research methods
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
dualism
belief that the human body and mind are separate
materialism
belief that if something isn’t physically there, its not real, therefore the mind does not exist
determinsism
idea that free will does not exist
nature
biology - genes and DNA
nurture
our upbringing and environment
nomothetic approach
research methods including experiments, questionnaires, observations and interviews with closed questions. produces quantitative data in large samples of people
idiographic approach
research methods including questionnaires and interviews with open questions, and case studies. produces qualitative data from in-depth studies of individuals
introspection
paying attention to your own mental state and processes without replying on your memory
operationlising
making something more specific and measurable (less vague)
hypothesis
a statement made before a study describing the relationship between variables
participant variables
differences in participants that can effect DV (age, gender, intelligence, personality)
situational variables
factors in the environment that may effect DV (noise, weather, temperature, time of day, instructions)
extraneous variable
any variable that may effect DV other than the intentional IV
confounding variables
a sort of extraneous variable that varies with the IV
demand characteristics
any cue from the researcher or research situation that may reveal purpose of study. this could alter participants behaviour
investigator effects
investigators behaviour that may impact results conscious/unconscious
randomisation
chance methods to control effects of bias when deciding groups and order in investigations
standardisation
using exactly the same procedures and instructions for all participants in a study
independent group design
participants in each group represent one experimental condition (IV)
+ no order effects, less demand characteristics
- no control over participant variables, lots of participants needed
SOLUTION: random allocation
matched pairs
pairing participants based on a characteristic that may effect DV
+ no order effects, less demand characteristics
- time consuming, expensive and difficult
laboratory experiment
experiment taking place in special place where variables can be easily controlled. easy to repeat and greater accuracy but the situation is artificial
field experiment
more natural environment, some variables can be controlled but ethical considerations of privacy and consent
quasi experiment
IV naturally exists rather than determined by researcher (gender differences). controlled conditions and replicable but can’t randomly allocate participants
natural experiment
IV is not presented by researcher (impacts of an earthquake). provides rare reasearch opportunity but difficult to replicate and randomise participants
confederates
actors in an experiment
mundane realism
similarty to everyday life
internal validity
how well designed the experiment including how extraneous variables are controlled.
external validity
how confident we are that the results of an experiment tells us something about society
5 sampling methods
opportunity- people available nearby
stratified- identifying sub groups and collecting a representative amount of each
systematic- selecting every nth name in a list
random- completely unbiased, computer generator ect.
volunteer- advertising the need of participants for a study
participants in a study have the right to:
informed consent
not to be deceived
protection from harm
privacy and confidentiality
right to withdraw
presumptive consent
asking a similar group of people to the participants if they would consent to taking part in the study
prior general consent
asking participants to give consent to a range of studies, not knowing which one is actually happening
retrospective consent
asking for consent after the study has happened, during the debrief
debrief
meeting with researcher and participants after the study, full disclosure, when consent is given to use data ect.
statistical tests
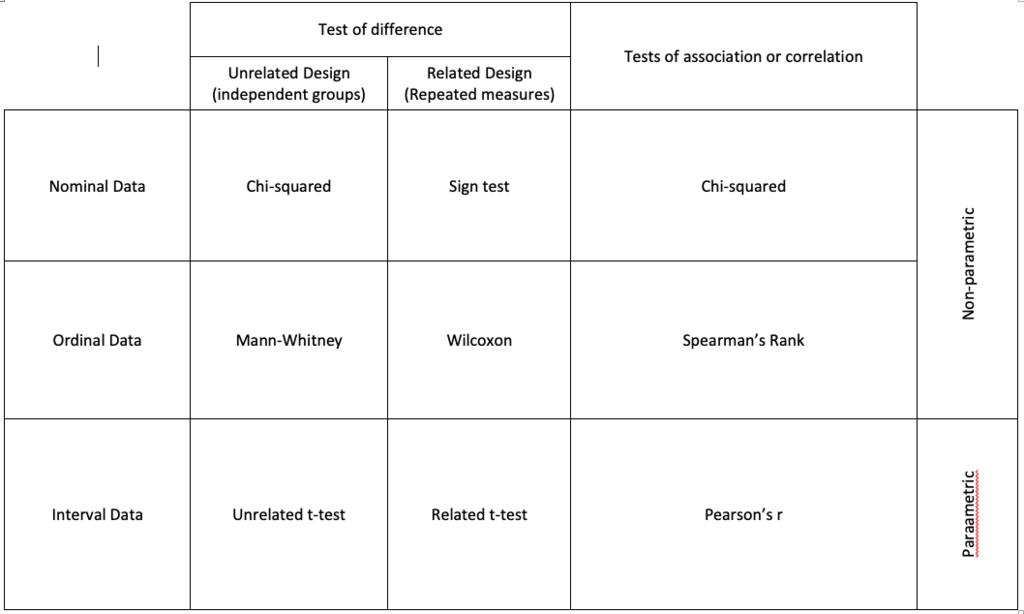
rule of Rs
if statistical test has an R in, calculated value > critical value means significant results
null hypopthis
prediction that there is NO correlation/difference between variables
concurrent validity
if results from an experiment agrees with existing results
face validity
a good appearance of measuring the correct variables its meant to
temporal validity
how old the investigation is
ecological validity
mundane realism - how close to real life it is
test-retest method
for experiments and correlations, testing the same participants twice and comparing results, correlation coefficent of 0.8 is good
inter-observer reliability
for observations, two observers correlate their findings and results, 0.8 is good
difference between reliability and validity

content analysis
a method of quantifying qualitative content via categorisation, a form of (indirect) observation that examines forms of media that people produce
thematic analysis
using qualitative data only, using descriptions to analyse data, NO NUMBERS
falsifiable
if there is a clear way to show if something is true/false
paradigm
unproven story used to prove facts within a branch of study
The Empirical Method
drawing conclusions based on what is repeatedly observed through the sences, rather than abstract ideas like love or maths
crisis in scientific knowledge
too many ideas do not fit the paradigm, causing a paradigm shift - the original theory is destroyed and replaced by a new one