neuron quiz
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
nature vs. nurture
all things psychological are simultaneously biological
Darwin’s Role
Natural Selection
Mutation
Evolutionary Psychology
Behavior genetics
evolutionary psychology
boils down the cause of our adapting behavior through generations to our need to survive and reproduce
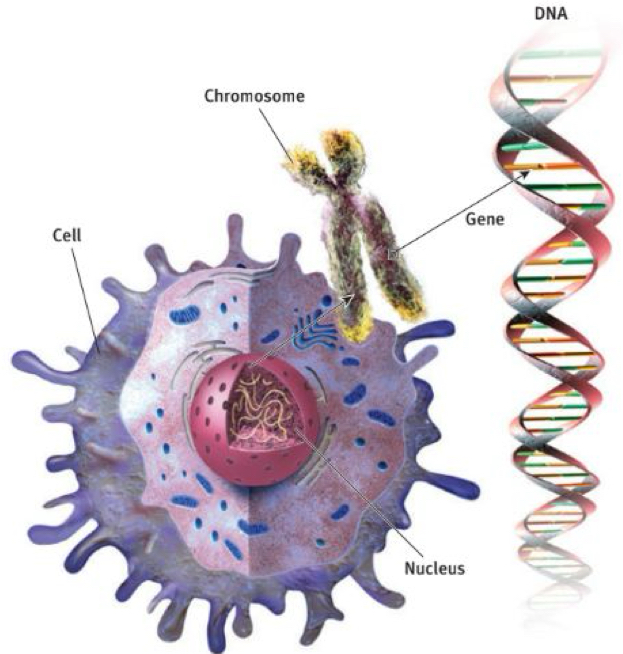
cellular structure
46 chromosomes = all cells except reproductive
23 chromosomes in sperm/egg cells
found in the nucleus
contains DNA
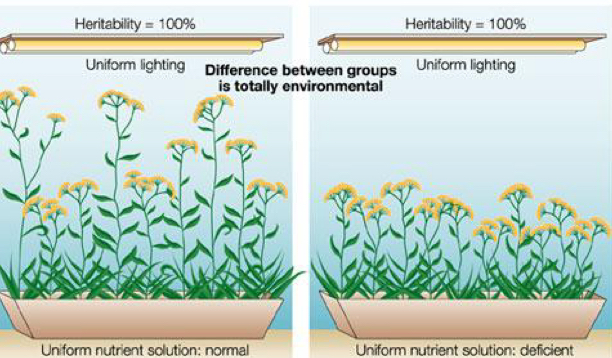
heritability
tells us NOTHING about individuals
an ESTIMATE of variation in a population
a correlation between nature and nurture in a population
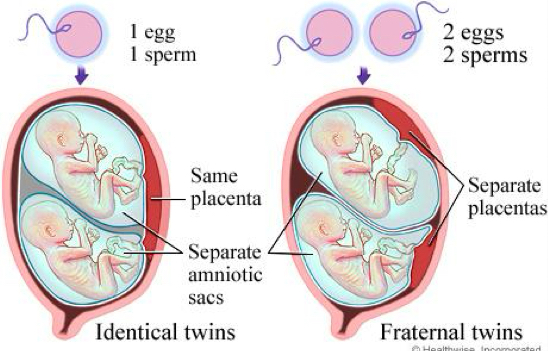
twin studies
What two systems make up the nervous system?
central nervous system & peripheral nervous system
What makes up the central nervous system?
brain & spinal chord
What two systems make up the peripheral nervous system?
somatic nervous system & autonomic nervous system
What two systems make up the autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic nervous system & parasympathetic nervous system
What is the function of the dendrites?
receive messages from other cells
What is the function of the cell body?
the cell’s life-support center
What is the function of the axon?
passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
What is the function of the terminal branches of axon?
form junctions with other cells
What is the function of the neural impulse?
action potential; electrical signal travelling down the axon
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
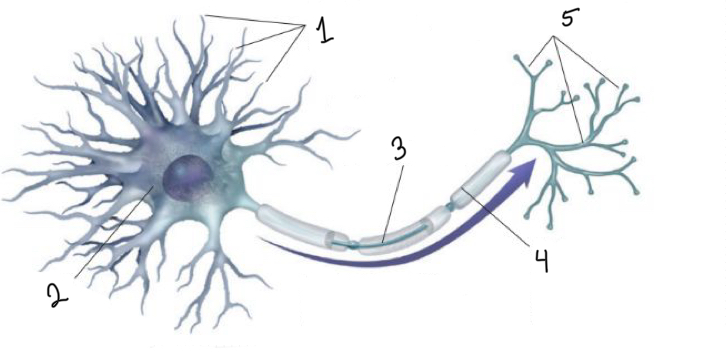
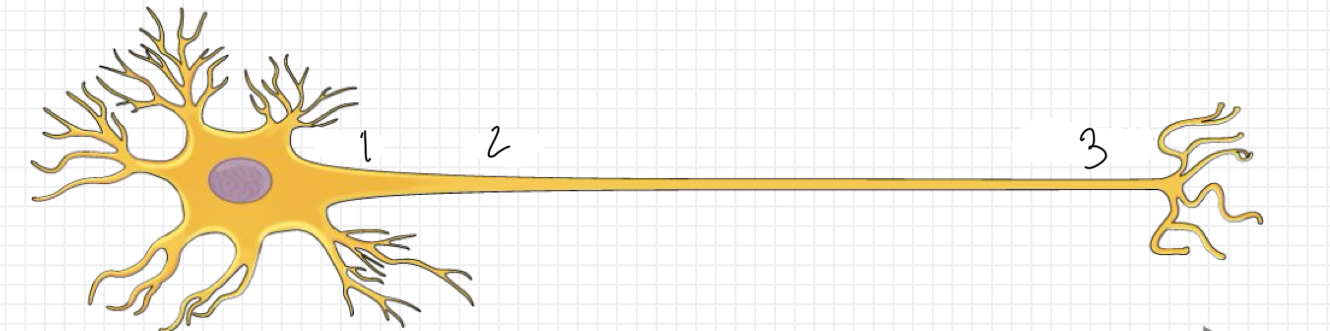
What is represented by number 1?
dendrites
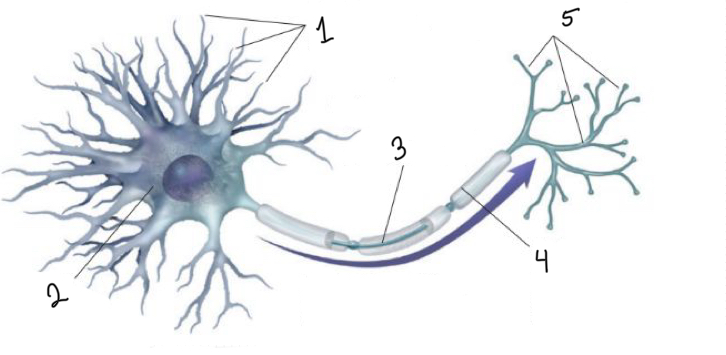
What is represented by number 2?
cell body
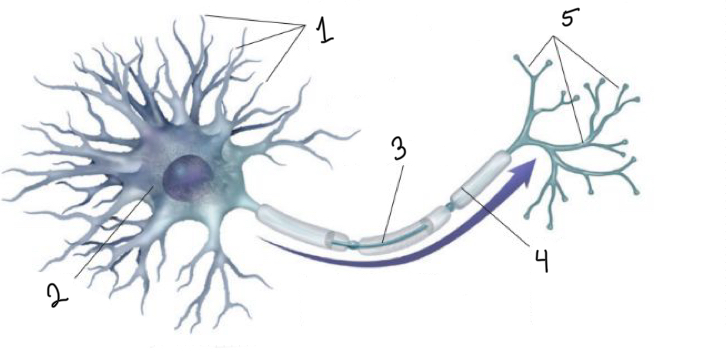
What is represented by number 3?
axon
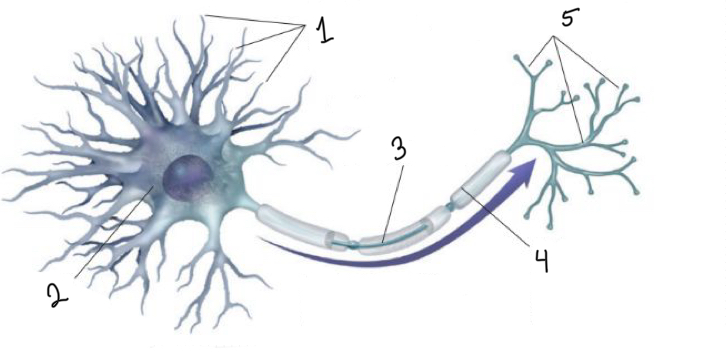
What is represented by number 4?
myelin sheath
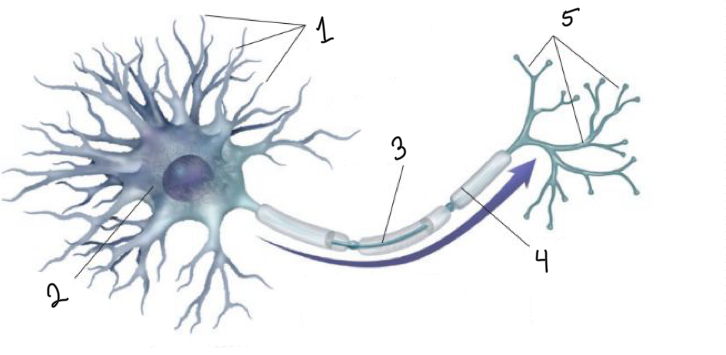
What is represented by number 5?
terminal branches of axon
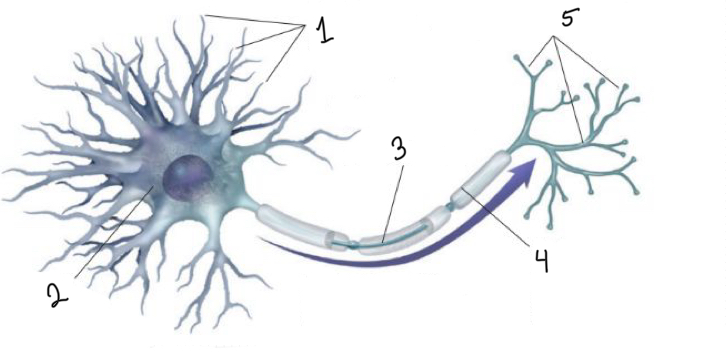
What is represented by the blue arrow?
neural impulse
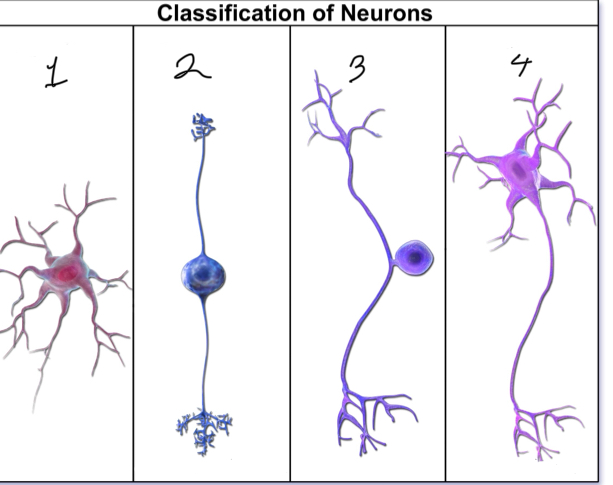
What is represented by number 1?
anaxonic neuron
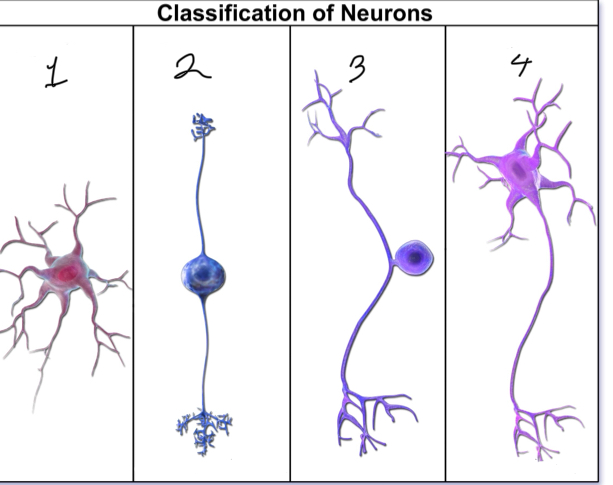
What is represented by number 2?
bipolar neuron; interneuron/afferent
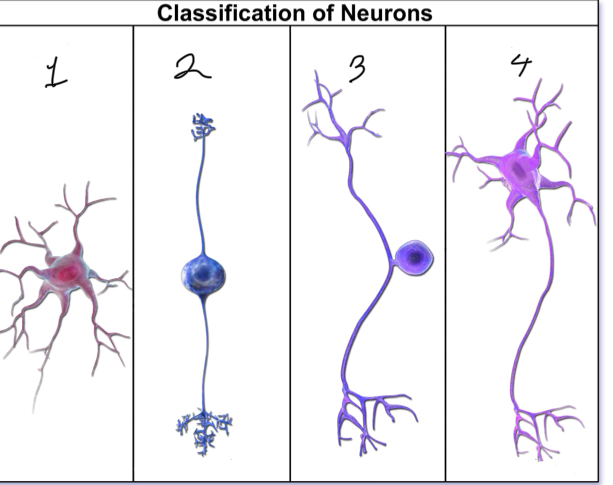
What is represented by number 3?
unipolar neuron; sensory
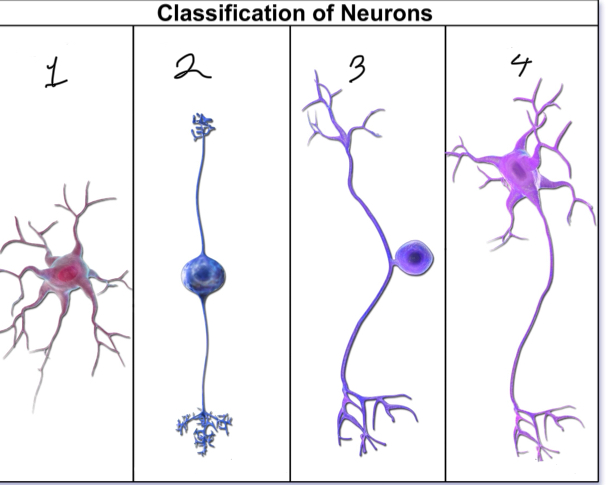
What is represented by number 4?
multipolar neuron; motor/efferent
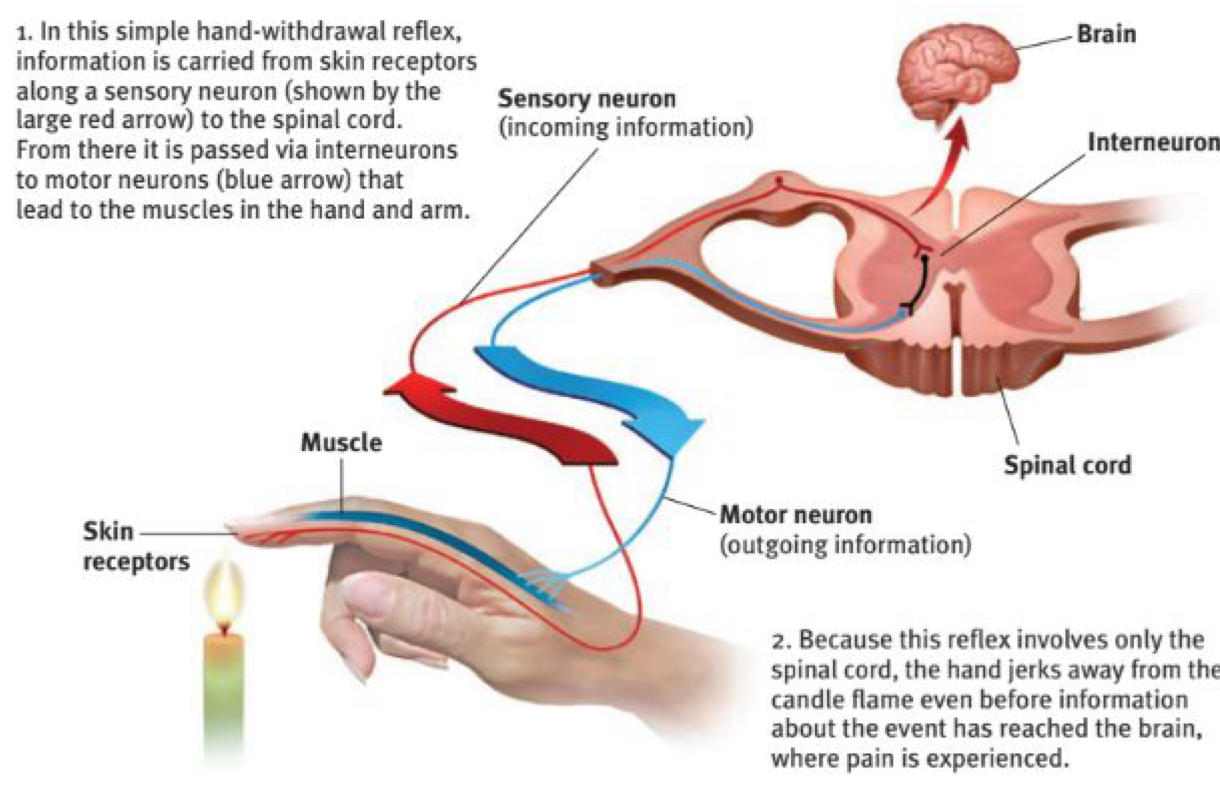
The neural chain
interneurons make reflexes happen
bypass the brain at first-avoid severe burns
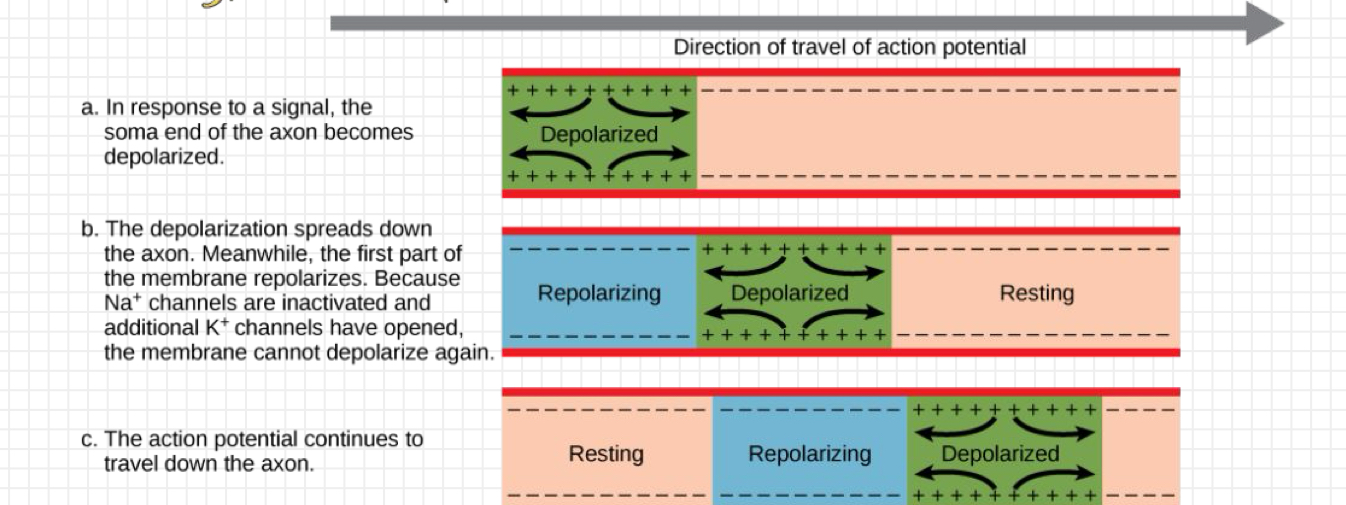
Creating an action potential
changes in potential (movement of sodium [+] and potassium [-]) lead to the inside of the neuron becoming less negative, relative to the outside.
this is how a neuron fires!
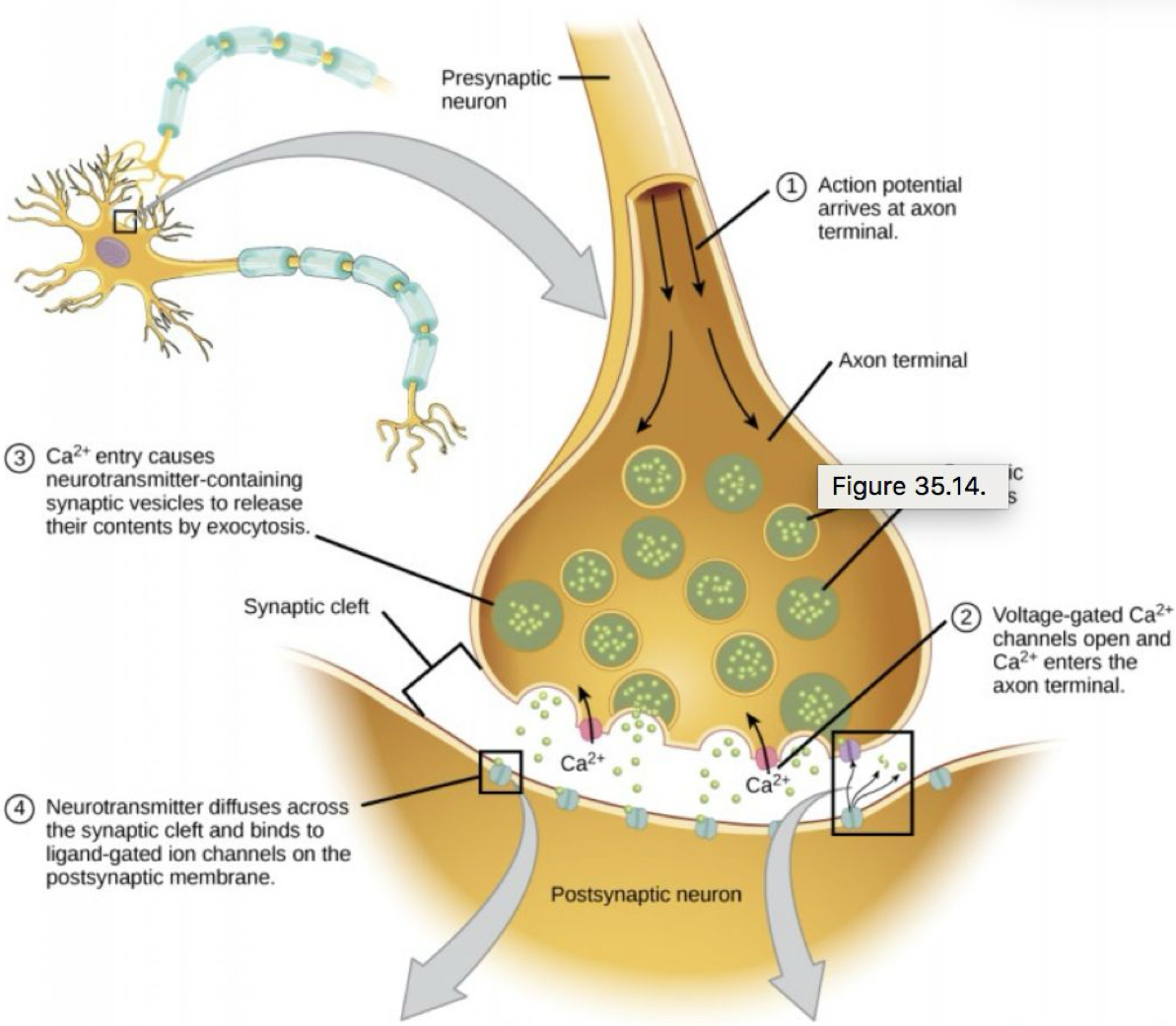
reuptake
excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed, drift away, or are broken down by enzymes
occurs at the synapse
action potential
changes in electrical voltage
produces a neural impulse
neurotransmitter
molecules are released into the synaptic cleft and bind to the receptor sites on the receiving neuron
the receiving neuron becomes more likely to fire or less likely to fire
What are the functions and malfunctions of acetylcholine (ach)?
function: enables muscle action, learning and memory
malfunctions: alzheimer’s disease, ACH-producing neurons deteriorate
What are the functions and malfunctions of dopamine?
functions: influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
malfunctions: excess dopamine receptor activity linked to schizophrenia. Starved of dopamine, the brain produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson’s Disease.
What are the functions and malfunctions of seratonin?
function: affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal
malfunction: undersupply linked to depression; prozac and some other antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels
What are the functions of norepinephrine?
functions: helps control alertness and arousal
malfunction: undersupply can depress mood
What are the functions and malfunctions of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)?
function: a major inhibitory neurotransmitter.
malfunction: undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
What are the functions and malfunctions of glutamate?
functions: a major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory.
malfunctions: oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures (this is why some people avoid MSG, monosodium, glutumate in food)
What is represented by number 1?
soma
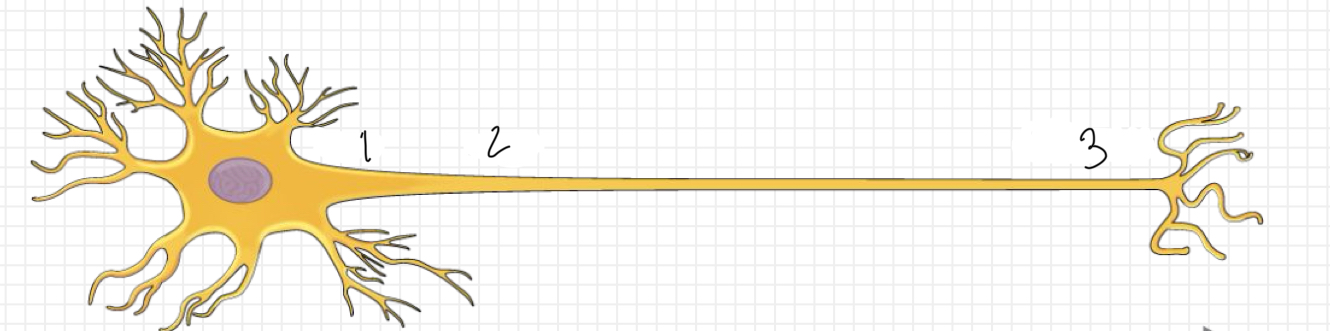
What is represented by number 2?
axon
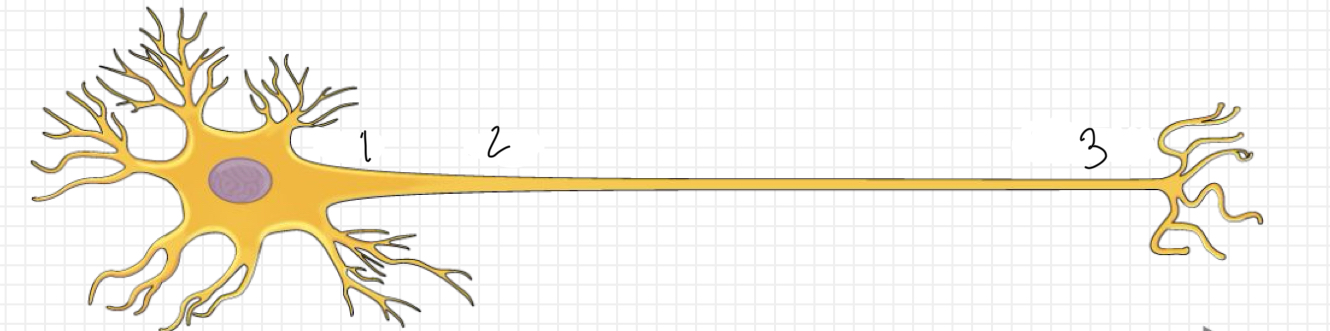
What is represented by number 3?
axon terminal
direction of travel of action potential
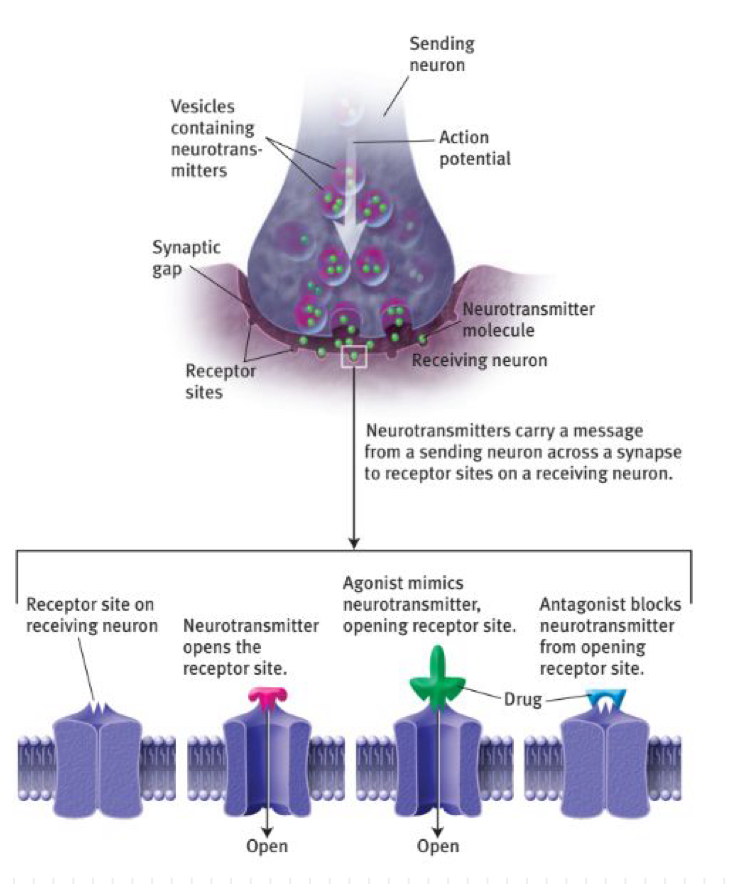
what are agonists?
mimic the action of neurotransmitters
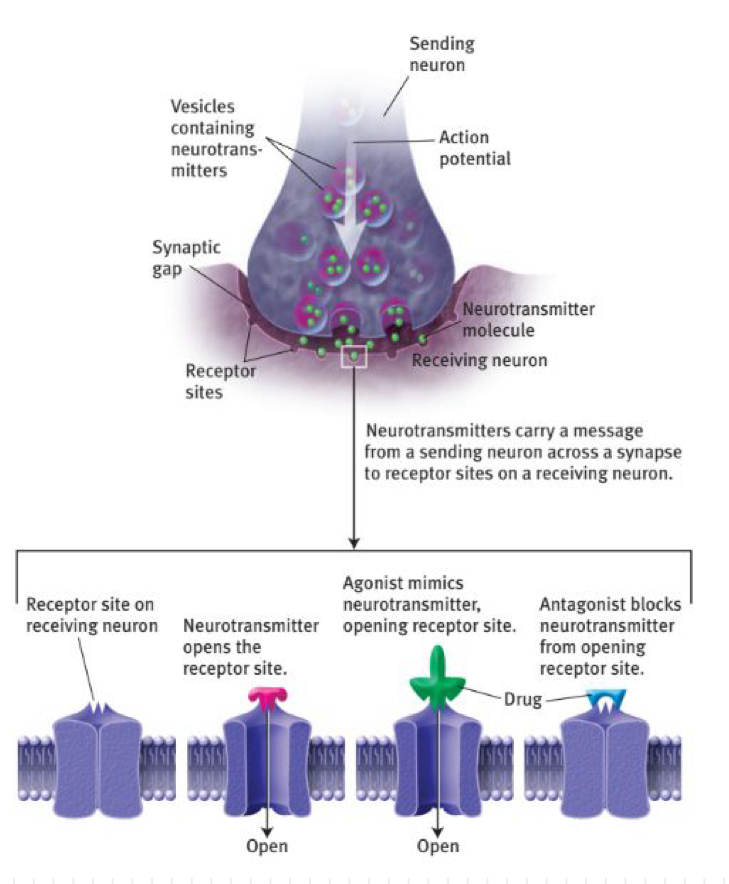
what are antagonists?
oppose the effects of a neurotransmitter, or block its effects
what is morphine?
Often acts as a neuromodulator
chemicals that increase or decrease the effectiveness of neurotransmitters
what are endorphines?
The brain has systems for releasing endorphins under extreme conditions of stress or exercion
Runner’s high