Introduction to Isotopes, Radioactivity, and Radioactive decay
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons (atomic number) but different number of neutrons (different atomic mass)
What is the kinetic isotope effect?
The change in the rate of a chemical reaction when an atom in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes.
What are the uses of the kinetic isotope effect?
Determining which bonds are broken in the RDS
Studying enzyme catalysed reactions
Investigating reaction transition states and bond strength differences
Name the three types of radiation
Alpha, beta, gamma
The decay of unstable atomic nuclei:
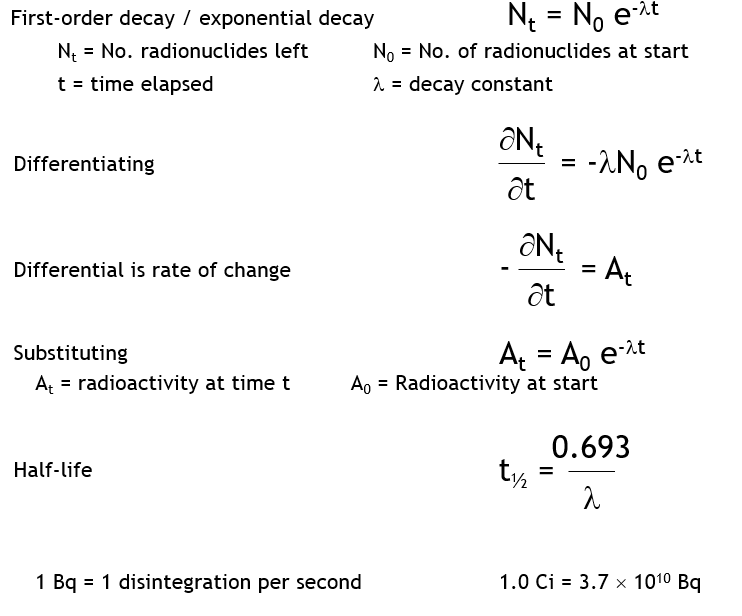
What is the exponential decay law?
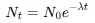
What is the Activity-time relationship?
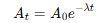
What is the link between activity and number of nuclei?
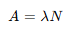
What’s the half life equation for nuclei?
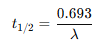
1 bq =
1 bq = 1 disintegration per second
1 Ci =
1 Ci = 3.7 × 1010 Bq

18F decays to 18O, with a half life of 109.7 minutes. What is the decay constant for 18F?
Remember to convert units if it has to be in seconds or something.

What’s the relationship between the decay constant and the half life?
The decay constant (λ) and the half-life (t₁/₂) are inversely related.
When one increases, the other decreases.
What is radiolabelling?
A technique in which a radioactive isotope is incorporated into a molecule so that the molecule can be tracked or detected by measuring the radiation it emits.