IB Physics SL - CHAPTER 8
5.0(1)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:04 PM on 3/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Specific energy
Specific energy is the measure of the amount of energy per unit mass of a fuel. (Unit: J/kg)
2
New cards
Energy density
**Energy density** is the measure of the amount of energy per unit **volume** of a fuel. (Unit: J/m^3)
3
New cards
Density from energy density and specific energy
Density = Energy density/Specific energy
4
New cards
Sankey diagrams
Represent energy transfers.
5
New cards
Primary energy source
A primary energy source is one that is found in the natural environment.
6
New cards
Secondary energy source
A secondary source is processed or refined primary resources (into useful energy).
7
New cards
Renewable energy source
A renewable energy source is one that is reproduced at a higher rate than it is consumed.
8
New cards
Non-renewable energy source
A non-renewable energy source is one that is not reproduced at a higher rate than it is consumed.
9
New cards
The 3 main uses of energy resources
1. Transport
2. Electricity generation
3. Heating
10
New cards
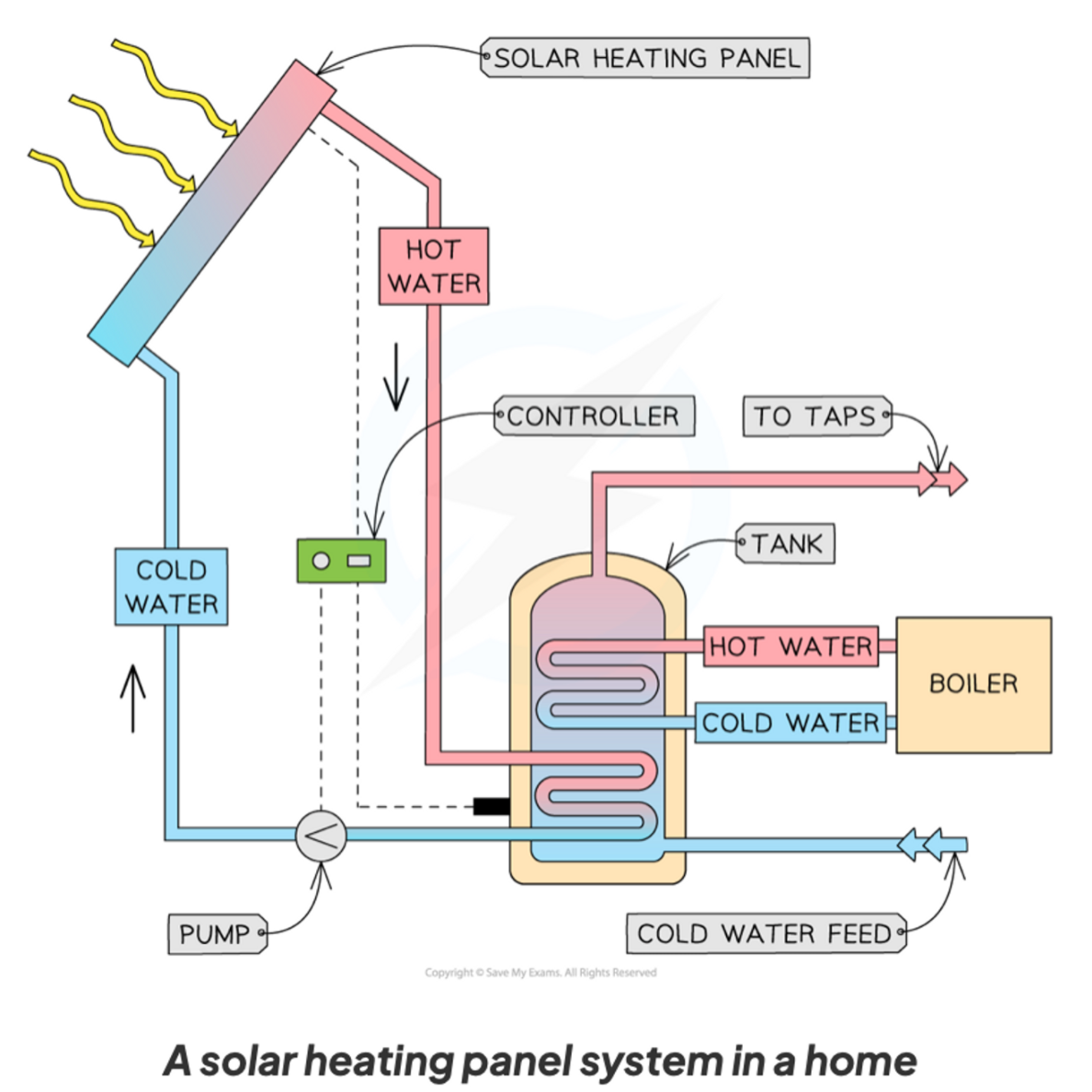
Solar heating panels
Solar heating panels use thermal radiation to warm water.
11
New cards
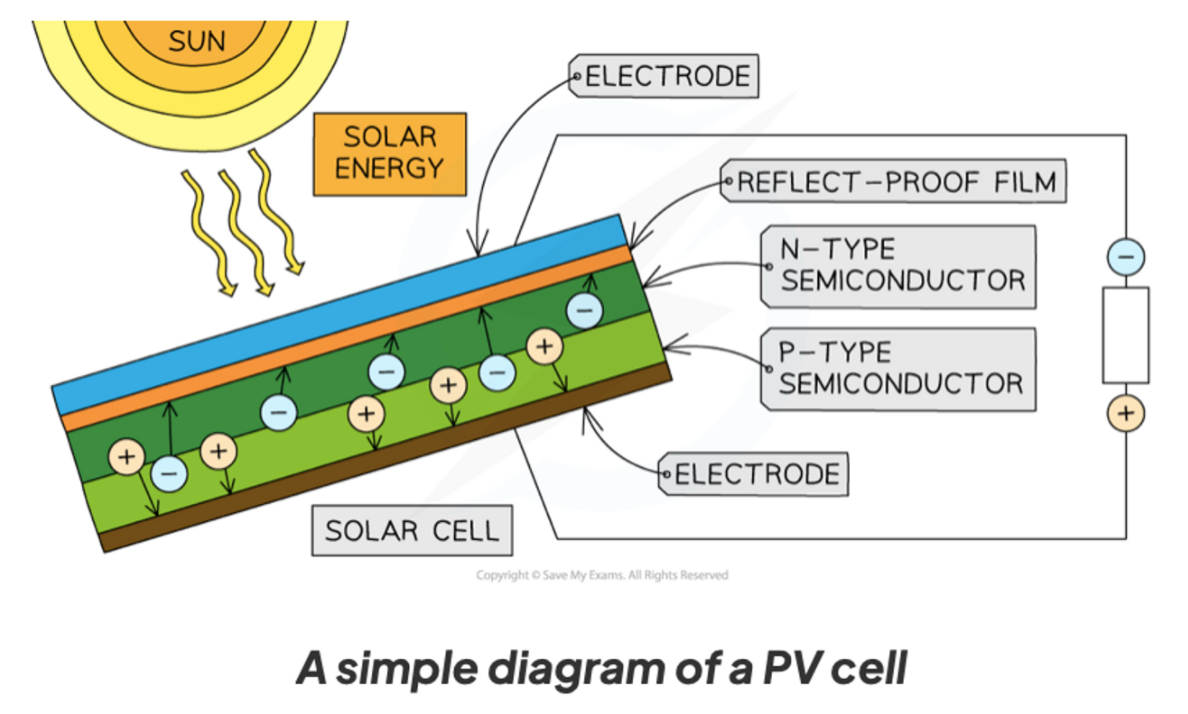
Photovoltaic cells
Photovoltaic cells use light to create energy.
12
New cards
Advantages of solar panels
* Unlimited supply of energy
* Clean to produce the electicity
* Freely available everywhere
* Cheap maintenance
* No fuel is required for energy
* Clean to produce the electicity
* Freely available everywhere
* Cheap maintenance
* No fuel is required for energy
13
New cards
Disadvantages of solar panels
* Impacted by poor weather
* Limited efficiency
* Only available during the day
* Requires large investment upfront
* Needs large areas
* Limited efficiency
* Only available during the day
* Requires large investment upfront
* Needs large areas
14
New cards
The equipment involved in nuclear power
Control rods: Absorb neutrons.
Moderators: Slows down neutrons.
Shielding materials: Absorb hazardous radiation.
Uranium fuel: Producers heat when reacting.
Water: Turns to steam and turn turbines.
Moderators: Slows down neutrons.
Shielding materials: Absorb hazardous radiation.
Uranium fuel: Producers heat when reacting.
Water: Turns to steam and turn turbines.
15
New cards
Advantages of nuclear power
* Extensive reserves of fissionable materials
* Increasingly refine technology available
* No greenhouse gases produced
* A large amount of power is produced
* Increasingly refine technology available
* No greenhouse gases produced
* A large amount of power is produced
16
New cards
Disadvantages of nuclear power
* Hazardous radioactive waste materials produced
* Dangerous if the power plant goes significantly wrong
* Danger of misuse of nuclear material (nuclear bombs)
* Problems with mining fuel
* Dangerous if the power plant goes significantly wrong
* Danger of misuse of nuclear material (nuclear bombs)
* Problems with mining fuel
17
New cards
Calculating power obtained from nuclear power
?
18
New cards
The equipment involved in burning fossil fuels
Boiler: Burns fossil fuels.
Condenser: Cools water.
Fossil fuel: Produces heat when burned.
Water: Turns to steam and turn turbines.
Condenser: Cools water.
Fossil fuel: Produces heat when burned.
Water: Turns to steam and turn turbines.
19
New cards
Advantages of burning fossil fuels
* Extensive infrastructure in place
* High energy density of fuel
* Available energy at any time
* Well-known and developed technology
* High energy density of fuel
* Available energy at any time
* Well-known and developed technology
20
New cards
Disadvantages of burning fossil fuels
* Produces greenhouse gases
* Unsustainable
* Produces pollution
* Unsustainable
* Produces pollution
21
New cards
Calculating power obtained from burning fossil fuels
?
22
New cards
The equipment involved in wind electricity generators
Wind generators: Uses wind to turn turbines.
23
New cards
Advantages of wind electricity generators
* Clean energy generation
* Freely available
* Is always sustanable and will never run out
* Freely available
* Is always sustanable and will never run out
24
New cards
Disadvantages of wind electricity generators
* Not consistent energy production
* Needs favourable local conditions to be placed in windy locations
* Can by visually unappealing
* Needs favourable local conditions to be placed in windy locations
* Can by visually unappealing
25
New cards
Calculating power obtained from wind electricity generators
P = 1/2 · pAv^3
26
New cards
The equipment involved in hydroelectric power
Reservoir: Stores large bodies of water high up.
Dam: Holds water in its reservoir.
Control gate: path leading water to turine
Dam: Holds water in its reservoir.
Control gate: path leading water to turine
27
New cards
Advantages of hydroelectric power
* Clean energy generation
* Sustainable
* Can be stored for when needed
* Sustainable
* Can be stored for when needed
28
New cards
Disadvantages of hydroelectric power
* Large areas and changes to the environment are needed
* It relies on suitable locations
* A large initial investment is required
* It relies on suitable locations
* A large initial investment is required
29
New cards
Calculating power obtained from hydroelectric power
P = mgh/∆t = p∆Vgh/∆t
30
New cards
Conduction
Conduction is a method of thermal energy transfer that occurs when two solids come in physical contact with one another.
31
New cards
Conduction occurs by
1. Atomic vibrations, or
2. Free electron collisions
32
New cards
Convection
Convection is a method of thermal energy transfer that occurs due to the movement of atoms in liquids and gases, resulting from variations in density within the liquid or gas.
33
New cards
Convection occurs by
1. Convection current
34
New cards
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is a method of thermal energy transfer that occurs by means of electromagnetic radiation normally in the infrared region.
35
New cards
Thermal radiation occurs by
Electric charges within the atoms in a material vibrate causing electromagnetic radiation to be emitted.
36
New cards
Perfect black-body
A perfect black-body is an object that absorbs all radiation incident on it and does not reflect or transmit any radiation in return.
37
New cards
Wien’s displacement law
The formula is:
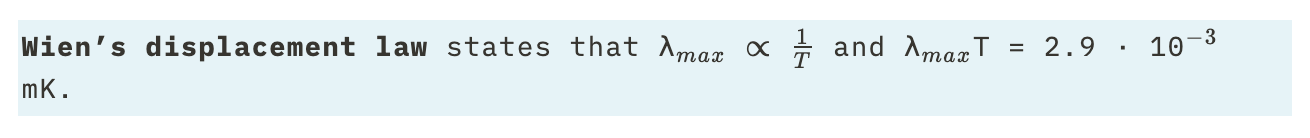
38
New cards
Stefan-Boltzmann’s law
The formula is:

39
New cards
The solar constant
The solar constant is the amount of solar radiation across all wavelengths that is incident in one second on one square meter of the Earth’s athomosphere at the mean distance of Earth from the Sun.
40
New cards
Albedo
Albedo, *a*, is the proportion of radiation incident on and scattered by a given surface.
a = total scattered power/total incident power
a = total scattered power/total incident power
41
New cards
Albedo of a planet
Albedo of a planet is the ratio between the total scattered radiation and the total incident radiation of that planet. (Earth = 0.3)
42
New cards
Earth’s albedo varies daily because
* Time of year
* Latitude (North/South/etc.)
* Terrain
* Latitude (North/South/etc.)
* Terrain
43
New cards
Emissivity
Emissivity, *e*, is the power radiated by a surface divided by the power radiated from a black body of the same surface area and temperature.
e = power radiated by an object/power emitted by a black body
e = power radiated by an object/power emitted by a black body
44
New cards
Greenhouse gases
Most effect
* Carbon dioxide
* Water vapor
Less effect
* Ozone
* Methane
* Nitrous oxides
* Carbon dioxide
* Water vapor
Less effect
* Ozone
* Methane
* Nitrous oxides
45
New cards
Consequences of global warming contributes to even warming conditions
* Ice and snow will melt (darker surface)
* The solubility of carbon dioxide in the sea will decrease (more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere)
* Surface water will evaporate (more water vapor in the atmosphere)
* The solubility of carbon dioxide in the sea will decrease (more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere)
* Surface water will evaporate (more water vapor in the atmosphere)
46
New cards
Calculating power obtained from solar panels
Power = Area · Intensity · Time · Efficiency