propability
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
propability

propability rules
Rule 4 (rule of addition): The probability of either one of several events happening is the added probability of each individual event. 𝑃(𝐴 ∪ 𝐵) = 𝑃(𝐴) + 𝑃(𝐵) (“𝐴 ∪ 𝐵” means “A or B or both occurring”)
Rule 5 (rule of multiplication): If A and B are independent of each other: 𝑃(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) = 𝑃(𝐴) ∗ 𝑃(𝐵)

Probability as Frequency
Bayesian approach: probability is degree of belief in an event: “I believe that there is a 10% chance of selecting a left-handed person based on my past experience of how many people I know who are lefthanded” • Frequentist approach: probability is the long run frequency of an event if repeated many times: “To determine probability, I need to select you at random and ask whether you are left-handed, and work out what the frequency of lefthanders is
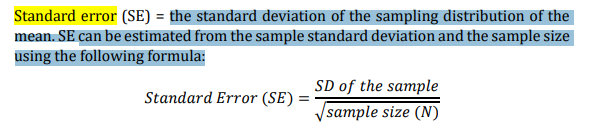
sampling error
the difference between the means of the population and the sample
The sampling distribution of the mean follows two rules in relation to the population distribution:
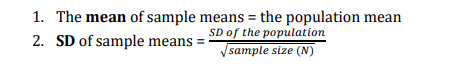
The central limit theorem:
The means of all our samples are normally distributed – even when the underlying data (e.g., heights) are not normally distributed.
the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the mean. SE can be estimated from the sample standard deviation and the sample size using the following formula: