AP chem unit 2
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Davis North allegheny 2025-26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
light is described in terms of waves and particles. when talking about spectrophotometry what do we view them as?
it is most convenient to view them as a stream of discrete particles called photons (when they ENTER the molecule
the spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light by wavelength
energies relationship with frequency
proportional ( E = hv , h is plancks constant/ v is frequency)
the three possible situations to occur when light strikes and object
reflected
absorbed
transmitted through the object
how does color occur?
absorption of visible light
absorption
the process by which chemical species selectively remove certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
how does a photon affect an atom
a photon converts the atoms/molecule to a more energetic or excited state → energy is lost as heat
what is the effect of the absorption of specific wavelengths
Species which absorb visible light will appear to the eye as the complementary color of the region of the spectrum which has been observed
what happens if no visible light is absorbed
object appears colorless
How do wavelengths help identify materials
the specific wavelengths that are absorbed are unique to each atom/molecule → useful in identifying an unknown (qualitative analysis)
quantitative analysis (in the experiment)
how much material is present in an unknown sample (more concentrated solution absorbs more/transmits less light → appears more intensely colored)
calibration curve (experiment)
the slope/line of known concentrations —> used to find unknown
visible colorimetry
using a series of known concentrations to approximate the concentration of an unknown (by visual comparison)
not used bc not very accurate
how does spectrophotometry work
LED + tungsten bulb used to transmit light thru the sample
transmitted light passes thru a diffractor
light is sorted/collected by a detector
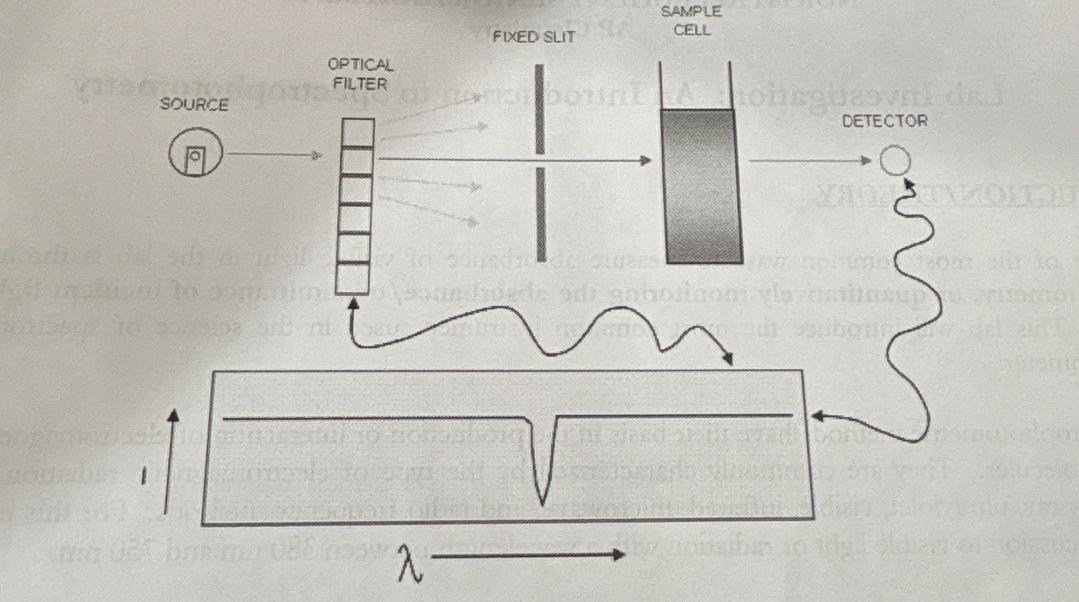
Why do we calibrate the spectrophotometer w/ a blank
to compensate for…
small reflective losses for the cuvette
any absorption by the container/ solvent in which the sample is dissolved
What is transmittance
ratio of the intensity of light transmitted through the sample to that transmitted through the blank
%T = blue/pink
How is absorbance related to transmittance
logarithmically
absorbance = log(100/ %T)
How do we choose the wavelength to test the absorbance at
wavelength of maximum absorbance is used because
gives the highest sensitivity
largest absorbance change per concentration change
most reliable measurements
small errors in wavelength near the maximum have little effect on absorbance.
Measurements are also typically kept within the 0.2-0.7 absorbance range
ensure accumulation, since Beer’s Law is most linear there
what is the wavelength of maximum absorbance called
working wavelength (found from absorbance/wavelength graph)
What is Beers Law!
equation for the relationship between the intensity and the concentration of a thing (directly proportional relationship)
Equation of beers law (and its components)
A = εbc
A: Absorbance (unitless)
ε: proportionality constant known as molar absorptivity (unique to each thing & wavelength)
probability of a photon being absorbed + causing an electronic transition ( L / mol*cm)
b: amt of solution light passes thru
c: concentration of solution (mol/L)
How does an air bubble affect the results
the light is reflected off the bubble, making the reader detect a high absorbance than present (light is moved away from the detector so not all is accounted for)
subatomic particles
Subatomic particles are particles smaller than an atom. They include protons, neutrons, and electrons which make up atoms.
cathode rays
streams of negatively charged particles
alpha particles
Helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons)
law of conservation of mass
made by antoine Lavoisier, reactants must equal the total mass of the products
Law of multiple proportions
John Dalton, given compound should always contain the same combo of atoms
electrons
subatomic particle w/ negative electric charge
if <4 degree --> Uv
if >4 degree --> visible
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
no electron is emitted until the light reaches threshold frequency
the more intesnse the light beam, the more e- emitted
emitted e- move faster if light applied has higher frequency
percent composition
mass of element/total mass of element
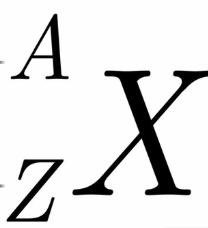
What is A
# of protons and neutrons in nucleus
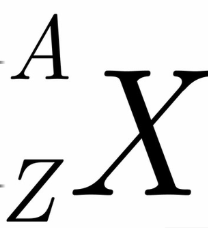
What is Z
Atomic number/protons
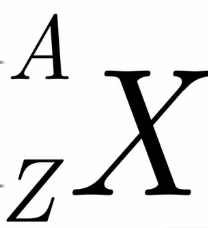
What is X
chemical symbol for element
formula for average atomic mass
(mass1 * abundance/percentage1) + (mass2 * abundance/percentage2)
5 part of mass spectrometry
Vaporization
dissociation/ionization (becomes +1 charge)
Acceleration
Deflection
Detection
equation when frequency given
E=hv
E= energy of a photon
h= 6.636 × 10-34
v= frequency
what is plancks constant
h= 6.636 × 10-34
how to find energy when wavelength given
E= hc/lambda
E= energy of a photon
h= 6.636 × 10-34
c= 3 × 108
lambda= wavelength
relationship between amplitude and energy
porportional
Convert FM to Hz
FM = MHz
96.1 —> 9.61 × 109
wavelength of red light
700 nm
wavelength of green light
550 nm
wavelength of violet light
400 nm
what equation do you use when given wavelength and speed of light
c = wavelength x frequency
what happens when two waves combine on peaks
they combine (constructive)
what happens if they meet at a peak and a trough
they cancel out (destructive)
ground state
lowest energy level of an electron occurs in the orbit closest to the nucleus
excited state
specific amt of energy(quanta) needed to excite electron to higher level
visible spectroscopy
most effective on transition metal ions
debroglie matter waves
matter waves support the bohr idea of orbits with only certain allowable energies and no e- spiraling into the nucleus
bohr model and emisson spectrum, how do they connect
the model talks about quantized energy levels, the emission spectrum comes from the differences in energy levels of an atom (spectral lines)
axis of mass spectrum
x = mass numbers
y = abundance (relative or percent)
axis of UV-Vis graphs
x = wavelength (nm)
y = absorbance
axis of photoelectron spectroscopy
x = energy
y = relative # of electrons
how does gold foil experiment work
rutherford shot alpha particles at a thin peice of gold
particles deflected off the gold nucleus (most of the mass was empty space)
gold chosen bc malleable
shot w/ higher energy = more angled deflection/ less overall e- deflected & vice versa