Blood Bank Reagents
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the 4 basic categories of reagents?
RBCs w/ known Ags
Antisera w/ known Abs
Antiglobulin reagents: anti-IgG (anti-immunoglobulin G)
Potentiators (enhance Abs)
Reagent Regulation & QC
FDA criteria
Specificity: recognition of the antigenic determinant and its corresponding antibody
Potency: Strength of rxn
determine the accuracy and precision of equipment, reagents, and procedures
statement, documentation, corrective action
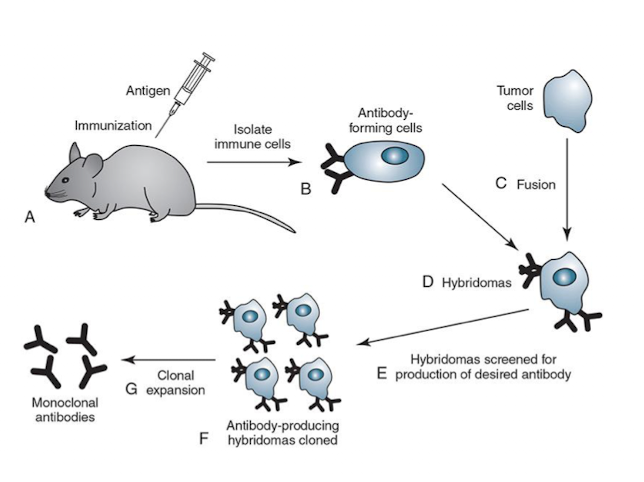
Commercial Antibody Reagents
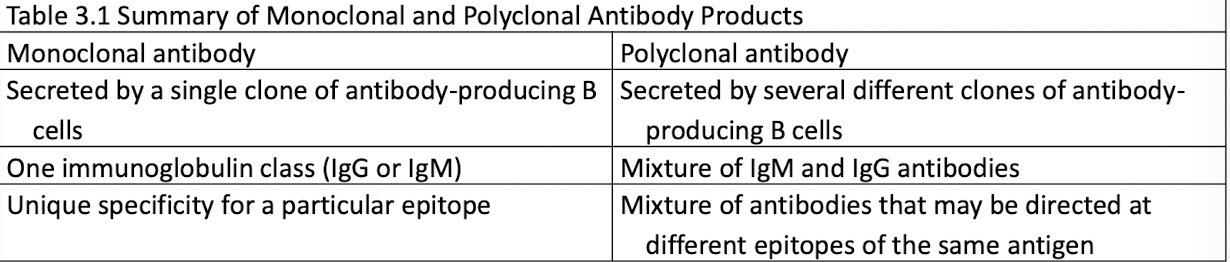
Polyclonal Antibodies
Ex: Antihuman globulin (AHG)
Monoclonal Antibodies
Ex: anti-A, anti-c, & anti-IgG Abs
Polyclonal Antibodies
made from several diff clones of B cells that secrete Abs of DIFF. specificities
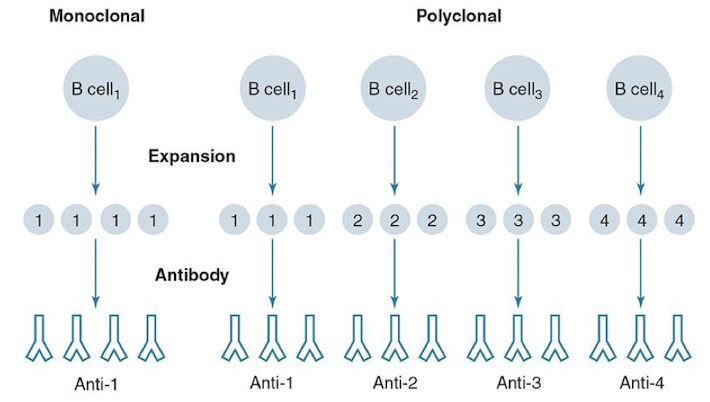
Monoclonal Antibodies
Made from single clones of B cells that secrete Abs of SAME specificity, recognizes single epitope
Monoclonal Abs vs Polyclonal Abs
ABO Typing
Anti-A & Anti B reagents used to determine ABO blood type
Both Antisera directed toward specifics on the pt’s RBCs
Anti-A → A ag
Anti-B → B ag
ABO Red Cell Testing (ABO Forward Grouping)
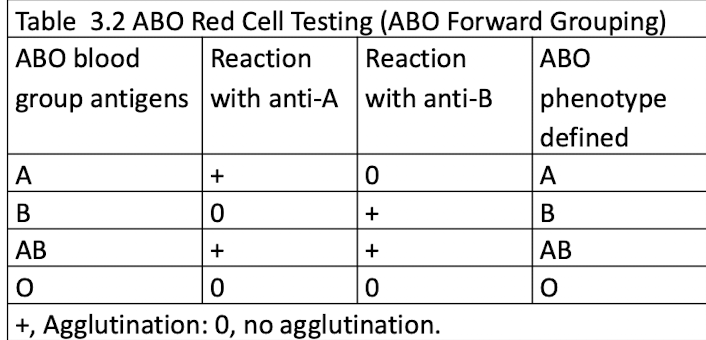
ABO Typing Reagent Testing
Reagents are formulated to give a strong reaction (3+ to
4+)
Testing is performed in the immediate-spin (IS) phase
Confirmation testing to check expected ABO Abs
D Antigen Typing Importance
Most important in Rh blood group system due to INCREASED immunogenicity
AABB requires all blood samples typed for D antigen
D Antigen Typing Procedure

commercial anti D + pt & donor RBCs
Agglutination = presence of D antigen
No agglutination = absence of D antigen
(-) control reagent to ensure lack of false (+) result
Anti D Reagents: high vs low
High-Protein Reagents
Contain polyclonal antibodies
~ 20% bovine albumin
Promotes false (+) agglutination
Low-protein reagents
monoclonal abs (IgM) or mono/polyclonal blend
~ 6% bovine albumin
replaced high-protein reagents
Low-Protein Reagent Control
Ex: Monoclonal Control
ensure that typing results are correct, SHOW NO AGGLUTINATION
False(+) agglutination can result from
Strong cold autoantibodies
Protein abnormalities
When is a separate control used?
used if RBCs agglutinate with all ABO antisera
is not needed if there is a (-) result using any of the ABO low-protein reagents
What are Reagent RBCs and when are they used?
vials contain known Ags to confirm the presence of Abs in patient serum or plasma
Procedures that use commercial RBCs include:
ABO serum testing
Screening tests
Antibody identification
A1 and B Cells
cells combined with the patient’s serum or plasma to determine the reverse grouping; Pts have Abs directed against the Ag of the ABO system that is lacking on their RBCs
Can be from a single donor or a pool of donors
2-5% conc.
Negative for Rh antigens (D, C, and E)
ABO Serum Testing (Reverse Grouping)
Screening Cells
used in Ab screen (detection) tests for unexpected Abs
Available in sets of 2 or 3 vials
Each vial may be from a 1 donor or 2 donors (pooled together)
Pooled cells can be used for donor testing
single-donor vials used when about to receive a transfusion (e.g., recipient)
Single-donor cells tend to give stronger rxn
Screening Cells Antigram
shows the antigen profile
cells must express antigens associated w/ the most clinically significant Abs
screening cells are regulated by the FDA for:
D, C, E, c, e, M, N, S, s, P1, Lea, Leb, K, k, Fya, Fyb, Jka, and Jkb
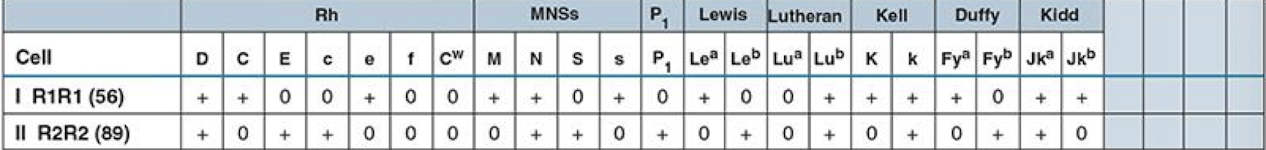
Panel Cells
like screening cells but w/ 10+ vials
used for identifying Abs in a procedure called an Ab pane
Each lot of panel cells will have an antigram that shows the antigenic profile of each vial

Antiglobulin Test
Principle of test
Commercial antibody with a specificity toward human globulins is used to agglutinate antibody- coated RBCs
Reagent contains antibodies toward:
IgG (anti-IgG) and/or
Complement (anti-C3d, anti-C3b)
What are the two types of Antiglobulin test and how do they differ?
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
IgG or Complement on RBCs in VIVO
Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT)
IgG or Complement on RBCs in VITRO
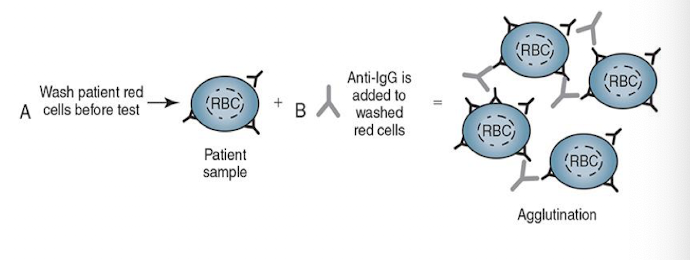
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
Detects IgG or complement bound to RBCs IN VIVO
AHG reagent is added after RBCs washed
Agglutination demonstrates whether IgG or complement was attached to the RBCs
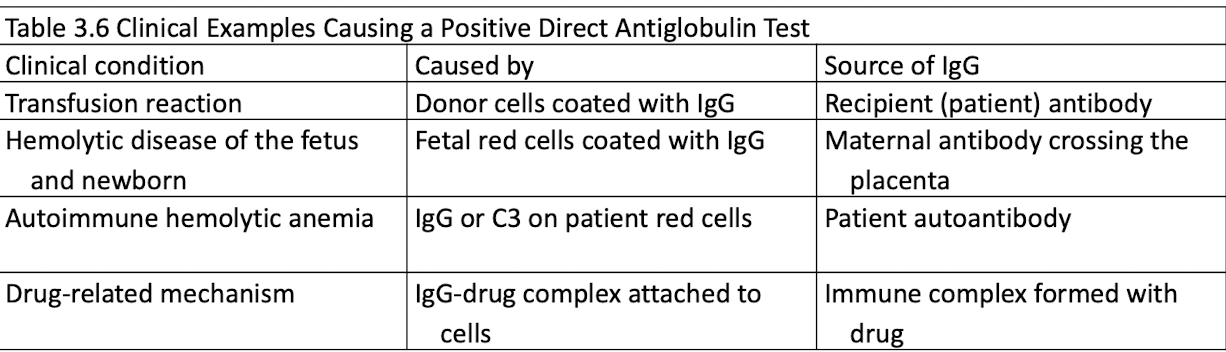
Positive DAT Usages
Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT)
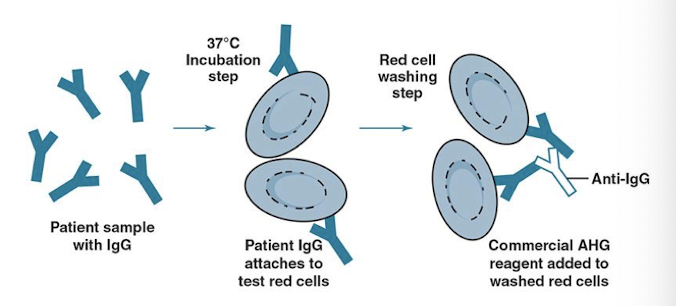
Detects IgG or complement bound to RBCs IN VITRO
Two-step procedure
Antibodies (in serum/plasma) incubated at 37° C with RBC antigens in vitro
RBC suspension is washed and then combined with AHG reagent to detect agglutination
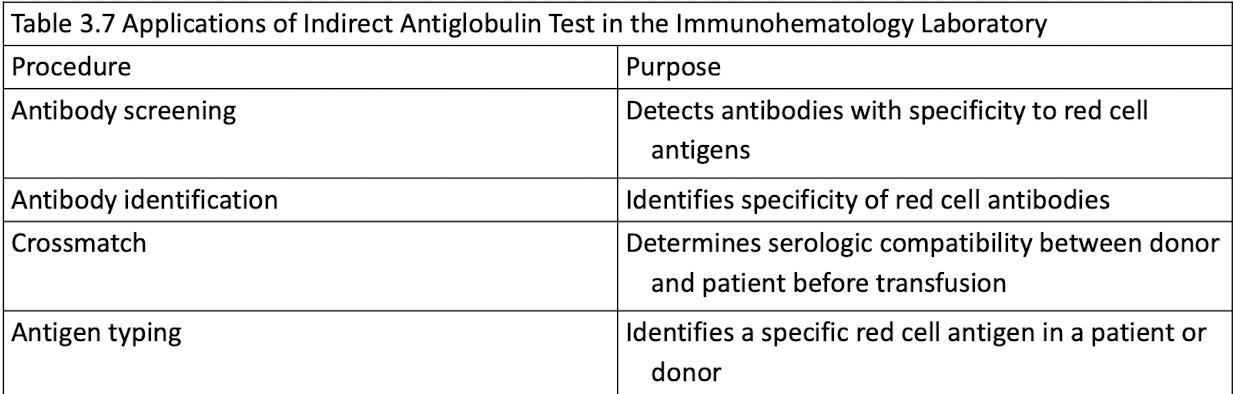
Applications of IAT
Common Sources of False-Positive Error in Antiglobulin Testing
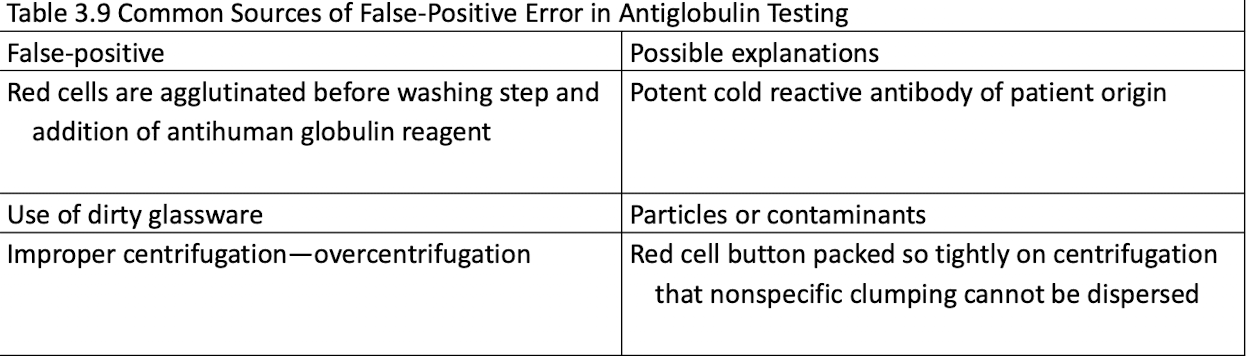
Common Sources of False-Negative Error in Antiglobulin Testing
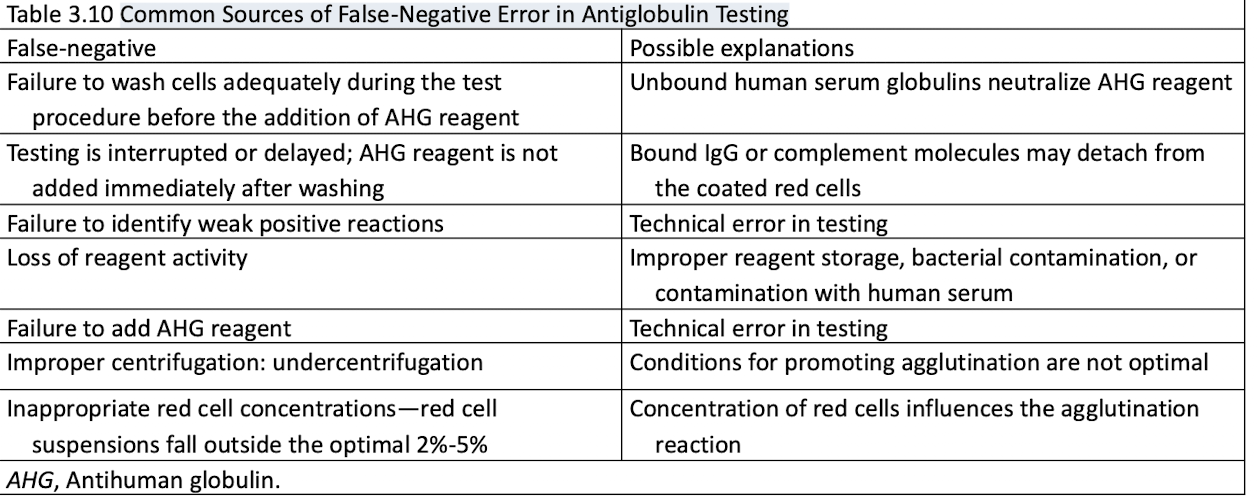
Antiglobulin Reagents: Poly VS Monospecific AHG
Containing BOTH anti-IgG and anti- C3d antibodies VS containing either anti-IgG or anti- C3b/C3d, but NOT both
Polyspecific AHG
Contains both anti-IgG and anti- C3d antibodies
from polyclonal or monoclonal sources
Agglutination = IgG or complement is coating the RBCs
If positive, a differential DAT is performed
Monospecific AHG
Contains either anti-IgG or anti-C3b/C3d, but not both
Anti-IgG combines with human gamma chains
Anti-C3b/C3d specifically detects complement proteins as a result of activation of the classical pathway
Intravascular hemolysis
Extravascular hemolysis
IgG-Sensitized Cells
Required by AABB as a control system when AHG results are negative
When added to a negative AHG test, reagent should cause agglutination
Commercial reagents are type O RBCs prepared with IgG antibodies attached
What are potentiators? What are the types of potentiators?
Reagents that enhance the detection of IgG antibodies by increasing their reactivity
Low ionic strength saline - LISS
Polyethylene glycol - PEG
Proteolytic enzymes: Papain and Ficin
Bovine serum albumin - BSA
Potentiators
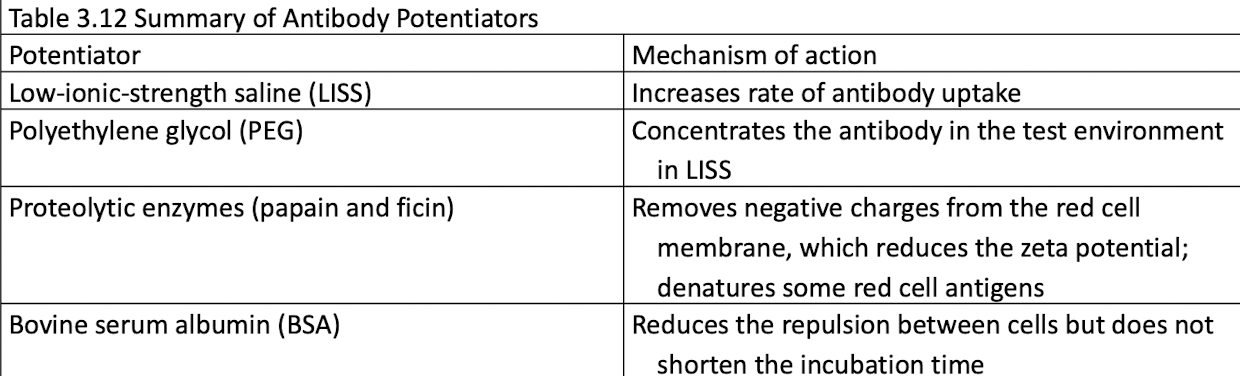
Bovine Serum Albumin
Available in 22% or 30% concentration
Allows antibody-sensitized cells to become closer together than is possible with saline
Favors direct agglutination with Rh antibodies
Enhances sensitivity of the IAT
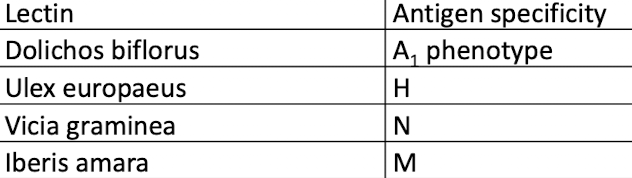
Lectins purpose and common types
Seed extracts that have specificity toward certain RBC antigens
Bind to carbohydrate determinants of RBC antigens
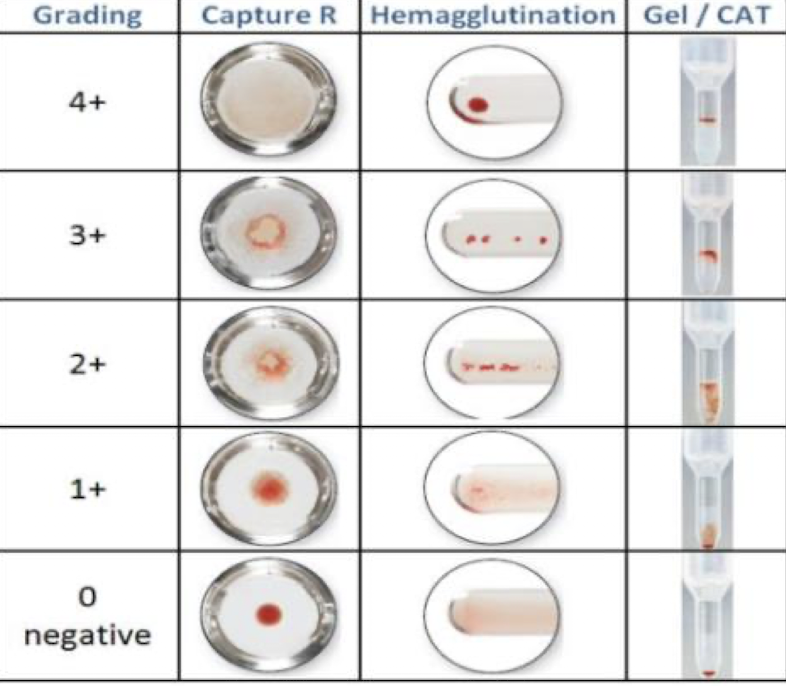
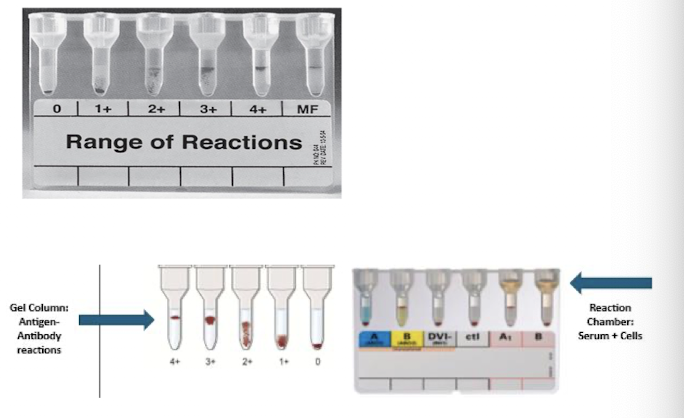
Gel Technology
Dextran acrylamide gel traps agglutinated cells.
Gel particles + reagents predispensed in microtubes.
Add RBCs/plasma/serum, incubate, centrifuge.
Agglutinates trapped at top (4+), nonagglutinated cells at bottom (0).
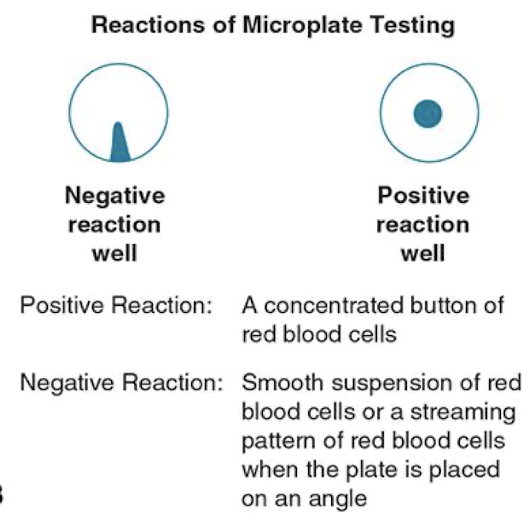
Microplate Testing
96-well microtiter plate replaces test
tubes
A concentrated button indicates a
reaction
Dispersed cells indicate no reaction
Solid Phase vs Hemagglutination and Gel
Uses microplate wells with immobilized reagent
Cells that adhere to the sides and bottom of the wells are (+)
Cells that settle to the bottom of the wells are (-)