nervous system pt2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:17 AM on 2/22/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
hippocampus
A portion of the limbic system that is important for memory and learning.
2
New cards
frontal lobe (picture)
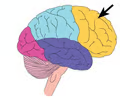
3
New cards
parietal lobe (picture)
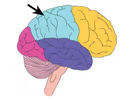
4
New cards
temporal lobe (picture)
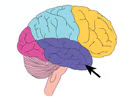
5
New cards
occipital lobe (picture)
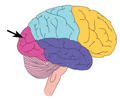
6
New cards
temporal lobe
An area on each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex near the temples that is the primary receiving area for auditory information
7
New cards
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
8
New cards
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
9
New cards
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
10
New cards
amygdala
Part of the limbic system, responsible for the emotional reactions of fear and anger.
11
New cards
pineal gland (picture)
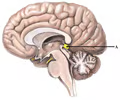
12
New cards
pineal gland
A brain structure located near the thalamus that secretes melatonin.
13
New cards
medulla oblongata (picture)
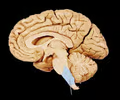
14
New cards
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
15
New cards
pons (picture)
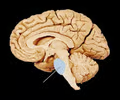
16
New cards
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
17
New cards
midbrain (picture)
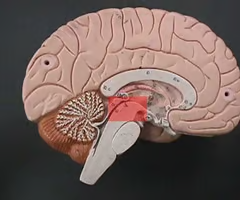
18
New cards
midbrain
The portion of the brain responsible for visual and auditory startle reflexes.
19
New cards
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
20
New cards
thalamus (picture)
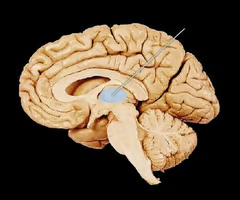
21
New cards
thalamus
A structure in the forebrain through which all sensory information (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral cortex.
22
New cards
corpus callosum (picture)
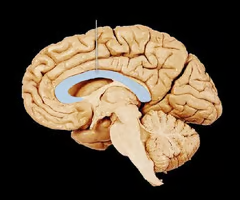
23
New cards
corpus callosum
The large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
24
New cards
basal ganglia
Large clusters of neurons, located above the thalamus and under the cerebral cortex, that work with the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex to control and coordinate voluntary movements.
25
New cards
right brain
controls the left side of the body; known for being visual, creative, emotional, and holistic in thought
26
New cards
left brain
controls the right side of the body; known for being logical, analytical, and factual
27
New cards
astrocyte (picture)
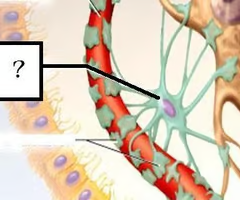
28
New cards
astrocyte
The neuroglia that helps to structurally support the neurons and chemically protects them.
29
New cards
microglia (picture)
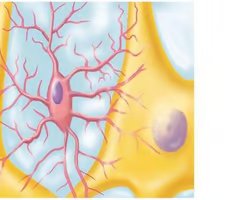
30
New cards
microglia
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
31
New cards
oligodendrocyte (picture)
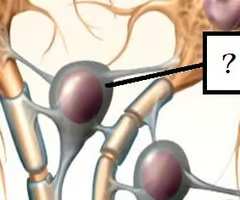
32
New cards
oligodendrocyte
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
33
New cards
ependymal cells (picture)
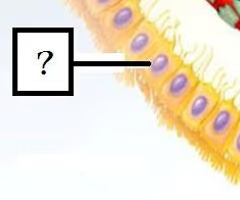
34
New cards
ependymal cells
Line the ventricles of the brain and produce cerebrospinal fluid, which physically supports the brain and serves as a shock absorber
35
New cards
dura mater
Outermost layer of the meninges
36
New cards
pia mater
thin inner layer of the meninges
37
New cards
arachnoid
middle layer of the meninges
38
New cards
peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord.
39
New cards
central nervous system
made up of the brain and spinal cord
40
New cards
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
41
New cards
sensory neurons
carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord and brain
42
New cards
motor neurons
neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors
43
New cards
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
44
New cards
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles
45
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
46
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight