1.6 Nervous System and Hormones 🧠
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Biology Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Cells, Living Processes & Biodiversity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Nervous system
network of nerve cells and fibres to transmit nerve impulses between parts of the body
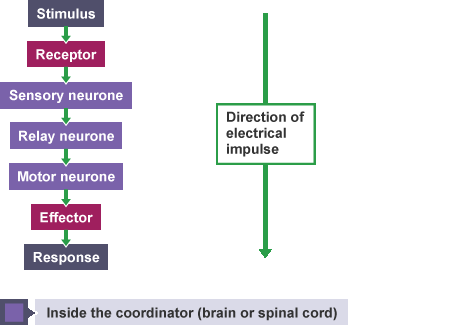
Stages of electrical impulses mnemonic
Simon- Stimulus
Receives- Receptor
Scented- Sensory Neurone
Red- Relay Neurone (or association)
Motors- Motor Neurone
Every- Effector
Rest day- Response
Neurones
transmit electrical impulses quickly, making up peripheral nervous system
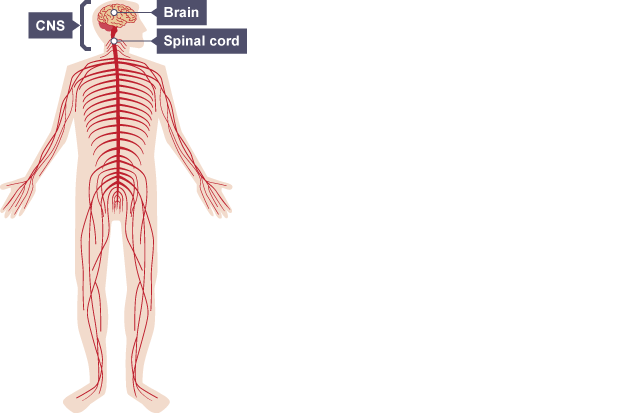
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and the spinal cord
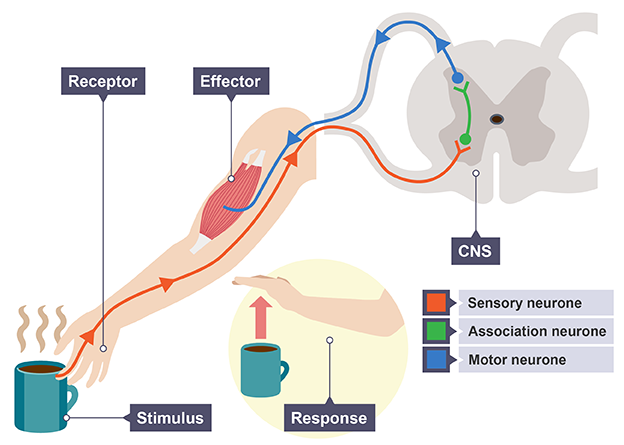
Stimulus
change in our surroundings/ environment
Receptors
structures that are sensitive to specific stimuli
Coordinator (CNS)
formulates and decides a response before impulses are sent to an effector
Sensory neurone
carries impulses from the receptor to the coordinator
Relay/ Association neurone
connects sensory neurone to motor neurone via synapses
Motor neurone
sends impulses from the coordinator to effector
Effector
produces a response to stimulus e.g muscles contracting or glands secreting
Reflex arc
fast and short nerve pathway for reflex actions
Voluntary responses
require conscious thought and involve brain so are a lot slower due to thinking
Involuntary responses
happen quickly without thinking usually protecting the body from harm
Nervous system communications
fast and short lived
electrical/ nerve impulses
travels by neurone to effector
involuntary or voluntary
Hormonal system communications
slow and lasting
hormones/ chemicals
travels through blood to organ
always involuntary
Similarities in the nervous and hormonal systems
send messages around our body and enable it to respond to stimuli
Eye
specialised sense organ that contains receptors sensitive to light
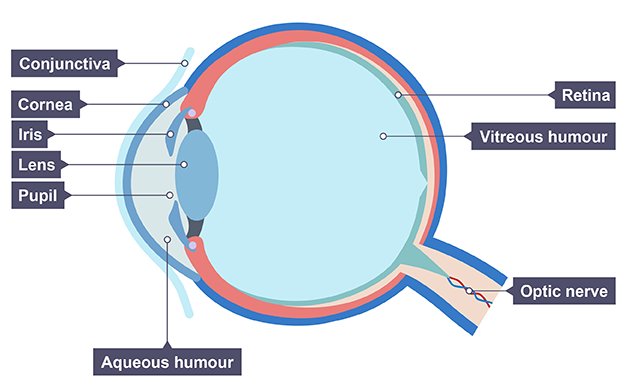
Conjunctiva
thin and transparent protective outer covering that prevents entry of microorganisms
Cornea
transparent part at front of eye, allowing light to enter with slight bending/ refraction
Pupil
opening in the iris that allows light into the eye
Iris
coloured part behind cornea that regulates size of pupil, controlling how much light enters
Lens
transparent to bend/ refract light, focusing towards the retina
Ciliary muscles
muscles which relax or tighten to adjust the suspensory ligaments
Suspensory ligaments
ligaments to adjust the shape of the lens
Aqueous humour
watery fluid in the front to maintain shape of the eyeball and lens
Vitreous humour
jelly like substance to maintain shape of eye and push retina against the wall
Retina
surface at the back of the eye containing light sensitive receptor cells
Optic nerve
carries neural impulses from the receptor cells to the brain
Reflex response to dim light
pupil dilates so more light can enter
Reflex response to bright light
pupil constricts so less light can enter
Accommodation
ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments change shape of lens to focus at different distances
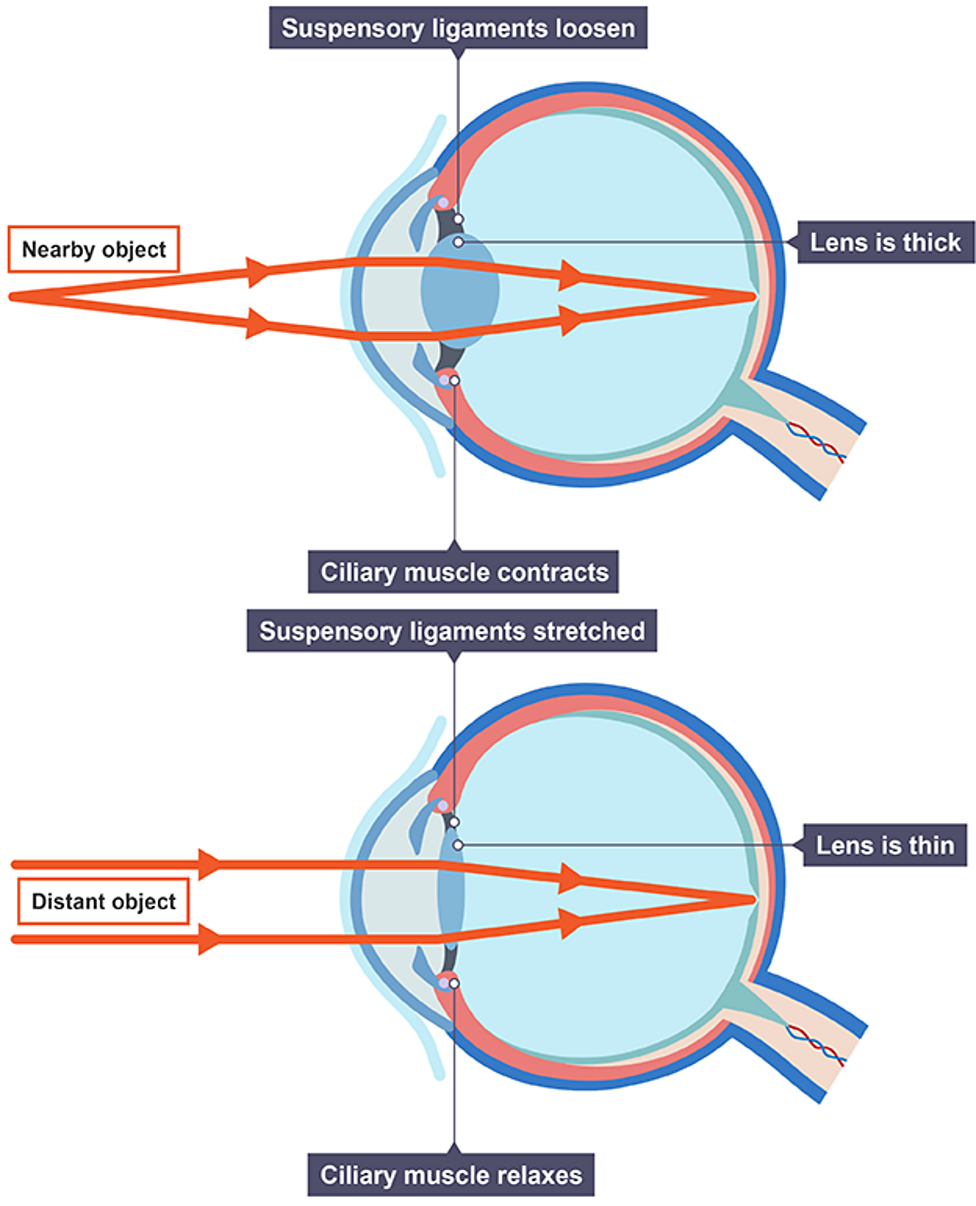
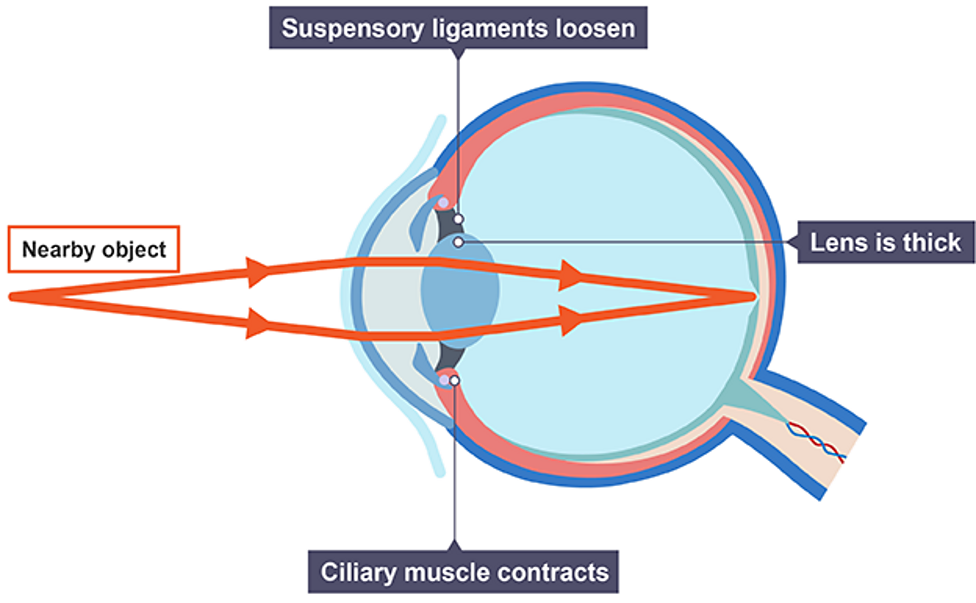
Focusing on a near object
ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligaments loosen
lens is thicker and refracts light rays strongly
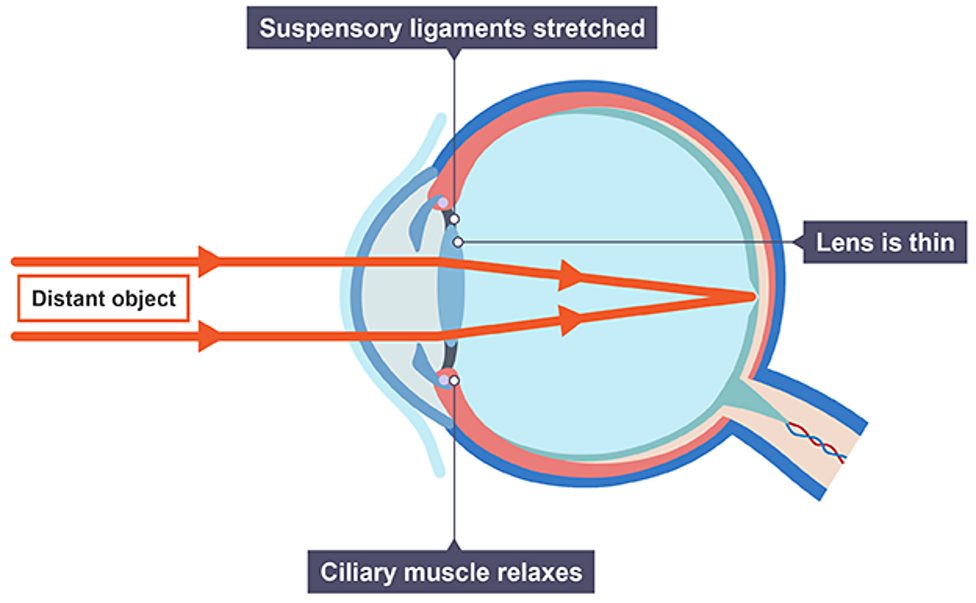
Focusing on a distant object
ciliary muscles relax
suspensory ligaments pull tight
lens is pulled thin and only slightly refracts light rays
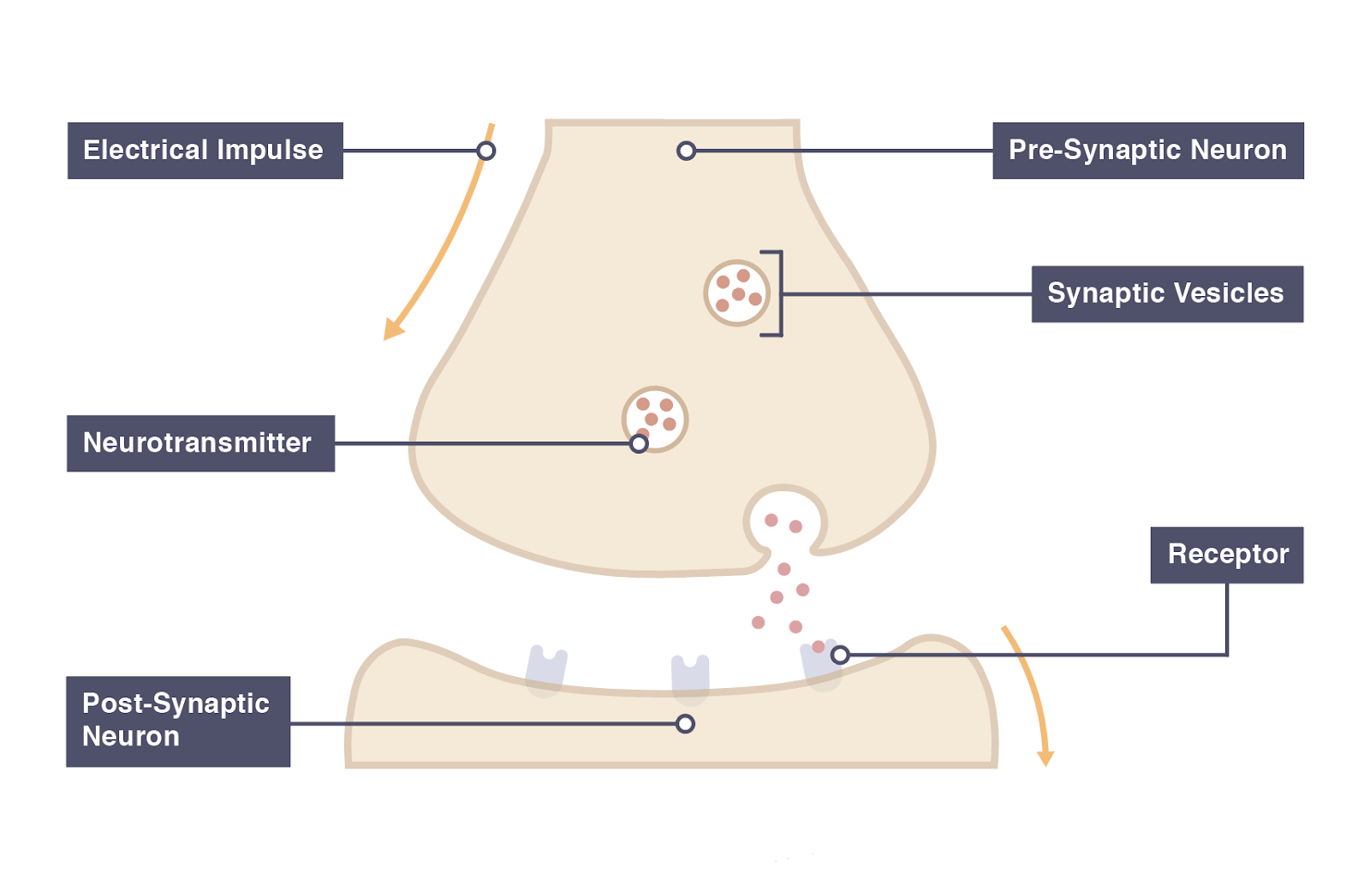
Synapse
junction between two neurones, creating a link, to allow impulses to pass between
Neurotransmitter
chemical released from ends of active neurone to diffuse across synapses
How are neurones transmitted across synapses
When impulses reach the end of axon, transmitter chemical is released
Chemical diffuses across the gap
If in high enough concentration an electrical impulse triggers in the next neurone, allowing the signal to continue
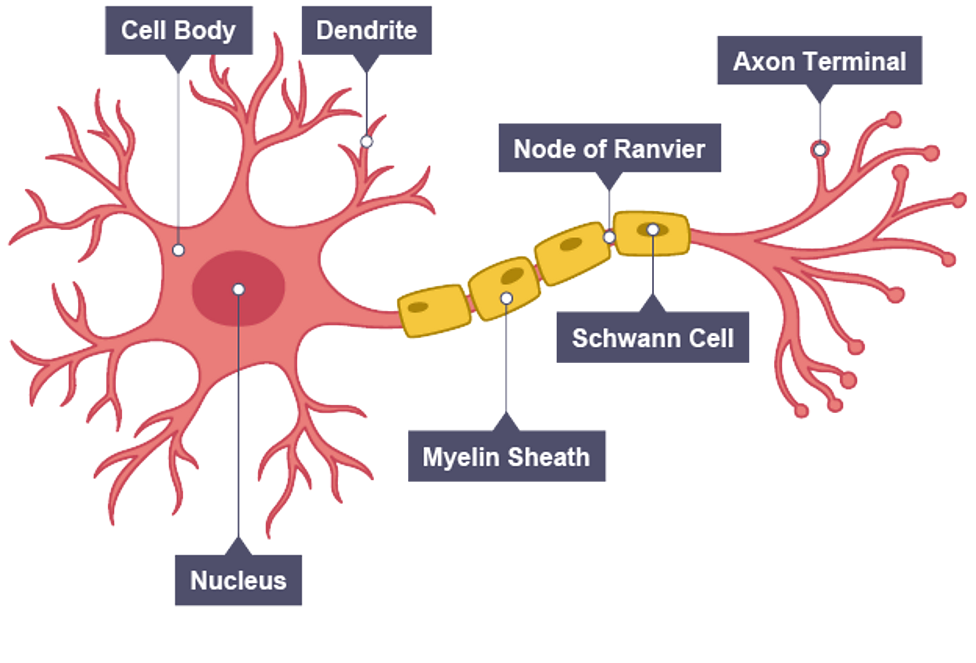
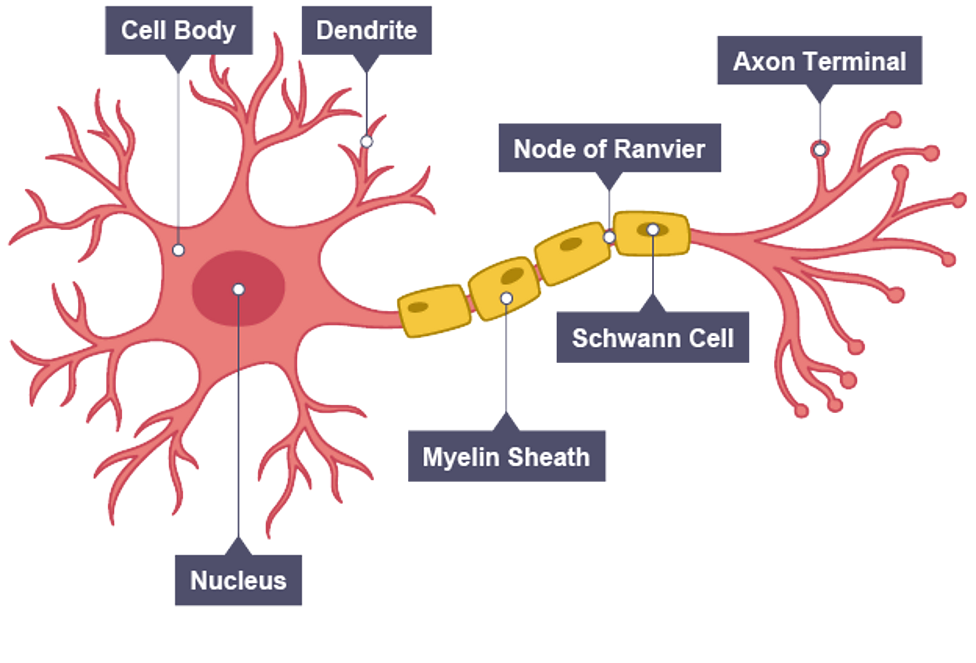
Adaptations of neurones
cell body contains cytoplasm and nucleus
long extension (axon) of cytoplasm allows nerve impulses to travel over long distances
myelin sheath is a fatty layer surrounding axon and acts as an insulator to speed up impulses
dendrite (branched ends) of axon allow many connections with other neurones
Homeostasis
maintaining constant internal environment for proper functioning of cells and enzymes in response to change
Hormones
chemical messengers produced by glands and released into blood, carrying to target organ
Examples of hormones
Insulin
ADH
Pancreas
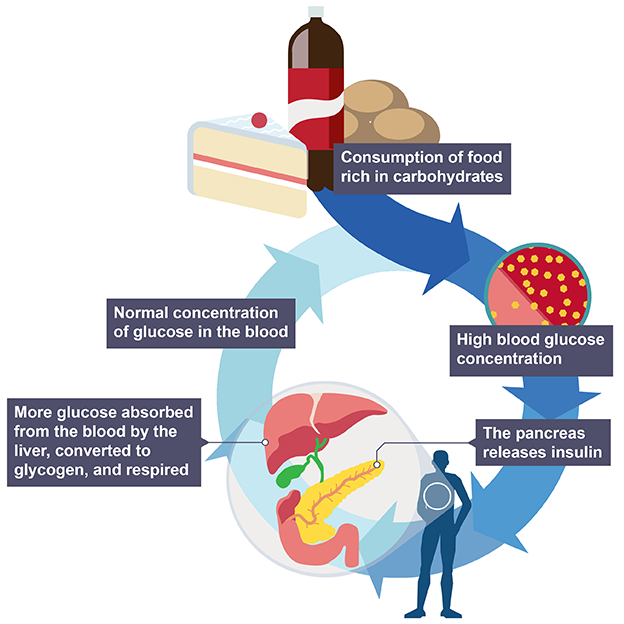
monitors blood glucose concentration and produces insulin in response to an increase
How does insulin lower blood glucose levels
pancreases detects increased blood glucose and produces insulin
increases glucose absorption from blood in liver and muscles
respires absorbed glucose
converts excess to glycogen which is stored
Glycogen
carbohydrate that acts as an energy and glucose store in animals
Diabetes
condition in which blood glucose level control fails
Type 1 diabetes
develops usually early in life
pancreas stops producing insulin
treated through insulin injections
Type 2 diabetes
progressive disease linked to lifestyle factors
pancreas gradually produces less insulin
treated in early stages by controlling diet/ exercise but may require insulin injections
Symptoms of diabetes
glucose in urine (high concentration filtered out)
high blood glucose levels
being thirsty
excessive urination
lethargy (feeling tired)
Increase in type 2 diabetes
poor diet leads to weight gain and obesity, which raises the risk
aging population where older people are more likely to develop it
modern, less active lifestyles with less exercise contributes
better awareness and improved medical testing so more are diagnosed
family history makes some people more likely to inherit it
increased access to foods such as sugars and lipids
Long-term effects of diabetes
eye damage
kidney failure
heart disease
strokes
Glucagon
released by the pancreas to convert glycogen in liver back into glucose to raise blood levels
Negative feedback cycle
change brings about process causing opposite effect, maintaining homeostasis
Purpose of negative feedback
ensure concentration does not deviate too far from normal, maintaining homeostasis
Osmoregulation
controls water levels in the body to bring volumes back to balance, as poor control can damage cells
Function of the kidneys
removing waste from body through urination and controlling water balance by osmoregulation
How water is gained
drinking, eating or product of respiration
How water is lost
evaporation in breathing, sweat by skin or production of urine
Filtration
separation of molecules depending on blood concentration, if too dilute less water is reabsorbed producing more urine
Selective reabsorption
reabsorbing only key molecules while leaving waste to be excreted
Excretion
molecules not reabsorbed are removed from the body through urination
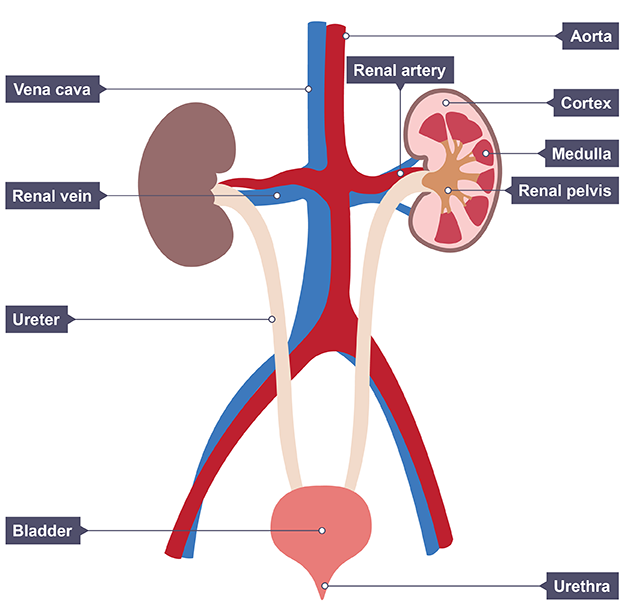
How the kidney works
Blood enters via renal artery
Substances are filtered out in cortex
In medulla some substances are reabsorbed back into blood until normal concentrations reached
Left overs pass into urine, which collects in pelvis
Urine passes into ureter and is stored in bladder
Urine passes out body from urethra
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
brain detects lower water levels and produces ADH in pituitary gland
causes kidneys to reabsorb more water into blood
produces lower volume of concentrated urine
returns blood water levels to normal
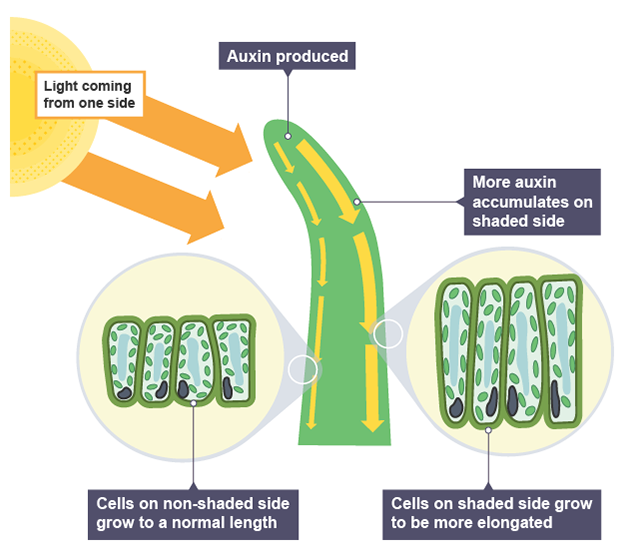
Auxins
plant hormone produced in shoots which controls cells growth in response to light
Phototropism
change in direction of plant in response to light
Purpose of phototropism
plant receives more light, so more photosynthesis and growth
Effect of auxins in shoots
Auxin is produced at tip of shoot and moves down
Light from one side causes uneven distribution on shaded side through diffusion
Cells on shaded side elongate faster (differential growth)
Causes stem to bend towards light
Foil covering plant shoot tips
shoots grow upwards but not towards light, suggesting the tips are sensitive to light