OB- Genetics & Operative Obstetrics
1/62
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is a teratogen?
Anything that disturbs fetal development (highly dependent on time of exposure)
What period during a pregnancy is the most vulnerable to the effects of teratogens?
1st trimester (organogenesis)
What is the minimum theoretical radiation threshold for fetal injury?
50 mSv
At what radiation level is fetal neurological injury thought to begin, if exposure occurs between 8-15 weeks?
200 mSv
What is the radiation dose associated with dental xrays?
0.06 mSv
What is the radiation dose associated with CXRs?
0.1 mSv
What is the radiation dose associated with head CTs?
1.5 mSv
What is the radiation dose associated with abdominal CTs?
5.3 mSv
What is the radiation dose associated with chest CTs?
5.8 mSv
What imagining modalities have no known or suspected radiation risks?
US & MRI
Is safety in pregnancy the same as safety in lactation?
No
Known teratogens chart
know the known teratogens column (especially accurate / retinol cream), dont worry about generally safe column
What are known chemical teratogenic risks?
Heavy metals such as mercury & lead (assoc w/ intellectual disability), pesticides (treating lice), organ solvents such as esters & alcohol
What is aneuploidy?
Extra or missing entire chromosome → typically d/t problems during meiotic nondisjunction, chromosomes fail to pair or separate
What is translocation?
Portion of chromosome is rearranged
What is deletion?
Portion of chromosome is missing
What chromosomal abnormality generally result in serious or lethal damage?
Autosomal abnormality → duplication or absence of large portions of the 22 autosome pairs
Which chromosomal anomaly tends to be less deleterious?
Sex chromosome errors
What is mosaicism?
2 different cell lines present d/t error in mitosis
The incidence of congenital anomalies ______ with maternal age
Rises
The is the MC trisomy, that is also commonly seen with older maternal patients?
Trisomy 21
What is trisomy 21 (3 copies of chromosome 21 / long arm)?
Down syndrome

Which trisomy has the following appearance?
Small head, upslanting palpebral tissues w/ epicanthic folds, low set / folded / dysplastic ears, flat nasal bridge
Open mouth, thick protruding tongue, & loose skin at nape of neck
Single palmar crease (Simian Crease), short broad hands, hypermonile joints, gap bt 1st & 2nd toe (sandal gap)
Tendency for subluxation of C spine → risk of paralysis, especially w/ intubation
Trisomy 21
What other conditions can be seen in trisomy 21?
Heart defects (AV septal defects MC), GI malformation, childhood leukemia, thyroid disease, & significant intellectual disability
What is trisomy 18?
Edwards syndrome
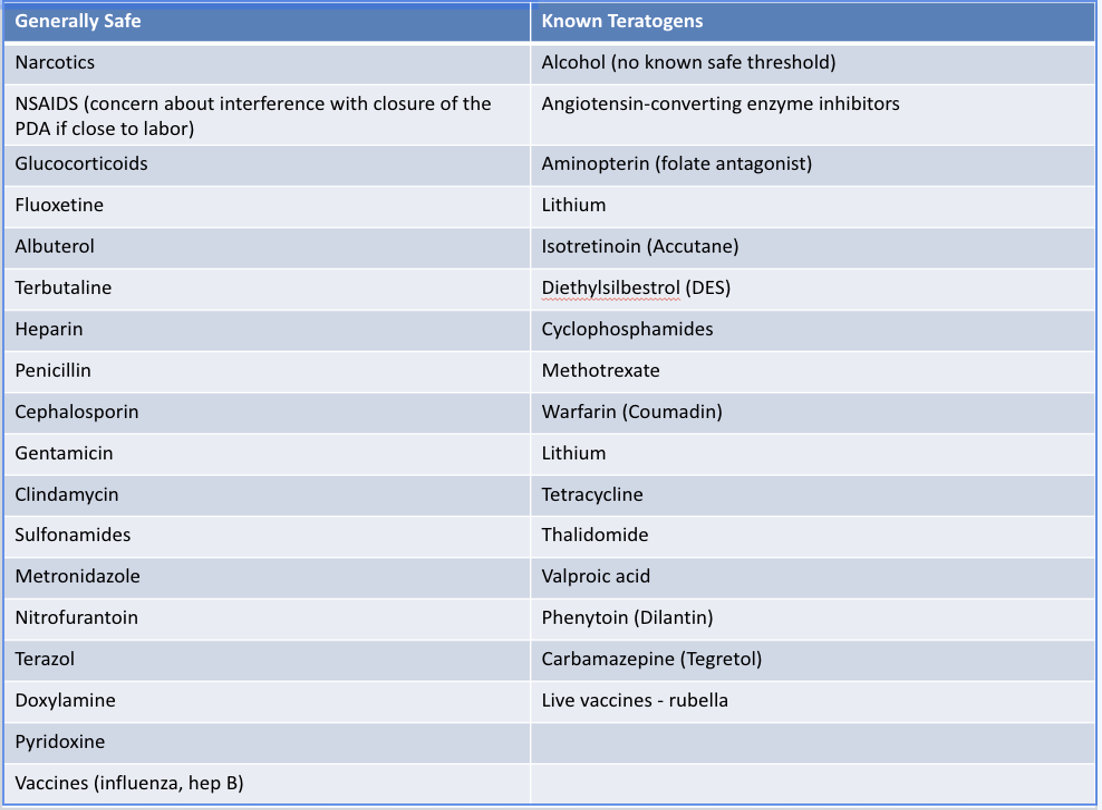
Which trisomy is 4x MC in females, presents with a profound intellectual disability, and less than 10% survive to age 1?
*hospice is an option for those born alive
Trisomy 18
What is trisomy 13?
Patau syndrome
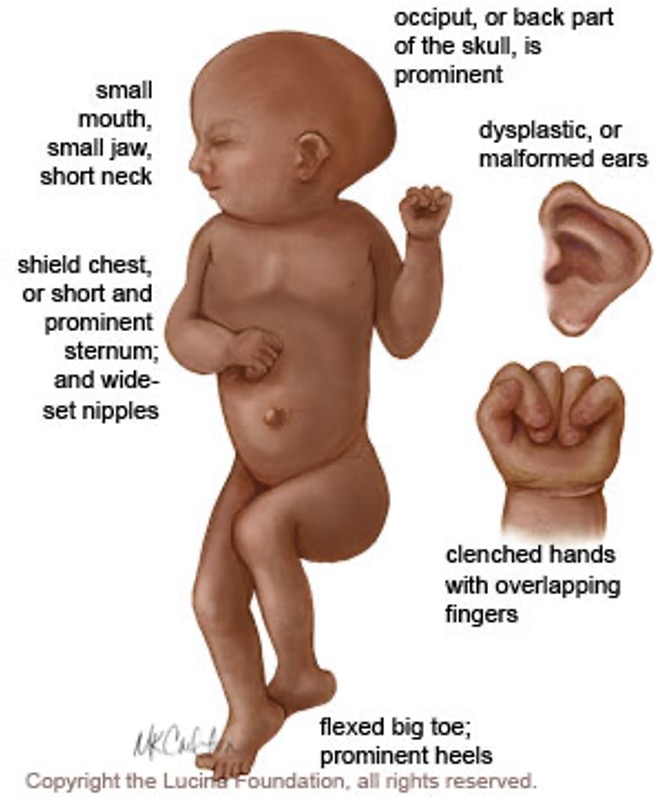
What trisomy presents most commonly presents with cardiac defects, most have missing portions of the brain, & less than 10% survive to age 1?
Trisomy 13
What is the MCC of aneuploidy in miscarriages (98% abort in first trimester)?
*those that survive to live birth often only have minor problems
Turner’s syndrome
What condition is an X chromosome abnormality of females with an absent or nonfunctional x sec chromosome → 45 X or 45 X0?
*can be mosaicism (only in come cells) or absence in all (gonadal dysgenesis)
Turner’s syndrome
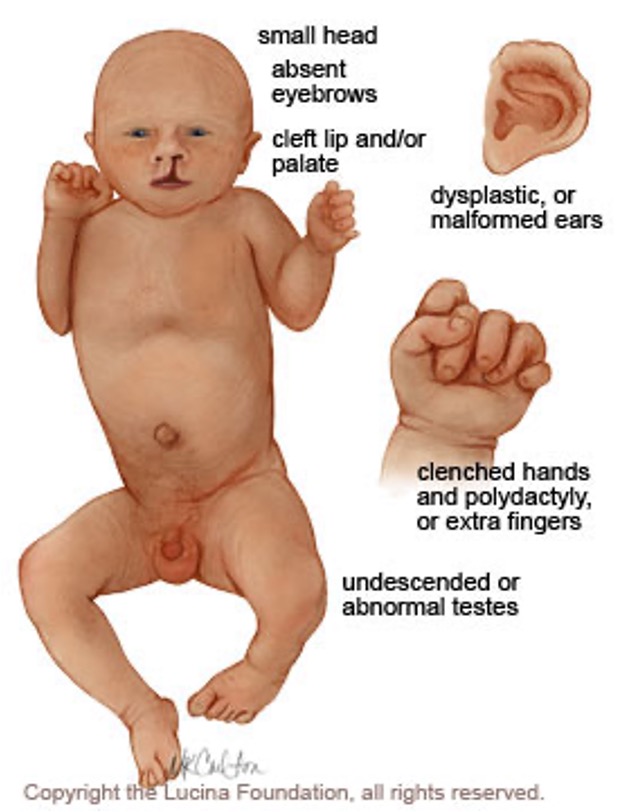
The following findings are commonly seen with what condition?
cystic hygroma, fetal hydrops
hypogonadism → delayed puberty (absence of breasts), infertility, primary amenorrhea (MC) or secondary w/ premature ovarian failure
CoA is common**; MVP, bicuspid AV, aortic dissection, HTN
horshoe kidney, hydronephrosis
hypothyroidism, osteoporosis, DM, DLD
telangiectasias of GI tract
Turner’s syndrome
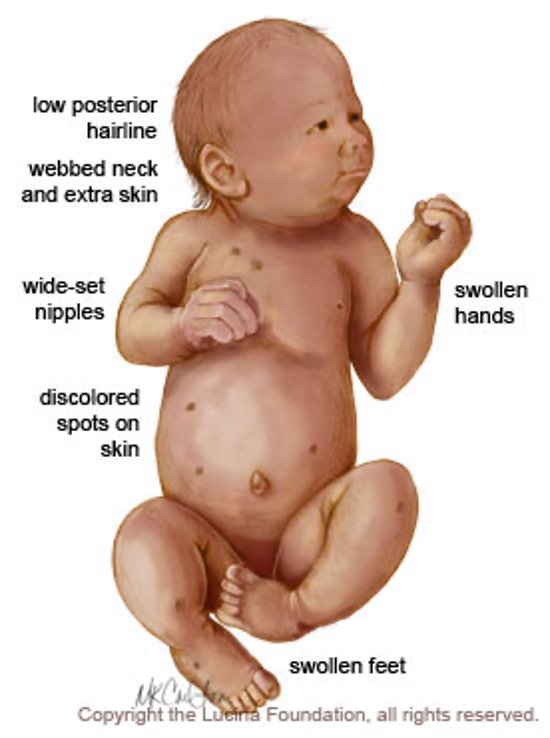
The following physical presentation is seen with what condition?
short stature
low posterior hairline, webbed neck, low set/prominent ears, high arched palate
broad chest w/ wide set nipples, lack of breast developemnt
short 4th metacarpals, nail abnormalities
intellectual impairments
Turner’s syndrome
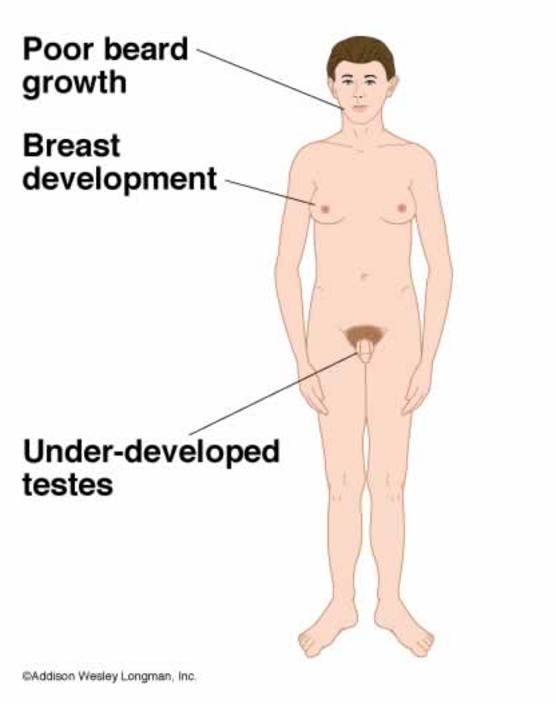
What condition has the following presentation?
phenotypic male
normal intelligence
intellectual disabilities and physical abnormalities if > 2 Y chormosomes
tall
emotional difficulties
learning disability
Jacob’s syndrome / XYY syndrome
What condition occurs in phenotypic males due to failure of separation of sex chromosomes or translocation, & is the MC chromosomal abnormality with hypogonadism?
Klinefelter’s syndrome / 47 XXY
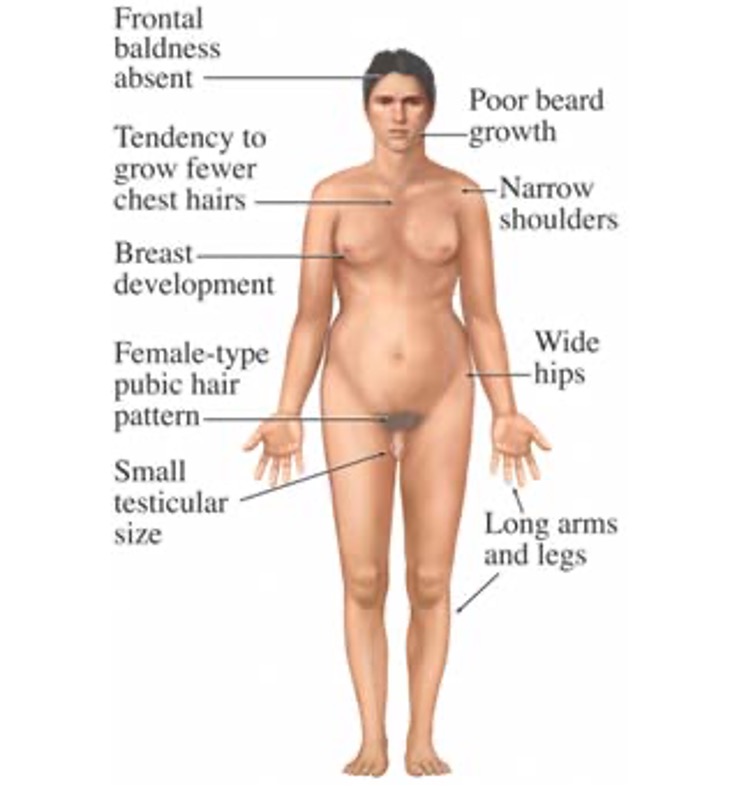
The following presentation is seen with what condition?
normal appearance before puberty
tall stature → long limbs & thin
normal intelligence, occasional mild developmental delay & expressive language disorders
small testes, scant pubic hair, reduced fertility
inc risk for GCT & breast CA
minority have breast development sufficient to warrant surgery
ice risk obesity in adulthood
Klinefelter’s syndrome / 47 XXY
The is the absence/dullness of sensibility to pain or the relief of pain without loss of consciousness?
Analgesia
What is the total loss of sensory perception & may include loss of consciousness?
Anesthesia
What is regional anesthesia/analgesia?
Region of body anesthetized w/o making person unconscious
What is the MC used local anesthetic?
Bupivacaine
What is added to local anesthetics to prolong duration & confines to the area affected by medication?
Vasoconstrictors (Epinephrine)
What may be a dded to the local anesthetic used in spinal epidurals to provide prolonged pain relief, block transmission of nerve signals & sensory signals, & limits motor?
Opioids
What kind of regional anesthesia?
pt loses sensation in legs & lower abdomen
used for labor pains, vaginal delivery & episiotomy
injected into epidural space → bolus or continuous infusion of bupivacaine via catheter
Lumbar epidural
What is a walking epidural?
Low dose CSE that generally preserves motor function
What is a combined spinal epidural (CSE)?
Narcatics (fentanyl) added to lumbar epidural
What are complications of lumbar epidurals?
Failure to anesthetize, venous pooling, HA, infx, misapplication of catheter placement, slower labor, drop in FHR
What kind of regional anesthesia?
loss of sensation of lower body & motor function
better for surgical management - C sections
anesthetic injected into spinal fluid (subarachnoid space) w/ fine needle & catheter (3.5 in)
may use 7 in long spinal needle for extremely obese pts
Spinal block
What kind of regional anesthesia?
quick pain relief to perineum, vulva & vagina
does NOT help abdominal labor pains
given in 2nd stage of labor just before delivery or for episiotomy
anesthetic is injected into pudendal canal near pudendal nerve
Pudendal block
Where are surgical incisions made in a cesarean section?
Through mother’s abdomen (laparotomy) and uterus (hysterectomy)
What are fetal indications for c-section?
Mal presentation, cephalo-pelvic disproportion (CPD), extreme prematurity, fetal intolerance to labor (non reassuring FHR), predicted macrosomia, multiple gestations, maternal active genital infx
If a patient wants a tubal ligation during the c-section, how far in advance might a patient on public assistance need special government papers signed?
30 days
What should you do before surgical prep for a c section if it is for a CPD and the head is engaged?
Gently push up on presenting part to dislodge it slightly
Who should you call to the OR during a c-section if the fetal is in distress?
Peds
What abdominal incision allows quicker access to the uterus & entry is commonly enhanced by diastases of the rectus muscles?
Midline infraumbilical incision (vertical)
Which c-section abdominal incision?
MC; preferred cosmetically
takes slightly longer to enter peritoneal cavity
less painful, less blood loss, shorter post op pain and lower analgesic requirement
smaller risk of developing incisional hernia
Transverse incision through lower abdomen
*MC pfannenstiel (bikini-low) or Maryland or Joel Cohen (high)
What are the 7 layers of c-section closure in order?
Uterus 1st layer - has to be placed
Uterus 2nd layer - leaves uterus stronger for VBAC attempts
Visceral peritoneum (not commonly used)
Parietal peritoneum (optional)
Fascia - necessary
SC tissue - reduces wound comps if incision > 2cm
Skin - closed w/ staples or dissolving sutures / steristrips
What complications are seen with c-sections?
Blood loss requiring blood transfusion, inc risk endometritis (give props cephalosporin at time of cord clamping), DVT, damage to adjacent organs, maternal death
When should a patient urinate after removal of a foley?
Within 4 hours (replace foley for another 12 hrs if not)
What are potential causes of a fever post op from a c section?
Wind: atelectasis, PNA (24 hrs)
Water: UTI (POD 2-3)
Wound: incisional infx, endomyometritis, septic shock (POD 3-5)
Walking: DVT< PE, pelvic thromboembolism (POD 5-7)
Wonder: meds
When can dressing be removed after c-section?
24-48 hrs (attending specific)
*may become soaked w/ serosanguinous fluid in first 12-24 hrs → replace
What is wound dehiscence?
Separation of a wound, usually during staple removal 1-2 wks post op
What is the management for c-section wound dehiscence?
Explore entire wound to determine depth, open if needed, props abx (keflex, bactrim, clindamycin), close FU & wound exploration
if thru rectus fascia → back to OR
if SC layer → deride daily w/ sterile saline/H2O2 & pack w/ gauze
What pharmacology postpartum counseling is given to the patient after a c-section?
Continue prenatals, colace, Motrin, Percocet for breakthrough, & OCPs can be started 4-6 wks post partum (progesterone only if breastfeeding), IUD can be inserted 6 wks after vaginal delivery or 8wks after c section
What are the activity restrictions for patients after a c-section?
No lifting objects over baby’s weight, continue ambulation, no strenuous activity, NOTHING by vagina for 6 wks (sex, tampons, douches, bathtubs, hot tubs)