02 - Sensory Receptors
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
sensory modalities
each sensation has its own receptor type but uses same electrical language
photoreceptor → vision
chemoreceptor → taste, smell
mechanoreceptor → touch, proprioception, hearing
thermoreceptor → temperature
nociceptor → pain
labeled line theory
each modality signals separately to higher brain centers
action potentials look alike, but it allows brain to know what signal is based on where it came from
transduction vs perception
transduction → converts stimulus to electrical signal
perception → brain’s interpretation
context is important in perception
periphery sensory receptor
most touch axons are myelinated, so they are fast
cell body in dorsal root ganglion
one branch to skin (receptor)
one branch to spinal cord, which goes to brain
mechanoreceptor model
PIEZO2 channel = molecule that transduce touch into electrical signal
mechanical force stretches membrane
stretch opens mechanosensitive ion channels
sodium enters, potassium leaves → depolarization
channels open stochastically → more pressure = more channels open
stochastic channel opening
individual ion channels open all-or-nothing
open/close probabilistically
electric potential → sum of all currents from all channels in cell
graded receptor potential → many channels opening together
formation of action potential
stimulus opens mechanosensitive channels
graded receptor potential forms
potential spreads locally (decremental)
voltage-gated Na+ channels activated
action potentials generated
stronger stimulus → more action potentials
longer stimulus → more firing duration
AP propagate without decrement
NT released at terminal
slowly vs rapidly adapting receptors
slowly adapting → responds to sustained pressure
potential is the largest at the beginning and persists for whole duration of stimulus
action potential duration is increased, lasting the duration of the stimulus
rapidly adapting → responds to changes in pressure
potential is shorter, peaking when there are changes in pressure
no action potential when at steady-state
cutaneous mechanoreceptors
Meissner’s corpuscle → superficial, rapidly adapting, small receptive field
Merkel cells → superficial, slowly adapting, small receptive field
Pacinian corpuscle → deep, rapidly adapting, large receptive field
most sensitive receptor to vibration
Ruffini endings → deep, slowly adapting, large receptive field
Pacinian corpuscle
deep mechanoreceptor that is rapidly adapting and has large receptive field
response to stimuli dominated by response at time of transition in pressure
when capsule removed → response changes from rapid to slow
capsule converts sustained pressure into transient signals
receptive field
area of skin where stimulation affects a neuron’s firing
one axon = one receptive field
small receptive field → high spatial resolution
large receptive field → poor localization, loss of definition
skin is covered with overlapping receptive fields
two-point discrimination
tests minimum distance to detect two separate points
discrimination due to density of receptors and cortical representation
best discrimination → fingers, lips
worst discrimination → back, thighs
temperature sensation
separate receptors for warm and cold sensations
cold fibers → 5-36ºC
send signals to small myelinated Aδ fibers
warm fibers → 30-45ºC
send signals to unmyelinated C fibers
for temperatures outside the ranges of cold and warm fibers, they are perceived as pain
TRP receptors
transient receptor potentials (TRP) respond to different temperature ranges
TRPV1 → activates with heat and capsaicin
TRPM8 → activates with cold and menthol
three neuron chain
first order neuron → signal from receptor ending travels to dorsal root ganglion cells to medulla ipsilaterally
synapse at cuneate nucleus
if from the face, first synapse is in trigeminal nucleus
second order neuron → axon crosses midline and travels up to thalamus (midbrain)
synapse at ventral posterior nucleus
third order neuron → axon travels to primary somatosensory cortex
processing at relay stations
convergence → many signals combine into one
convergence along sensory pathways towards CNS
divergence → one signal divides into many
lateral inhibition → inhibit nearby axons
regulates size of receptive field to sharpen spatial contrast
strongly activated neurons inhibit neurons
weak signals suppressed
descending modulation → cortex sends signals down
somatosensory cortex organization
amount of area devoted to each part of the body is proportional to number of axons from that body part or surface or density of sensory innervation of the region
medial → legs
lateral → face
hands and lips → large representation
due to small receptive fields and high spatial resolution
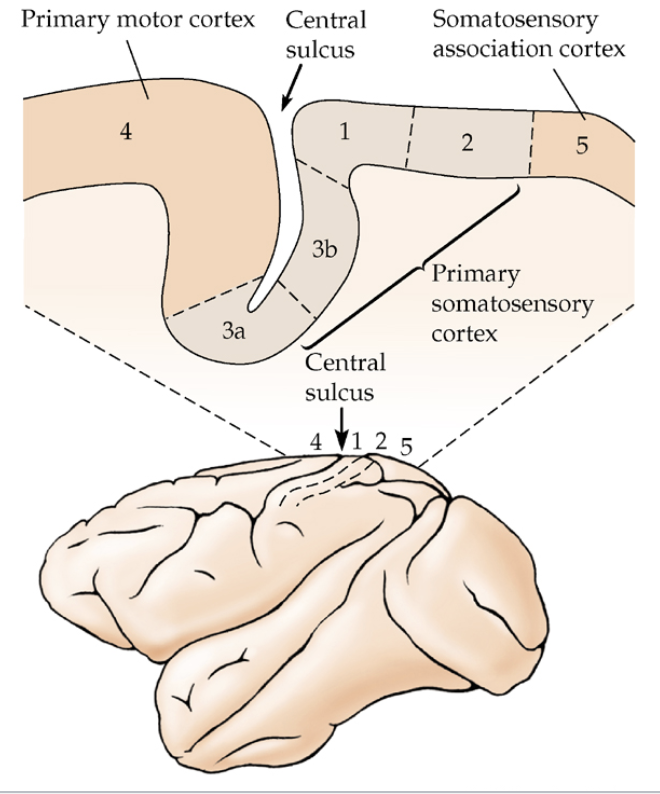
subdivisions of somatic sensory cortex
areas 3b & 1 → inputs form touch receptors
areas 3a & 2 → inputs from proprioreceptors
area 5 → combines input from both kinds of receptors (association cortex)
cortical columns
cells in cortex are arranged in columns of similar fields
cells stacked vertically respond to same skin region
different layers = different processing
plasticity
map in somatic sensory cortex is not fixed, and are modifiable with experience
amputated finger → cortical map reorganizes
higher-order cortical processing
receptive fields of cortical cells are larger than those of peripheral neurons, varying in different regions of somatic sensory cortex
areas 1 & 2 → cells respond to much larger receptive areas
area 3b → cells respond to very small receptive fields
area 5 → some cells respond to touch from either hands
shows convergence
orientation-sensitive neuron & direction-sensitive neuron → cortex can extract patterns, not just intensity