3. Antibodies in Medicine + Interpreting Data about Vaccines and Antibodies.
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Monoclonal antibodies
Are antibodies produced by a single group of genetically identical B-cells/ plasma cells. They are all identical in structure.
why are antibodies
specific their binding sites have a unique tertiary structure complementary to only 1 type of antigen.
How are monoclonal antibodies used to target cancer cells?
Cancer cells have tumour markers that aren’t found on any other cell in the body.
Monoclonal antibodies can be made that will bind to the tumour markers.
You can also attach anti-cancer drugs to these antibodies, meaning the drug will only accumulate in spaces in the body where there are cancer cells.
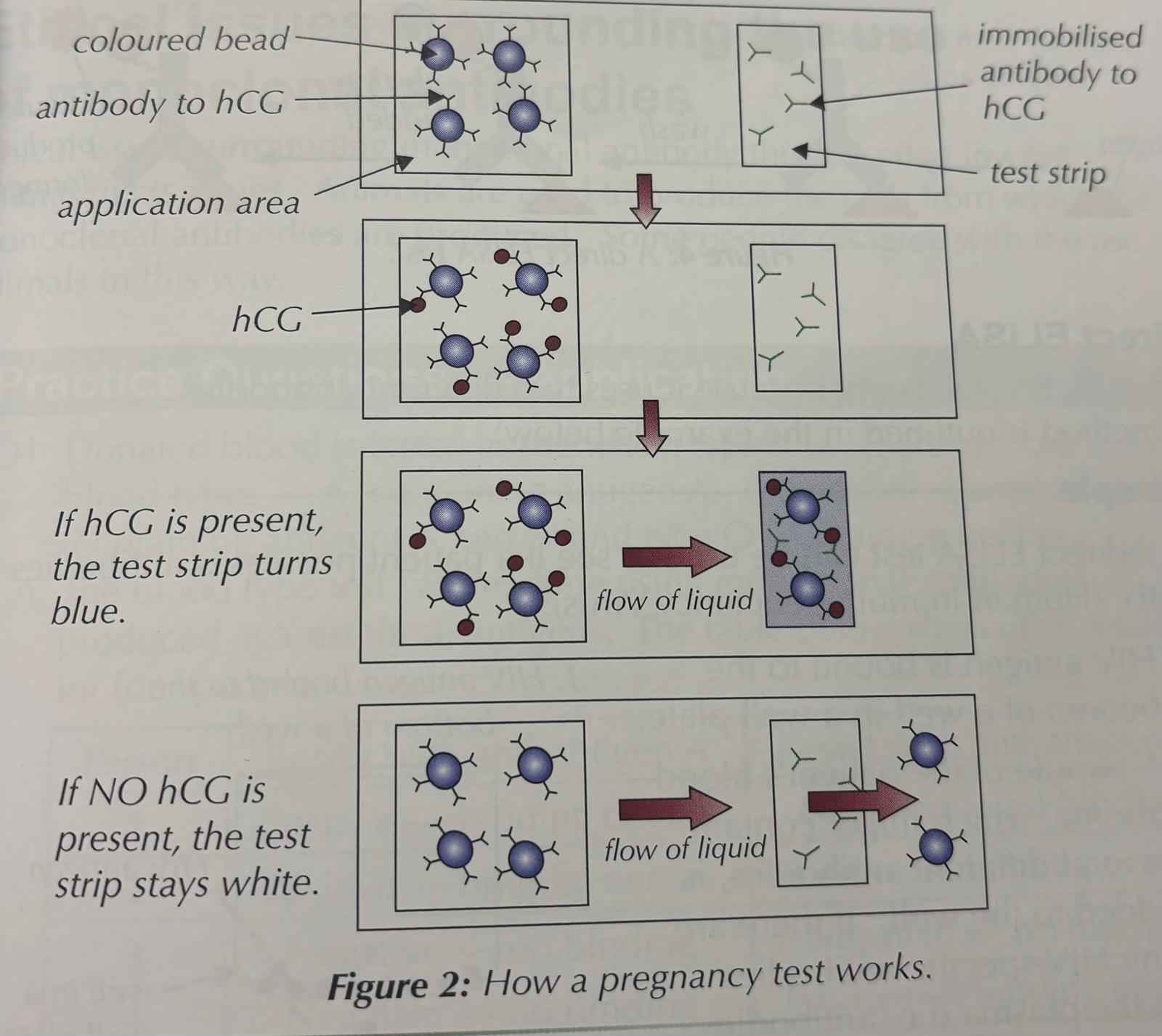
How are monoclonal antibodies used in pregnancy?
Application area contains antibodies that are complementary to the hCG protein, bound to a coloured bead (blue).
When urine is applied, any hCG will bind to the antibody on the beads, forming an antibody-antigen complex.
The urine moves up the stick to the test strip, carrying any beads with it.
The test contains antibodies to hCG that are stuck in place.