AP Macroeconomics Unit 5
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Just some useful notes for the AP Macro...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
(5.1) How does fiscal and monetary policy adjust inflationary and recessionary gaps?

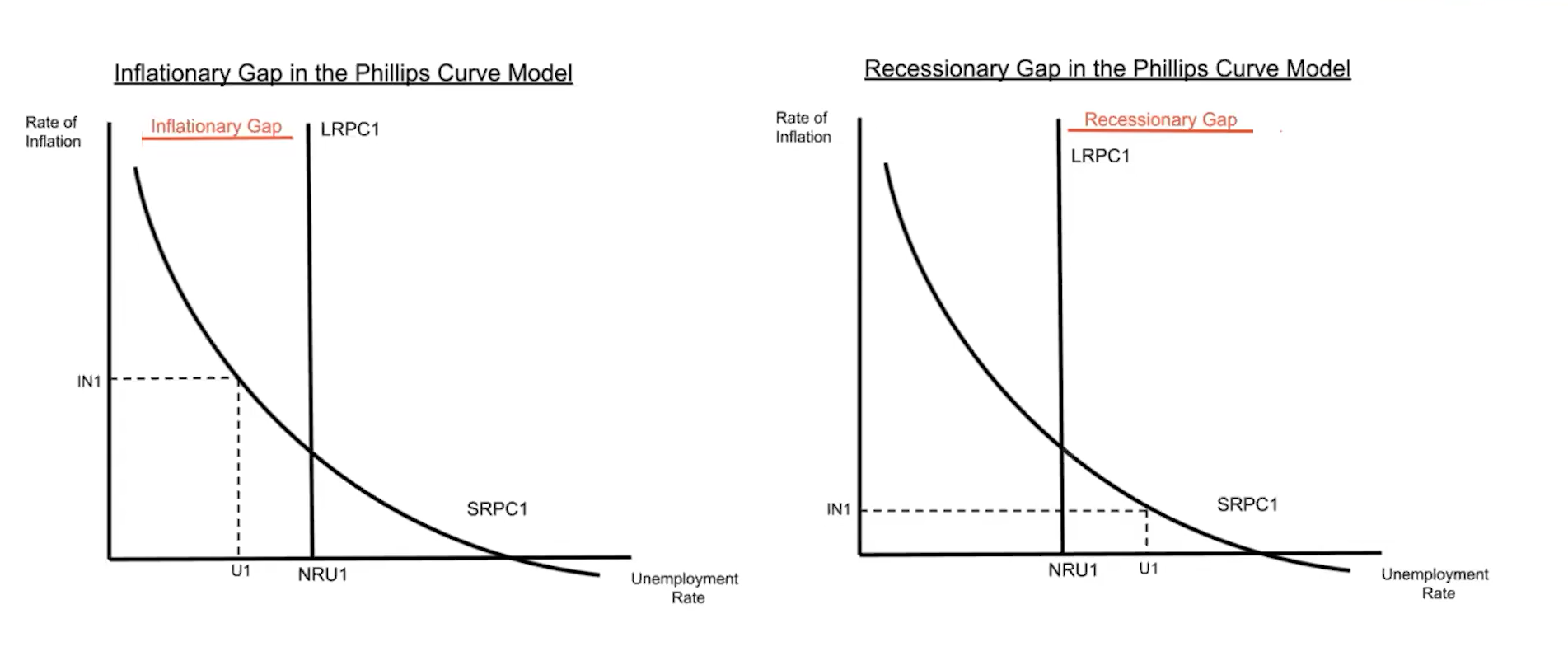
(5.2) Inflationary and recessionary gaps in the Phillips Curve Model
(5.2) Supply/Demand shocks on the Phillips Curve Model

(5.2) When does the long-run Phillips curve shift?
The long-run Phillips curve shifts when there is a change in the structural and/or frictional unemployment rates
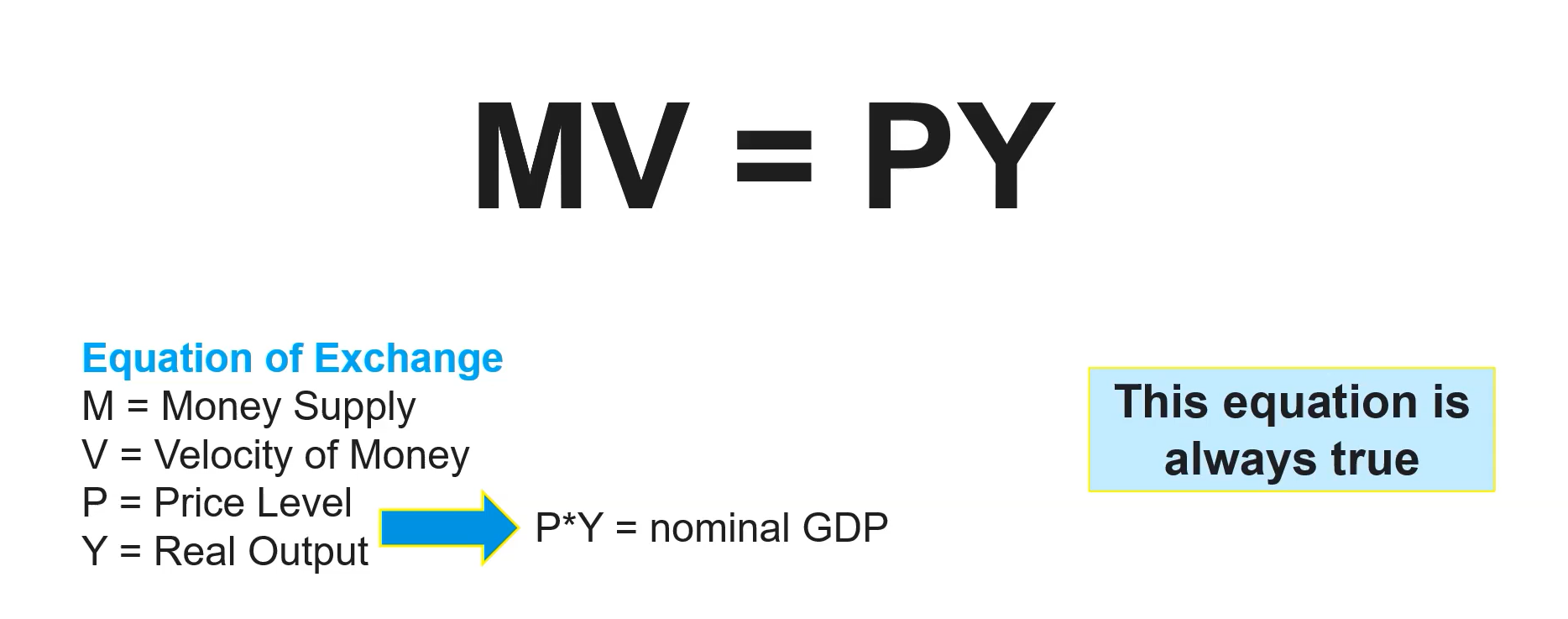
(5.3) Equation of exchange
(5.3) Neutrality of monetary policy
Changes in money supply have no effect on real variables in the long run
(5.3) Quantity theory of money
There exists a direct relationship between changes in money supply and price level in the long run
(5.4) A government must pay interest on its accumulated debt, thus increasing the national debt and increasingly foregoing using those funds for alternative uses.
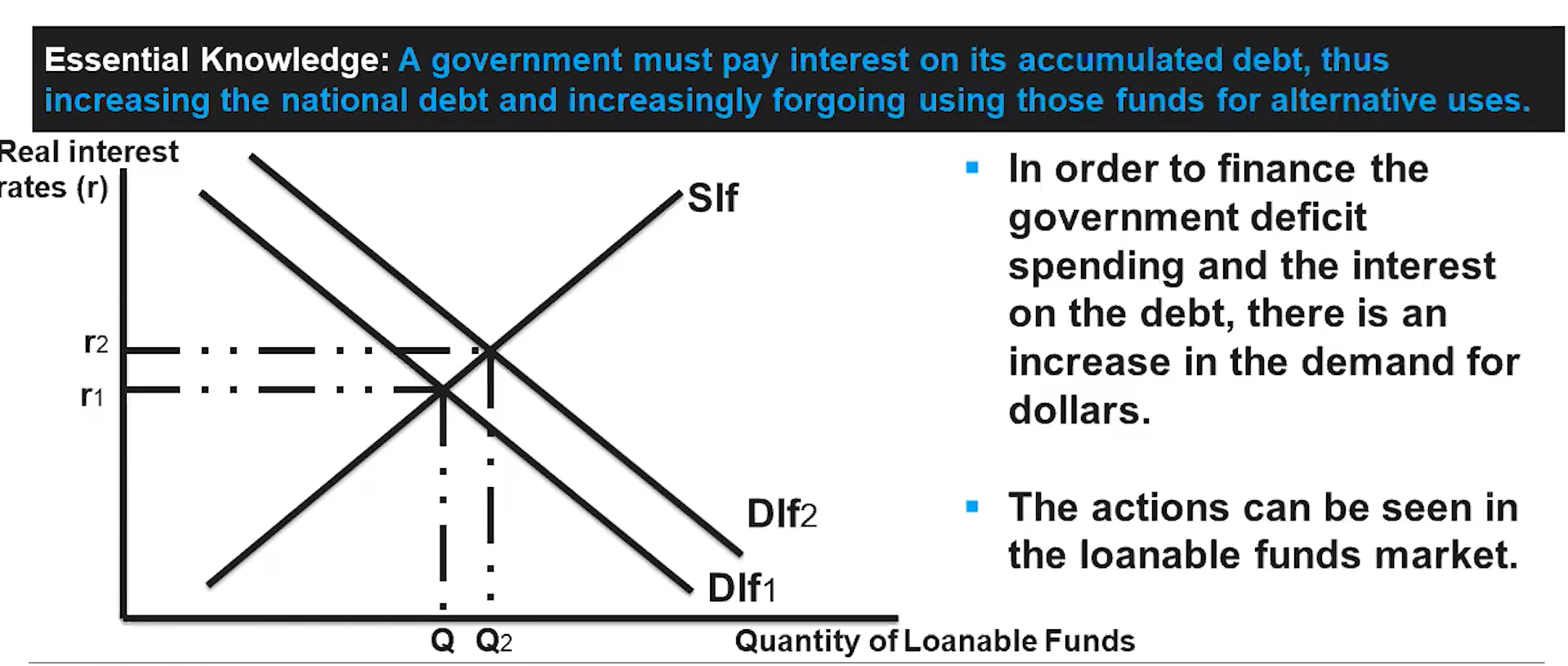
(5.4) Fiscal Policy and the Budget Balance

(5.5) How does crowding out occur?
Expansionary fiscal policy is used to close a recessionary gap (AD↑GDPR↑E↑PL↑). Government budget deficit spending leads to increase in borrowing (DL↑RIR↑). Increasing interest rates leads to decrease in interest sensitive spending (AD↓GDPR↓E↓PL↓)
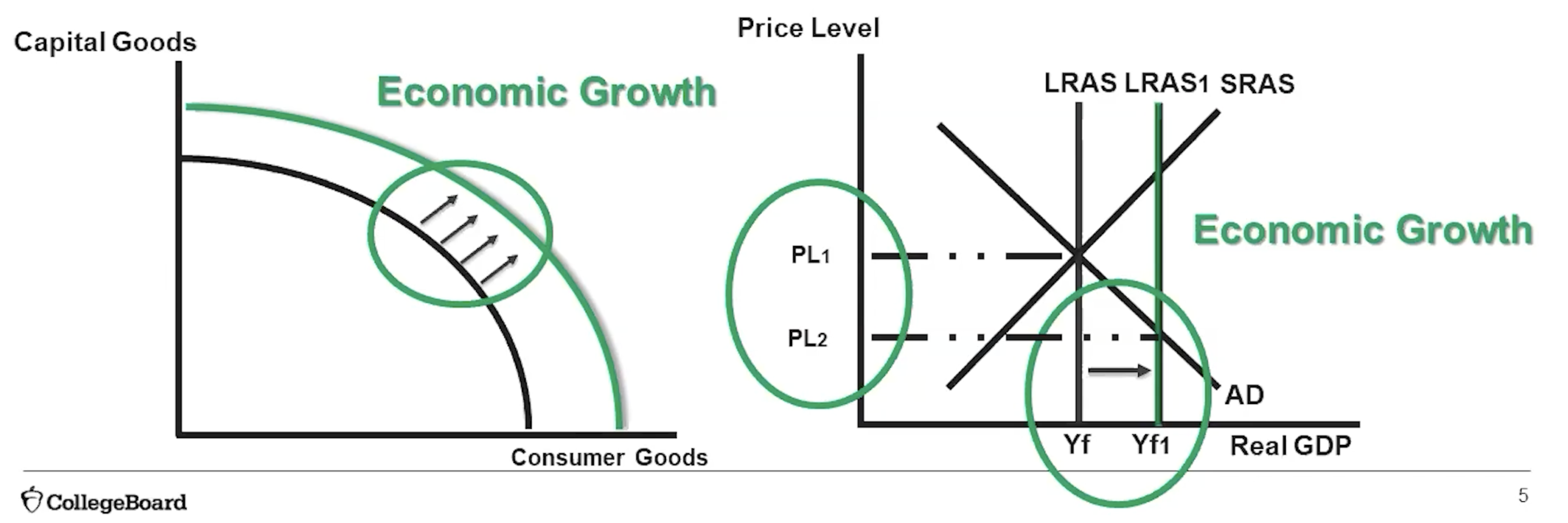
(5.6) What causes economic growth?
↑Investment Spending → ↑Capital Stock Formation → ↑Productivity