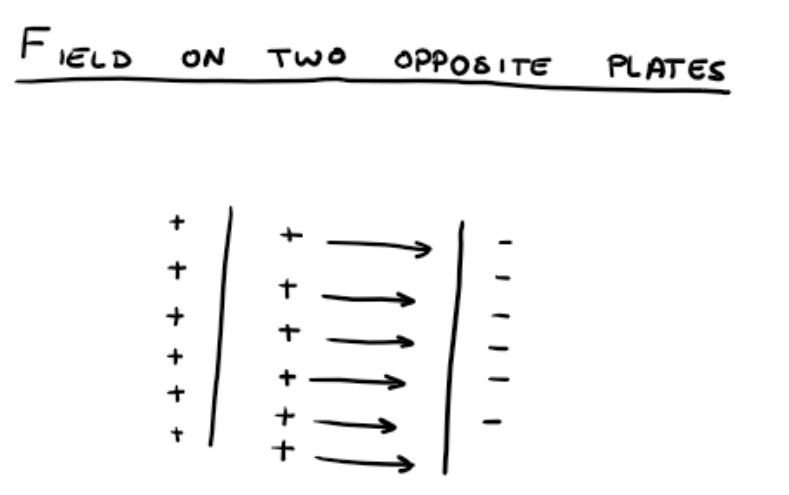
what does the electric field look like on two opposite plates
which way does current and the electrons flow in a circuit
the current from + to -
the electrons from - to +