AP Macroeconomics Unit 5: Long-Run Consequences of Stabilization Policies
1/30
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Fiscal and Monetary Policy Actions in the Short Run
Fiscal and Monetary Policies are implemented in order to reduce output gaps in the short run
The unique combination of policies will influence aggregate demand, real output, the price level, and interest rates
In some cases, policies will have contradictory results
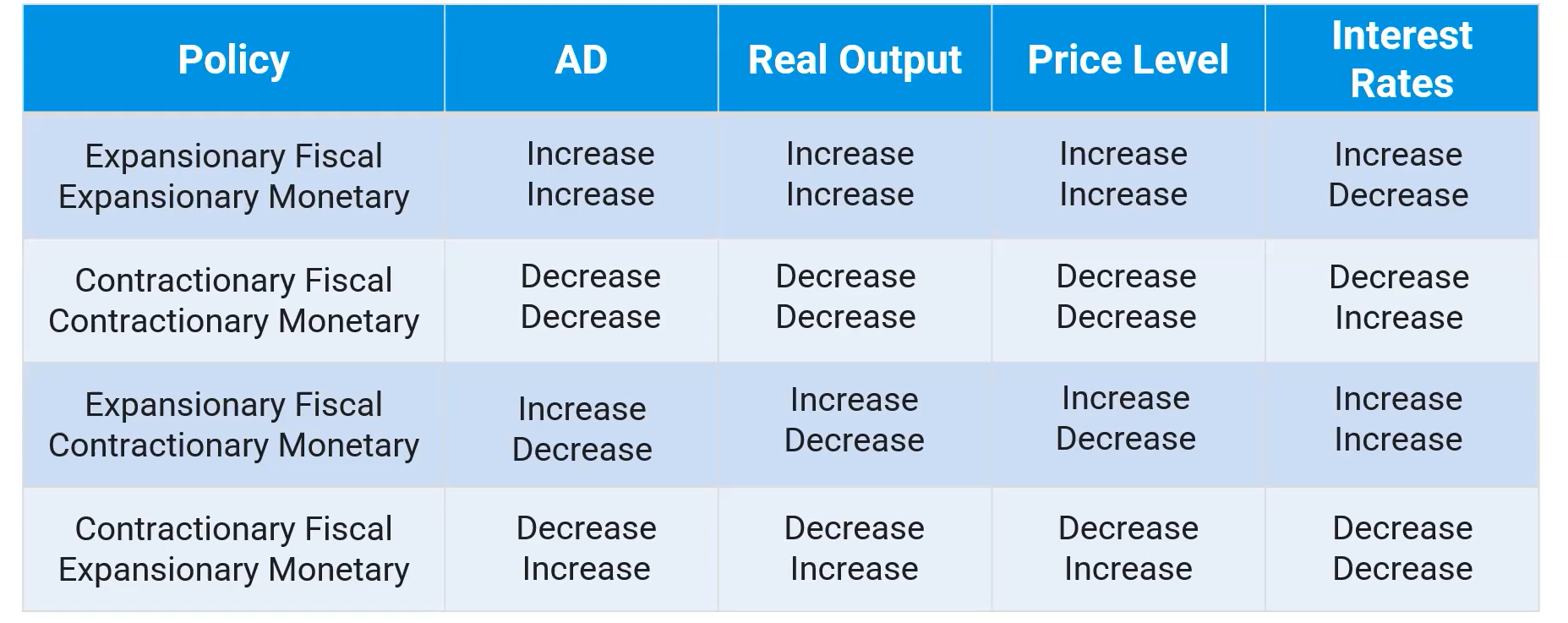
Short-Run Phillips Curve
Shows the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment
Rate of inflation and unemployment (the point on the line) moves up/down as AD/GDP changes

Short-Run and Long-Run Phillips Curve
Long-run Phillips curve shows the natural rate of unemployment
Also called “Full Employment”
Equilibrium occurs where the SRPC and LRPC intersect
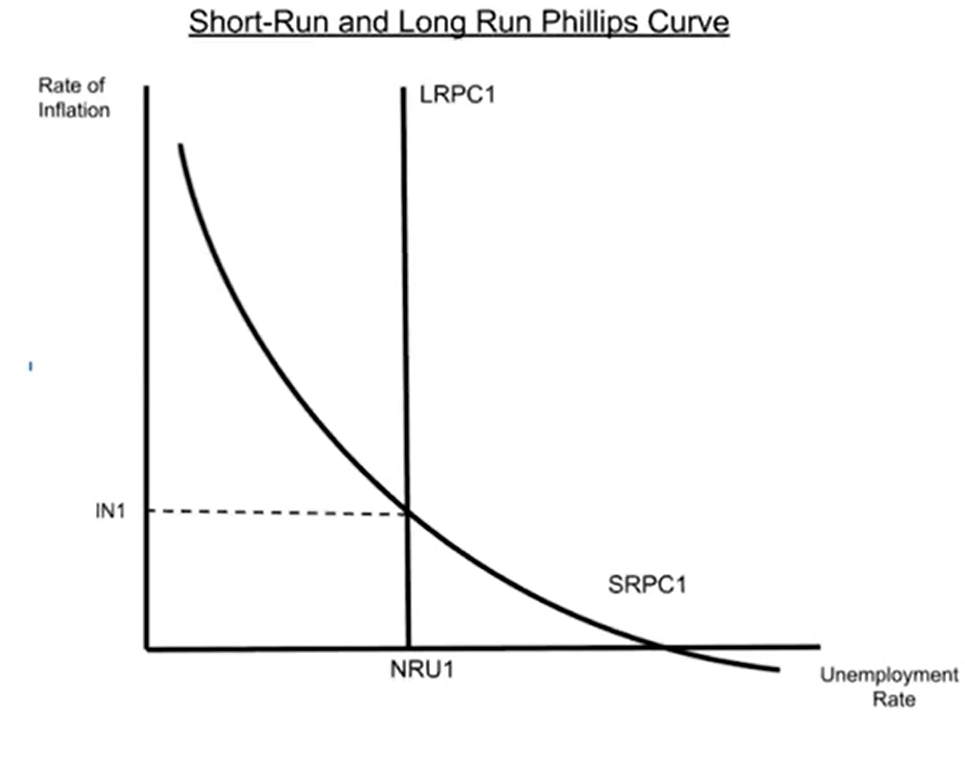
Inflationary Gap In the Phillips Curve Model
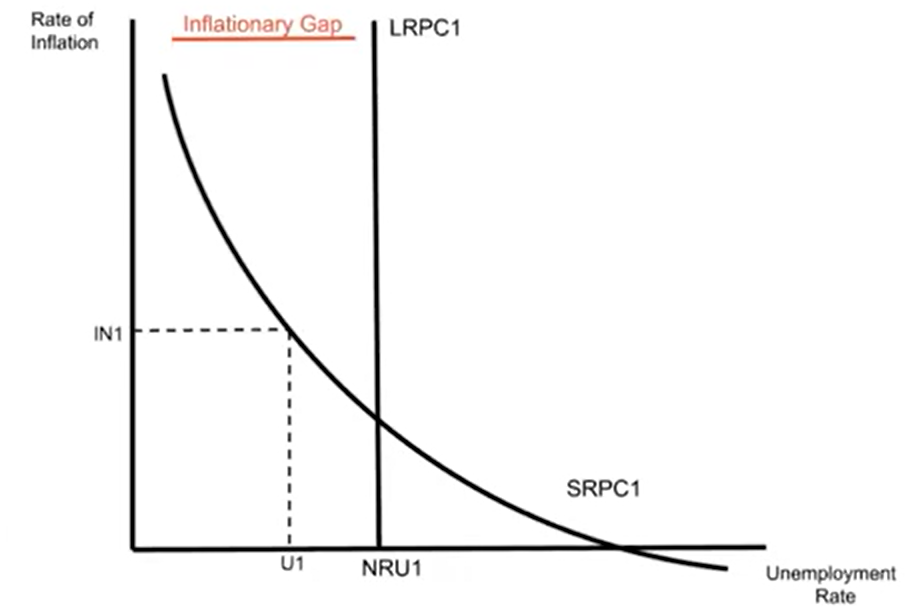
Recessionary Gap in the Phillips Curve Model
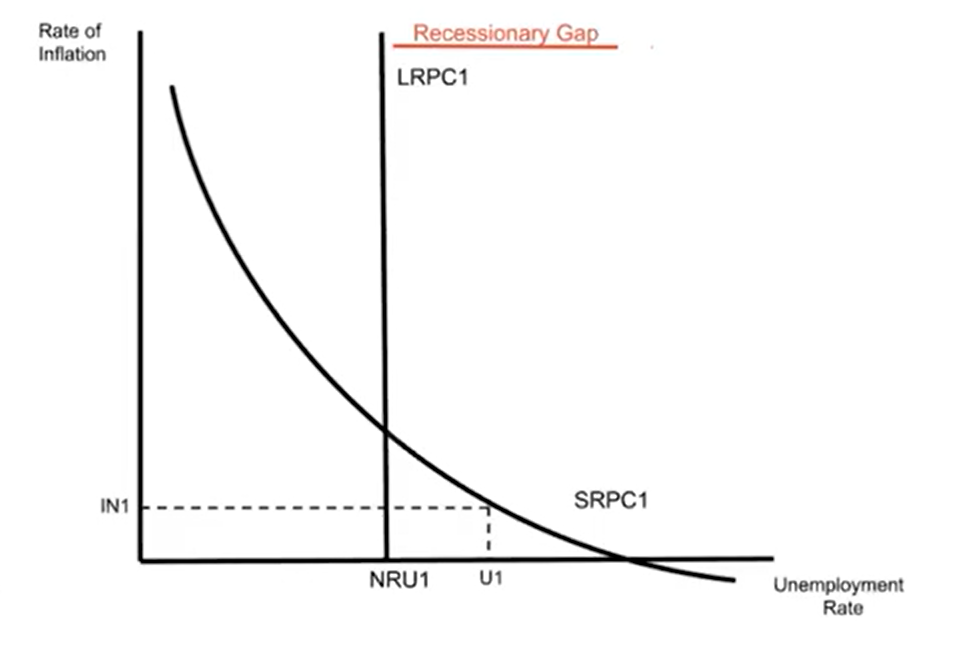
Long run equilibrium in the Phillips Curve
The economy is always operating at some point on the short-run Phillips Curve
Long run equilibrium occurs where SRPC intersects LRPC
If the economy is operating at a point to the left of the LRPC, it’s in an inflationary gap.
If the economy is operating at a point to the right of the LRPC, it’s in a recessionary gap.
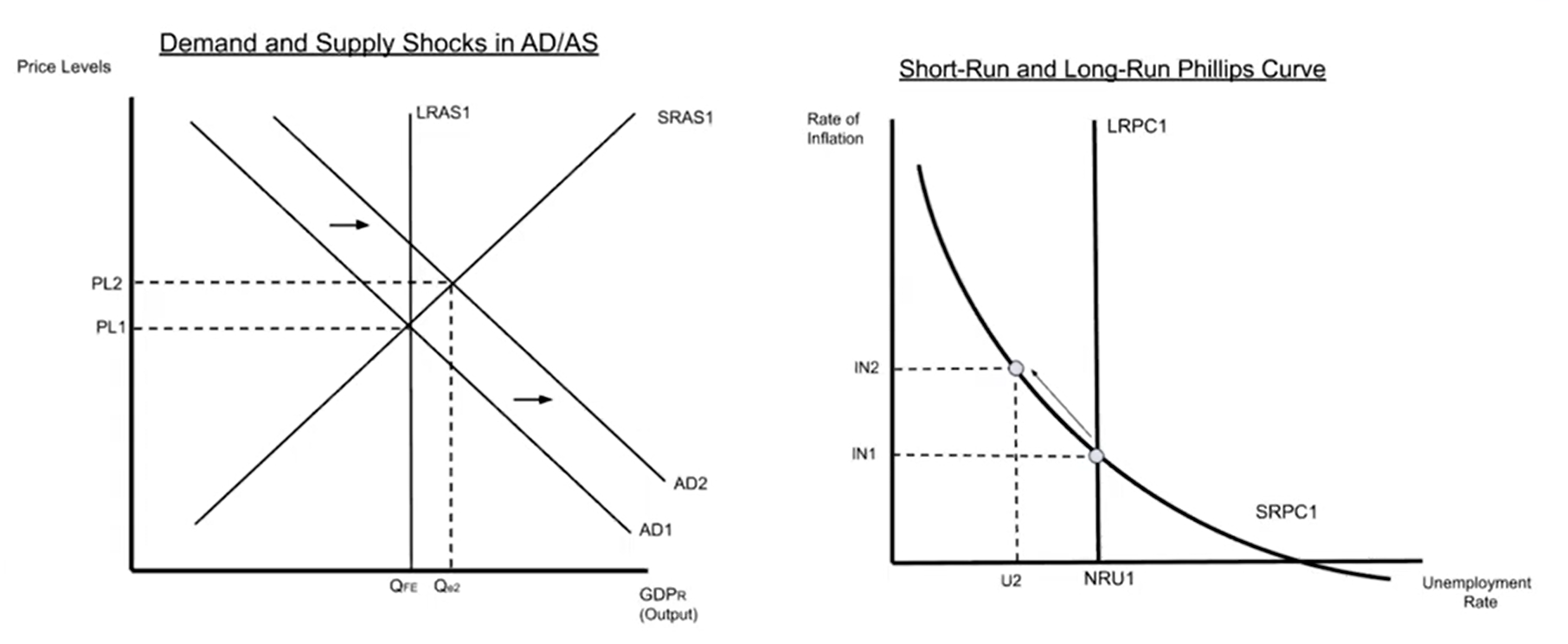
Demand Shocks & the Phillips Curve
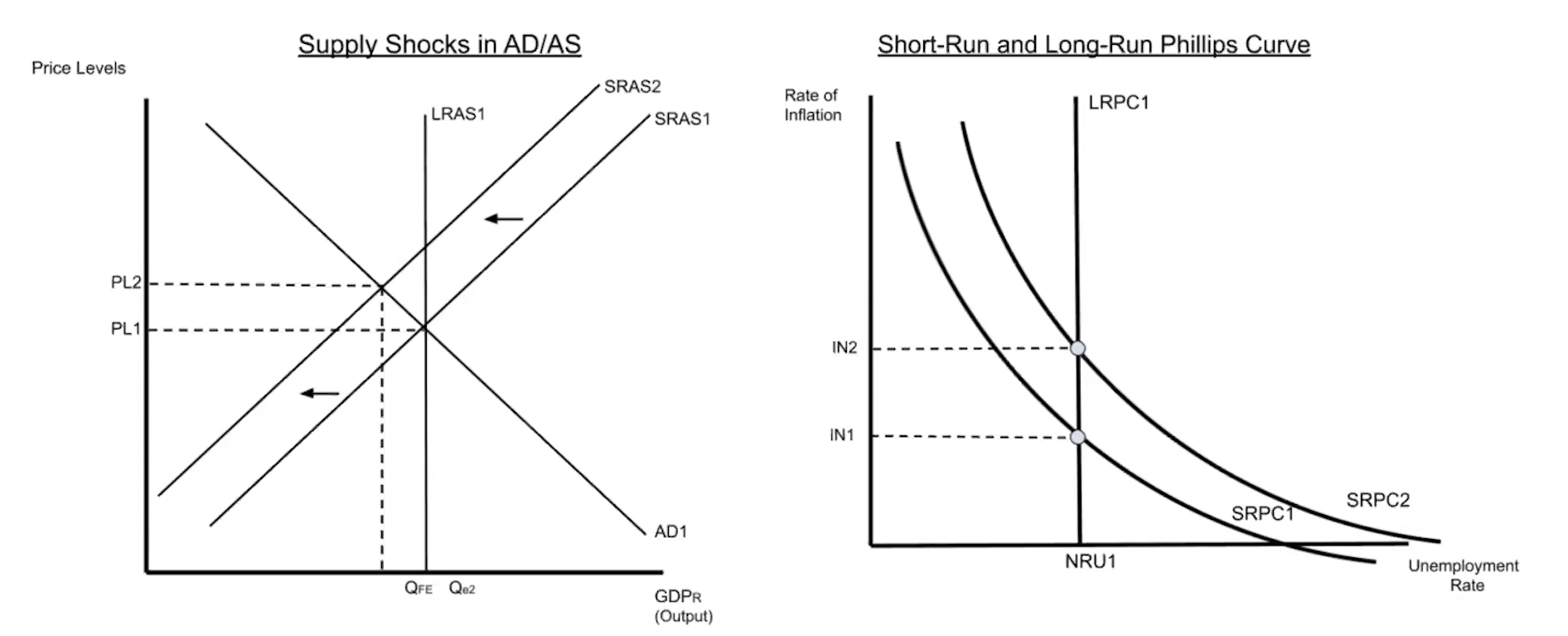
Supply Shocks & the Phillips Curve
Long-Run Impacts and Corrections of the Phillips Curve
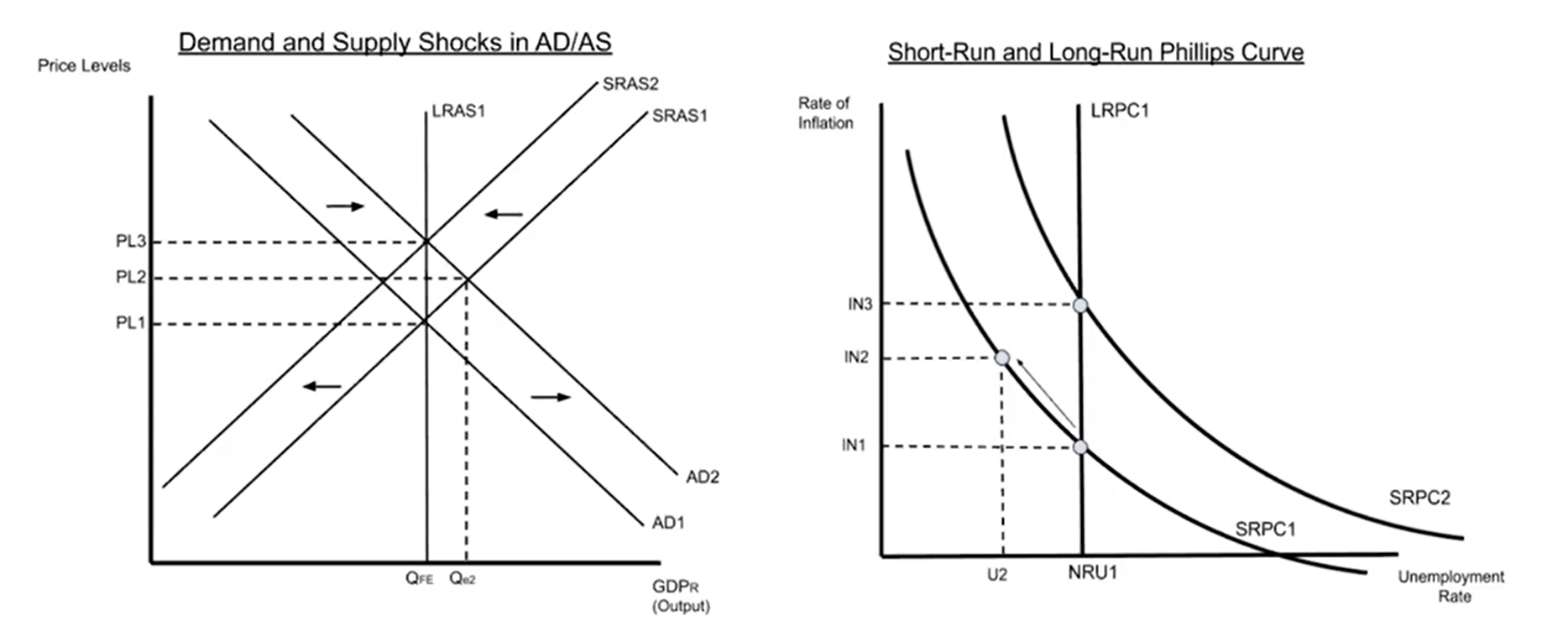
Factors that shift the LRPC
Decreasing Structural and/or Frictional Unemployment Will Decrease LRPC
Workforce becomes better qualified to fill job openings (structural)
Improved job finding/matching time (frictional)
More recruiting firms, headhunters, etc.
Increasing Structural and/or Frictional Unemployment Will increase LRPC
Sliders and Shifters of the Phillips Curve
Demand shocks cause slides on the SRPC
Supply shocks cause shifts in the SRPC
Slides/shifts move in the opposite direction as the preceding AD/AS shift
Long-run equilibrium is restored as AD/AS corrects to restore equilibrium
Long-run Phillips curve can shift when there is a change in the structural and/or frictional unemployment rates.
Equation of Exchange
M = Money Supply
V = Velocity of Money
P = Price Level
Y = Real Output
P x Y = Nominal GDP
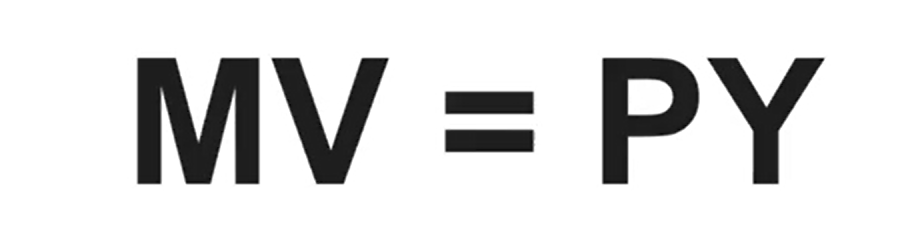
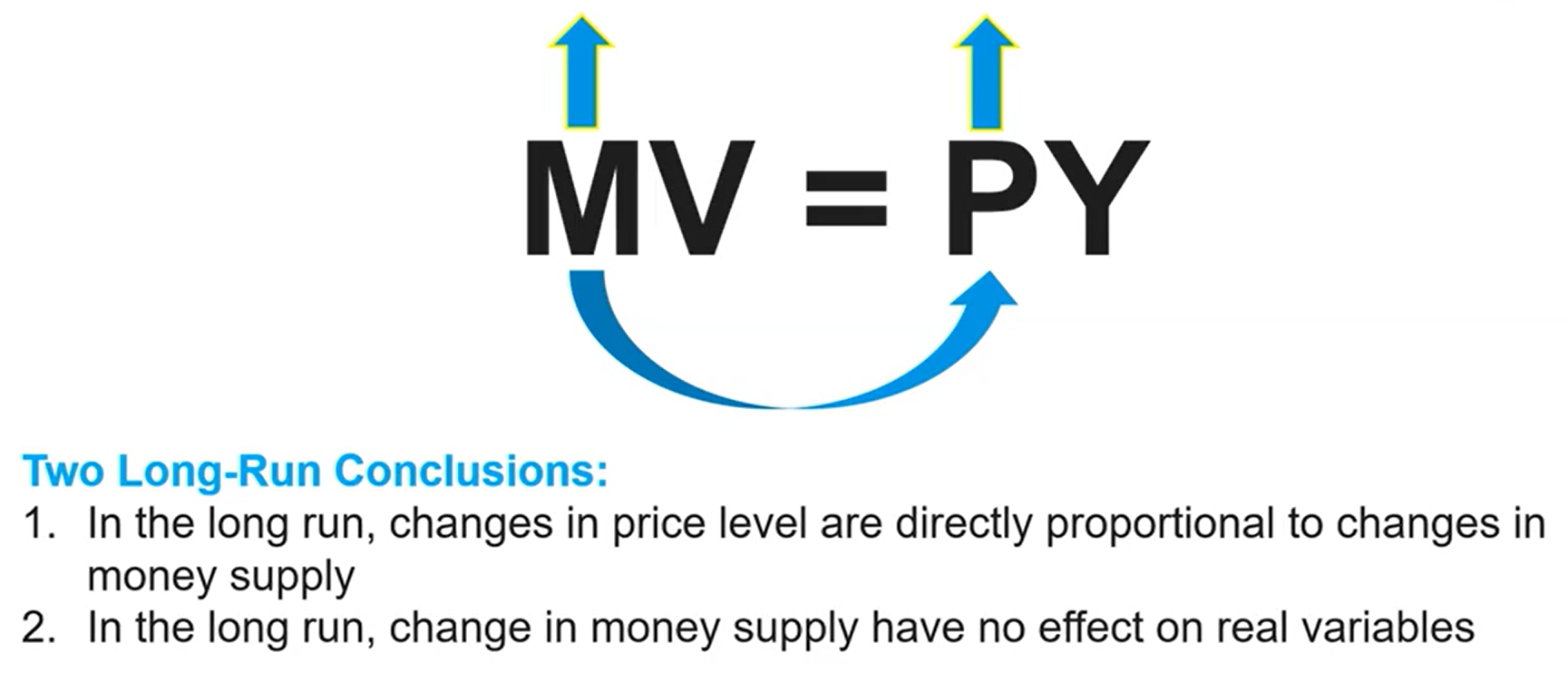
Two Long-Run Conclusions About Money Growth and Inflation
The equation of exchange is always true and leads to two long-run conclusions:
There exists a direct relationship between changes in money supply and the price level in the long-run —> Quantity theory of money.
Changes in money supply have no effect on real variables in the long run —> Neutrality of monetary policy
Essential Knowledge of Money Growth and Inflation

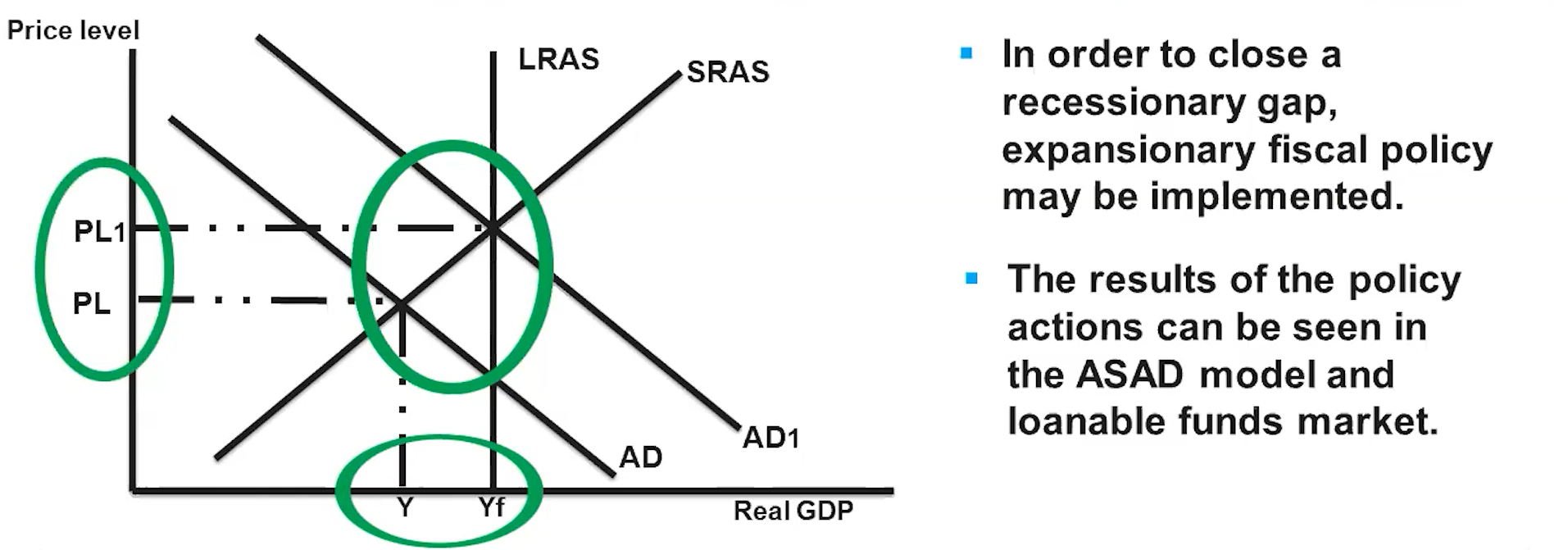
Crowding Out
When government budget deficits have a negative effect by driving up interest rates and reducing investment due to expansionary fiscal policy
It occurs from deficit spending that increases interest rates.
The government’s increase in deficit spending, due to expansionary fiscal policy, causes real interest rates to increase in the loanable funds market.
The increase in real interest rates leads to less creation of capital stock, which results in less economic growth

Crowding Out in AD/AS Graph
Crowding Out in the Loanable Funds Market
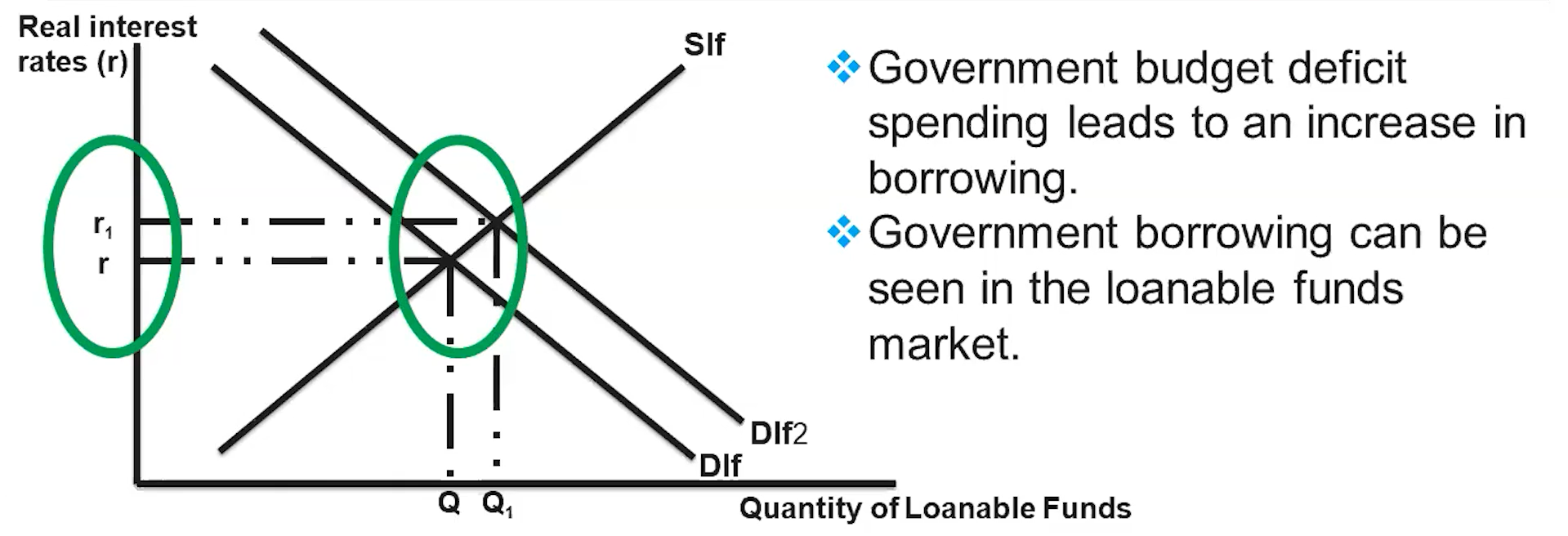
Crowding Out Essential Knowledge
Private domestic investment spending drives economic growth
Investment spending is spending on capital stock
Greater amounts of capital stock increase the capacity of the economy to produce goods and services
A decrease in investment spending causes the economic growth rate to slow, because fewer capital goods are being produced relative to the economy’s productive capacity.
The increase in deficit spending leads to an increase in the Real interest rate, which leads to a decrease in investment spending, which results in less economic growth.
GDP per capita
GDP divided by the size of the population; it is equivalent to the average GDP per person. Key measure for comparing economies of other countries.
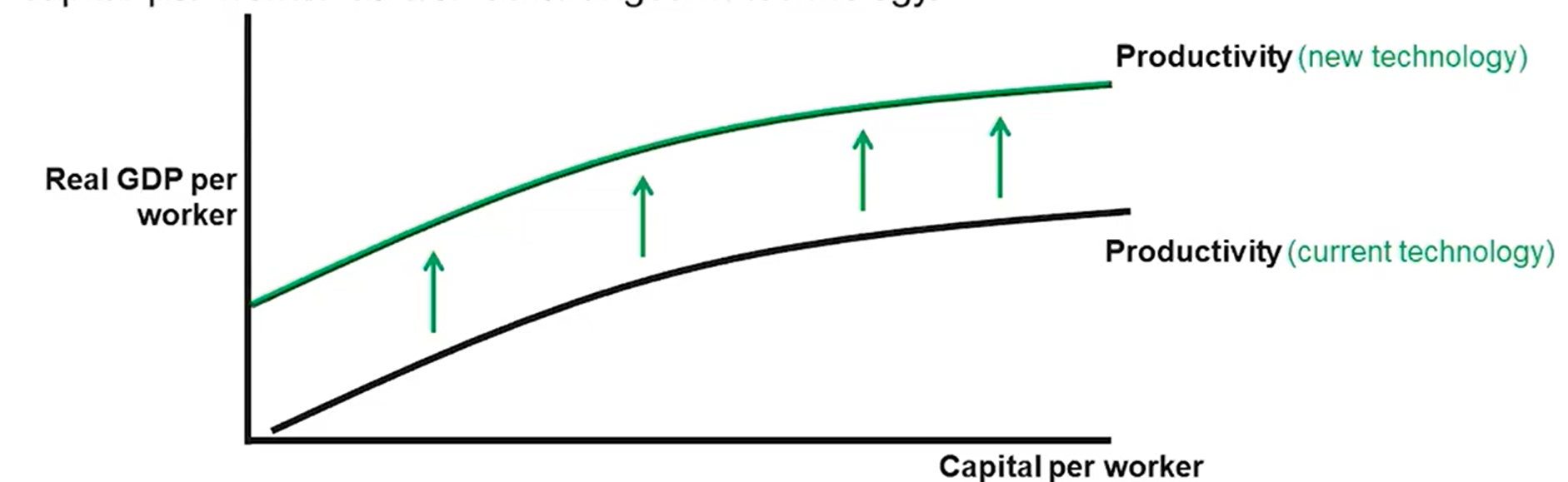
Productivity
Output per worker.
Today’s workers are more productive due to changes in physical capital, human capital, and technology. This change is considered capital stock formation, which is essential to economic growth.
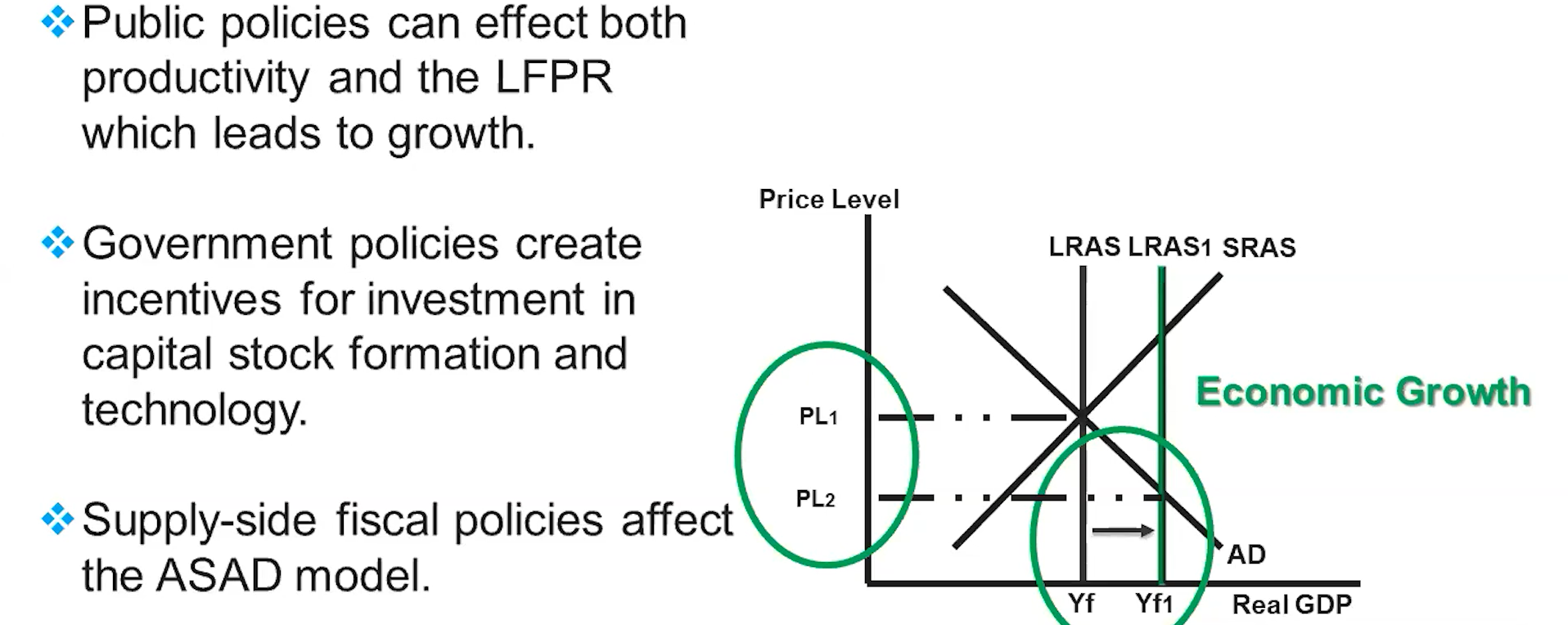
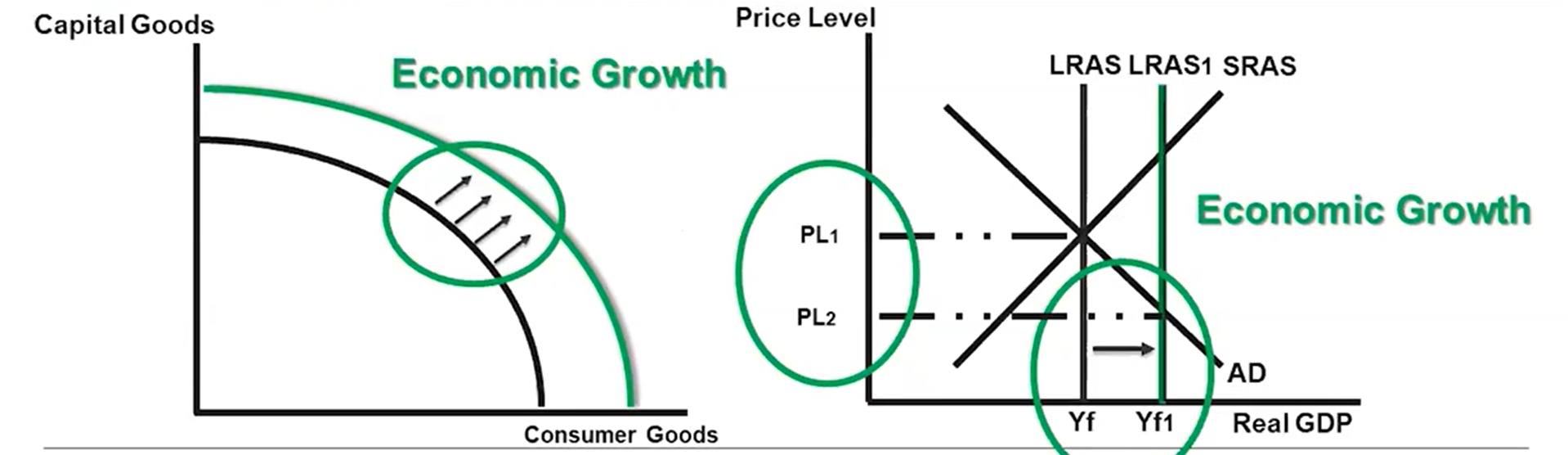
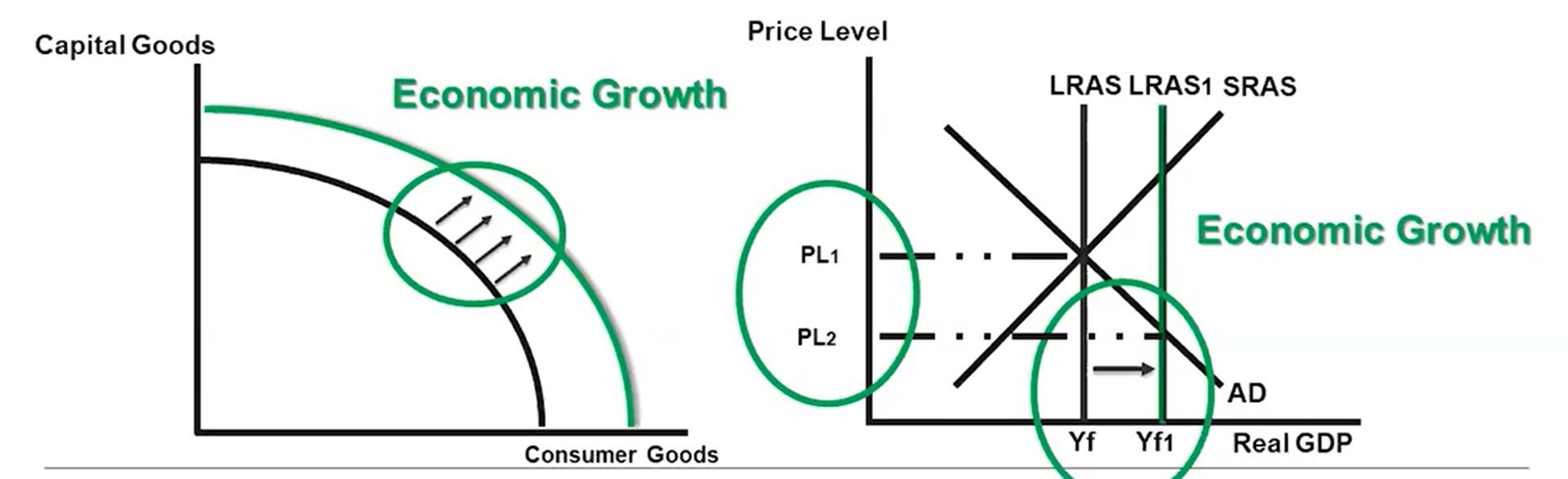
Economic Growth
An increase in real GDP per capita over time, illustrated by outward shifts of the PPC and LRAS
Determinants of Economic Growth
Changes in the levels of Capital stock formation and technology. Physical capital, human capital, and technology are the keys to changes in productivity, which lead to growth.
Increases in productivity
Through Capital Stock Formation: development of capital stock (physical and human)
Investment spending leads to CSF
Increase the use of new and better technologies
The Aggregate Production Function
_____ shows that productivity or output per capita is positively related on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as changes in technology
Economic Growth on the PPC and the AD/AS Model
Supply-Side Fiscal Policies
Government policies that promote economic growth by influencing both short-run and long-run aggregate supply, which eventually leads to economic growth.
Goal: Increase our productivity of our current resources and increase our amount of new resources.
Goal: increase in investment and productivity in order to increase GDP per capita or growth through public policy.
Increase each of the following through policies:
Human capital per worker
Government spending on education and job training and/or tax credits for education or job training.
Ex: Headstart, special education, Job corps, student loans, GI bills
Technology
Government spending on technology and/or tax credits for research and development.
Ex: renewable energy, carbon emissions, SpaceX, education
Physical capital per worker
Government spending on infrastructure and/or tax credits for investment spending on physical capital.
Ex: electric grid, highway system, waterways
Goal: Increase our productivity and LFPR (Labor Force Participation Rate)
Public Policy and Economic Growth Examples:
Increase age when individuals can collect retirement benefits.
Increase the number of individuals to enter the labor force with tax credits.
Increase spending on programs for older workers to continue working.
Household Economic Behavior

Business Economic Behavior

The Main Ways Public Policy Effects Economic Growth