Physics I Exam 1 Chapter 1-3 terms
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Physics
Physika-Aristotle, study of nature/of matter and energy
Theory
something that hasn’t been disproven
Units
standardized way to measure quantities
What are some examples of Units?
Mass, time, distance, temperature
SI/MKS
Meters, Kilograms, Seconds, Celsius
CGS
Centimeters, Grams, Seconds, Celsius
Significant Figures
how many digits you reliably know in a number/measurement
Scalar
magnitude or quantity
Scalar examples
speed, mass, distance (length), energy
Vector
magnitude and direction
Vector examples
velocity, momentum, force, acceleration, position in space
Speed: Scalar or Vector?
Scalar
A mass: Scalar or Vector?
Scalar
distance (length): Scalar or Vector?
Scalar
energy: Scalar or Vector?
Scalar
Velocity: Scalar or Vector?
Vector
Momentum: Scalar or Vector?
Vector
Force: Scalar or Vector?
Vector
Acceleration: Scalar or Vector?
Vector
Position in space: Scalar or Vector?
Vector
All unit vectors have a magnitude that equals…
1
Kinematics
describes motion of things (position, velocity, acceleration)
Dynamics
how forces influence motion
What branch of physics is Kinematics and Dynamics known for?
Mechanics
Average Speed
the distance traveled divided by the time required to cover the distance
Total distance traveled / total time
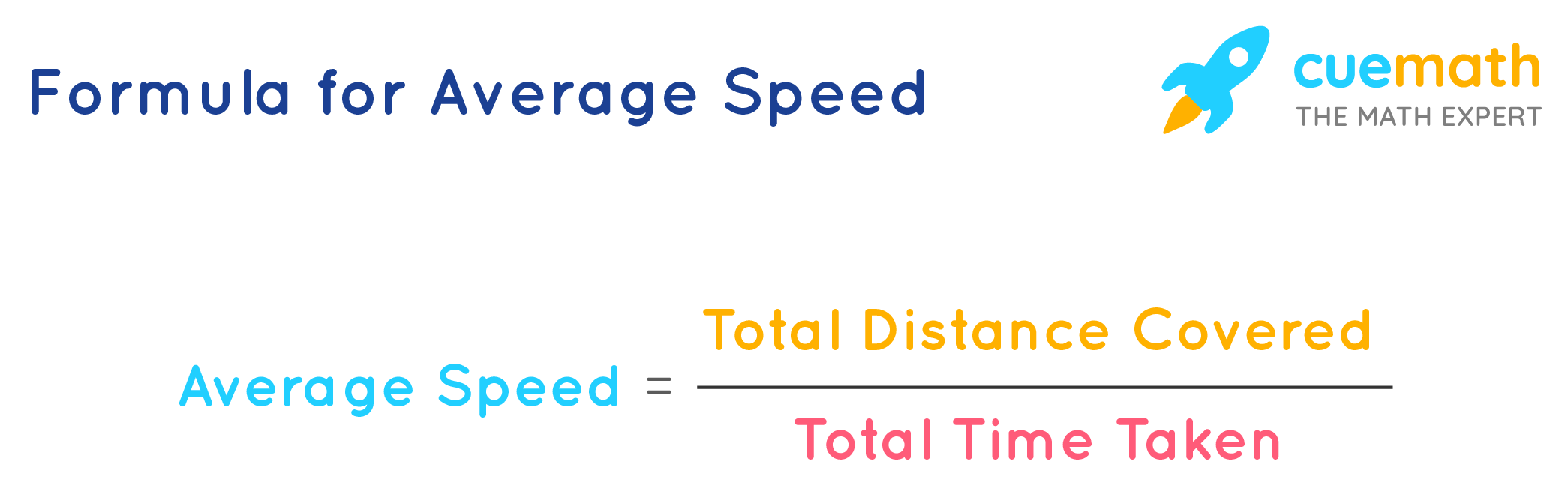
Average velocity
the displacement divided by the elapsed time
xf-x0 / tf-t0
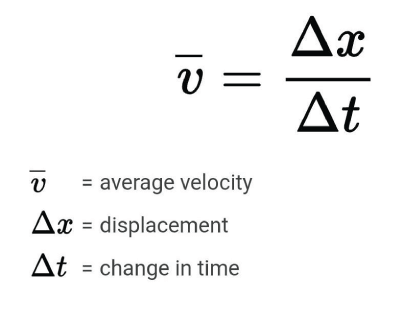
Instantaneous velocity
indicates how fast the car moves and direction of motion at each instant of time
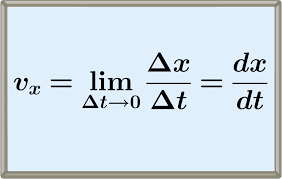
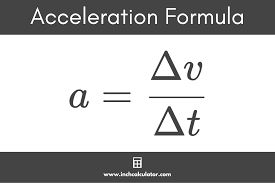
Acceleration
a change in velocity is combined with the time during which the change occurs
Velocity is a change in…
position
Acceleration is a change in…
velocity
Constant acceleration is…
velocity changing at the same rate
The 4 kinematic equations

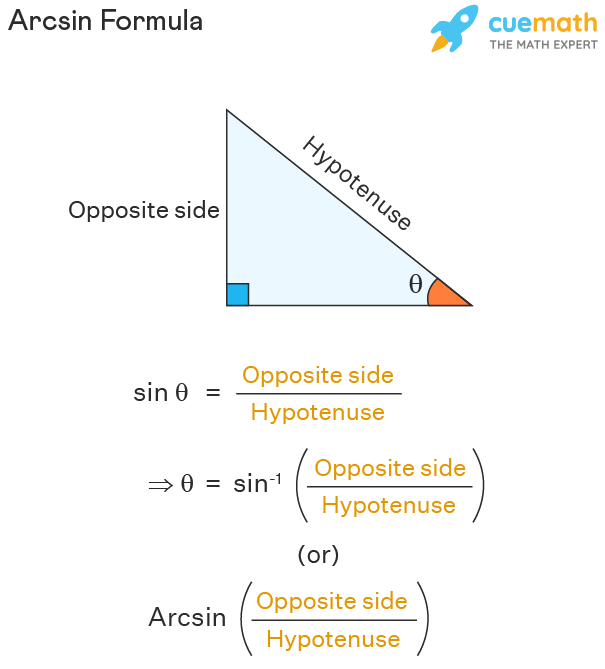
Trig sin equations
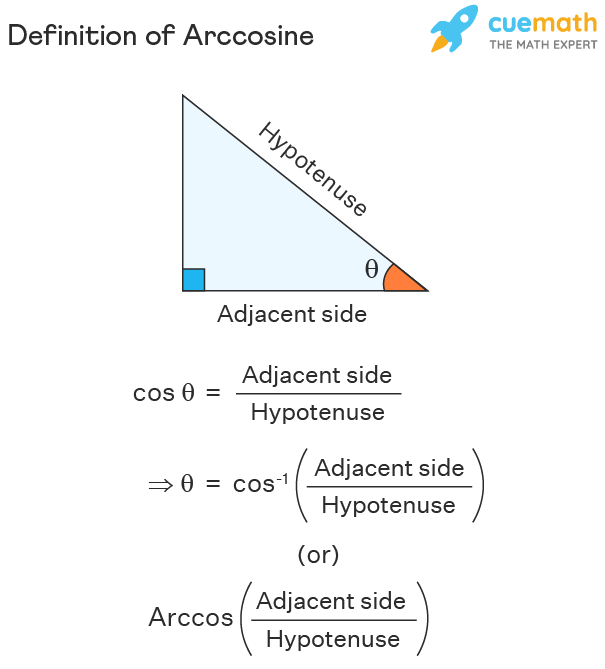
Trig cos equations
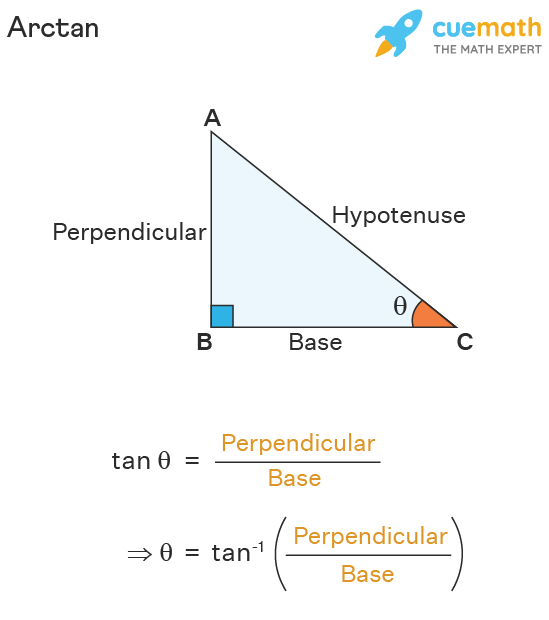
Trig tan equations
Law of cosines
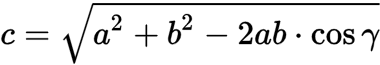
Law of sines
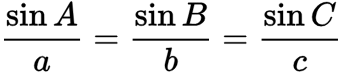
How to find the Magnitude of a vector
You must break it up into its x and y (and z) parts. You can only add like vectors:C=A+B= (Ax+Bx)x^+(Ay+By)y^+(Az+Bz)z^
What is the magnitude of a vector?
The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of the vector a is denoted as ∥a∥
r0
initial position (kinematics in 2D)
rf
final position (kinematics in 2D)
∆r
rf - r0
Sinθ =
opposite over hypotenuse (a/c)
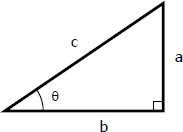
Cosθ =
adjacent over hypotenuse (b/c)
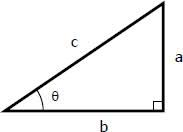
Tanθ=
opposite over adjacent (a/b)
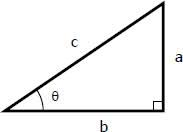
Inverse sin
θ=sin-1(a/c)
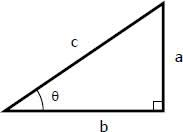
Inverse cos
θ=cos-1(b/c)
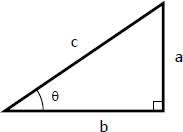
Inverse tan
θ=tan-1(a/b)
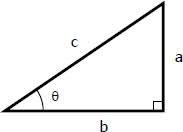
volume of a cylinder
V= (π)r2h
Circumference of a circle
2(π)r