MicroEcon Midterm 1 Vocab
1/9
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
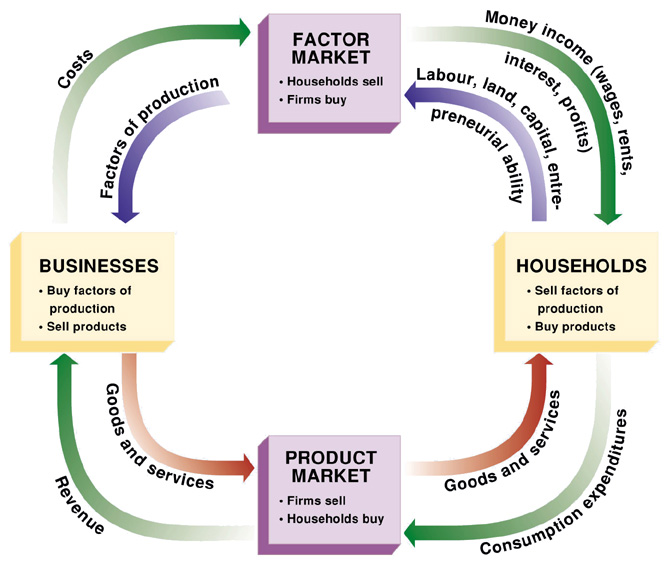
Circular Flow Diagram
Resources flow from households to businesses through the resource market, and products flow from businesses to households through the product market. Opposite these real flows are monetary flows. Households receive income from businesses (their costs) through the resource market, and businesses receive revenue from households (their expenditures) through the product market.
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
In any market what can we make what is possible.
Shortage
The amount by which the quantity demanded of a product exceeds the quantity supplied at a particular (below-equilibrium) price.
Surplus
The amount by which the quantity supplied of a product exceeds the quantity demanded at a specific (above equilibrium) price
Shift (graph)
Indicates a change in demand or supply caused by factors other than price. (consumer income)
Movement Along (graph)
Refers to a change in quantity demanded or supplied solely due to a change in the price of the good.
Inelastic
Product or resource demand for which the price elasticity of demand is less than 1, so that any given percentage change in price leads to a smaller percentage change in quantity demanded. As a result, quantity demanded is relatively insensitive to (inelastic with respect to) price.
Elastic
Product or resource demand whose price elasticity of demand is greater than 1, so that any given percentage change in price leads to a larger percentage change in quantity demanded. As a result, the quantity demanded is relatively sensitive to (elastic with respect to) price.
Comparative Advantage
A situation in which a person or country can produce a specific product at a lower opportunity cost than some other person or country; the basis for specialization and trade.
Unemployment
The failure to use all available economic resources to produce desired goods and services: the failure of the economy to fully employ its labor force.