ap chem chapter 2 and 6 (electronic structure of atoms)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(electronic structure of atoms)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
atomic weight
The weighted average mass of an element's isotopes, measured in atomic mass units (amu). It reflects the relative abundance of each isotope.
atomic weight equals
(mass x abundance) + (mass x abundance) + …
mass number equals
all the protons and neutrons
for a neutral atom, the number of protons (atomic number) equals
the number of electrons
isotope notation
top left = mass number
bottom left = atomic number
if one isotope of an element has the majority of percent abundance, then
the atomic weight of the element should be closest to the mass of that isotope
Electromagnetic Radiation
the Wave-like motion of energy through space
all light and Electromagnetic Radiation moves at…
the speed of light ( which is c) = 3x108 m/s
Wavelength (λ)
Distance from 1 peak in a wave to the next peak
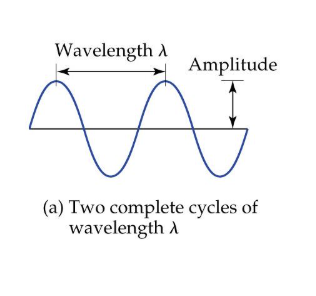
Frequency (ν or nu)
How many wavelengths pass a point in a second
amplitude
half the height of the largest wave
visible light is from wavelengths of
400 nm to 750 nm (violet to red; opposite rainbow order)
metric conversions
TGMKHDaBDCM(micro)NP (12, 9, 6, 3, 2,1, 0, -1,-2,-3,-6,-9,-12)
max plank said that when solids are heated, they
emit radiation
max plank said that energies were emitted (from heated objects) or absorbed came in discrete bundles called
quanta
in rutherford’s nuclear-atom model,
the heavy subatomic particles (protons and neutrons) reside in the nucleus
rutherford gold foil exp
led to discovery of nucleus (which disproved the plum pudding model)
with only knowing the atomic number ( the amount of protons) of an element, you can find the…
mass number
the first number in isotope form is…
the mass number
all the orbitals in a given subshell have the same values of ___ quantum numbers
azimuthal (L) and magnetic (ML)
excluding s orbitals, most magnetic quantum of any electron (in any subshell) are in the…
multiples
orbital
probability of where electrons are?
excluding n = 1 shells, all other shells contain ___ p orbitals
3
electronic anomalies for transition metals (d block)…
colums Cu and Cr
aufbau principle
lowest energy orbitals are filled first
orbitals can only contain a max of…
2 electrons
hund’s rule
when degenerate orbitals (those of identical energy) are avaliable, electrons enter these orbitals singly, b4 any spin pairing takes place
pauli exclusion principle
when 2 electrons enter the same orbital they must have opposite spins (+1/2 or -1/2) so that each electron has a unique set of quantum numbers
Cr and Cu achieve extra stability by forming…
half and completely filled d sub shells