topic 6-inheritance
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
difference between meiosis and mitosis
meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed.
sexual reproduction example
Sexual reproduction involves the joining (fusion) of male and female gametes:
sperm and egg cells in animals
pollen and egg cells in flowering plants.
what happens in sexual reproduction
In sexual reproduction there is mixing of genetic information which leads to variety in the offspring
what does the formation of gametes involve
The formation of gametes involves meiosis.
what is asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and no fusion of gametes. There is no mixing of genetic information. This leads to genetically identical offspring (clones). Only mitosis is involved.
meiosis and fertilisation
meiosis halves the number of chromosomes in gametes and fertilisation restores the full number of chromosomes.
how do cells in reproductive organ divide
Cells in reproductive organs divide by meiosis to form gametes.
what happens when a cell divides to form gametes
copies of the genetic information are made
the cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes
all gametes are genetically different from each other.
fertilisation
Gametes join at fertilisation to restore the normal number of chromosomes. The new cell divides by mitosis. The number of cells increases. As the embryo develops cells differentiate.
Advantages of sexual reproduction:
produces variation in the offspring
if the environment changes variation gives a survival advantage by natural selection
natural selection can be speeded up by humans in selective breeding to increase food production.
Advantages of asexual reproduction:
only one parent needed
more time and energy efficient as do not need to find a mate
faster than sexual reproduction
many identical offspring can be produced when conditions are favourable
.
how can some organisms reproduce
Some organisms reproduce by both methods depending on the circumstances.
examples of organisms that can reproduce by both methods
Malarial parasites reproduce asexually in the human host, but sexually in the mosquito.
Many fungi reproduce asexually by spores but also reproduce sexually to give variation.
Many plants produce seeds sexually, but also reproduce asexually by runners such as strawberry plants, or bulb division such as daffodils.
dna
The genetic material in the nucleus of a cell is composed of a chemical called DNA. DNA is a polymer made up of two strands forming a double helix.
where can the DNA be found
The DNA is contained in structures called chromosomes.
what is a gene
A gene is a small section of DNA on a chromosome. Each gene codes for a particular sequence of amino acids, to make a specific protein.
genome of an organism
The genome of an organism is the entire genetic material of that organism.
importance of studying human genome
The whole human genome has now been studied and this will have great importance for medicine in the future.
benefits to studying human genome
search for genes linked to different types of disease
understanding and treatment of inherited disorders
use in tracing human migration patterns from the past.
what is DNA
polymer of molecules called nucleotides -DNA as a polymer made from four different nucleotides.
what does each nucleotide consist of
Each nucleotide consists of a common sugar and phosphate group with one of four different bases attached to the sugar.
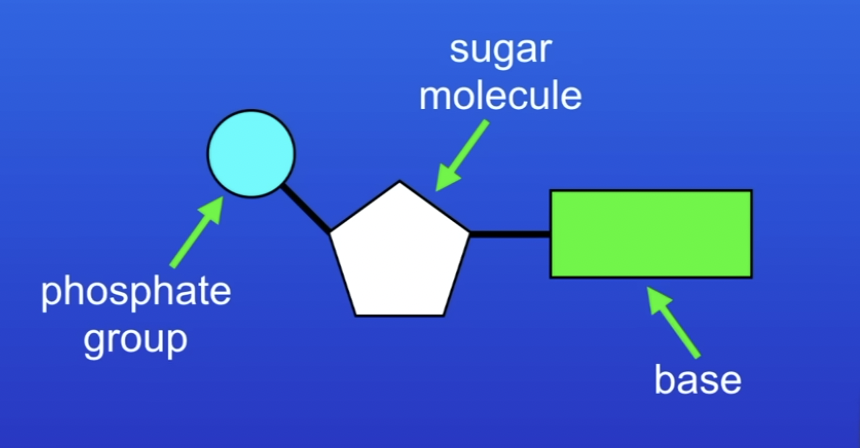
the four different bases
A,C, G, T
whats a key fact of DNA strands
they are complementary which means that the same bases always pair on the opposite strands A-T C-G
how is a particular amino acid made
A sequence of three bases is the code for a particular amino acid
how is a particular protein assembled
The order of bases controls the order in which amino acids are assembled to produce a particular protein.
what do the long strands of DNA consist of
The long strands of DNA consist of alternating sugar and phosphate sections. Attached to each sugar is one of the four bases.
what is the DNA polymer made of
The DNA polymer is made up of repeating nucleotide units.
how many different types of mino acids
20
how is the shape of the protein determined
the specific order of the amino acids determne the shape of protein
protein synthesis
the first stage takes place in the nucleus and the second stage takes place in the cytoplasm
the first stage is called transcription -the base sequence of the gene is copied into a complementary template molecule (messenger RNA or mRNA which is a single stranded molecule which is a single stranded molecule)
the mRNA will pass out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm
the second stage of protein synthesis is called translation In this stage, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome and amino acids are brought to the ribosome on carrier molecules(they are called trasnfer RNA or tRNA)
the ribosomes now reads the triplet of bases on the mRNA and uses this to join together the correct amino acids in the correct order
When the protein chain is complete it folds up to form a unique shape. This unique shape enables the proteins to do their job as enzymes, hormones or forming structures in the body such as collagen.
how is the sequence of the protein determined
the base sequence of a gene determines the amino acid of a protein.When the protein chain is complete it folds up to form a unique shape. This unique shape enables the proteins to do their job as enzymes, hormones or forming structures in the body such as collagen.
mutation
a random change to a base -Mutations occur continuously. Most do not alter the protein, or only alter it slightly so that its appearance or function is not changed.
why does sometimes mutations have no effect
this is because different base triplets can sometimes encode for the same amino acid -the mutation has had no effect on the protein’s shape or function
what happens when a mutation has an effect
A few mutations code for an altered protein with a different shape. An enzyme may no longer fit the substrate binding site or a structural protein may lose its strength.
non-coding parts of DNA
Not all parts of DNA code for proteins. Non-coding parts of DNA can switch genes on and off, so variations in these areas of DNA may affect how genes are expressed.
alleles
different forms of genes
what are the characteristics controlled by a single gene
what do the alleles do
The alleles present, or genotype, operate at a molecular level to develop characteristics that can be expressed as a phenotype.
difference between dominant and recessive allele
A dominant allele is always expressed, even if only one copy is present. A recessive allele is only expressed if two copies are present (therefore no dominant allele present).
difference between homozygous and heterezygous
If the two alleles present are the same the organism is homozygous for that trait, but if the alleles are different they are heterozygous.
what are most characteristics due to
Most characteristics are a result of multiple genes interacting, rather than a single gene.
how are inherited disorders passed on
Some disorders are inherited. These disorders are caused by the inheritance of certain alleles.
cystic fibrosis
(a disorder of cell membranes) is caused by a recessive allele.
polydactyly
(having extra fingers or toes) is caused by a dominant allele.
what happens in embryo screening
embryos are tested to see if they have the alleles for inherited disorders. embryos which do not have the defective alleles are implanted into the woman. these can develop into healthy offsprings
issues with embryo screening
-expensive and that money can be used elsewhere in the health service
-often a large number of embryos are created but only small number are implanted. that means that some healthy embryos are destroyed and people think that is unethical
-in the future we may be able to screen embryos to produce offsprings with desirable features. many people think this is unethical
gene therapy
correcting faulty alleles and use this to treat inherited disorders and at the moment this is experimental
make sure to learn family trees
what sex chromosomes do males have
XY
what sex chromosomes do females have
XX
how many pairs of chromosome determine sex
22 pairs control characteristics only, but one of the pairs carries the genes that determine sex.
variation
Differences in the characteristics of individuals in a population is called variation
what may the differences be due to
:
the genes they have inherited (genetic causes)
the conditions in which they have developed (environmental causes)
a combination of genes and the environment.
variation through phenotype
all variants arise from mutations and that: most have no effect on the phenotype; some influence phenotype; very few determine phenotype.
Mutations occur continuously. Very rarely a mutation will lead to a new phenotype. If the new phenotype is suited to an environmental change it can lead to a relatively rapid change in the species.
evolution
s a change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time through a process of natural selection which may result in the formation of a new species.
what does the theory of evolution by natural selection state
The theory of evolution by natural selection states that all species of living things have evolved from simple life forms that first developed more than three billion years ago.
what happens if two populations of one species become soo different
If two populations of one species become so different in phenotype that they can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring they have formed two new species.
what is selective breeding
Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process by which humans breed plants and animals for particular genetic characteristics.
how long have humans been doing this s
. Humans have been doing this for thousands of years since they first bred food crops from wild plants and domesticated animals.
what does selective breeding involve
Selective breeding involves choosing parents with the desired characteristic from a mixed population. They are bred together. From the offspring those with the desired characteristic are bred together. This continues over many generations until all the offspring show the desired characteristic.
The characteristic can be chosen for usefulness or appearance:
Disease resistance in food crops.
Animals which produce more meat or milk.
Domestic dogs with a gentle nature.
Large or unusual flowers.
what can selective breeding lead to
Selective breeding can lead to ‘inbreeding’ where some breeds are particularly prone to disease or inherited defects. |
genetic engineering
In genetic engineering, genes from the chromosomes of humans and other organisms can be ‘cut out’ and transferred to cells of other organisms. a process which involves modifying the genome of an organism by introducing a gene from another organism to give a desired characteristic.
what can plants be gentically modified to do
Plant crops have been genetically engineered to be resistant to diseases or to produce bigger better fruits. Gm crops will produce a greater yield than normal crops.GM crops include ones that are resistant to insect attack or to herbicides.
drawbacks of gm crops
Concerns about GM crops include the effect on populations of wild flowers and insects. Some people feel the effects of eating GM crops on human health have not been fully explored.
main steps in the process of genetic engineering.
enzymes are used to isolate the required gene; this gene is inserted into a vector, usually a bacterial plasmid or a virus
the vector is used to insert the gene into the required cells
genes are transferred to the cells of animals, plants or microorganisms at an early stage in their development so that they develop with desired characteristics.
what is modern medical research exploring
Modern medical research is exploring the possibility of genetic modification to overcome some inherited disorders.
what have bacteria cells been modified ro do
Bacterial cells have been genetically engineered to produce useful substances such as human insulin to treat diabetes.
what is tissue culture
Tissue culture: using small groups of cells from part of a plant to grow identical new plants.
what is tissue culture important for
This is important for preserving rare plant species or commercially in nurseries.
cutting
Cuttings: an older, but simple, method used by gardeners to produce many identical new plants from a parent plant.
embryo transplants
Embryo transplants: splitting apart cells from a developing animal embryo before they become specialised, then transplanting the identical embryos into host mothers.
adult cell cloning
The nucleus is removed from an unfertilised egg cell.
The nucleus from an adult body cell, such as a skin cell, is inserted into the egg cell.
An electric shock stimulates the egg cell to divide to form an embryo.
These embryo cells contain the same genetic information as the adult skin cell.
When the embryo has developed into a ball of cells, it is inserted into the womb of an adult female to continue its development.
how did Charles Darwin propose the theory of evolution
Charles Darwin, as a result of observations on a round the world expedition, backed by years of experimentation and discussion and linked to developing knowledge of geology and fossils, proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection.
natural selection
Individual organisms within a particular species show a wide range of variation for a characteristic.
Individuals with characteristics most suited to the environment are more likely to survive to breed successfully.
The characteristics that have enabled these individuals to survive are then passed on to the next generation.
where did Darwin publish his findings
Darwin published his ideas in On the Origin of Species (1859). There was much controversy surrounding these revolutionary new ideas.
The theory of evolution by natural selection was only gradually accepted because:
the theory challenged the idea that God made all the animals and plants that live on Earth
there was insufficient evidence at the time the theory was published to convince many scientists
the mechanism of inheritance and variation was not known until 50 years after the theory was published.
what are other theories
Other theories, including that of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, are based mainly on the idea that changes that occur in an organism during its lifetime can be inherited. We now know that in the vast majority of cases this type of inheritance cannot occur.
alfred russel wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace independently proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection. He published joint writings with Darwin in 1858 which prompted Darwin to publish On the Origin of Species (1859) the following year.
Wallace worked worldwide gathering evidence for evolutionary theory. He is best known for his work on warning colouration in animals and his theory of speciation.
Alfred Wallace did much pioneering work on speciation but more evidence over time has led to our current understanding of the theory of speciation.
speciation steps
(do later)
describe the development of our understanding of genetics including the work of Mendel
In the mid-19th Century Gregor Mendel carried out breeding experiments on plants. One of his observations was that the inheritance of each characteristic is determined by ‘units’ that are passed on to descendants unchanged.
understand why the importance of Mendel’s discovery was not recognised until after his death
In the late 19th Century behaviour of chromosomes during cell division was observed.
In the early 20th Century it was observed that chromosomes and Mendel’s ‘units’ behaved in similar ways. This led to the idea that the ‘units’, now called genes, were located on chromosomes.
In the mid-20th Century the structure of DNA was determined and the mechanism of gene function worked out.
This scientific work by many scientists led to the gene theory being developed.
Evidence for evolution
including fossils and antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
The theory of evolution by natural selection is now widely accepted.
Evidence for Darwin’s theory is now available as it has been shown that characteristics are passed on to offspring in genes. There is further evidence in the fossil record and the knowledge of how resistance to antibiotics evolves in bacteria.
fossils
Fossils are the ‘remains’ of organisms from millions of years ago, which are found in rocks.
how may fossils be formed
from parts of organisms that have not decayed because one or more of the conditions needed for decay are absent
when parts of the organism are replaced by minerals as they decay
as preserved traces of organisms, such as footprints, burrows and rootlet traces.
one problem with fossils and why cant scientist be certain about how life began on earth
Many early forms of life were soft-bodied, which means that they have left few traces behind. What traces there were have been mainly destroyed by geological activity. This is why scientists cannot be certain about how life began on Earth.
what can we learn from fossils
We can learn from fossils how much or how little different organisms have changed as life developed on Earth.
extinction
Extinctions occur when there are no remaining individuals of a species still alive.
factors which may contribute to extinction
-catastrophic event
-environment changes
-new disease or new predator
-neww and more succesful species evolces which will compete with it
why can bacteria evolve rapidly
Bacteria can evolve rapidly because they reproduce at a fast rate.
what does mutations of bacterial pathogens mean
Mutations of bacterial pathogens produce new strains. Some strains might be resistant to antibiotics, and so are not killed. They survive and reproduce, so the population of the resistant strain rises. The resistant strain will then spread because people are not immune to it and there is no effective treatment.
what is one common strain of bacteria
MRSA
To reduce the rate of development of antibiotic resistant strains:
doctors should not prescribe antibiotics inappropriately, such as treating non-serious or viral infections
patients should complete their course of antibiotics so all bacteria are killed and none survive to mutate and form resistant strains
the agricultural use of antibiotics should be restricted.
what is the problem with developmentt of new antibiotics
The development of new antibiotics is costly and slow. It is unlikely to keep up with the emergence of new resistant strains.
traditionally, how were living things classified as
Traditionally living things have been classified into groups depending on their structure and characteristics in a system developed by Carl Linnaeus.
how did Linnaeus classify living things
Linnaeus classified living things into kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
how are organisms named
Organisms are named by the binomial system of genus and species.
how were new models of classification proposed
As evidence of internal structures became more developed due to improvements in microscopes, and the understanding of biochemical processes progressed, new models of classification were proposed.
“three-domain system”
Due to evidence available from chemical analysis there is now a ‘three-domain system’ developed by Carl Woese
In this system organisms are divided into:
Archaea (primitive bacteria usually living in extreme environments)
Bacteria (true bacteria)
Eukaryota (which includes protists, fungi, plants and animals).