Chapter 7 Energy
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is a flashcard about the topic Energy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Conservation of Energy
The principle that energy can change forms but cannot be created or destroyed.
Chlorophyll
A pigment in plants that traps light energy and converts it into chemical potential energy during photosynthesis.
Chemical Potential Energy
Energy stored in substances which can be released through chemical reactions.

Fossil Fuels
Non-renewable energy sources formed from the remains of dead plants and animals over millions of years. It contains chemical potential energy.
Non-renewable Resources
Energy sources that cannot be replenished once depleted, such as coal, crude oil, and natural gas.
Renewable Sources of Energy
Energy sources that can be used repeatedly and are not depleted, such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
Hydroelectrical Power Station
A facility that generates electricity by using the gravitational potential energy of water flowing through turbines.
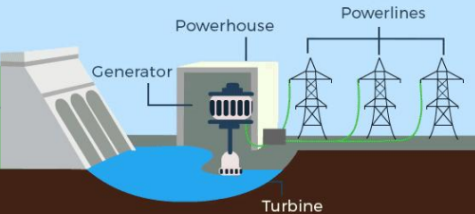
Gravitational Potential Energy
The energy stored in an object because of its position within a gravitational field.
Kinetic Energy
The energy of moving things.
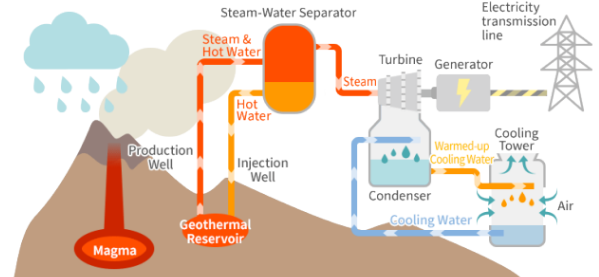
Geothermal Energy
Energy derived from the Earth's core, where hot rocks heat underground water to produce steam for electricity generation.
Biomass
Organic matter used to produce fuel for heat or electricity, derived from plant and animal waste.
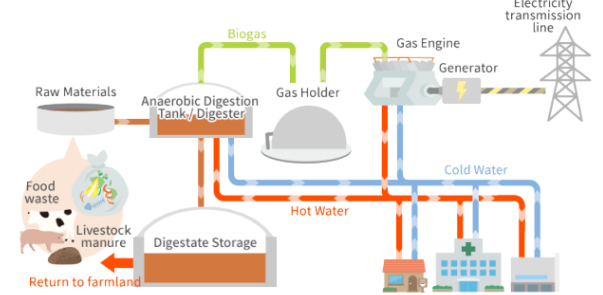
Biogas
Methane produced by bacteria decomposing organic waste, which can be used as a fuel source.
Solar Energy
Energy from the sun that is converted into electrical energy by solar cells.
Wind Energy
Energy generated by the kinetic energy of wind turning turbines to produce electricity.

Tidal Energy
Energy generated from the potential energy of tides, converted into electricity using turbines.
Tidal Barrages
Structures built across the mouth of a bay to harness tidal energy for electricity generation.
Energy Conservation
Practices aimed at reducing energy consumption, such as turning off electrical appliances when not in use.